Embed presentation
Downloaded 76 times
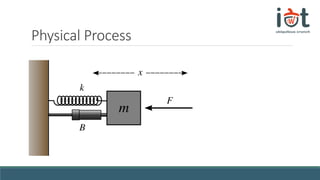
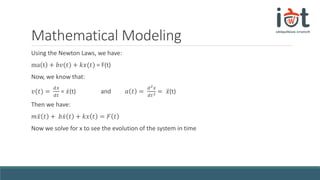
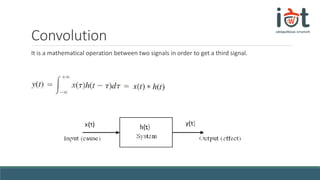
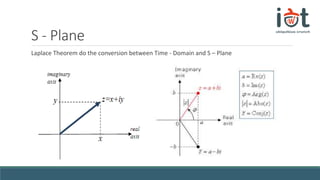
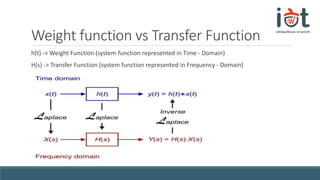
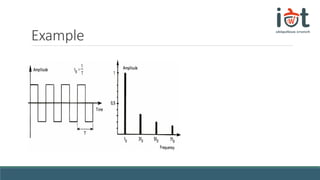

The document discusses transfer functions and their use in mathematical modeling of physical systems. It defines a transfer function as representing a system function in the frequency domain. An example differential equation for a physical system is given and the corresponding transfer function is derived by taking the Laplace transform. The transfer function is defined as the ratio of the output to input signals in the frequency domain. Convolution and the S-plane are also briefly introduced in relation to converting between the time and frequency domains.








