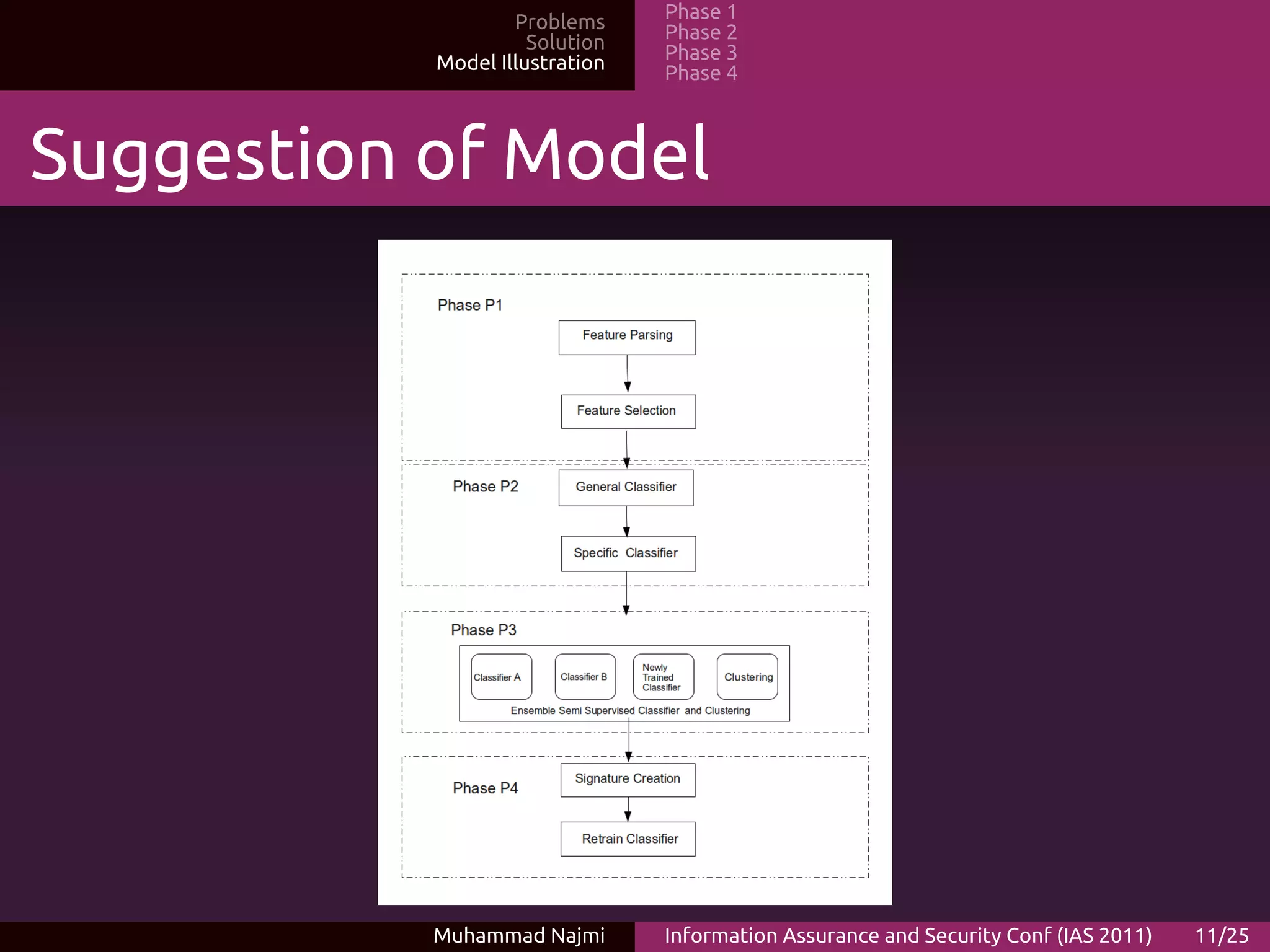
