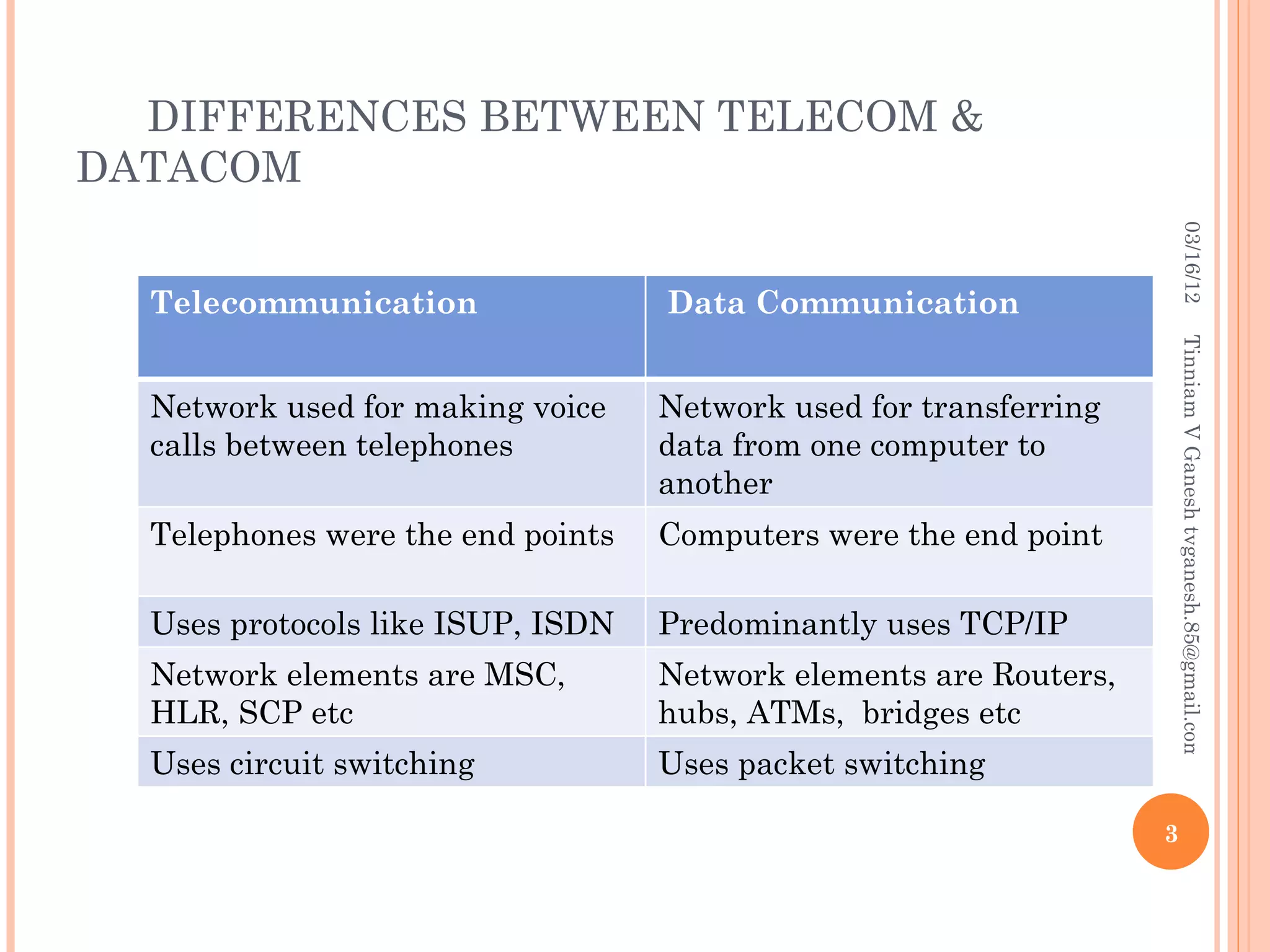
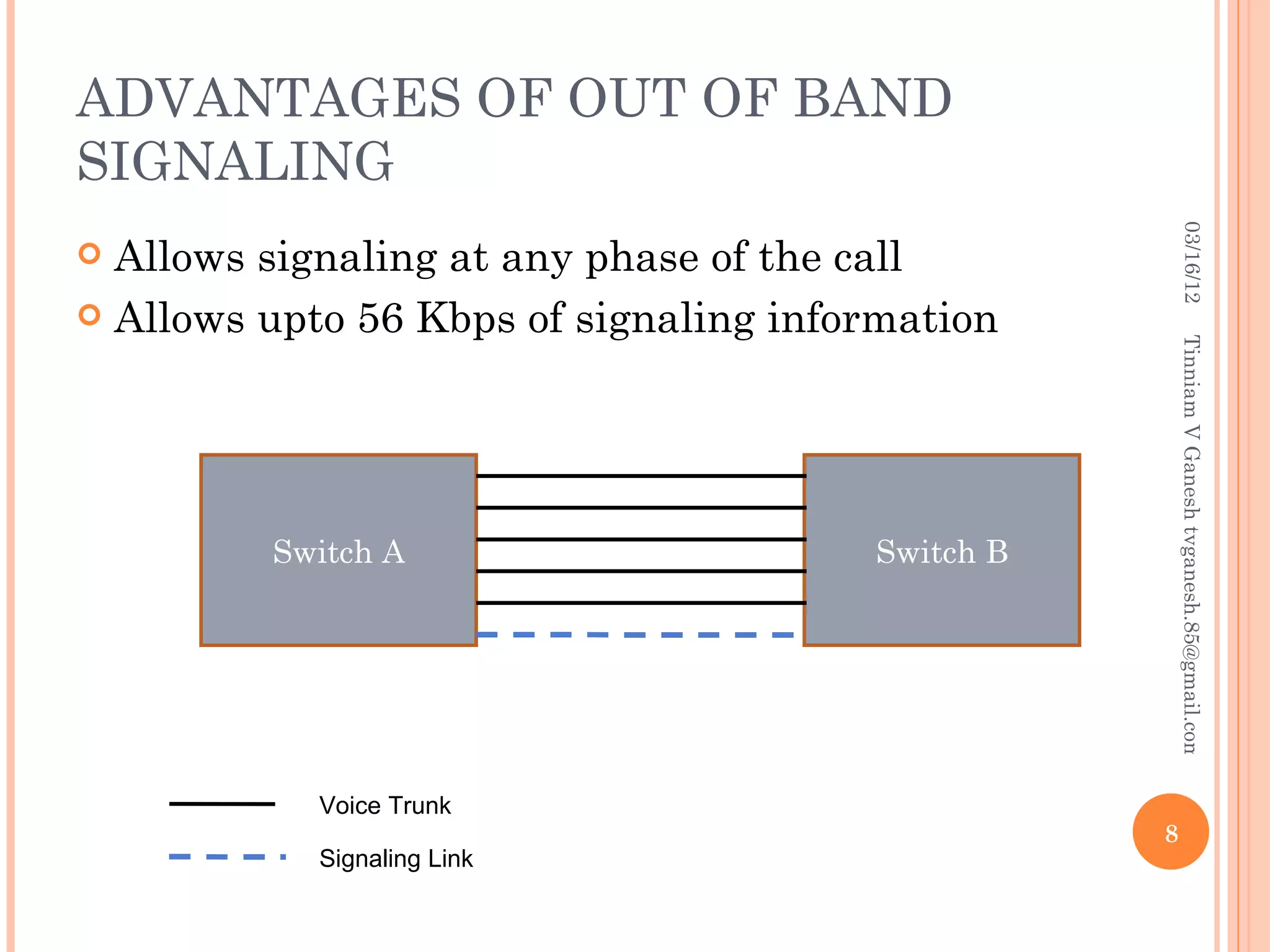
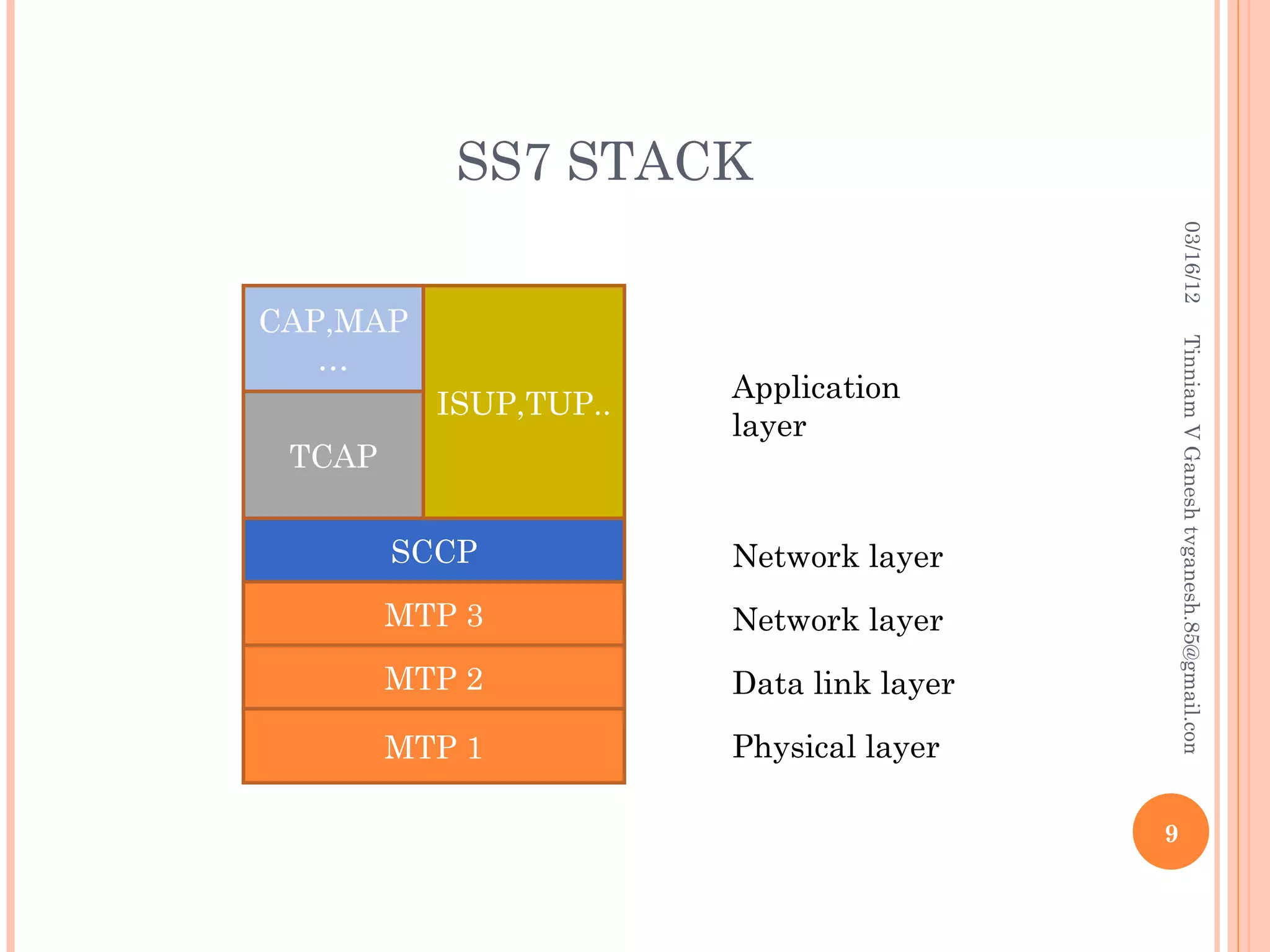
