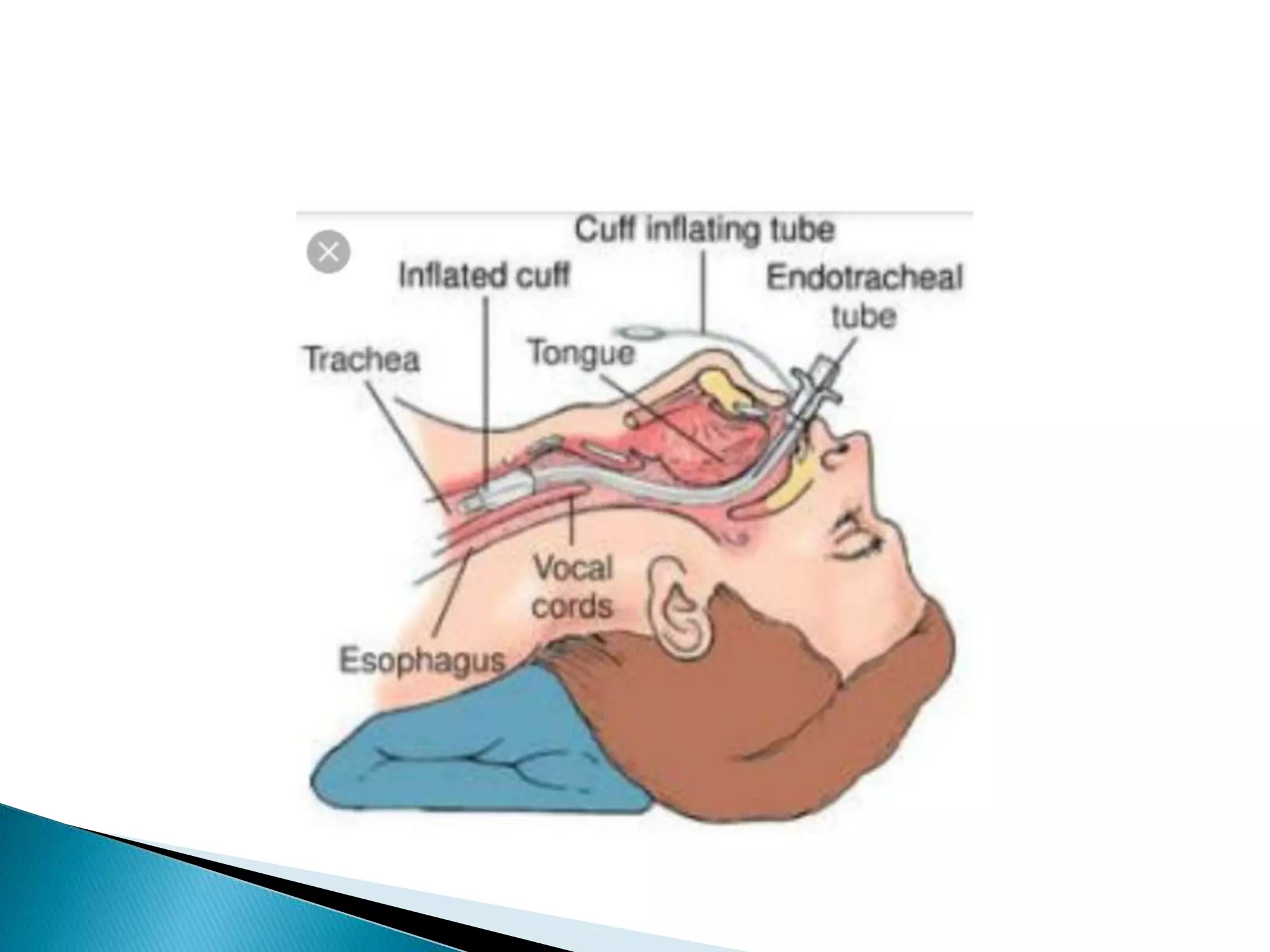
Endotracheal intubation involves inserting a tube into the trachea through the mouth or nose. It is done to administer oxygen, remove secretions, promote airway patency, or assist with breathing difficulties. The document discusses indications for intubation, equipment needed, steps for performing intubation, post-intubation care, complications, and the importance of documentation.