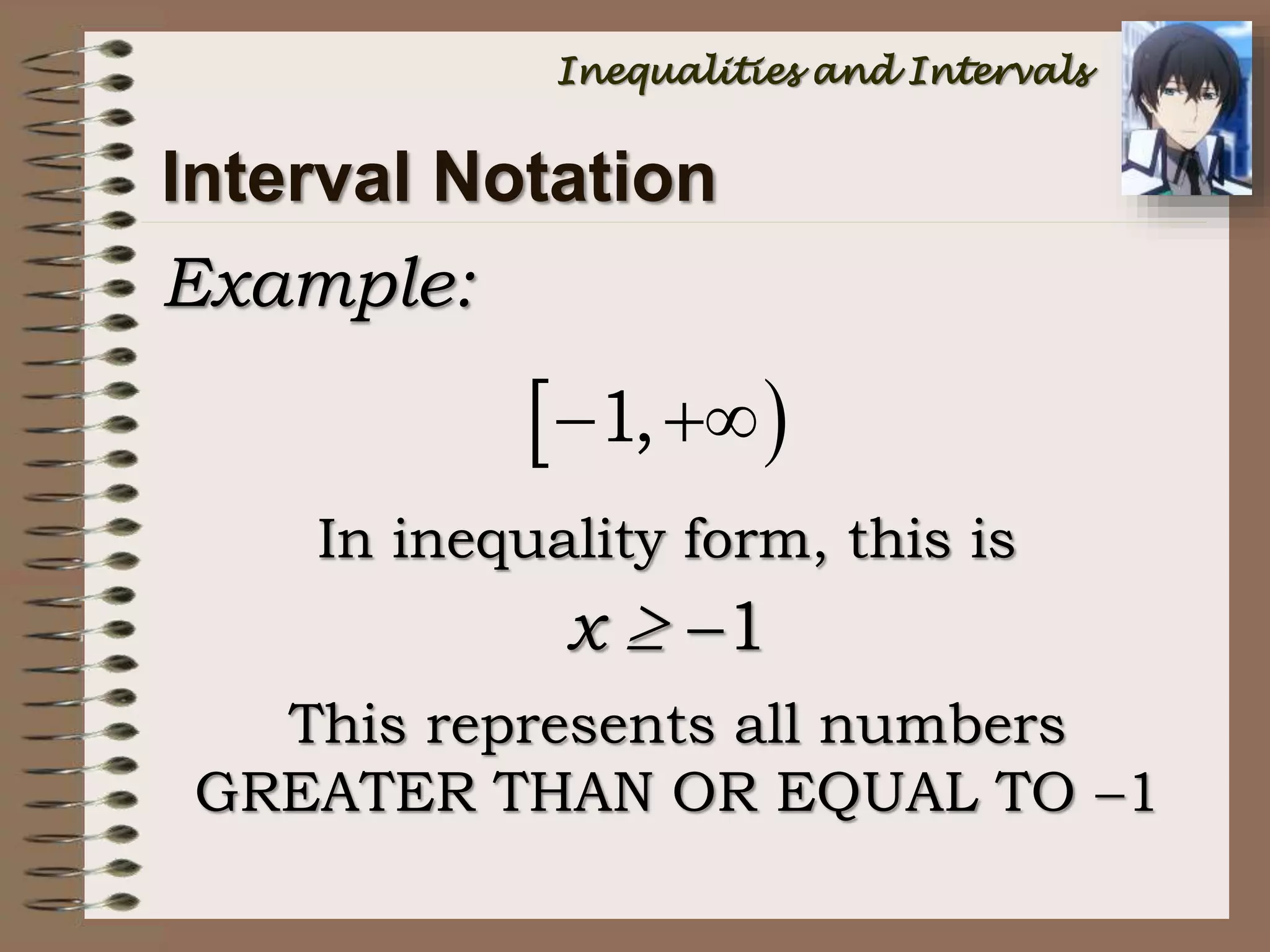
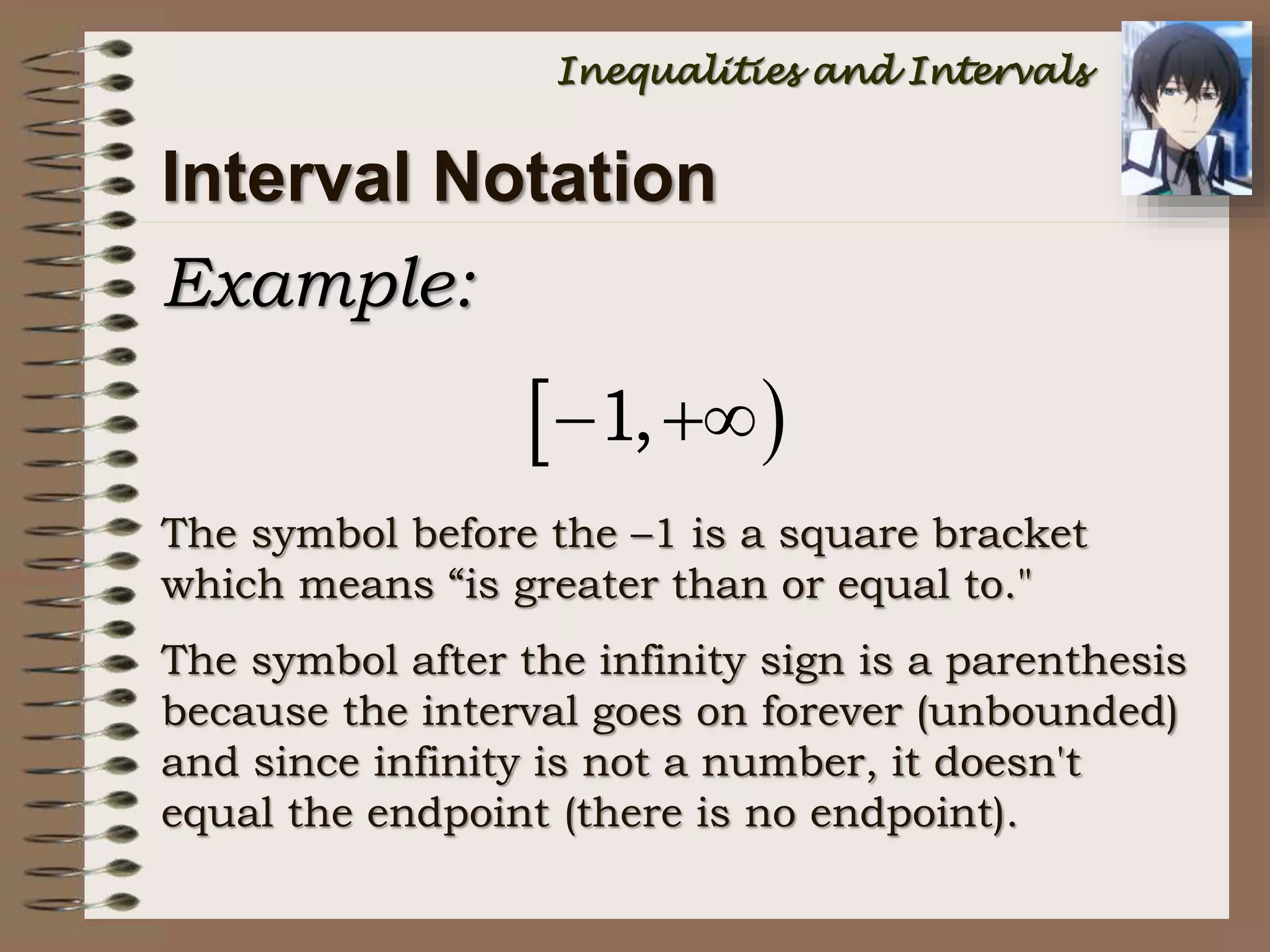
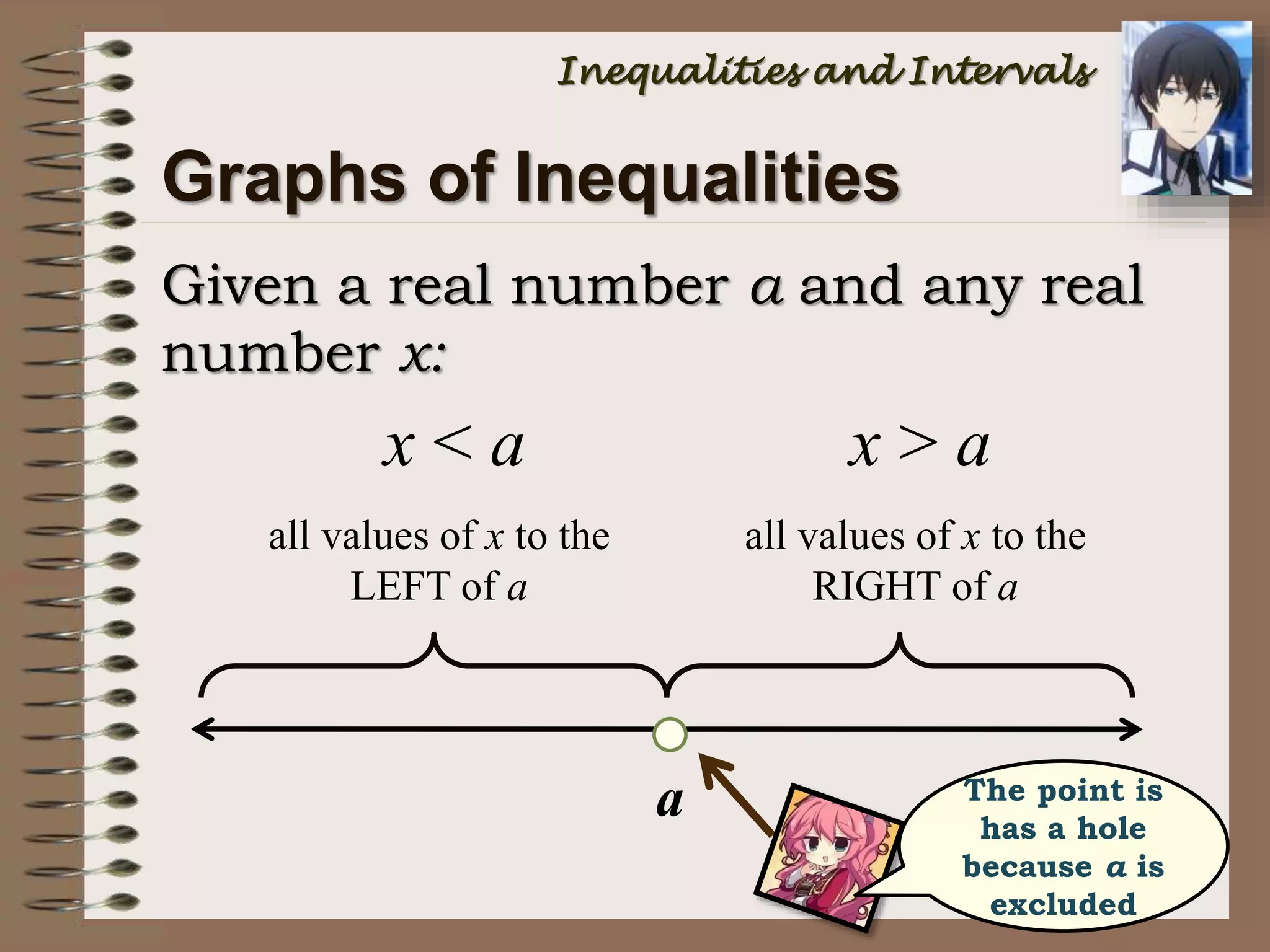
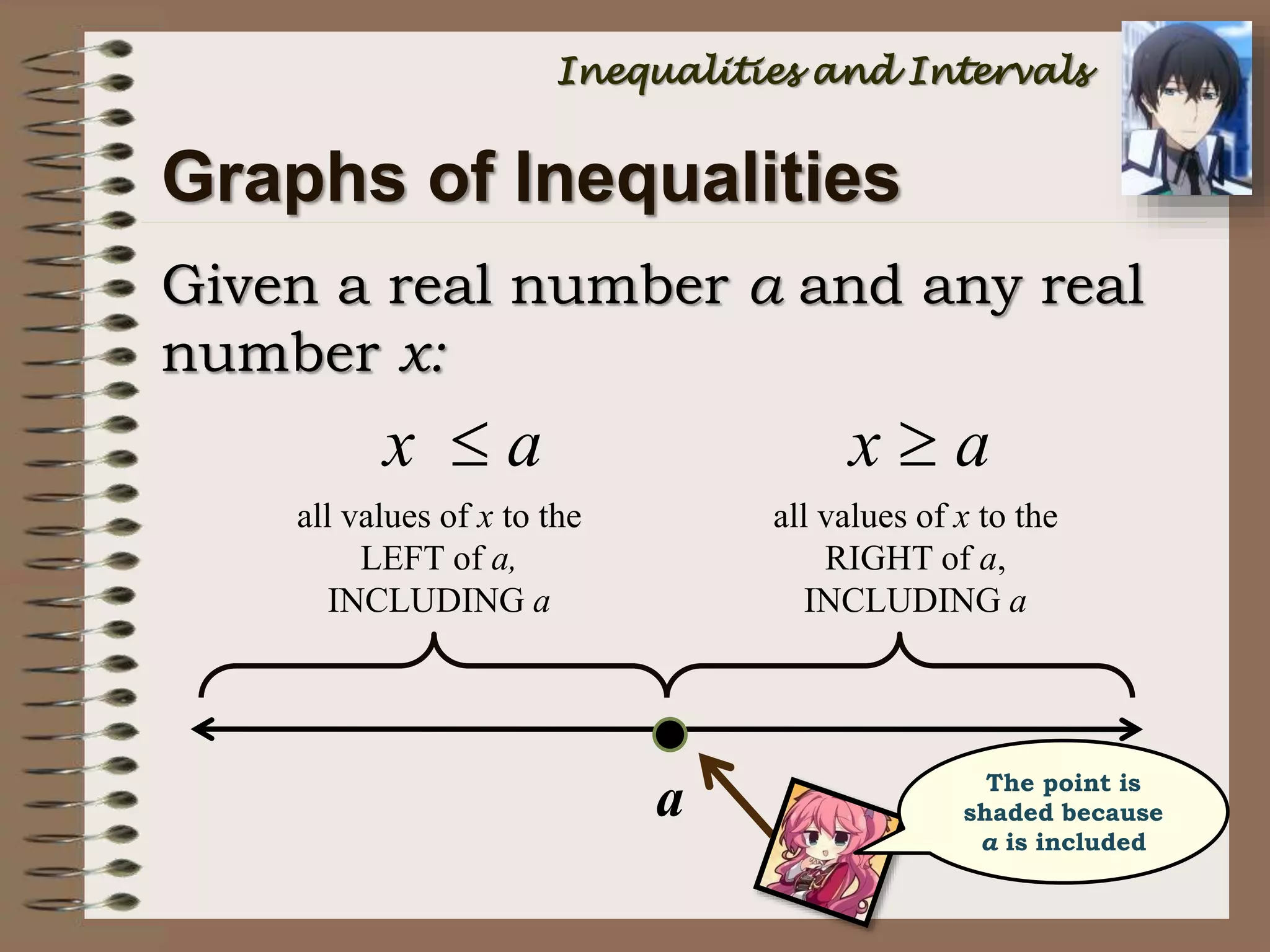
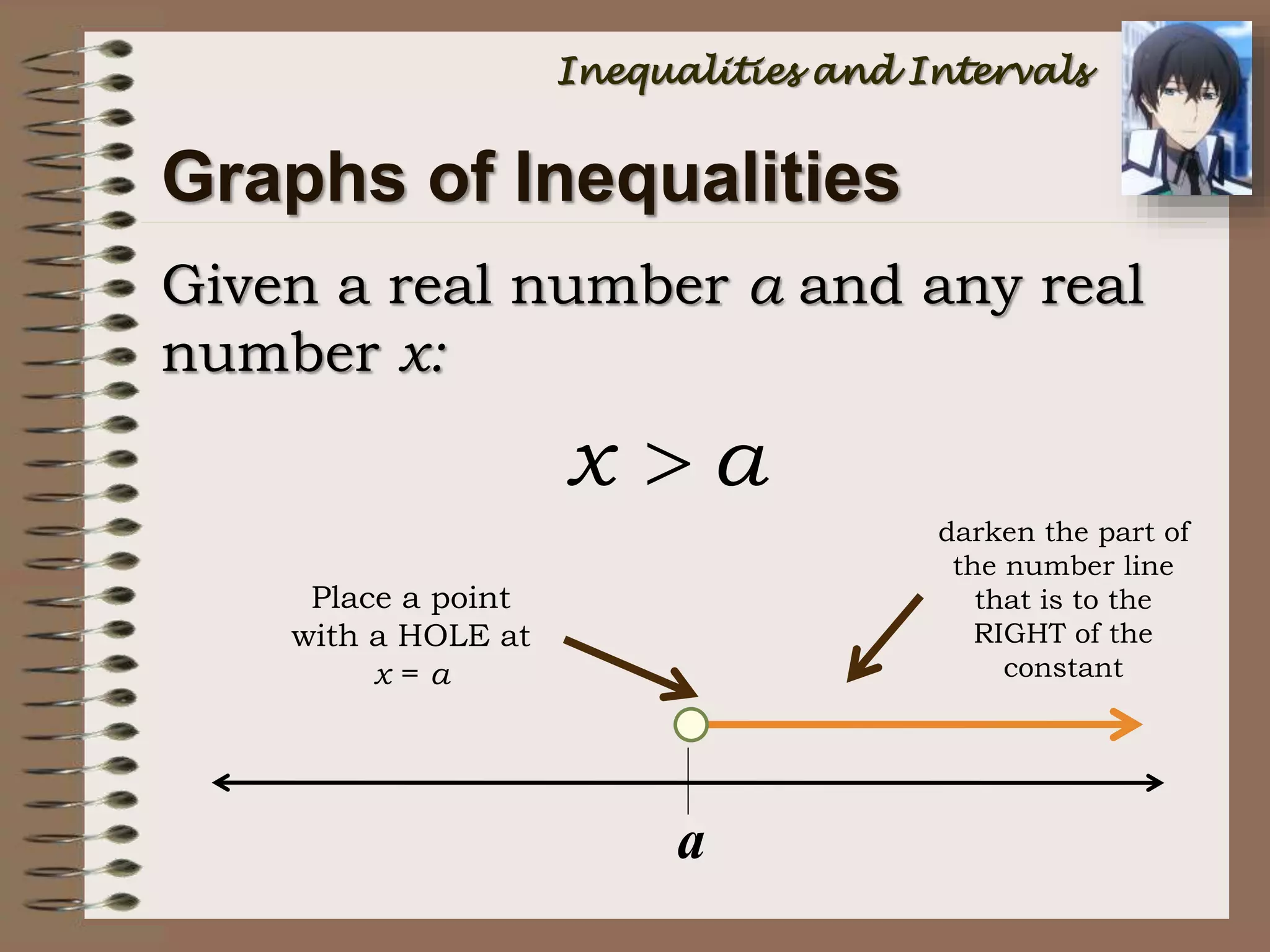
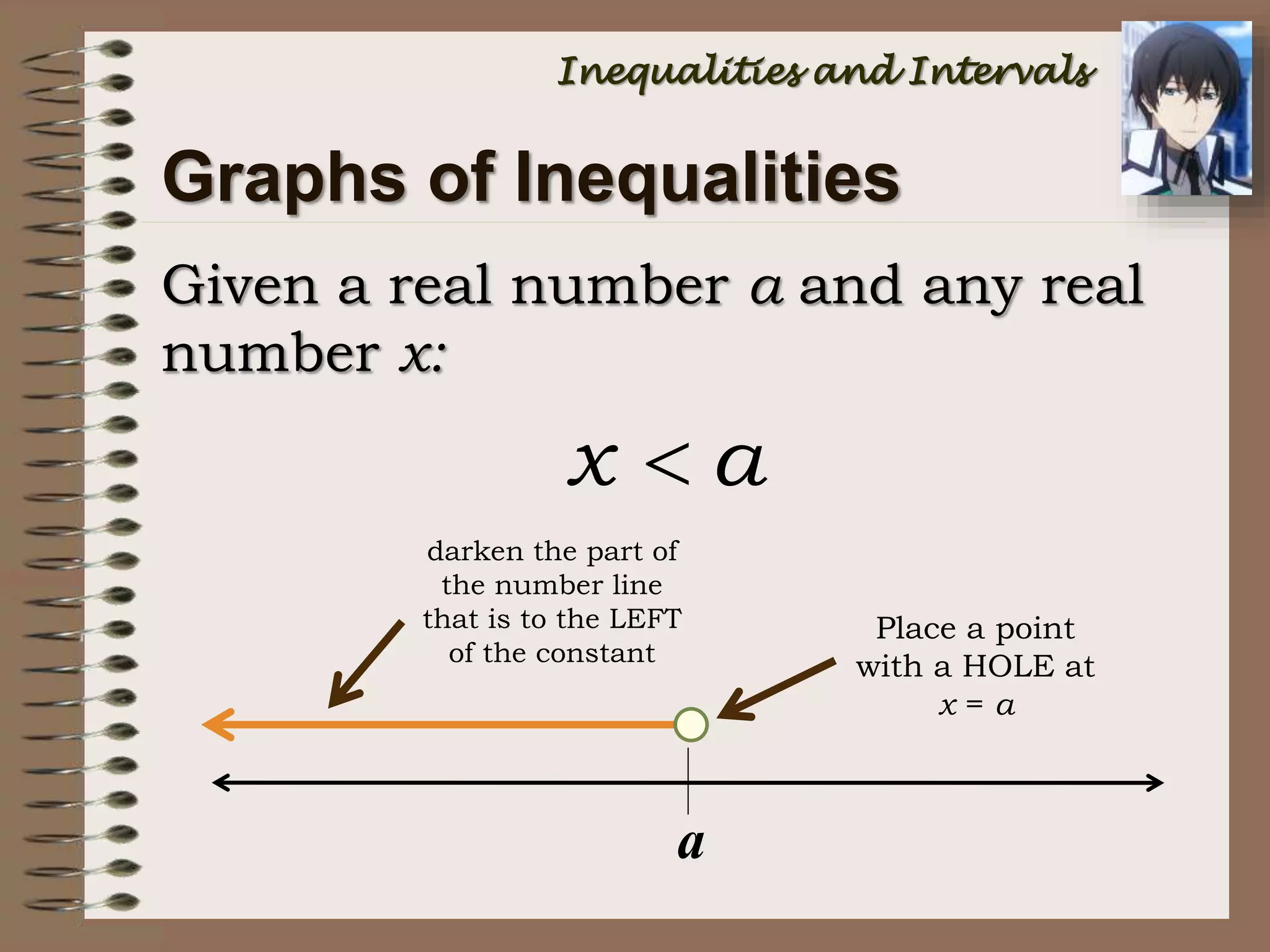
This document provides an introduction to inequalities and intervals. It