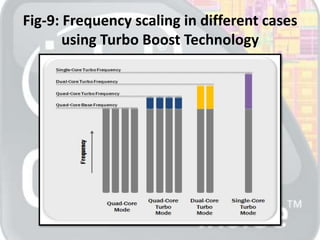
This document discusses the key features and technologies of Intel i7 Extreme processors, including Intel QuickPath Architecture, Intel Smart Cache Technology with an 8MB L3 cache, Hyper-Threading Technology, and Intel Turbo Boost Technology. It provides diagrams to illustrate how each technology works and the performance improvements it enables. In conclusion, the document states that Intel i7 processors provide higher performance demanded by today's users through the implementation of these new technologies.








![REFERENCES
[1]Intel i7 Developer’s Manual
[2]http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/processors/core/core-i7-
processor.html
[3]http://reviews.cnet.com/processors/intel-core-i7-965/4505-3086_7-
33366836.html
[4]http://www.intel.com/technology/product/demos/turboboost/demo.htm?
iid=tech_demo+tb
[5]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=llOXMPXH2VA
[6]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kkrqyEpINSQ
[7]http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/io/quickpath-
technology/performance-quickpath-architecture-paper.html
[8]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bE9EbQOeb_U
[9]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=An7w0laRGv8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/i7seminar-120306102319-phpapp01/85/Intel-i7-Technologies-18-320.jpg)

