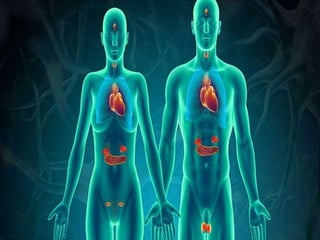
Human endocrine system
- 2. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM JAI NARAIN VYAS UNIVERSITY, JODHPUR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR:- ASHWIN SINGH CHOUHAN DEPARTMENT:- PHARMACOLOGY E-mail:- anshukavya1993@gmail.com
- 3. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The endocrine system is the collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood, among other things. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- 4. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FUNCTIONS Your endocrine system Makes hormones that control your moods, growth and development, metabolism, organs, and reproduction. Controls how your hormones are released. Sends those hormones into your bloodstream so they can travel to other body parts.
- 7. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- 8. PARTS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 9. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR HYPOTHALAMUS The hypothalamus is a small but important area in the center of the brain. It plays an important role in hormone production and helps to stimulate many important processes in the body and is located in the brain, between the pituitary gland and thalamus.
- 10. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The hypothalamus’ main role is to keep the body in homeostasis as much as possible. Homeostasis means a healthful, balanced bodily state. The body is always trying to achieve this balance. Feelings of hunger, for example, are the brain’s way of letting its owner know that they need more nutrients to achieve homeostasis. The hypothalamus acts as the connector between the endocrine and nervous systems to achieve this. It plays a part in many essential functions of the body such as: body temperature thirst appetite and weight control emotions sleep cycles sex drive childbirth blood pressure and heart rate production of digestive juices balancing bodily fluids
- 11. HORMONES OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus include: ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE, which increases how much water is absorbed into the blood by the kidneys CORTICOTROPIN-releasing hormone, which helps regulate metabolism and immune response by working with the pituitary gland and adrenal gland to release certain steroids GONADOTROPIN-releasing hormone, which instructs the pituitary gland to release more hormones that keep the sexual organs working JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 12. OXYTOCIN- A hormone involved in several processes, including the release of a mother’s breast milk, moderating body temperature, and regulating sleep cycles PROLACTIN-Controlling hormones, which tell the pituitary gland to either start or stop breast milk production in lactating mothers THYROTROPIN-Releasing hormone activates the thyroid, which releases the hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and developmental growth JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 13. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR PITUITARY GLAND The pituitary gland is small and oval-shaped. It’s located behind your nose, near the underside of your brain. It’s attached to the hypothalamus by a stalk like structure. The hypothalamus is a small area of your brain. It’s very important in controlling the balance of your bodily functions. It controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
- 15. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The pituitary gland can be divided into two different parts: the anterior and posterior lobe ANTERIOR LOBE The anterior lobe of your pituitary gland is made up of several different types of cells that produce and release different types of hormones, including: Growth hormone - Growth hormone regulates growth and physical development. It can stimulate growth in almost all of your tissues. Its primary targets are bones and muscles. Thyroid-stimulating hormon- This hormone activates your thyroid to release thyroid hormones. Your thyroid gland and the hormones it produces are crucial for metabolism. Adreno-corticotropic hormone- This hormone stimulates your adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other hormones.
- 16. Follicle-stimulating hormone- Follicle-stimulating hormone is involved with estrogen secretion and the growth of egg cells in women. It’s also important for sperm cell production in men. Luteinizing hormone- Luteinizing hormone is involved in the production of estrogen in women and testosterone in men. Prolactin- Prolactin helps women who are breastfeeding produce milk. Endorphins- Endorphins have pain-relieving properties and are thought to be connected to the “pleasure centers” of the brain. Enkephalins- Enkephalins are closely related to endorphins and have similar pain-relieving effects. Beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-This hormone helps to stimulate increased pigmentation of your skin in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 17. POSTERIOR LOBE The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland also secretes hormones. These hormones are usually produced in your hypothalamus and stored in the posterior lobe until they’re released. Hormones stored in the posterior lobe include: Vasopressin- This is also called antidiuretic hormone. It helps your body conserve water and prevent dehydration. Oxytocin- This hormone stimulates the release of breast milk. It also stimulates contractions of the uterus during labor. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 18. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR PINEAL GLAND The pineal gland (also called the pineal body or epiphysis) is a small endocrine gland in the brain. It is located near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two rounded thalamic bodies join.