defines inequalities as ranges of values rather than single numbers, showing that a quantity is greater than or less than another. Symbols for inequalities like <, >, ≤, ≥ are introduced. Compound inequalities representing values between two numbers are explained. Interval notation is defined using brackets and parentheses to indicate whether endpoints are included or not. Examples of writing inequalities as intervals and graphing intervals on number lines are provided.






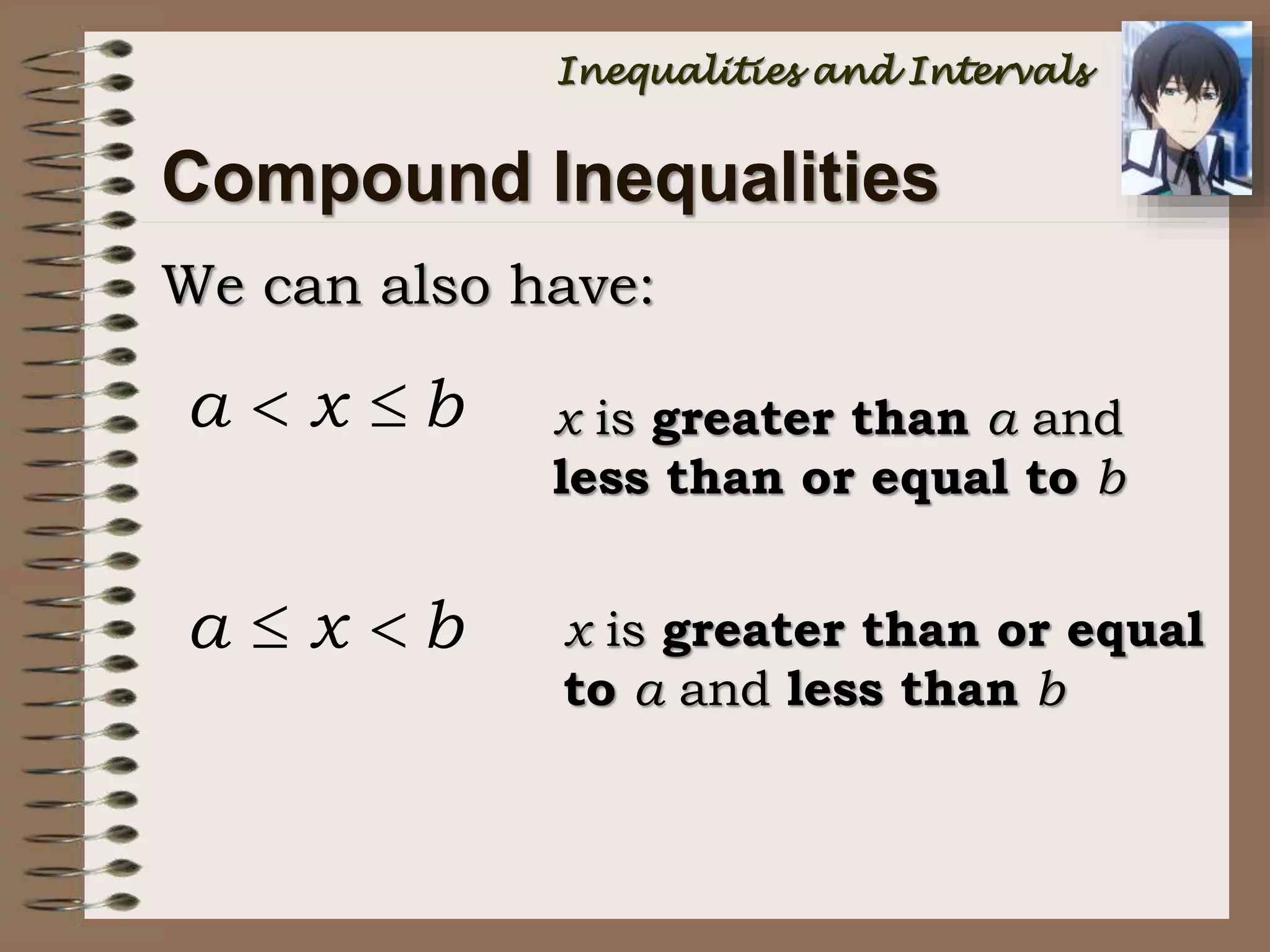



![Notations
• A parenthesis ( ) shows an open (not
included) endpoint
• A bracket [ ] shows a closed [included]
endpoint
