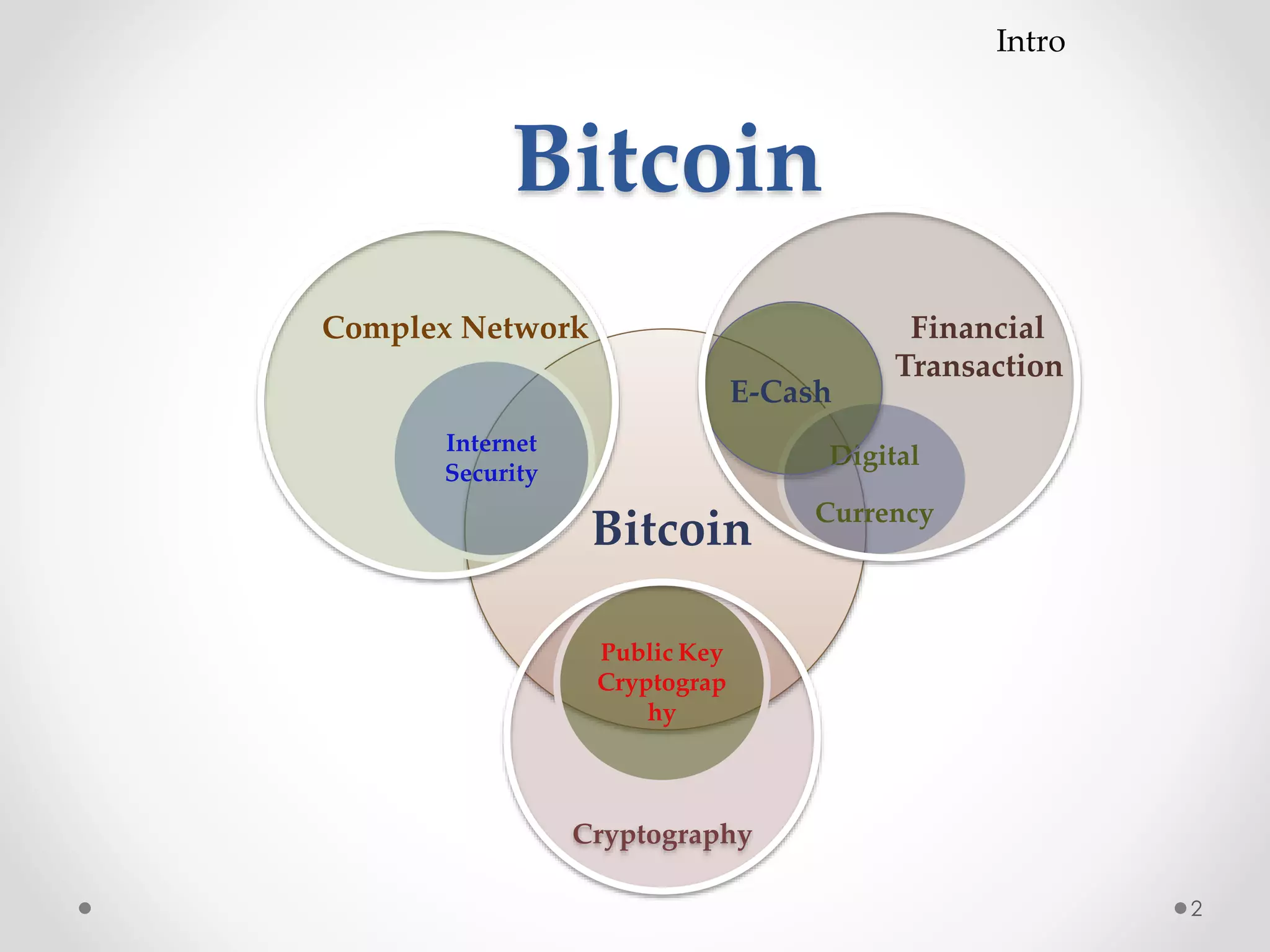
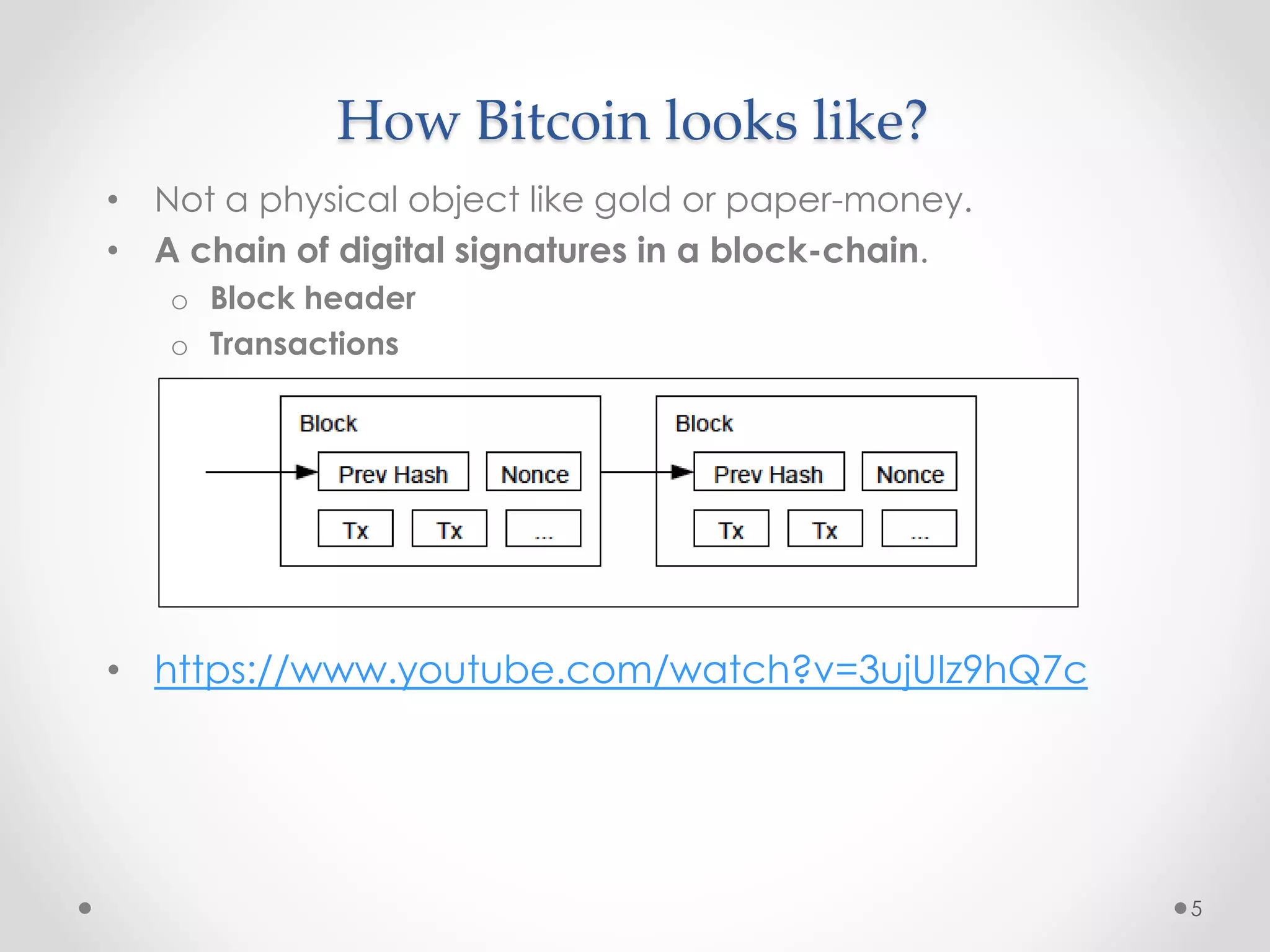
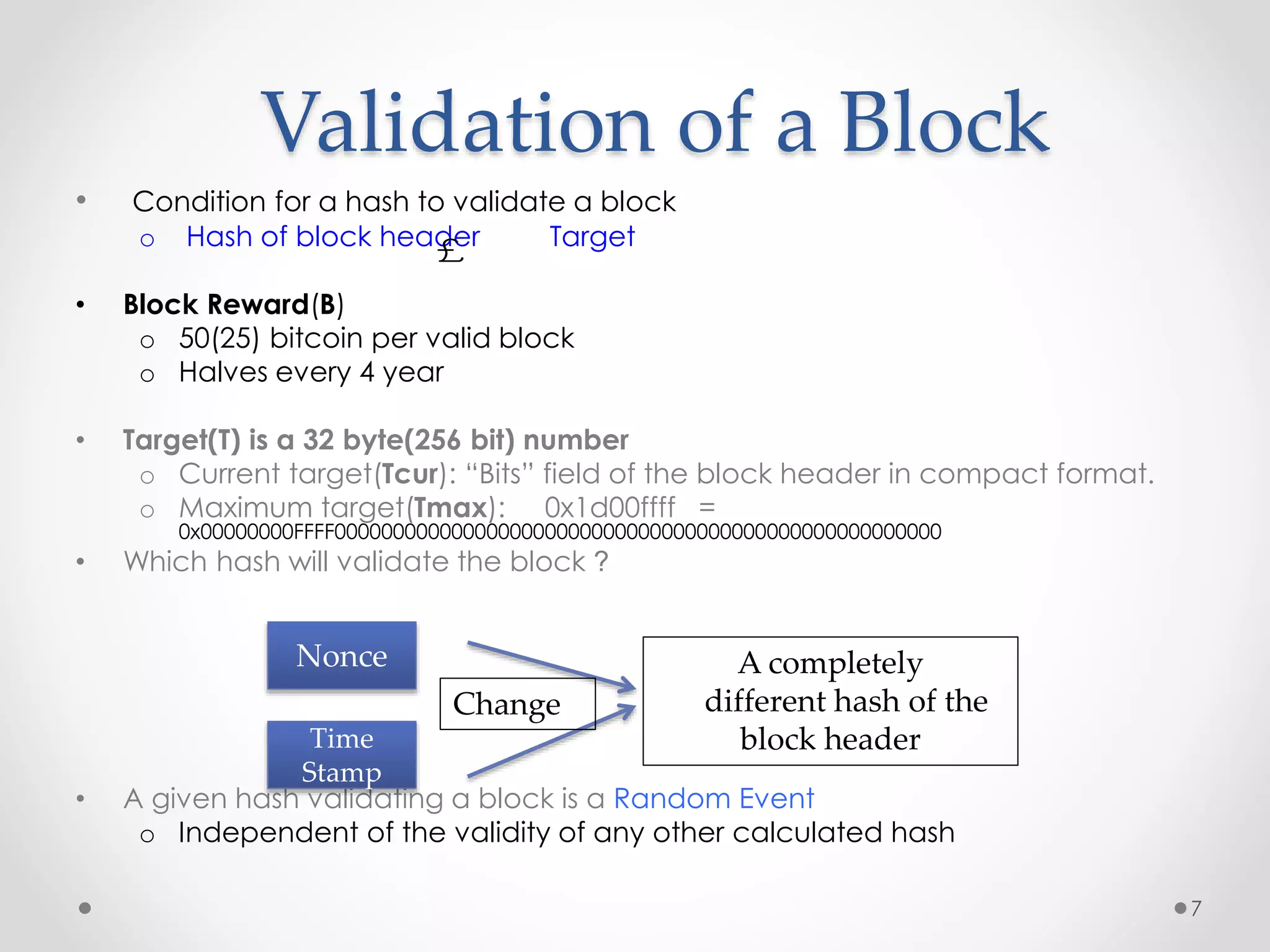
