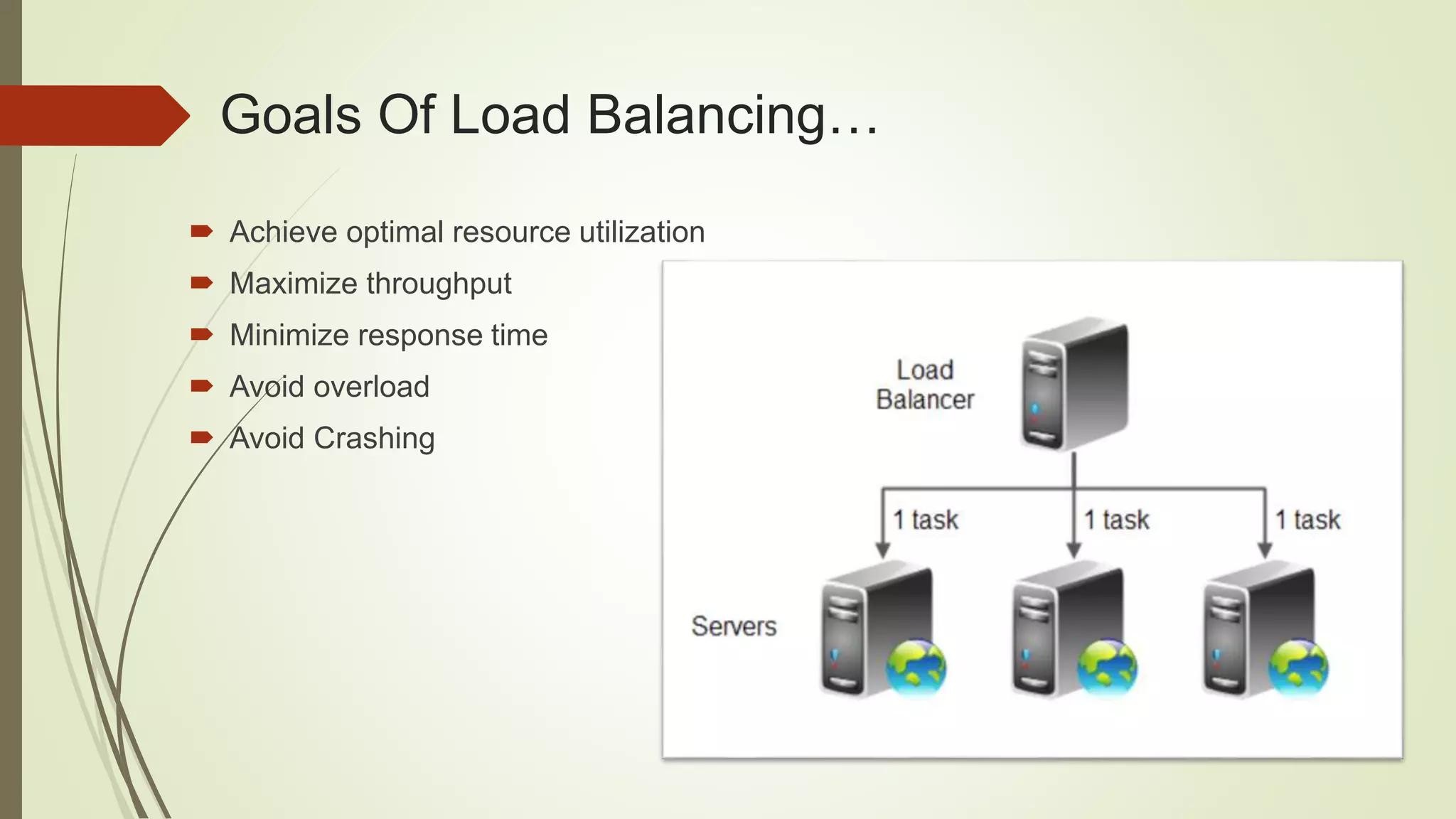
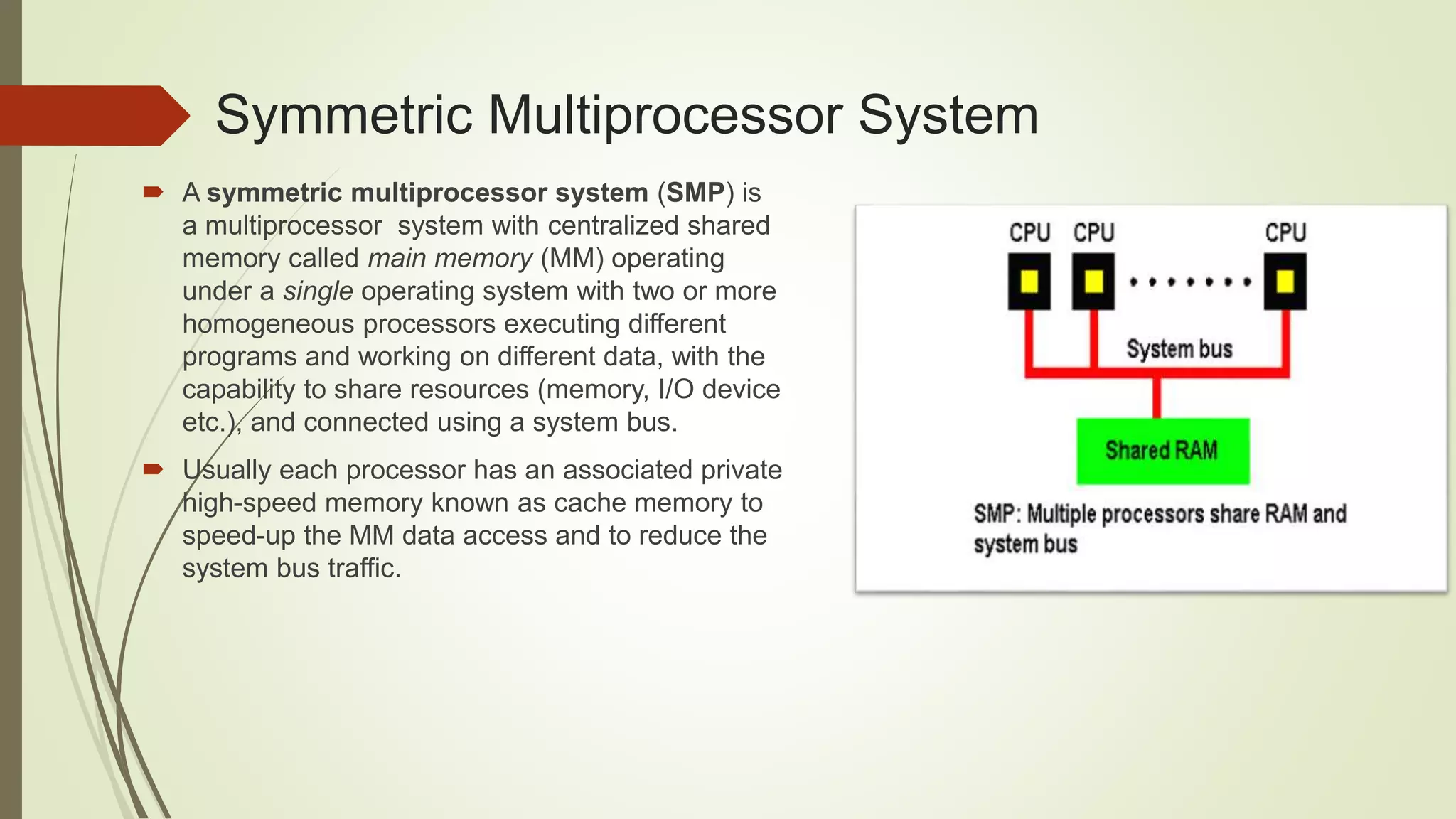
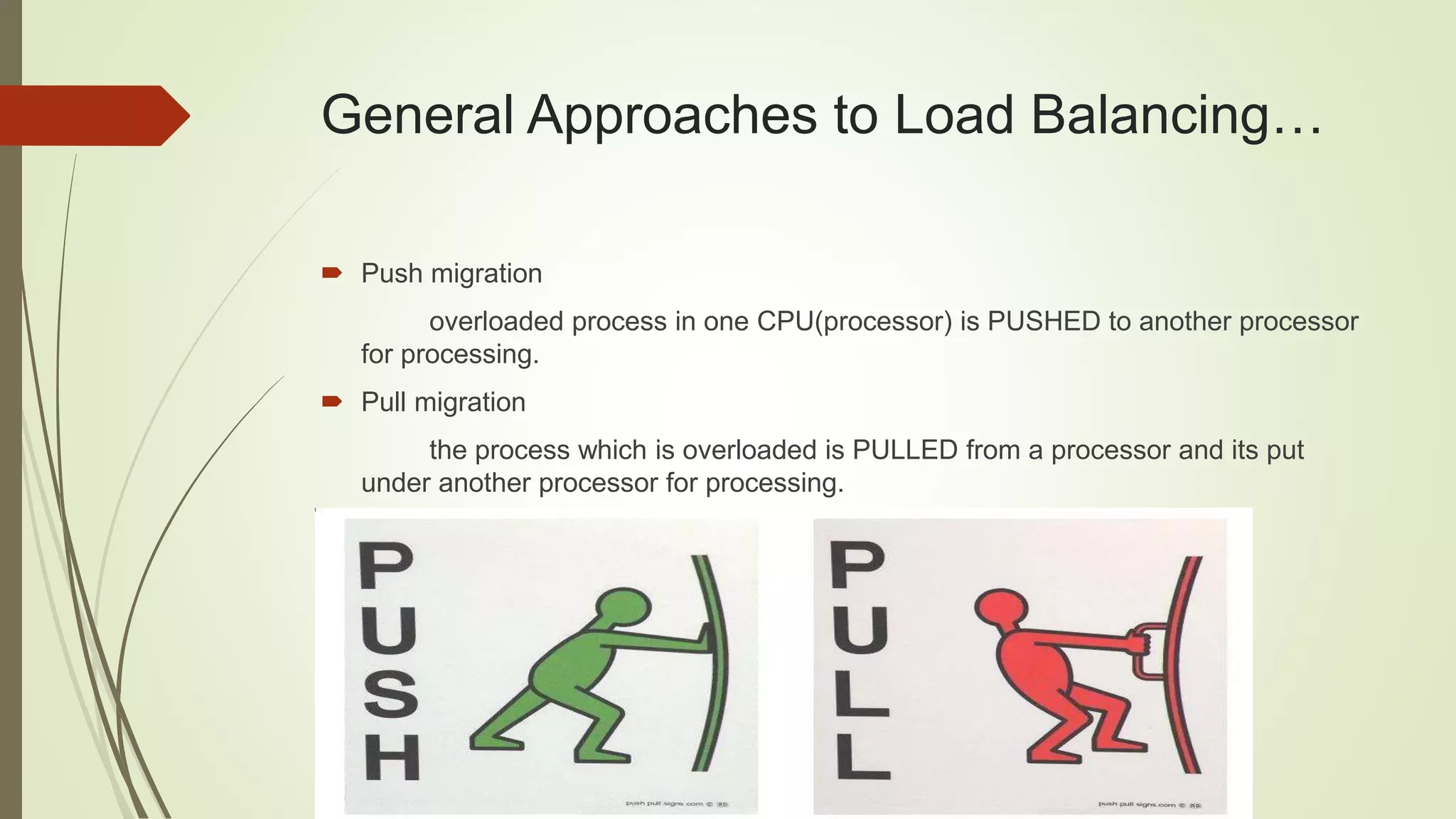
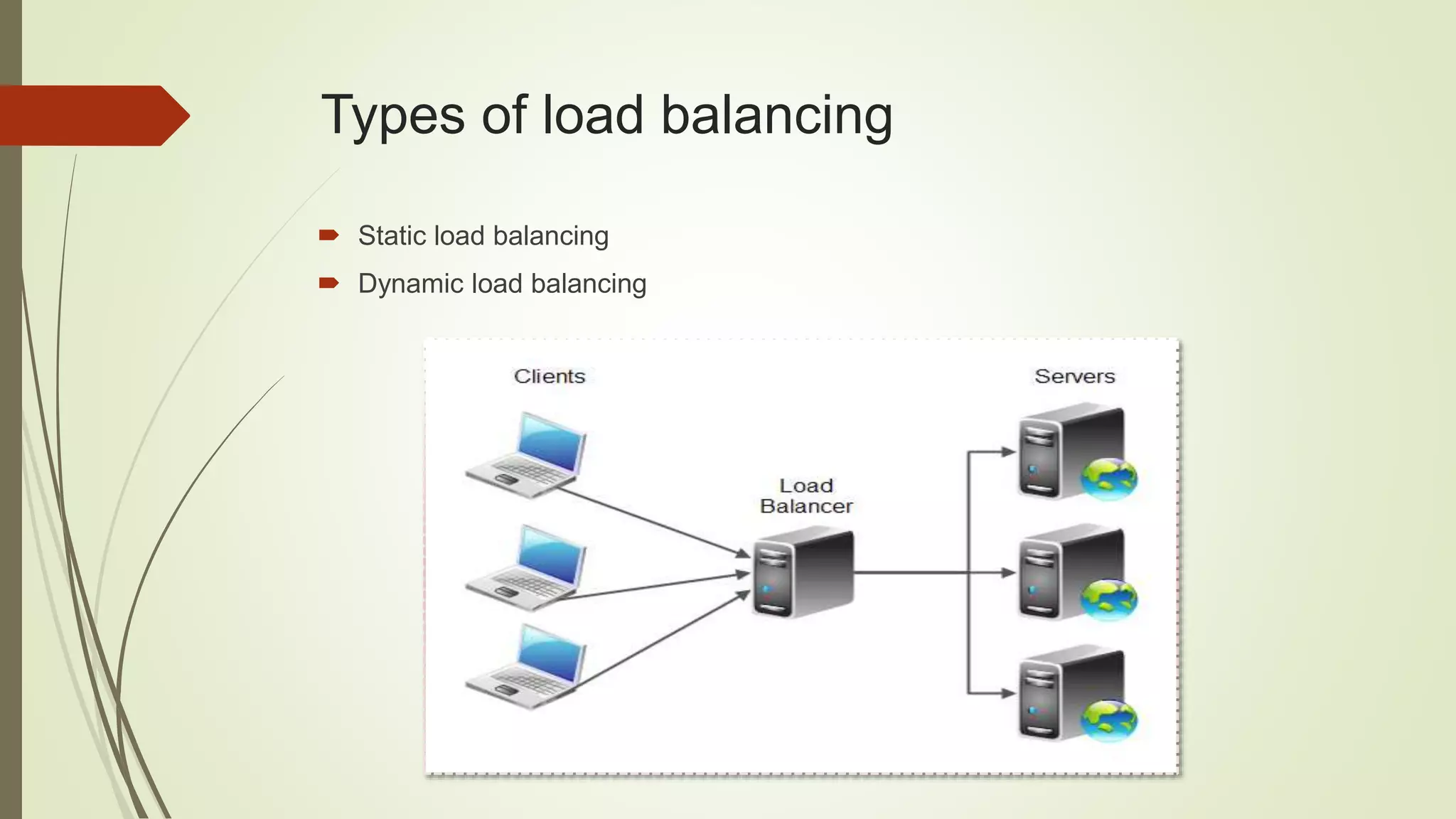
Load balancing aims to distribute work evenly across multiple computing resources like CPUs, servers, or disk drives. It helps maximize resource utilization, minimize response times, and avoid overloading or crashing systems. There are two main approaches: push migration moves processes from overloaded to underloaded CPUs, while pull migration moves processes from busy to idle CPUs. Load balancing can be static or dynamic. Dynamic load balancing continually monitors and adjusts to keep the workload balanced. Round robin load balancing schedules tasks to resources based on their weighted capacities to better handle differences in processing power. Load balancing principles can also apply to life by balancing responsibilities to manage everything effectively.