• The infinity symbol () is used to describe
very large or very small numbers
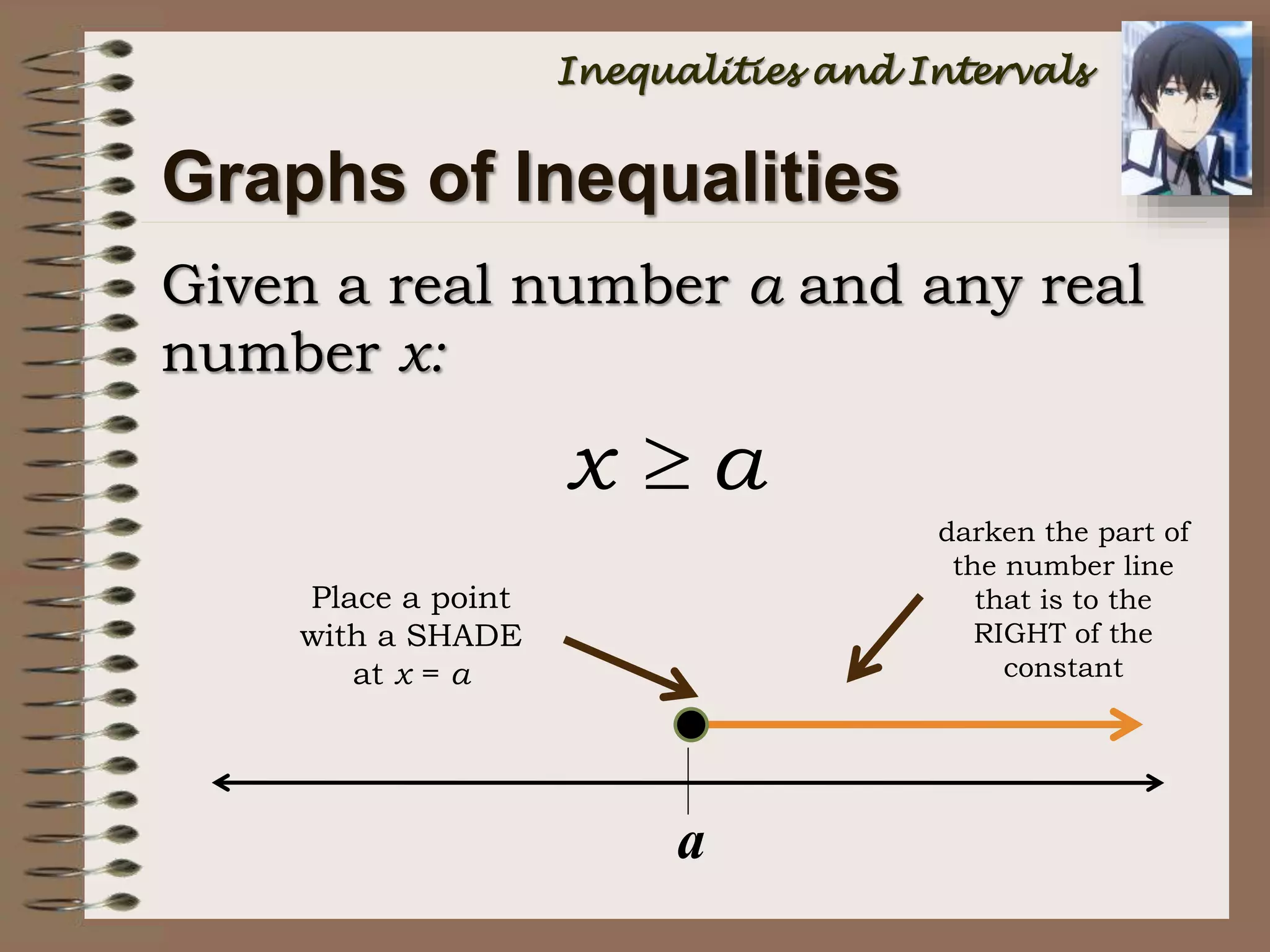
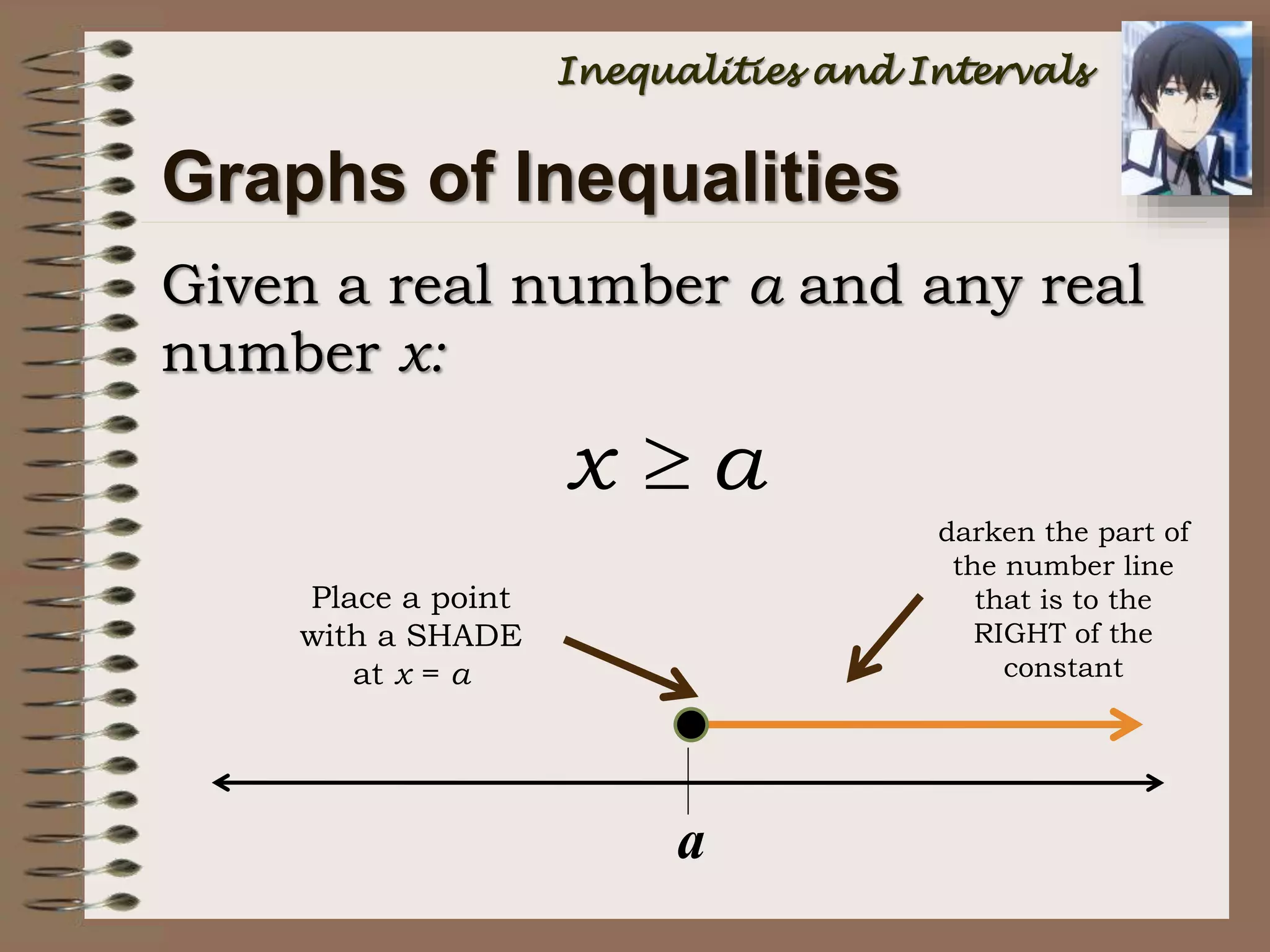
+ or - all numbers GREATER than another
- all numbers GREATER than another
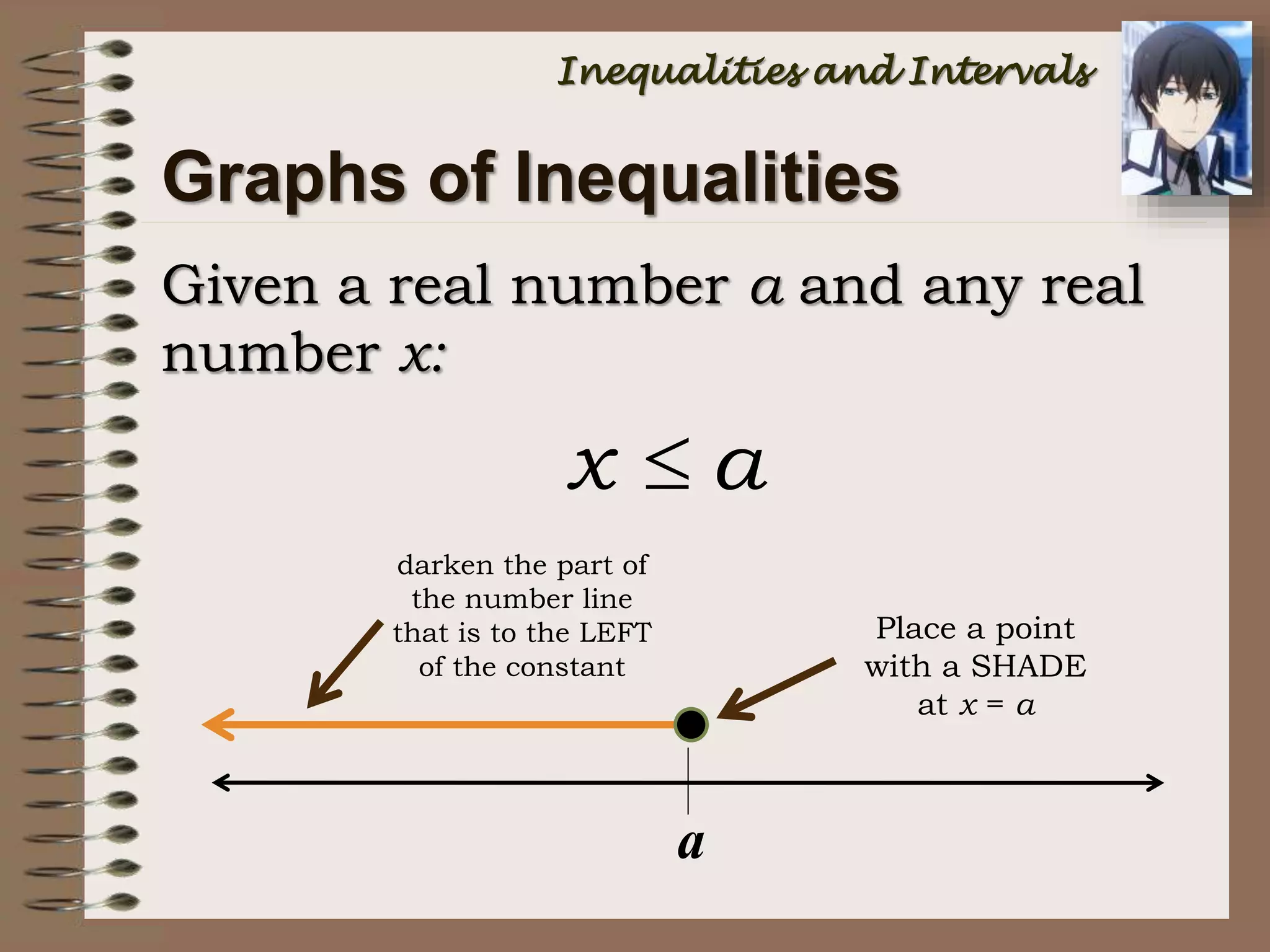
Note that “” is NOT A NUMBER!
Interval Notation
