This document defines and describes lightweight concrete. It discusses three main types of lightweight concrete: porous concrete, concrete without fine aggregate, and lightweight aggregate concrete.
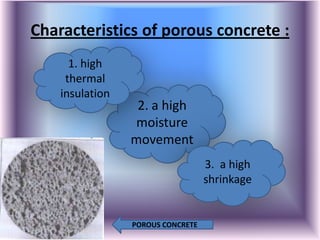
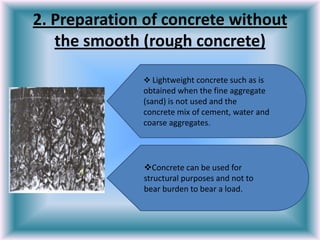
Porous concrete contains air bubbles that make it lightweight. Concrete without fine aggregate uses only cement, water, and coarse aggregates. Lightweight aggregate concrete uses lightweight aggregates like pumice or expanded clay instead of regular aggregates.
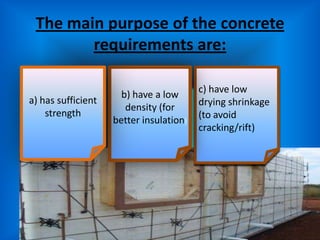
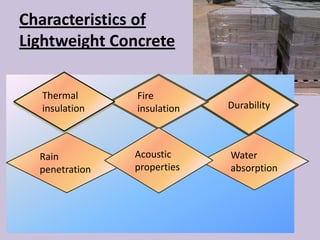
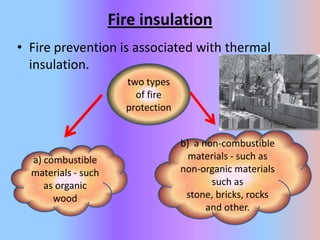
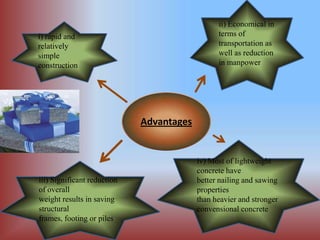
The document outlines the characteristics and advantages of lightweight concrete, including better thermal and fire insulation, durability in various environments, lower water absorption, and acoustic properties. It also notes some disadvantages like increased sensitivity to water content and difficulty in placement and finishing.