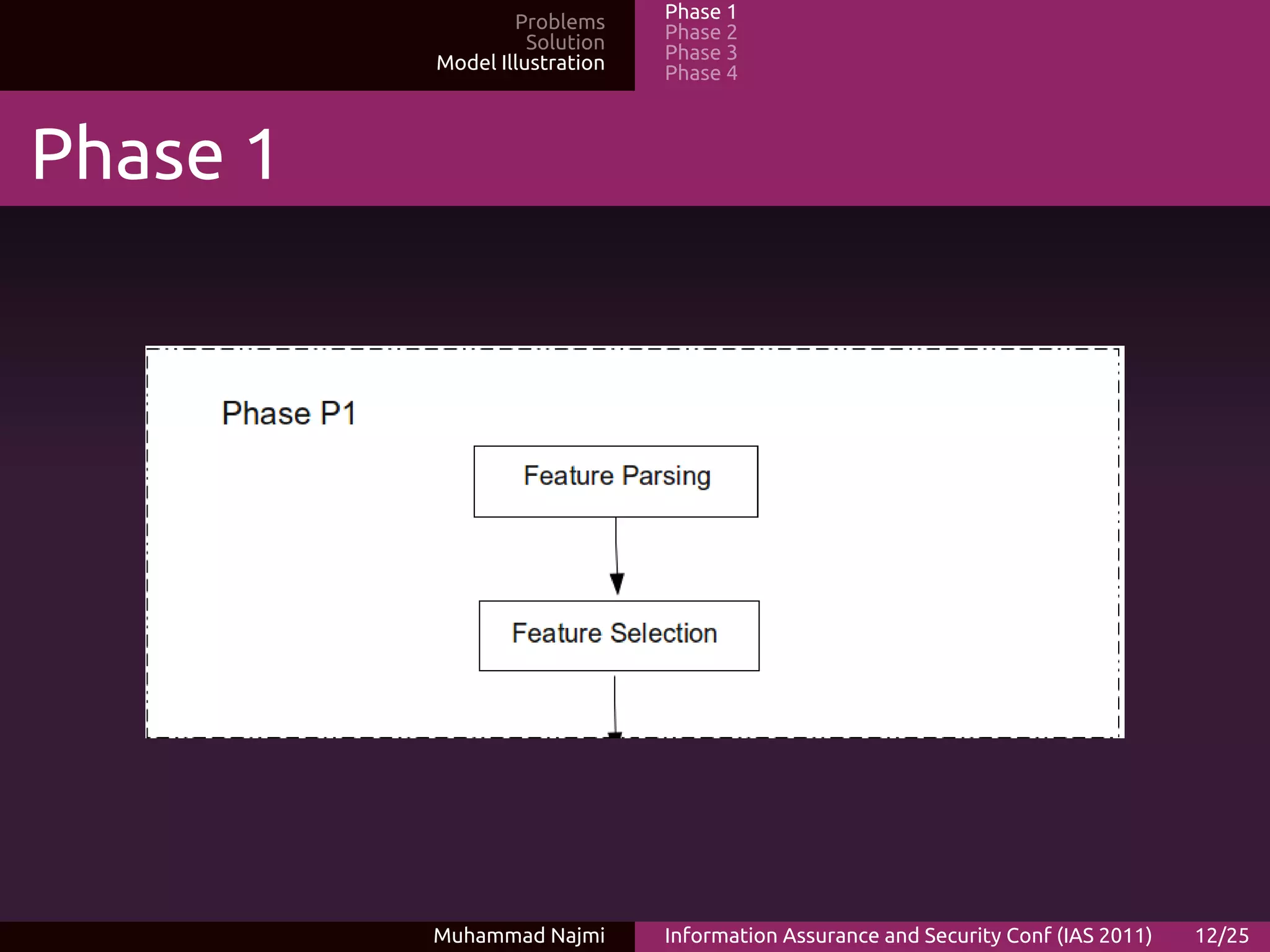