Inequalities and Intervals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/math7-inequalitiesandintervals-150207083129-conversion-gate02/75/Math-7-inequalities-and-intervals-32-2048.jpg)
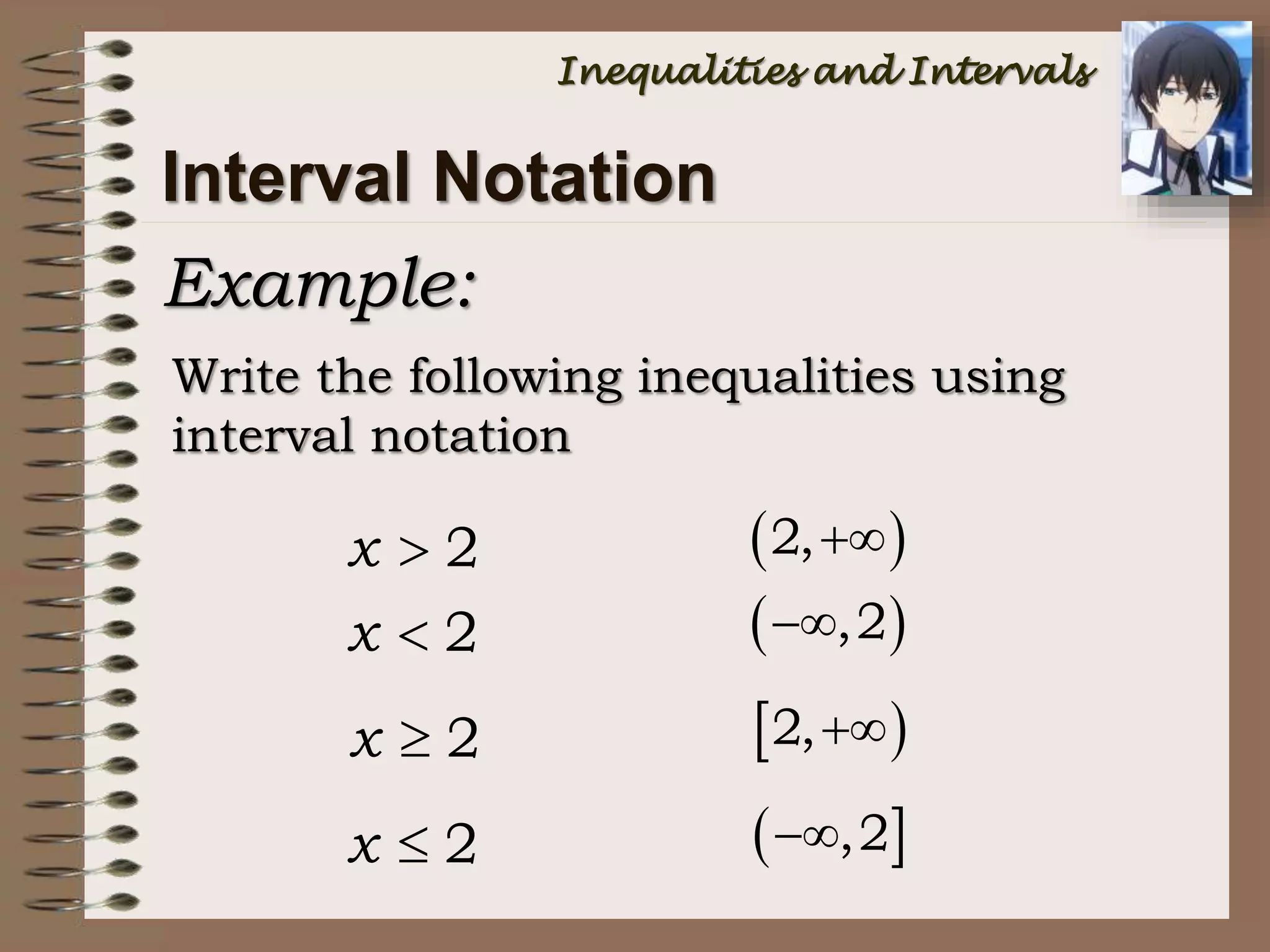
![Interval Notation
INEQUALITY SET NOTATION
INTERVAL
NOTATION
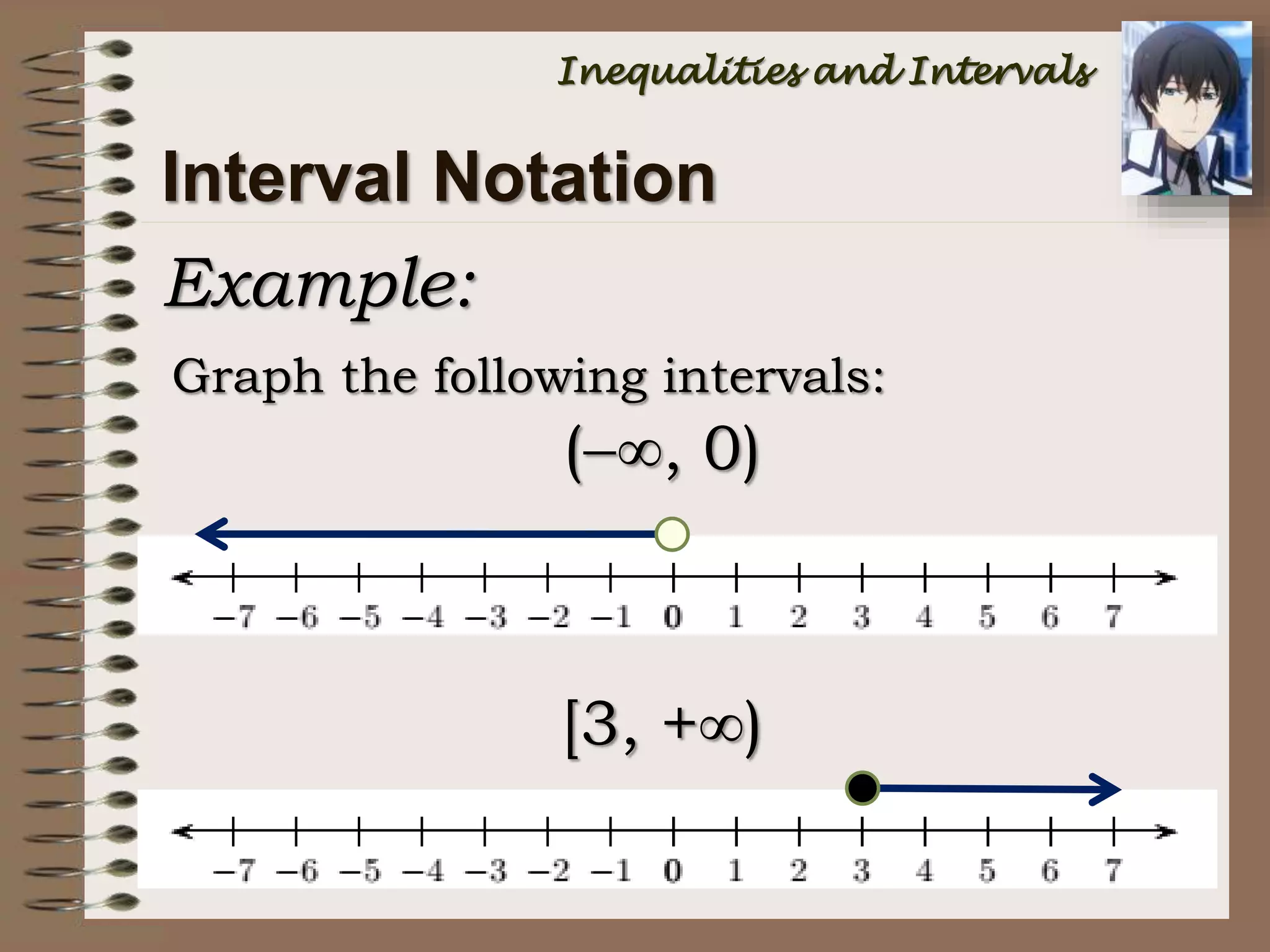
