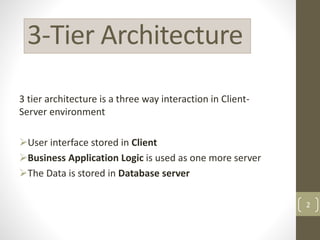
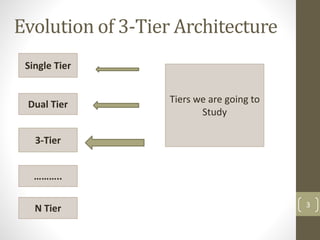
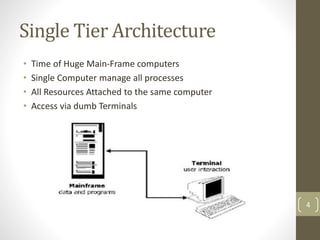
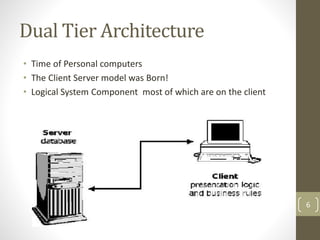
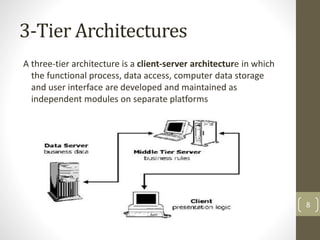
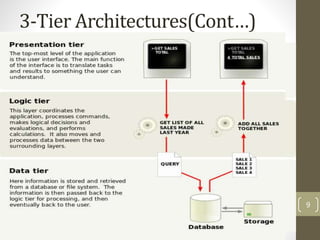
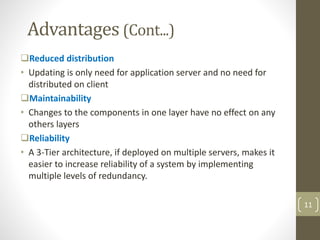
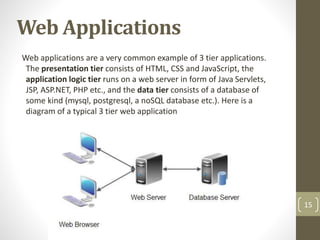
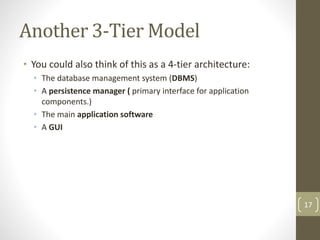
This document discusses 3-tier architecture, which divides applications into presentation, application, and data tiers. The presentation tier handles the user interface, the application tier contains business logic, and the data tier stores information in a database. 3-tier architecture provides benefits like scalability, improved security, reduced distribution complexity, and maintainability. However, it also increases complexity compared to 2-tier systems. The document uses web and mobile applications as common examples of 3-tier architectures and explains how each tier is separated but communicates through standard interfaces.