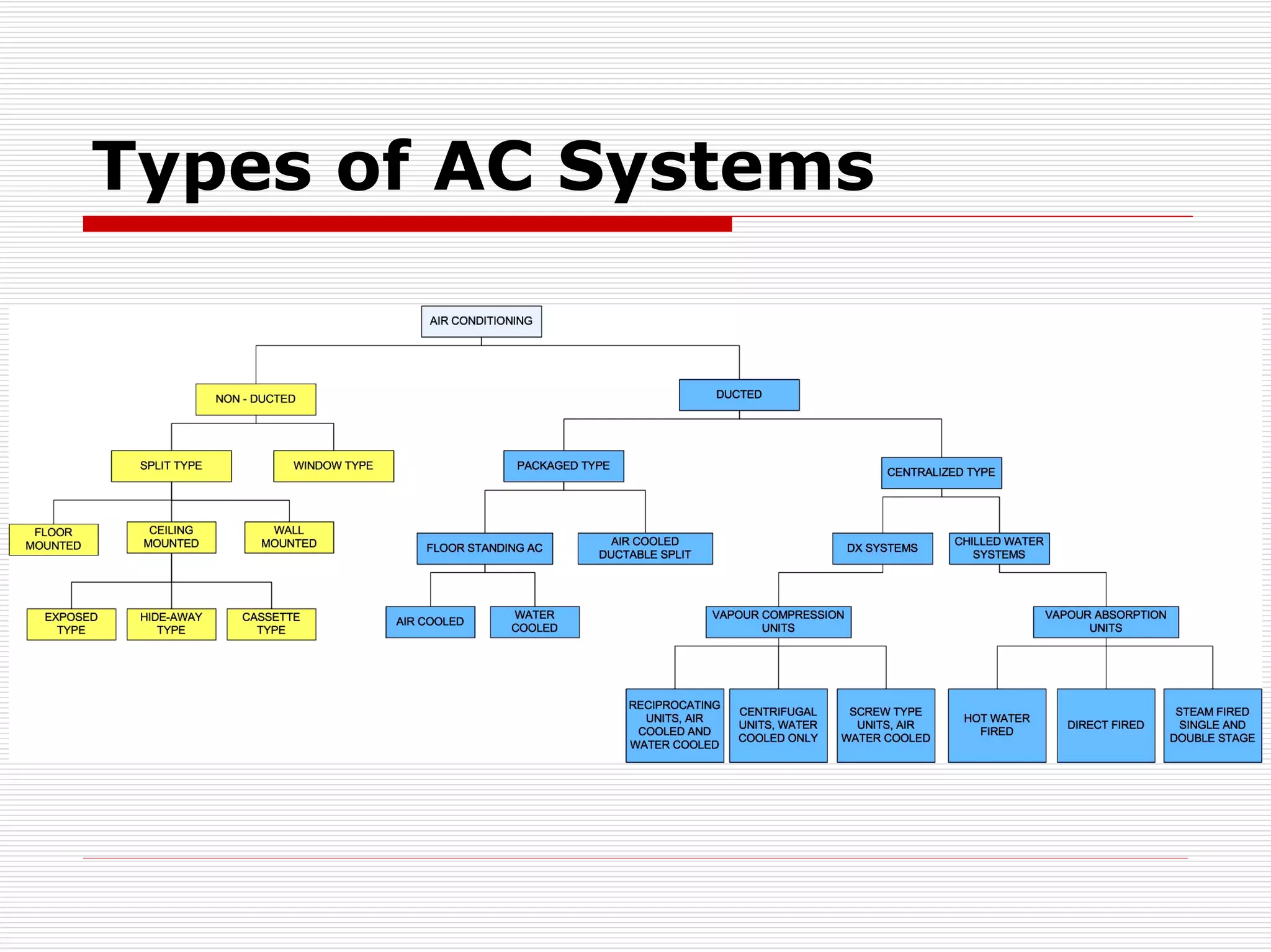
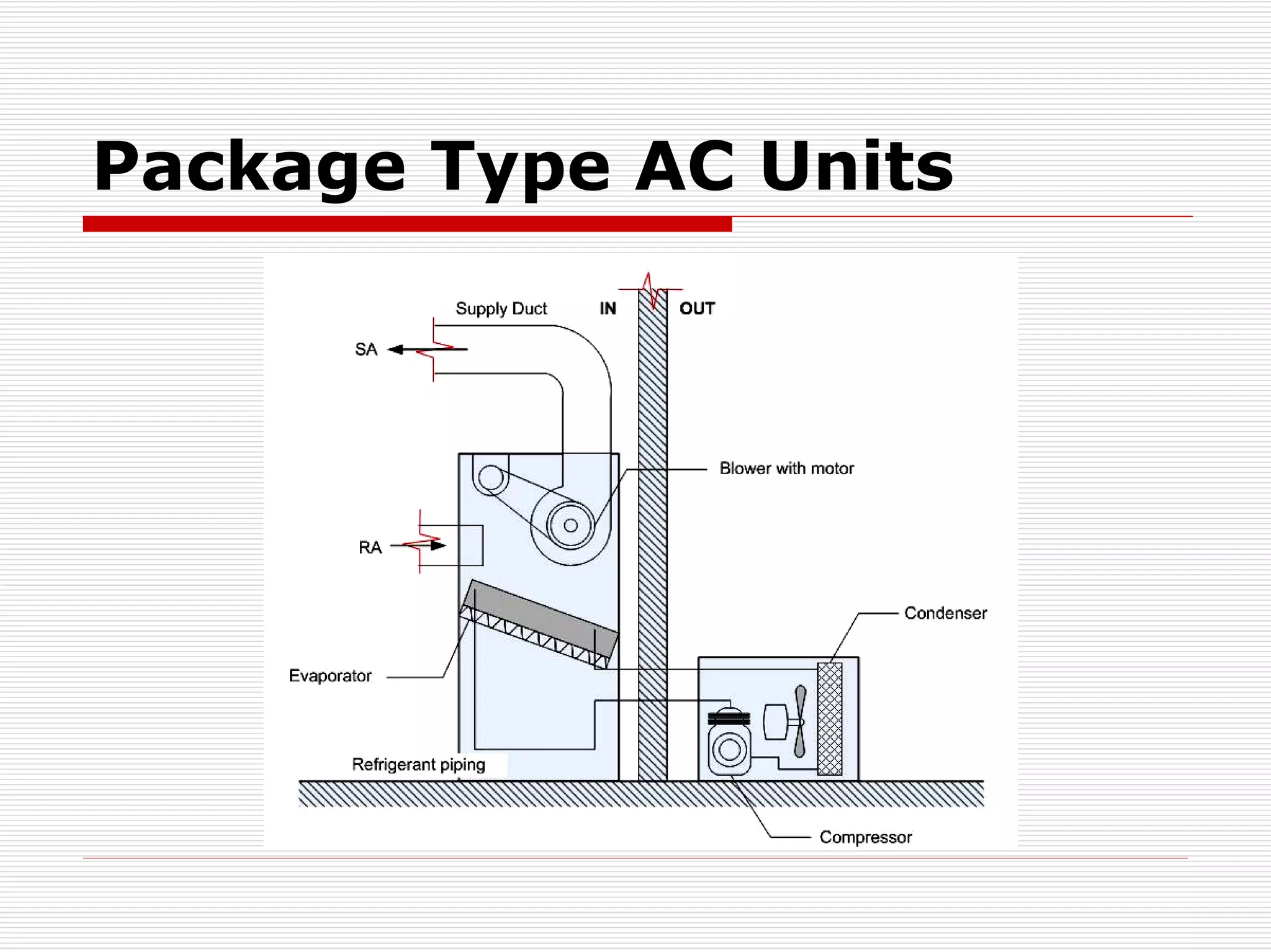
HVAC systems are used in many commercial and industrial applications to control temperature, humidity, and air quality. There are different types of air conditioning systems including window units, ductable split units, package units, direct expansion (DX) systems, and chilled water systems. When selecting an HVAC system, factors such as heating and cooling loads, efficiency, noise levels, installation requirements, and cost should be considered. Heating and cooling loads are calculated based on outdoor conditions, building materials, sunlight exposure, occupancy levels, ventilation needs, and other sources of heat gain or loss.