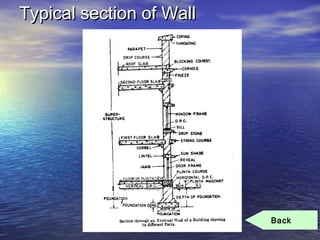
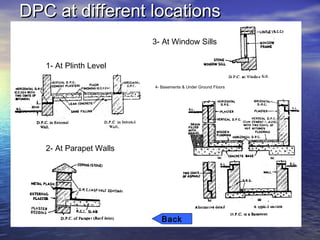
Dampness in buildings can cause health issues and damage to the structure. It is caused by factors like rain penetration, soil drainage issues, and defective construction. Remedies include installing damp proofing courses of flexible or rigid materials at locations like foundation level, parapets, and windowsills. Proper ventilation and moisture management can also help reduce excessive moisture in homes.