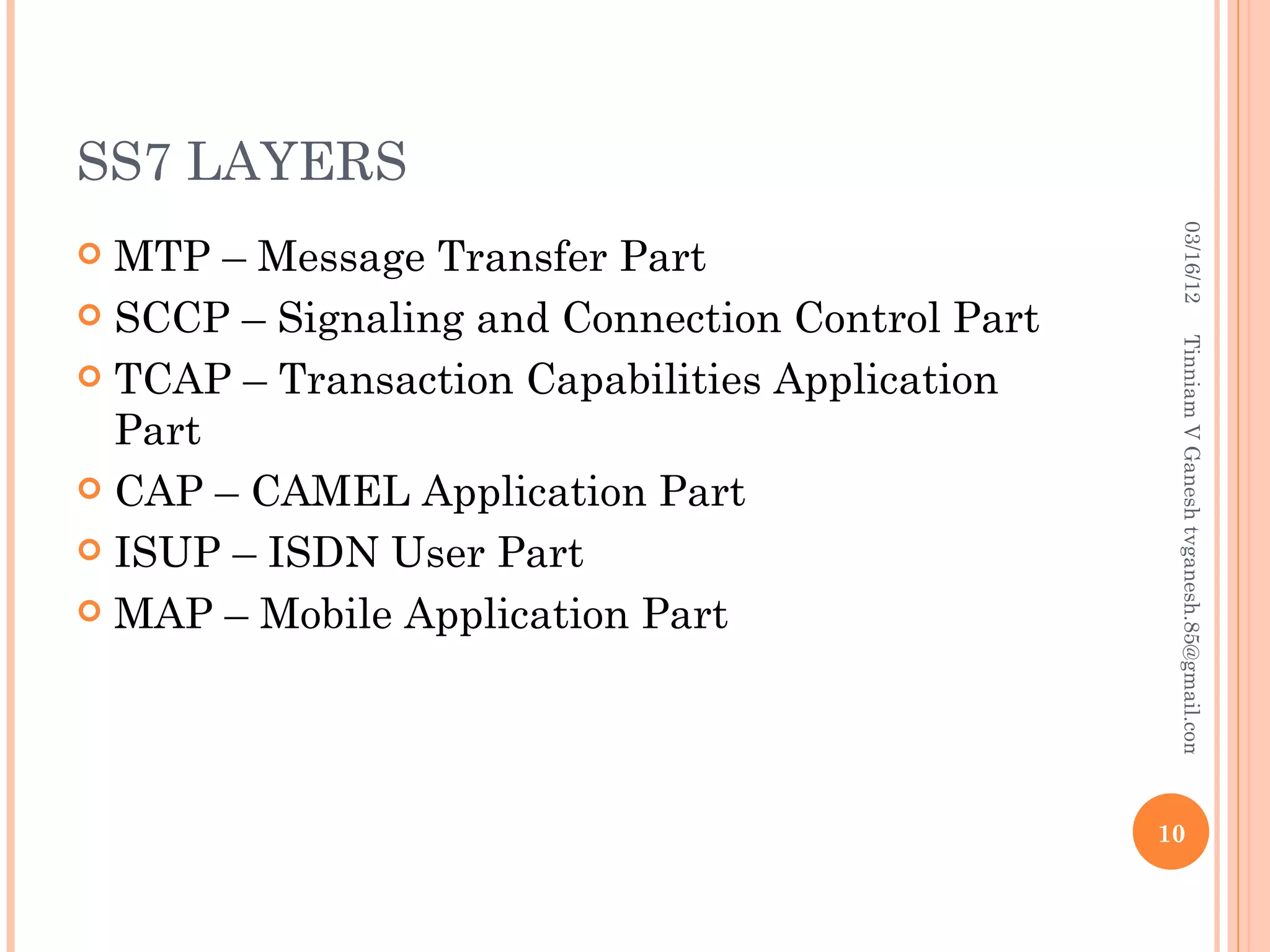
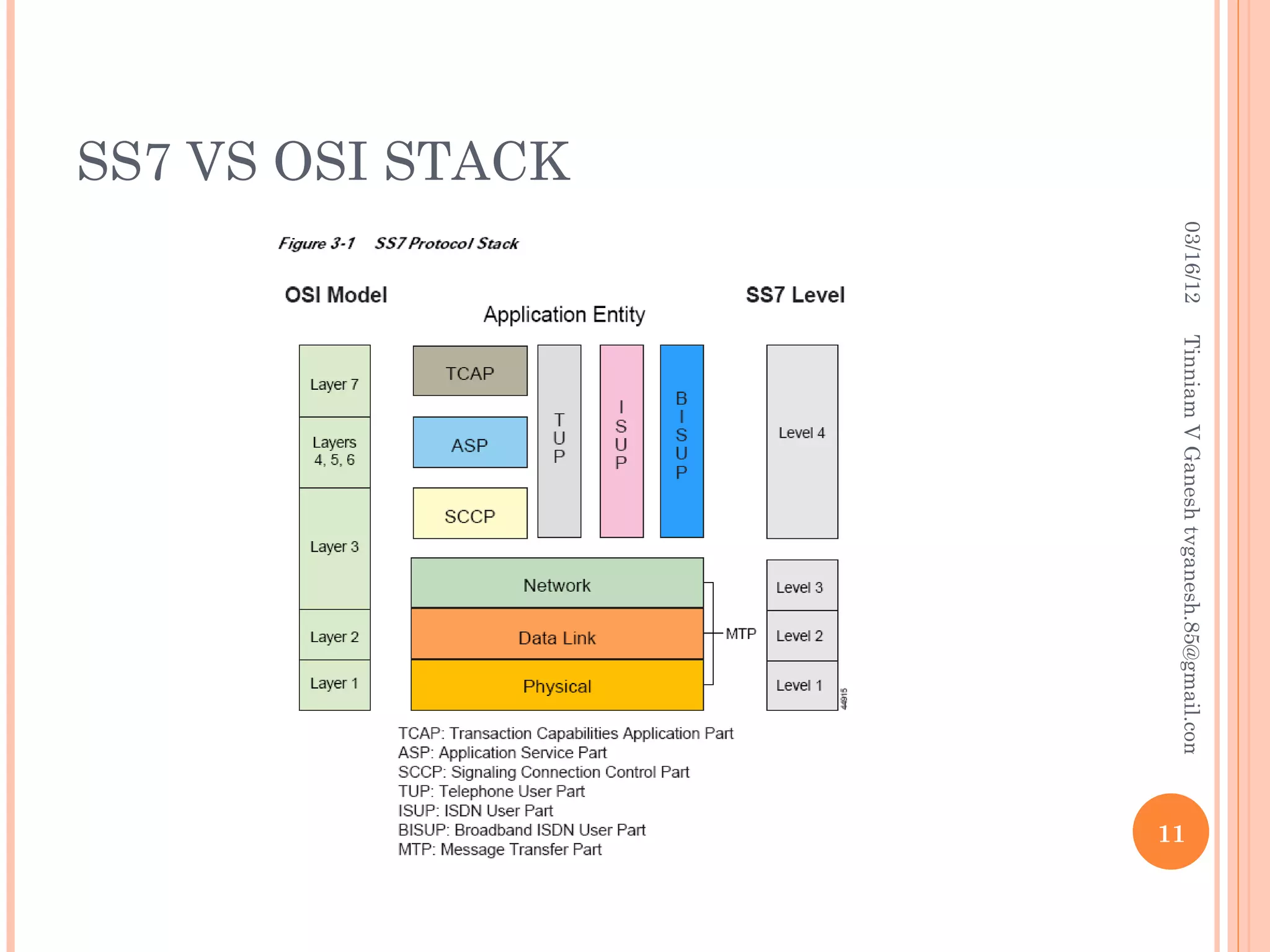
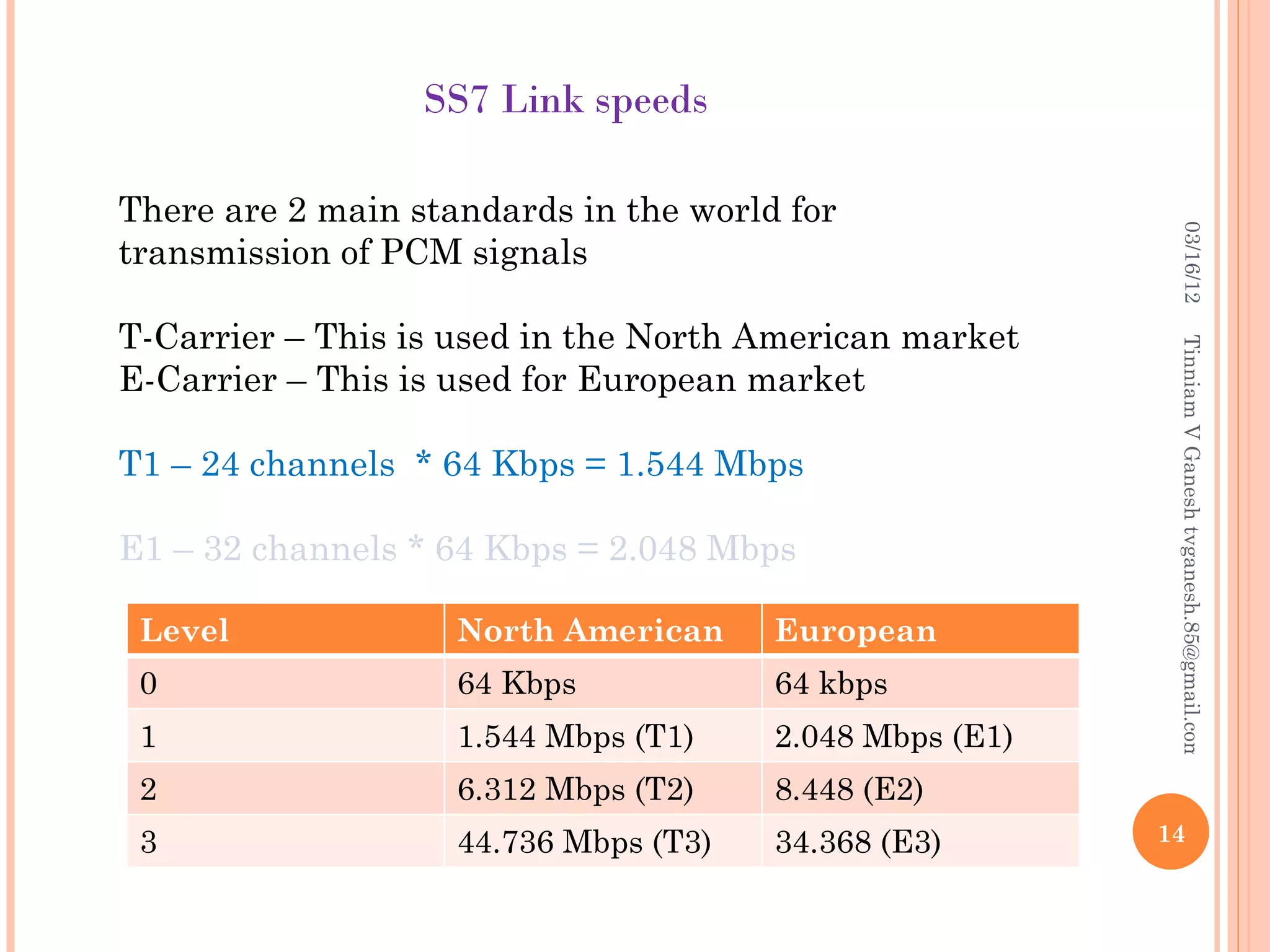