- 19. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The pineal gland is a reddish-gray body about the size of a pea (8 mm in humans) located just rostro-dorsal to the superior colliculus and behind and beneath the stria medullaris, between the laterally positioned thalamic bodies. It is part of the epithalamus.The pineal gland is a midline structure, and is often seen in plain skull X-rays, as it is often calcified. The main hormone produced and secreted by the pineal gland is melatonin. Secretion is highest at night and between the ages of 0-5. PINEAL GLAND HORMONES Melatonin While the full function of the pineal gland is still somewhat mysterious, we do know that it secretes the hormone melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone from the pineal gland that helps regulate biological rhythms such as sleep and wake cycles.
- 20. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR In other words, it's melatonin that directs your internal clock - the one that allows you to wake up about the same time every morning without an alarm clock. Melatonin is secreted in different amounts during the night and day. Melatonin secretions peak during the nighttime, and this makes you feel drowsy. While it does not necessarily induce sleep, it can promote sleep and allow a good night's rest. In fact, we see melatonin marked as a supplement to help people who deal with insomnia. Because melatonin secretions peak during puberty and then continue to drop through out life, it is thought that a lack of melatonin production is why so many elderly people report trouble sleeping.
- 21. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR THYROID GLAND The thyroid is a butterfly- shaped gland that sits low on the front of the neck. Your thyroid lies below your Adam’s apple, along the front of the windpipe. The thyroid has two side lobes, connected by a bridge (isthmus) in the middle. When the thyroid is its normal size, you can’t feel it. Brownish-red in color, the thyroid is rich with blood vessels. Nerves important for voice quality also pass through the thyroid
- 23. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR THYROID HORMONES Your thyroid makes 2 main hormones –triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Adequate amounts of iodine (a chemical element that’s an essential part of our diet) are needed for the thyroid to be able to make these hormones. Another hormone that’s produced in your thyroid gland is called calcitonin. This hormone, secreted by a small population of cells known as C cells, is involved in regulating the level of calcium and phosphate in your blood.
- 24. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The main thyroid hormones are secreted directly into the bloodstream and go to all parts of your body. Most T4 is converted to T3 (the active form of the hormone) in your organs and tissues. Thyroid hormones affect your body’s metabolic rate and regulate many of your bodily functions such as breathing, heart rate, body temperature, digestion and how quickly you burn calories. The amount of hormones your thyroid makes is usually tightly regulated. A part of your brain called the hypothalamus signals your pituitary gland (an important gland in your brain) to produce a hormone called thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then signals your thyroid to make T3 and T4. The level of thyroid hormones in your body then feeds back to the hypothalamus and the pituitary, which in turn adjust the release of TSH
- 25. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR PARATHYROID The parathyroid glands are tiny, round structures usually found embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland A thick connective tissue capsule separates the glands from the thyroid tissue. Most people have four parathyroid glands, but occasionally there are more in tissues of the neck or chest. The function of one type of parathyroid cells, the oxyphil cells, is not clear. The primary functional cells of the parathyroid glands are the chief cells. These epithelial cells produce and secrete the parathyroid hormone (PTH), the major hormone involved in the regulation of blood calcium levels.