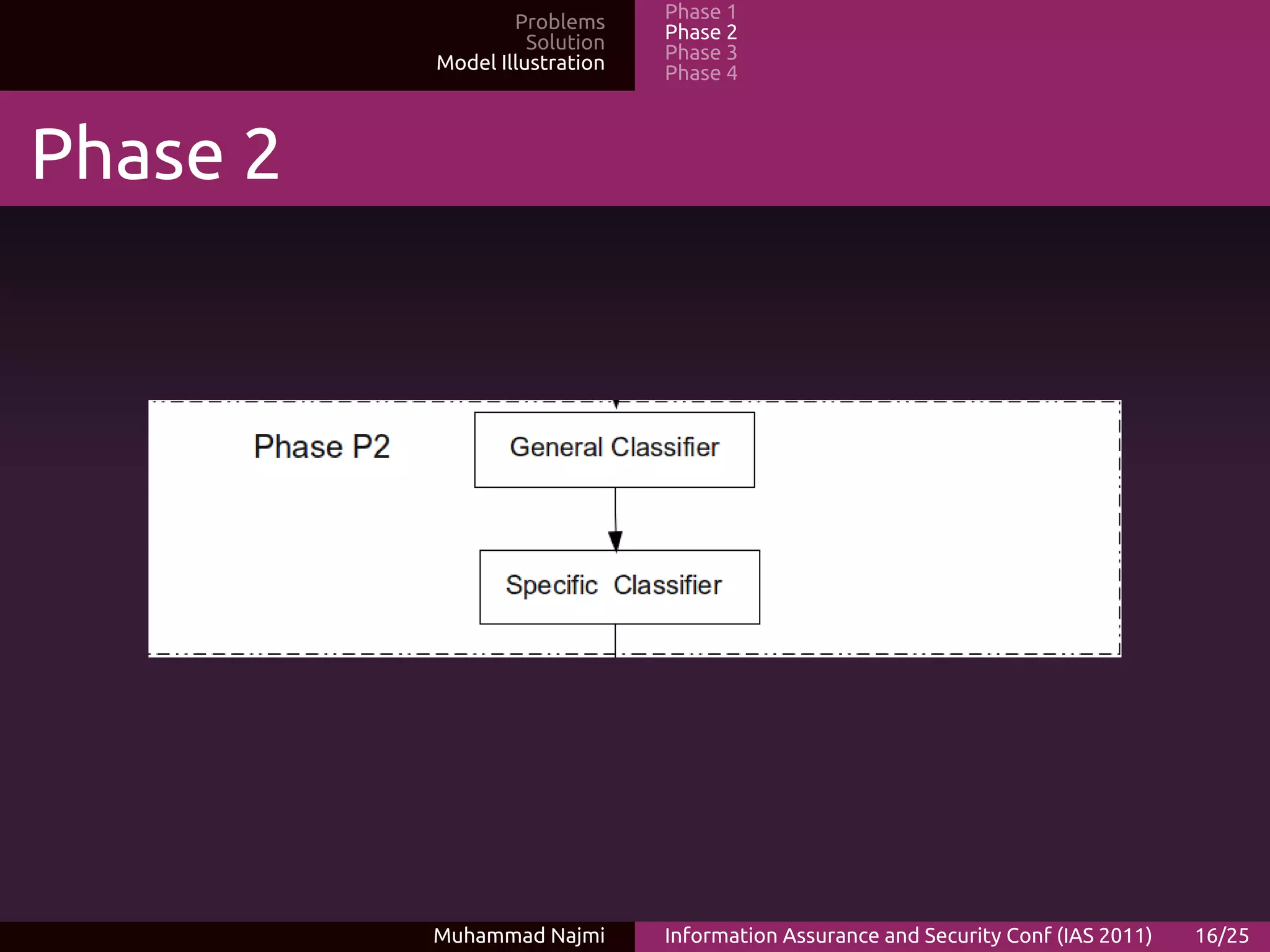