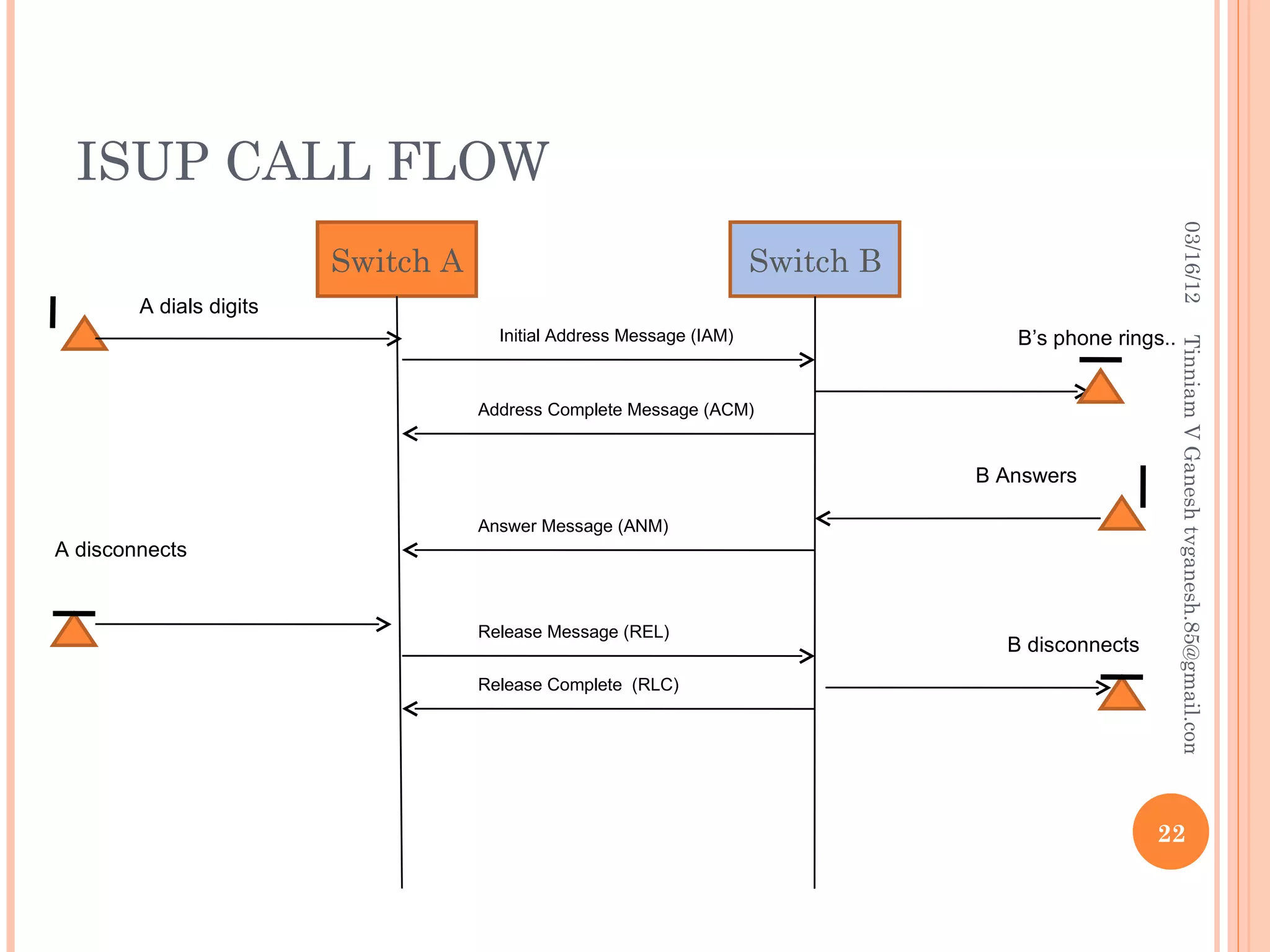
SS7 (Signaling System 7) is a set of telephony signaling protocols that are used to set up most of the world's public switched telephone network (PSTN) telephone calls. It uses a separate channel for signaling information rather than transmitting call setup and control data over the same channel as the actual voice circuit. The SS7 protocol stack has multiple layers including the MTP, SCCP and TCAP layers to transport signaling messages and route calls between network elements. Common SS7 protocols include ISUP, MAP, TCAP and CAP.