- 26. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The parathyroid glands produce and secrete PTH, a peptide hormone, in response to low blood calcium levels PTH secretion causes the release of calcium from the bones by stimulating osteoclasts, which secrete enzymes that degrade bone and release calcium into the interstitial fluid. PTH also inhibits osteoblasts, the cells involved in bone deposition, thereby sparing blood calcium. PTH causes increased reabsorption of calcium (and magnesium) in the kidney tubules from the urine filtrate. In addition, PTH initiates the production of the steroid hormone calcitriol (also known as 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D), which is the active form of vitamin D3, in the kidneys. Calcitriol then stimulates increased absorption of dietary calcium by the intestines. A negative feedback loop regulates the levels of PTH, with rising blood calcium levels inhibiting further release of PTH.
- 27. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR THYMUS The thymus gland is a small organ behind the breastbone that plays an important function both in the immune system and endocrine system. Though the thymus begins to atrophy (decay) during puberty, its effect in "training“T lymphocytes to fight infections and even cancer lasts for a lifetime.
- 28. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR CELLS OF THE THYMUS A number of different cell types are present within the thymus gland. Epithelial cells: cells that line body surfaces and cavities Kulchitsky cells: cells that are the hormone-producing cells of the thymus or neuroendocrine cells Thymocytes: cells that become mature T lymphocytes HORMONE PRODUCTION The thymus gland produces several hormones including: thymopoietin and thymulin, which are hormones that assist in the process where T cells differentiate into different types thymosin, which accentuates the immune response as well as stimulating pituitary hormones such as growth hormone thymic humoral factor, which acts similarly to thymosin, but increases the immune response to viruses in particular.
- 29. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The thymus gland may produce small amounts of some hormones produced in other areas of the body, such as melatonin and insulin. Cells in the thymus gland (such as epithelial cells) also have receptors through which other hormones can regulate its function.
- 30. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR ADRENALS Adrenal glands, also known as suprarenal glands, are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of both kidneys. Adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions. Adrenal glands are composed of two parts the cortex and the medulla which are each responsible for producing different hormones.
- 32. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR When adrenal glands don’t produce enough hormones, this can lead to adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease). Adrenal glands may develop nodules that can be benign or malignant, which can potentially produce excessive amounts of certain hormones leading to various health issues AADRENAL GLAND IS MADE OF TWO MAIN PARTS The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. The adrenal medulla is located inside the adrenal cortex in the center of an adrenal gland. It produces “stress hormones,” including adrenaline. The adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla are enveloped in an adipose capsule that forms a protective layer around an adrenal gland
- 33. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR HORMONES OF THE ADRENAL GLANDS Adrenal Cortex Hormones The adrenal cortex produces two main groups of corticosteroid hormones— glucocorticoids and mineralcorticoids. The release of glucocorticoids is triggered by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Mineralcorticoids are mediated by signals triggered by the kidney. When the hypothalamus produces corticotrophin- releasing hormone (CRH), it stimulates the pituitary gland to release adrenal corticotrophic hormone (ACTH). These hormones, in turn, alert the adrenal glands to produce corticosteroid hormones.
- 34. Glucocorticoids released by the adrenal cortex include: Hydrocortisone: Commonly known as cortisol, it regulates how the body converts fats, proteins, and carbohydrates to energy. It also helps regulate blood pressure and cardiovascular function. Corticosterone: This hormone works with hydrocortisone to regulate immune response and suppress inflammatory reactions. The principle mineralcorticoid is aldosterone, which maintains the right balance of salt and water while helping control blood pressure. There is a third class of hormone released by the adrenal cortex, known as sex steroids or sex hormones. The adrenal cortex releases small amounts of male and female sex hormones. However, their impact is usually overshadowed by the greater amounts of hormones (such as estrogen and testosterone) released by the ovaries or testes. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 35. ADRENAL MEDULLA HORMONES Hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla are Epinephrine: Most people know epinephrine by its other name—adrenaline. This hormone rapidly responds to stress by increasing your heart rate and rushing blood to the muscles and brain. It also spikes your blood sugar level by helping convert glycogen to glucose in the liver. (Glycogen is the liver’s storage form of glucose.) Norepinephrine: Also known as noradrenaline, this hormone works with epinephrine in responding to stress. However, it can cause vasoconstriction (the narrowing of blood vessels). This results in high blood pressure. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 36. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR PANCREAS The pancreas is an abdominal organ that is located behind the stomach and is surrounded by other organs, including the spleen, liver and small intestine. The pancreas is about 6 inches (15.24 centimeters) long, oblong and flat. The pancreas plays an important role in digestion and in regulating blood sugar. Three diseases associated with the pancreas are pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and diabetes.
