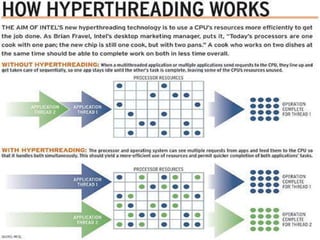
The document presents a technical seminar on hyper-threading technology, highlighting its benefits in improving overall system performance, increasing task execution efficiency, and enhancing multi-threaded application performance. Hyper-threading allows a single processor to operate like two logical processors, significantly boosting performance, especially on multi-processor systems. It emphasizes the compatibility of hyper-threading with existing software and discusses its positive impact on operating systems like Linux, showcasing potential speed improvements in various kernel versions.