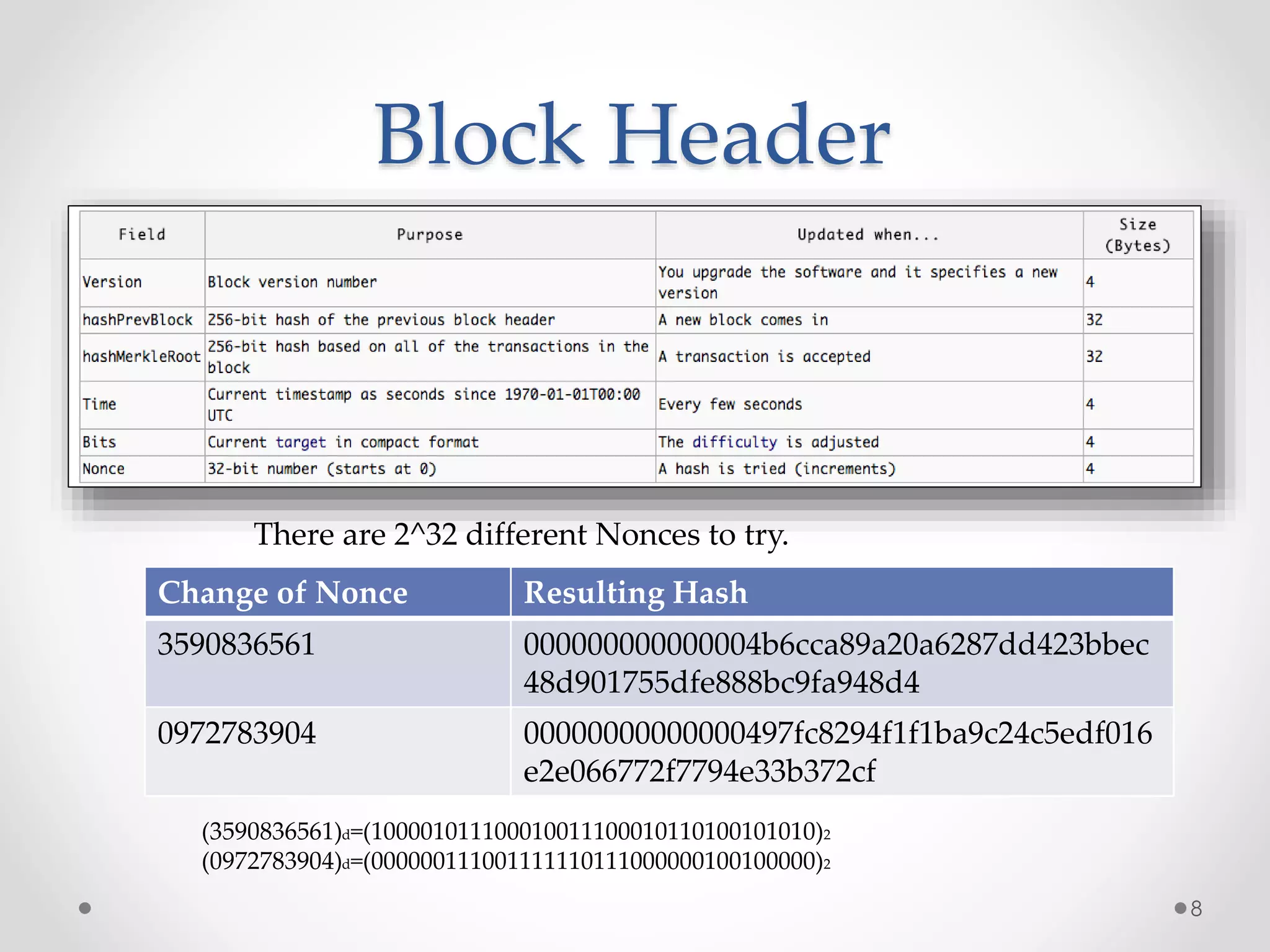
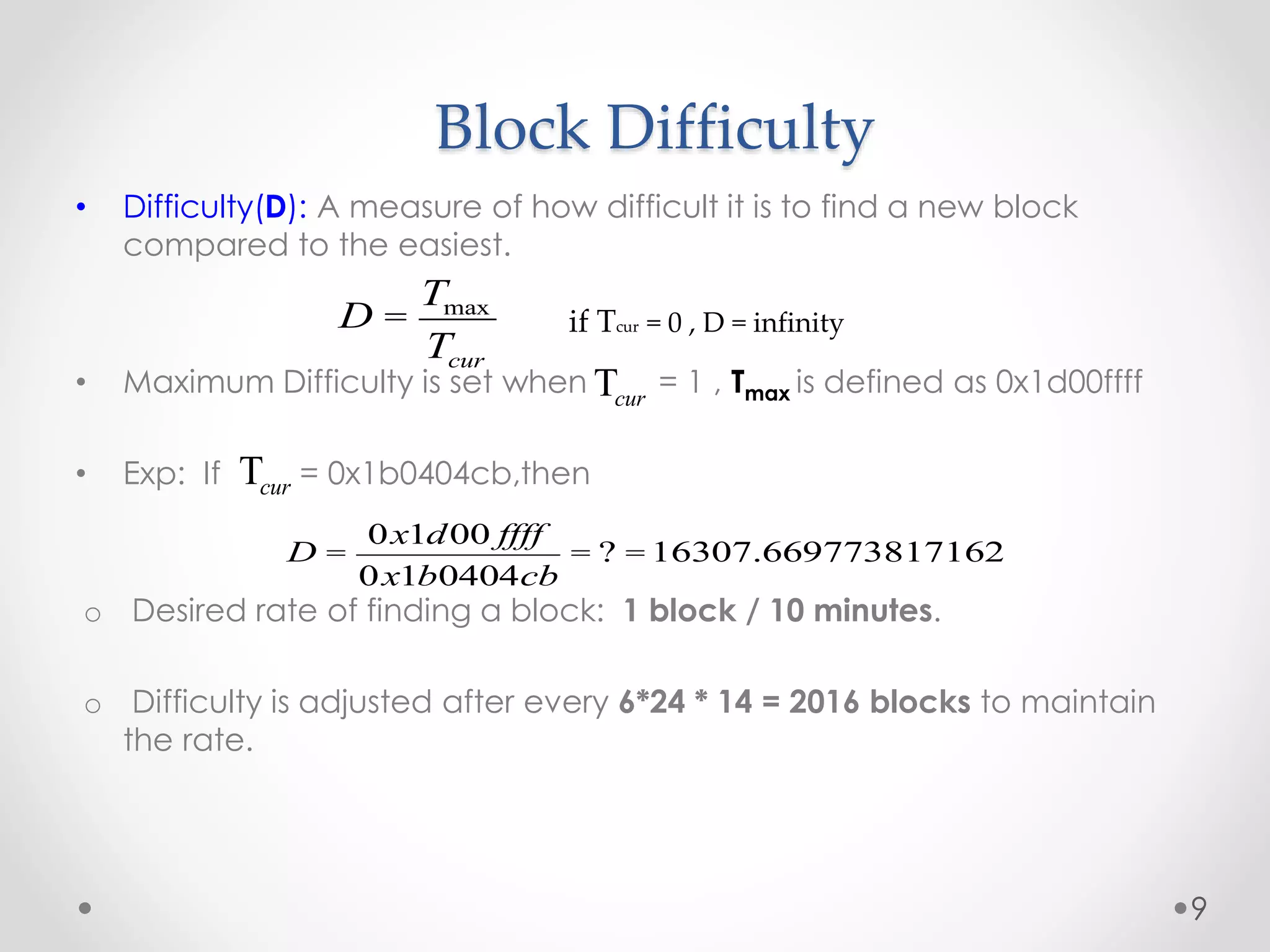
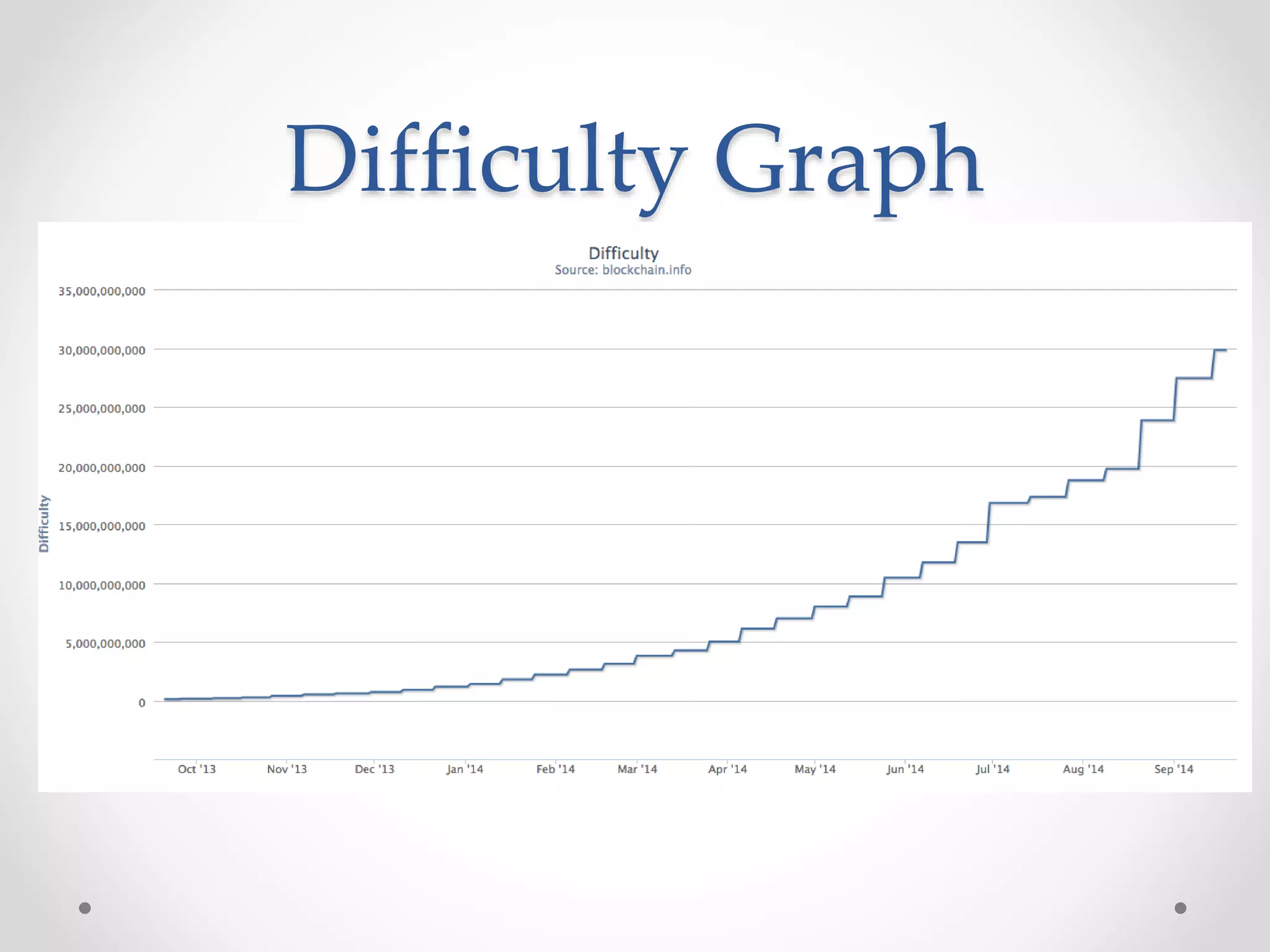
