The document outlines key topics related to browsing the internet, including:
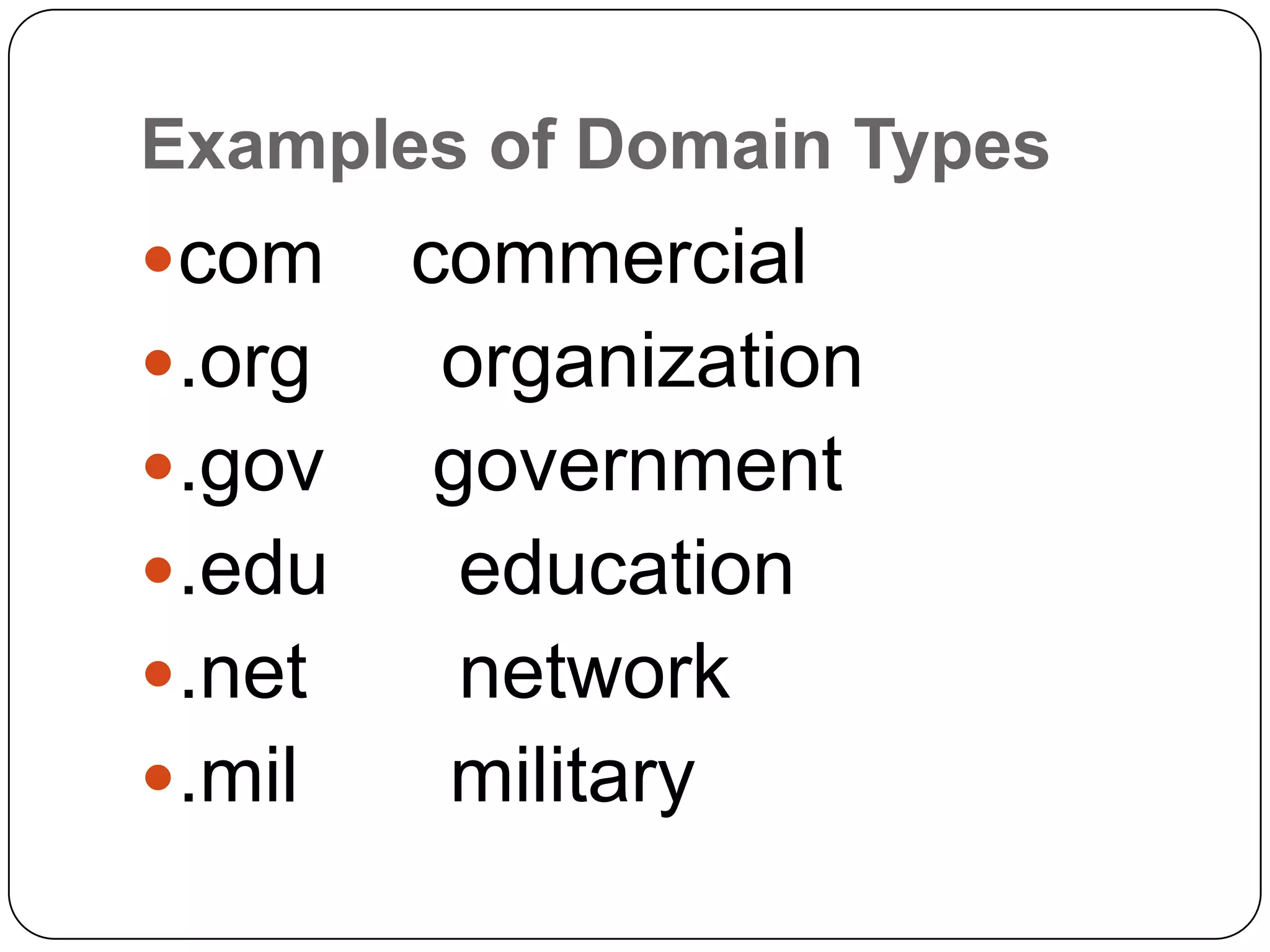
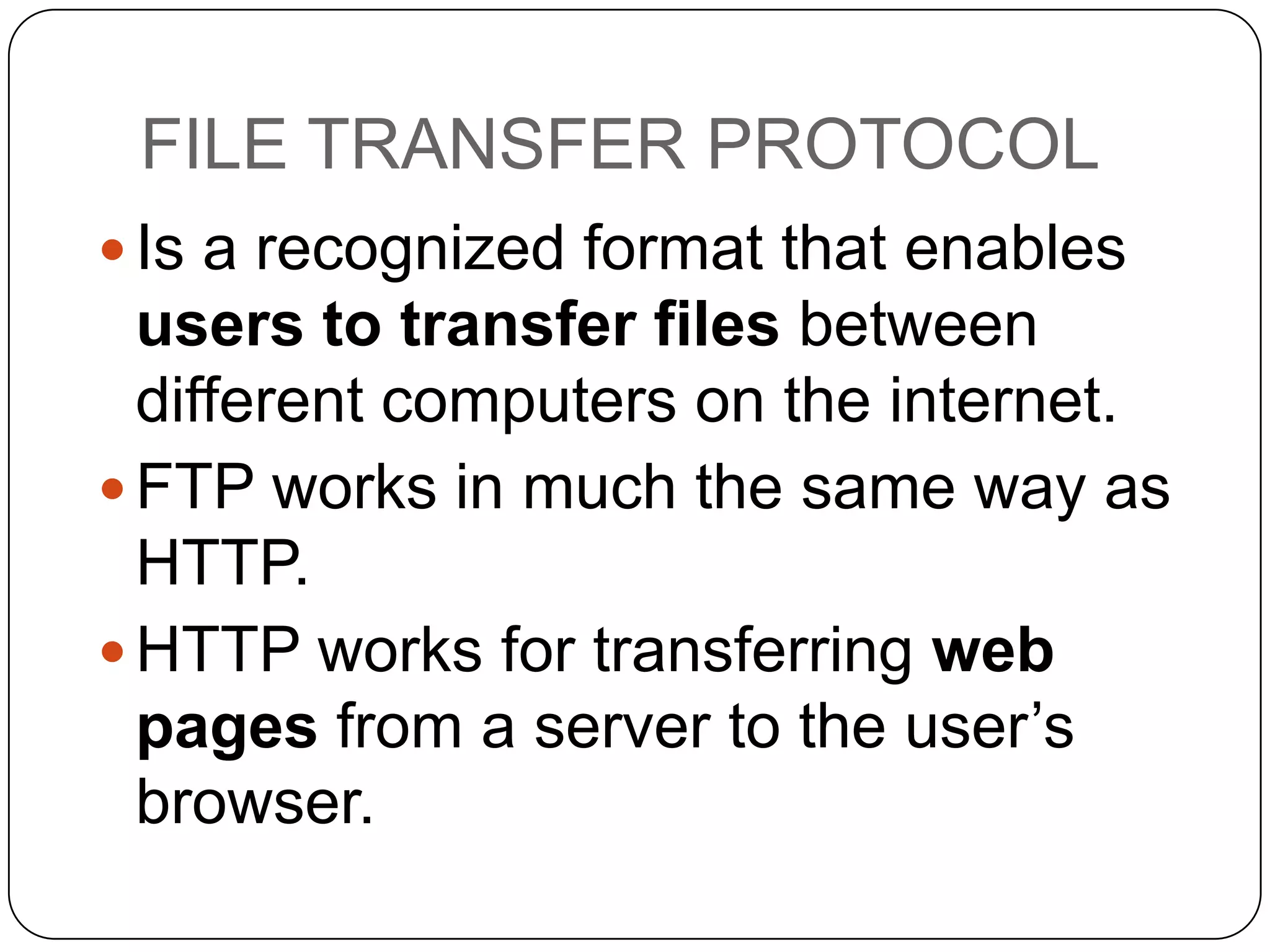
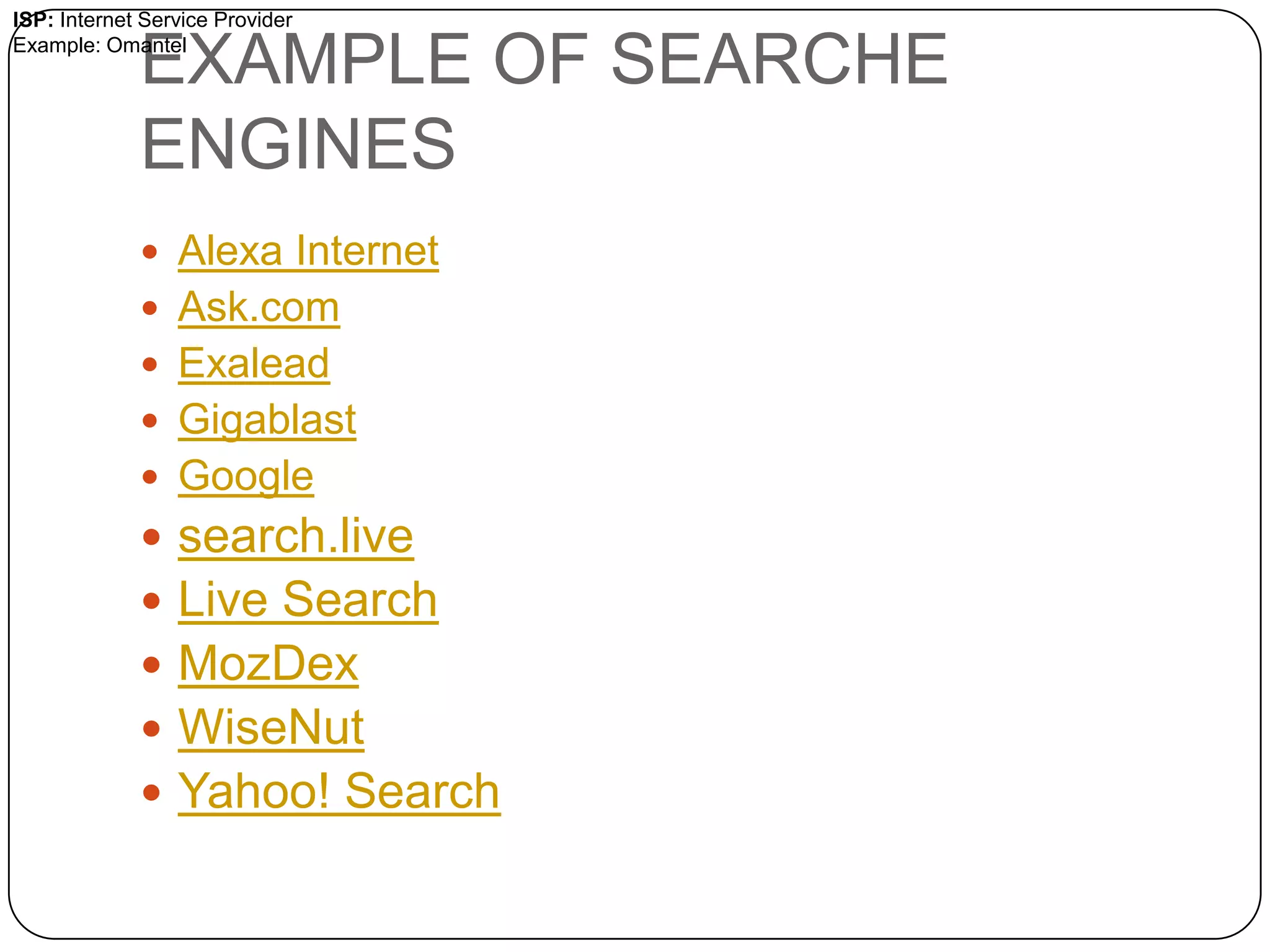
The internet is a global network that connects millions of computers, while the World Wide Web is a collection of web pages accessed via the internet using browsers. URLs uniquely identify web pages and include components like the protocol and domain name. Other important terms discussed include web sites containing pages linked through hyperlinks, web applications, browsers used to view pages, search engines to find sites, and ISPs that provide internet access.