x > a { x | x > a } (a, +)
x < a { x | x < a } (-, a)
x a { x | x a } [a, +)
x a { x | x a } (-, a]
Inequalities and Intervals
Unbounded Intervals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/math7-inequalitiesandintervals-150207083129-conversion-gate02/75/Math-7-inequalities-and-intervals-33-2048.jpg)
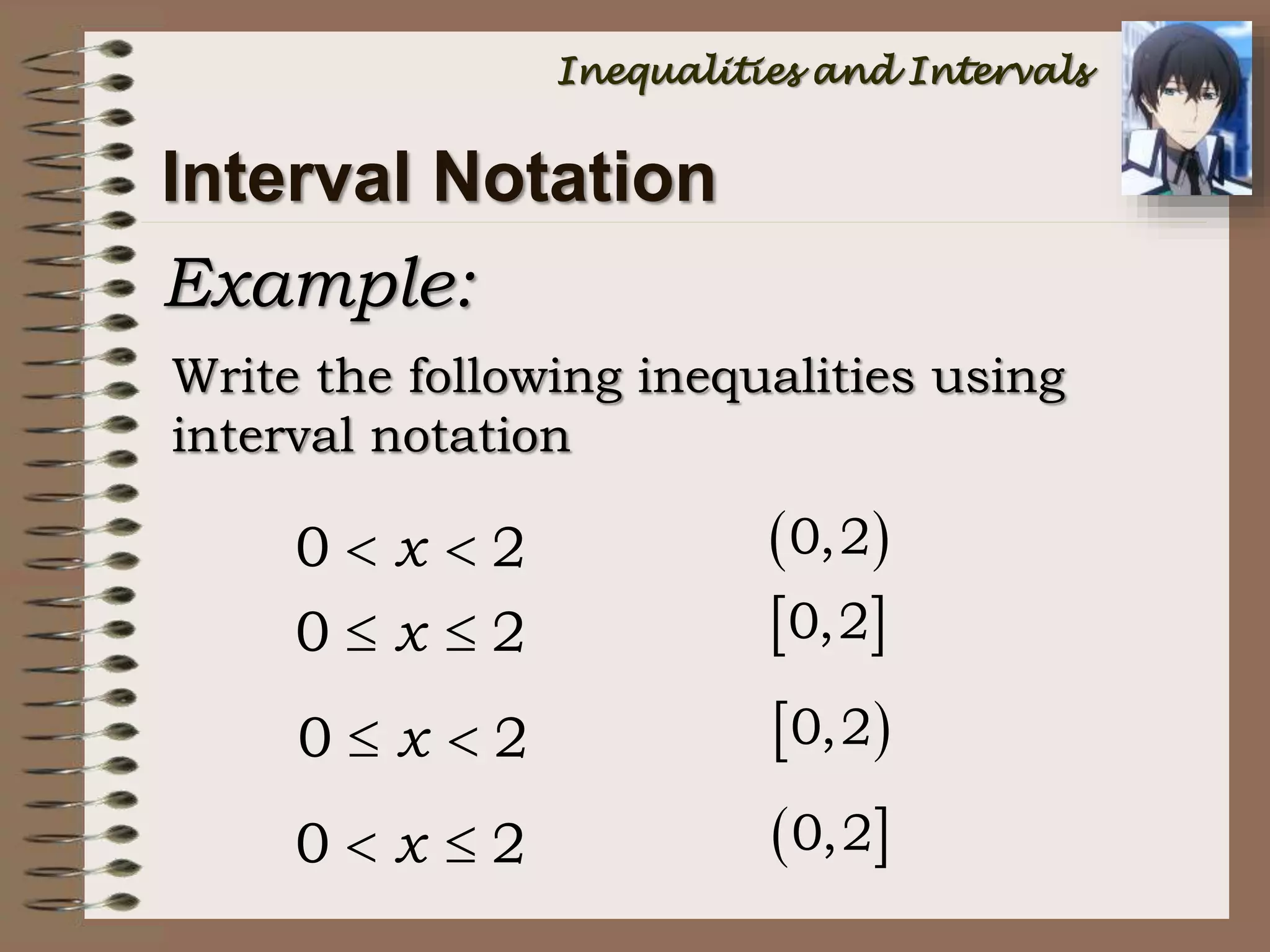
![Interval Notation
INEQUALITY SET NOTATION
INTERVAL
NOTATION
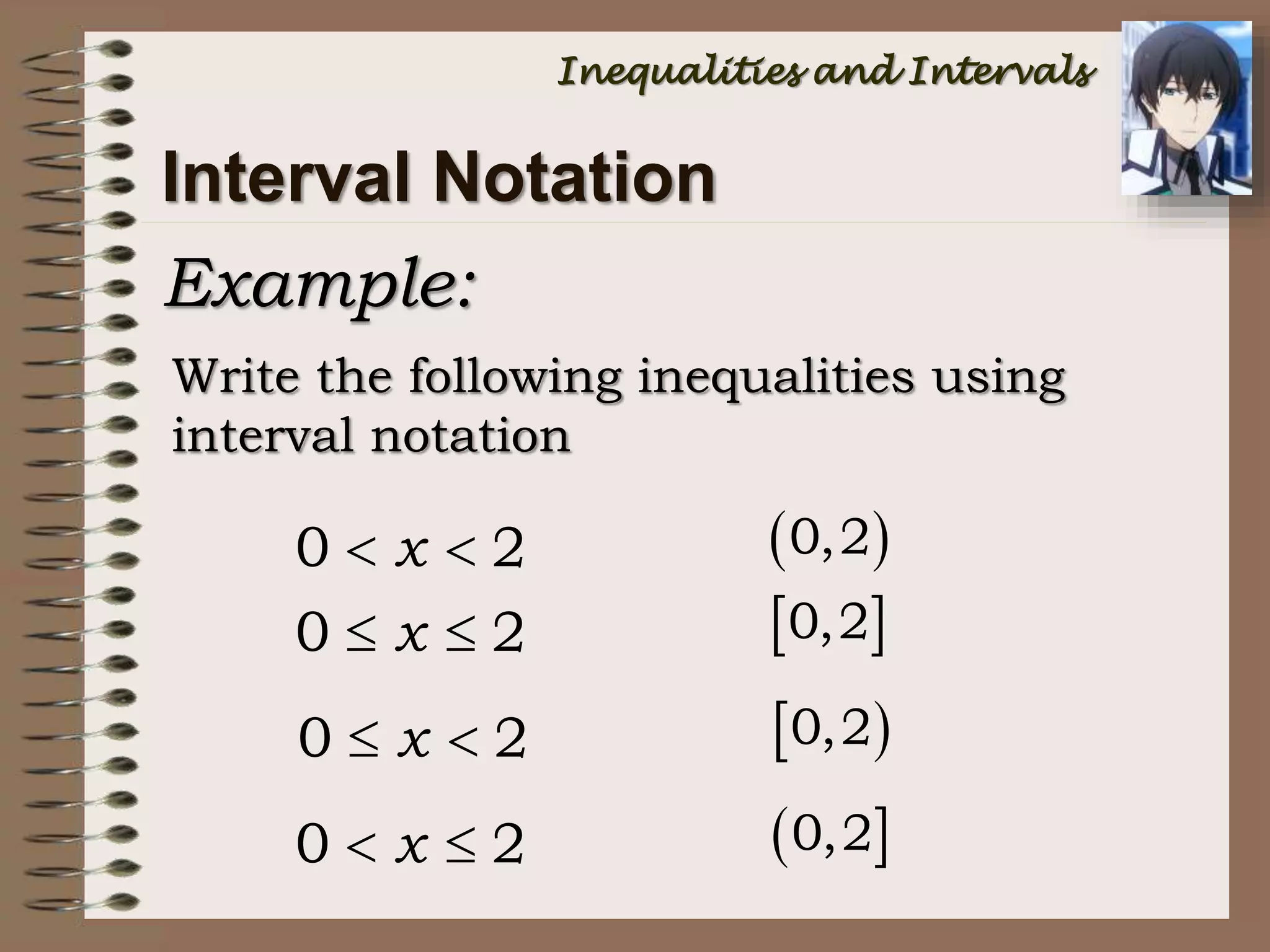
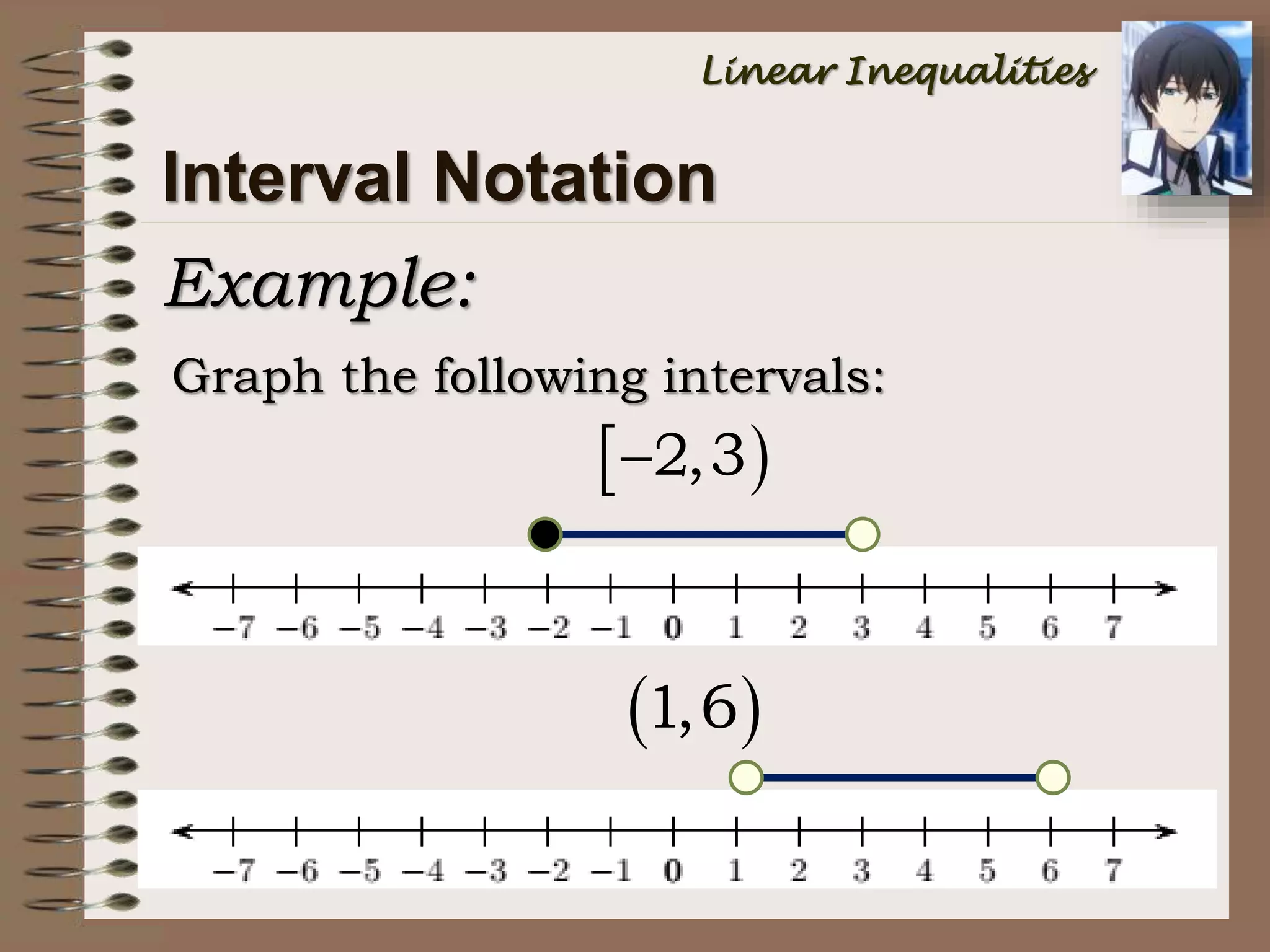
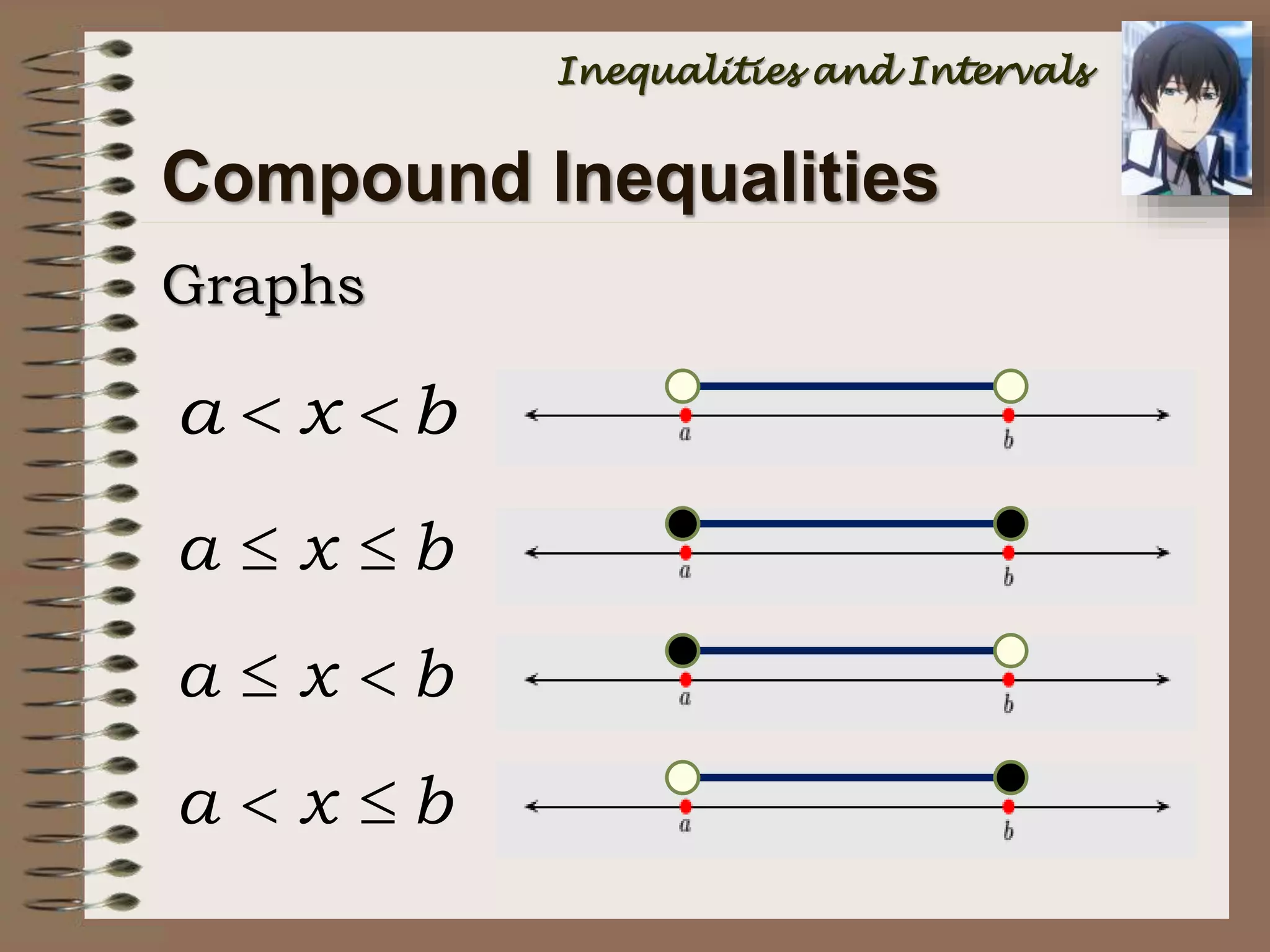
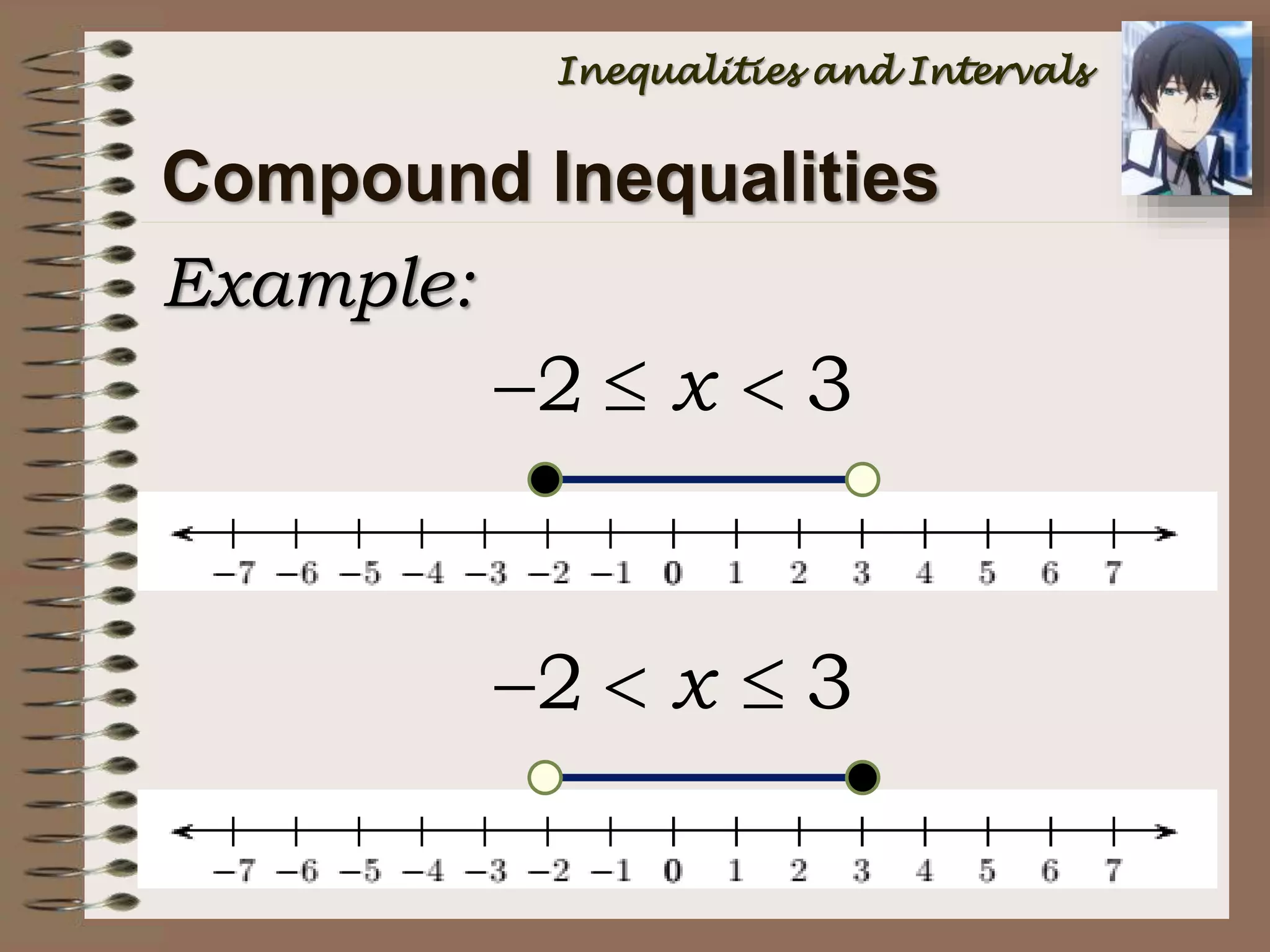
a < x < b { x | a < x < b } (a, b)