- 38. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The pancreas maintains the body’s blood glucose (sugar) balance. Primary hormones of the pancreas include insulin and glucagon, and both regulate blood glucose. Diabetes is the most common disorder associated with the pancreas. The pancreas is unique in that it’s both an endocrine and exocrine gland. In other words, the pancreas has the dual function of secreting hormones into blood (endocrine) and secreting enzymes through ducts (exocrine).
- 39. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR HORMONES OF THE PANCREAS The production of pancreatic hormones, including insulin, somatostatin, gastrin, and glucagon, play an important role in maintaining sugar and salt balance in our bodies. Primary hormones secreted by the pancreas include: Gastrin: This hormone aids digestion by stimulating certain cells in the stomach to produce acid. Glucagon: Glucagon helps insulin maintain normal blood glucose by working in the opposite way of insulin. It stimulates your cells to release glucose, and this raises your blood glucose levels.
- 40. Insulin: This hormone regulates blood glucose by allowing many of your body’s cells to absorb and use glucose. In turn, this drops blood glucose levels. Somatostatin: When levels of other pancreatic hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, get too high, somatostatin is secreted to maintain a balance of glucose and/or salt in the blood. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP): This hormone helps control water secretion and absorption from the intestines by stimulating the intestinal cells to release water and salts into the intestines.
- 41. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR OVARIES The ovaries are oval shaped and about the size of a large grape. They are located on opposite ends of the pelvic wall, on either side of the uterus. The ovaries are each attached to the fimbria (tissue that connects the ovaries to the fallopian tube). The ovaries are a pair of ova-producing organs (that is, they produce egg cells) that maintain the health of the female reproductive system
- 42. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The major hormones secreted by the ovaries are oestrogen and progesterone, both important hormones in the menstrual cycle. Oestrogen production dominates in the first half of the menstrual cycle before ovulation, and progesterone production dominates during the second half of the menstrual cycle when the corpus luteum has formed. Both hormones are important in preparing the lining of the womb for pregnancy and the implantation of a fertilised egg, or embryo. If conception occurs during any one menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum does not lose its ability to function and continues to secrete oestrogen and progesterone, allowing the embryo to implant in the lining of the womb and form a placenta. At this point, development of the foetus begins.
- 43. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR TESTES The testes are twin oval- shaped organs about the size of a large grape. They are located within the scrotum, which is the loose pouch of skin that hangs outside the body behind the penis. While this location makes the testes vulnerable to injury (they have no muscles or bones to shield them), it provides a cooler temperature for the organs. A cooler environment is necessary for healthy sperm production.
- 44. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR The main hormone secreted by the testes is testosterone, an androgenic hormone. Testosterone is secreted by cells that lie between the seminiferous tubules, known as the Leydig cells. The testes also produce inhibin B and anti- Müllerian hormone from Sertoli cells, and insulin-like factor 3 and oestradiol from the Leydig cells. Testosterone is important in the first stages of developing the male reproductive organs in a foetus. It also causes the development of male characteristics such as growth of facial hair, deepening of the voice and the growth spurt that takes place during puberty. Testosterone is important in maintaining these secondary male characteristics throughout a man’s life. From puberty onwards, testosterone provides the main stimulus for sperm production.