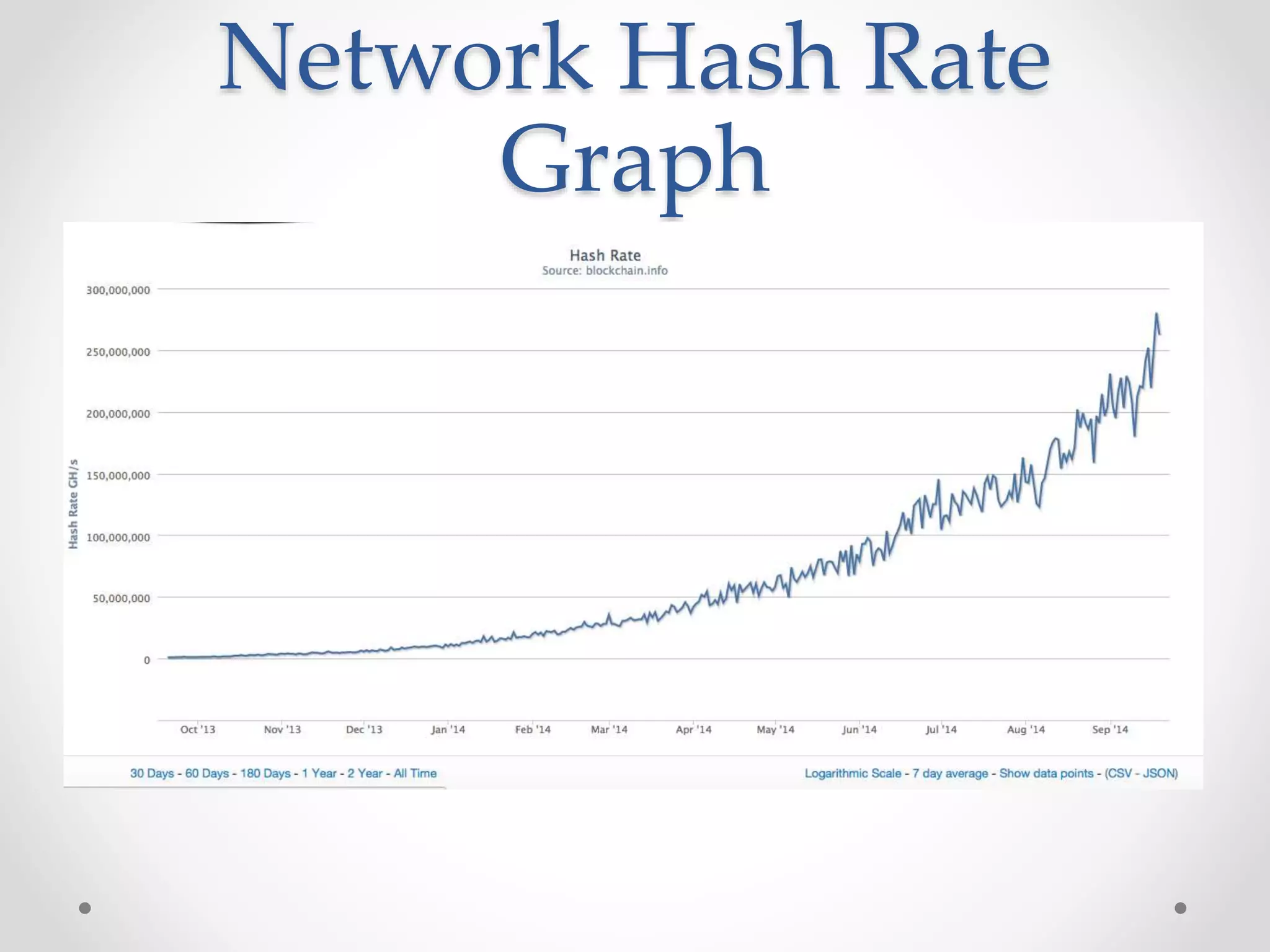
This document discusses Bitcoin, a digital currency that uses cryptography and a decentralized network to allow for secure transactions without a central authority. It provides an overview of how Bitcoin works, including how transactions are broadcast across the network and collected into blocks, how miners compete to validate blocks by solving cryptographic puzzles, and how the difficulty of these puzzles is adjusted to control block creation times. Key aspects like the blockchain, block headers, mining hardware, and the increasing network hash rate over time are also summarized.