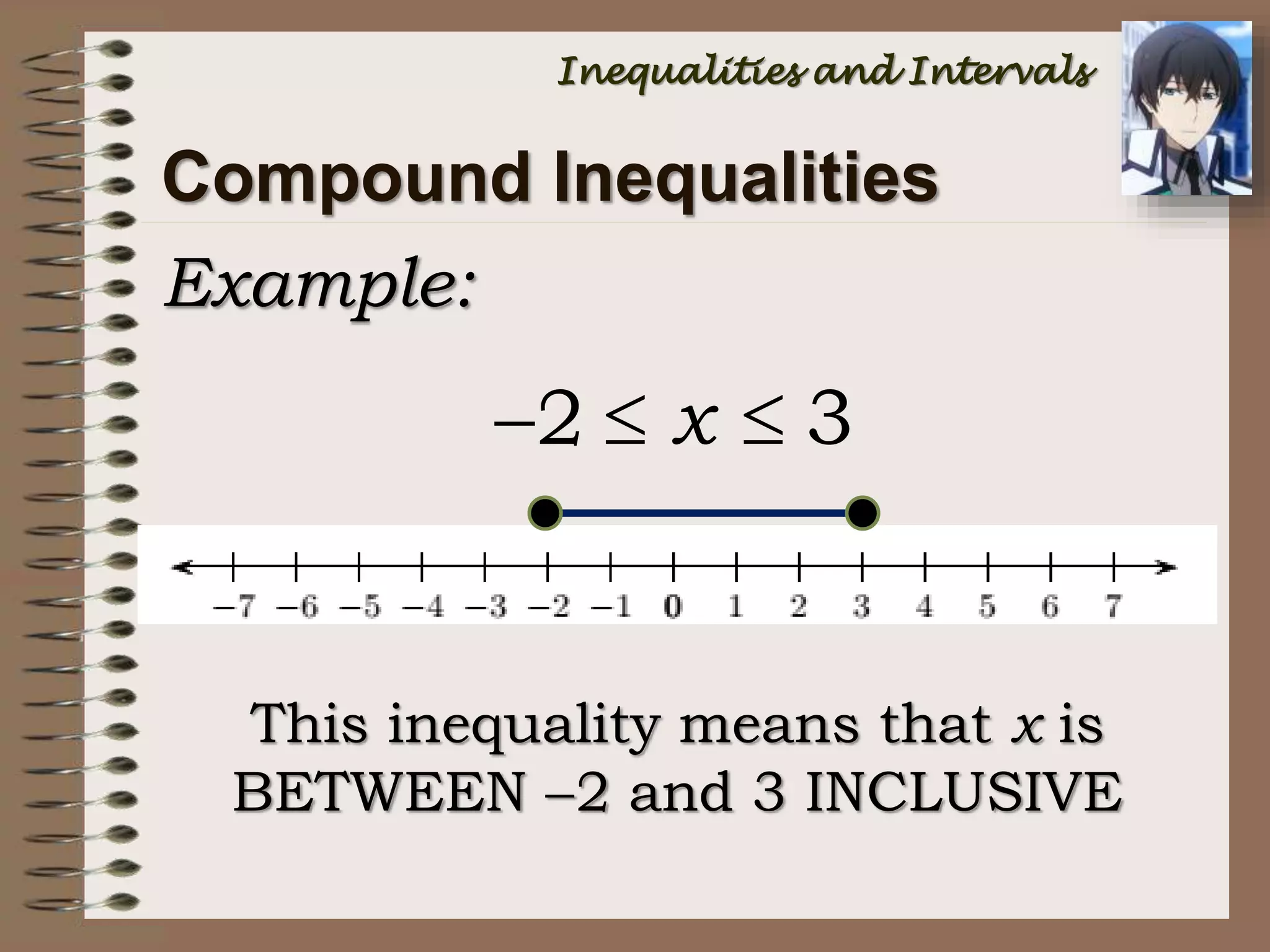
a x b { x | a x b } [a, b]
a < x b { x | a < x b } (a, b]
a x < b { x | a x < b } [a, b)
Bounded Intervals
Inequalities and Intervals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/math7-inequalitiesandintervals-150207083129-conversion-gate02/75/Math-7-inequalities-and-intervals-34-2048.jpg)