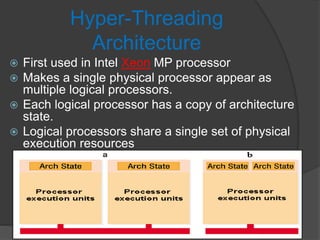
The document discusses hyper-threading (HT) technology, which enables a single processor to appear and function as multiple logical processors by duplicating the architectural state while sharing execution resources. HT allows two threads to run simultaneously, increasing processor efficiency. The main advantages are a 5% increase in die area size while avoiding performance loss with single threads and improving performance with multiple threads. Potential disadvantages include non-deterministic thread overhead and shared resource conflicts.