- 45. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS Acromegaly. Sometimes the pituitary gland makes too much growth hormone and your bones get bigger. It usually affects your hands, feet, and face. It usually starts in middle age. Adrenal insufficiency. When you have this, your adrenal glands don’t make enough of certain hormones, like cortisol, which controls stress. Cushing's disease. In this, your body makes too much cortisol. You could gain weight, get stretch marks, bruise easily at first, then get weakened muscles and bones and possibly develop a hump on your upper back.
- 46. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR Hyperthyroidism. This is when your thyroid gland makes more hormones than your body needs. You might hear it called overactive thyroid. It makes your system run fast and you might feel nervous, lose weight, and have a rapid heartbeat or trouble sleeping. Hypothyroidism. When your body doesn’t make enough thyroid hormone, your system slows down. You might feel tired, gain weight, have a slow heartbeat, and get joint and muscle pains. Hypopituitarism. Sometimes your pituitary gland doesn’t make enough of certain hormones and your adrenal and thyroid glands can’t work right.
- 47. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR Multiple endocrine neoplasia. This is a group of disorders that affect your endocrine system. It causes tumors on at least two endocrine glands or in other organs and tissues. Polycystic ovary syndrome. An imbalance of reproductive hormones can cause your ovaries to either not make an egg or not release it during ovulation. This can throw off your periods, cause acne, and make hair to grow on your face or chin. Precocious puberty . When glands that control reproduction don’t work properly, some kids start puberty abnormally early -- around 8 in girls and 9 in boys
- 48. Endocrine Gland Hormone Released Chemical Class Target Tissue/Organ Major Function of Hormone (1) Hypothalamus Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones Peptide Anterior pituitary Regulate anterior pituitary hormone (2) a. Posterior Pituitary Antidiuretic (ADH) Peptide Kidneys Stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys Oxytocin Peptide Uterus, mammary glands Stimulates uterine muscle contractions and release of milk by mammary glands b. Anterior Pituitary Thyroid stimulating (TSH) Glycoprotein Thyroid Stimulates thyroid Adrenocorticotropi c (ACTH) Peptide Adrenal cortex Stimulates adrenal cortex JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR SUMMARY
- 49. Gonadotropic (FSH, LH) Glycoprotein Gonads Egg and sperm production, sex hormone production Prolactin (PRL) Protein Mammary glands Milk production Growth (GH) Protein Soft tissue, bones Cell division, protein synthesis and bone growth (3) Thyroid Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronie (T3) Iodinated amino acid All tissue Increase metabolic rate, regulates growth and development Calcitonin Peptide Bones, kidneys and intestine Lowers blood calcium level JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 50. (4) Parathyroids Parathyroid (PTH) Peptide Bones, kidneys and intestine Raises blood calcium level (5) a. Adrenal Cortex Glucocorticoids (cortisol) Steroid All tissue Raise blood glucose level, stimulates breakdown of protein Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Steroid Kidneys Reabsorb sodium and excrete potassium Sex Hormones Steroid Gonads, skin, muscles and bones Stimulates reproductive organs and brings on sex characteristics b. Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine and norepinephrine Modified amino acid Cardiac and other muscles Released in emergency situations, raises blood glucose level, “fight or flight” response JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 51. (6) Pancreas Insulin Protein Liver, muscles, adipose tissue Lowers blood glucose levels, promotes formation of glycogen Glucagon Protein Liver, muscles, adipose tissue Raises blood glucose levels (7) Testes Androgens (testosterone) Steroid Gonads, skin, muscles and bone Stimulates male sex characteristics (8) Ovaries Estrogen and progesterone Steroid Gonads, skin, muscles and bones Stimulates female sex characteristics (9) Thymus Thymosins Peptide T lymphocytes Stimulates production and maturation of T lymphocytes (10) Pineal Gland Melatonin Modified amino acid Brain Controls circadian and circannual rhythms, possibly involved in maturation of sexual organs JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR
- 52. JNVU PHARMACY, JODHPUR THANK YOU