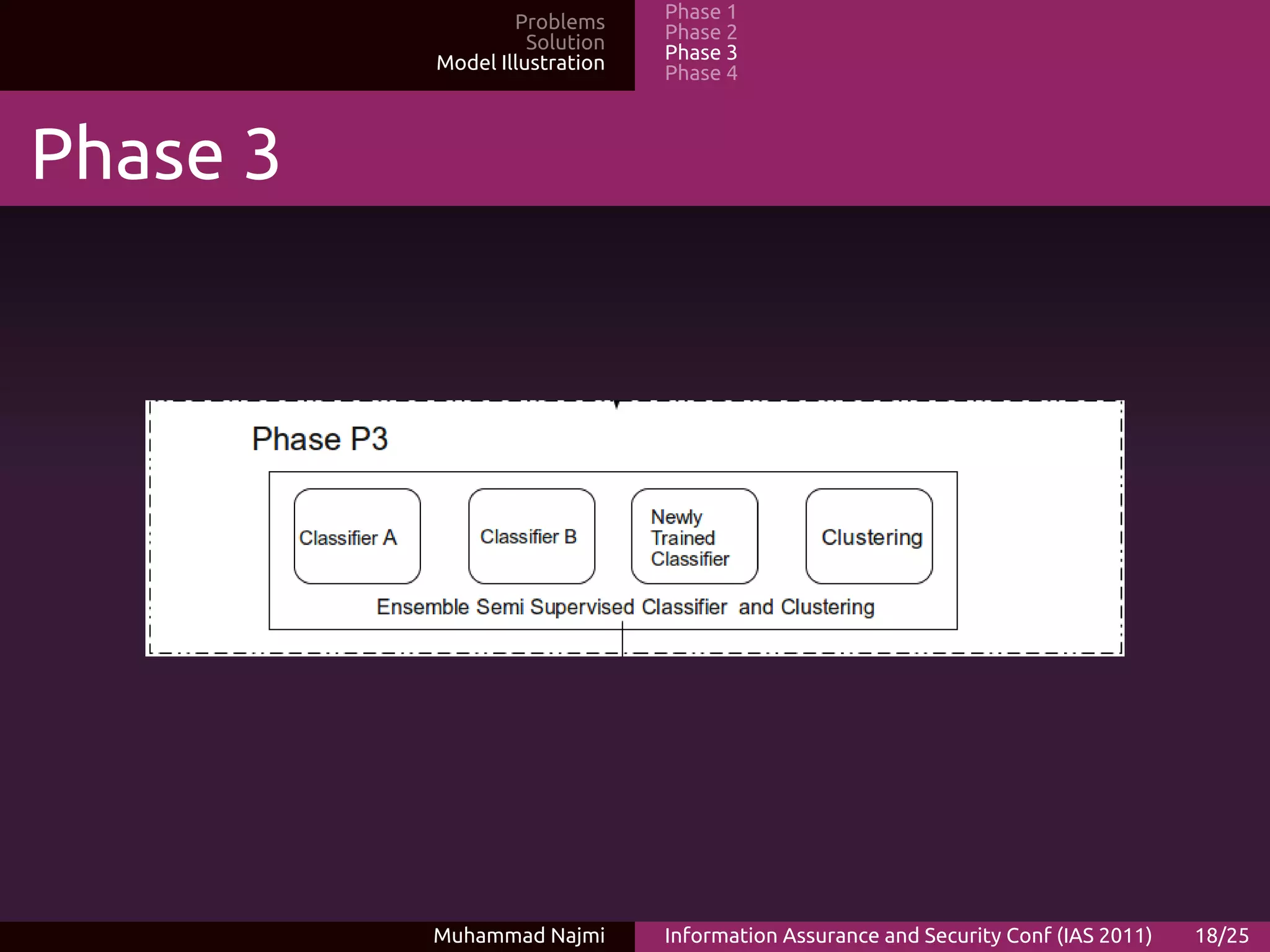
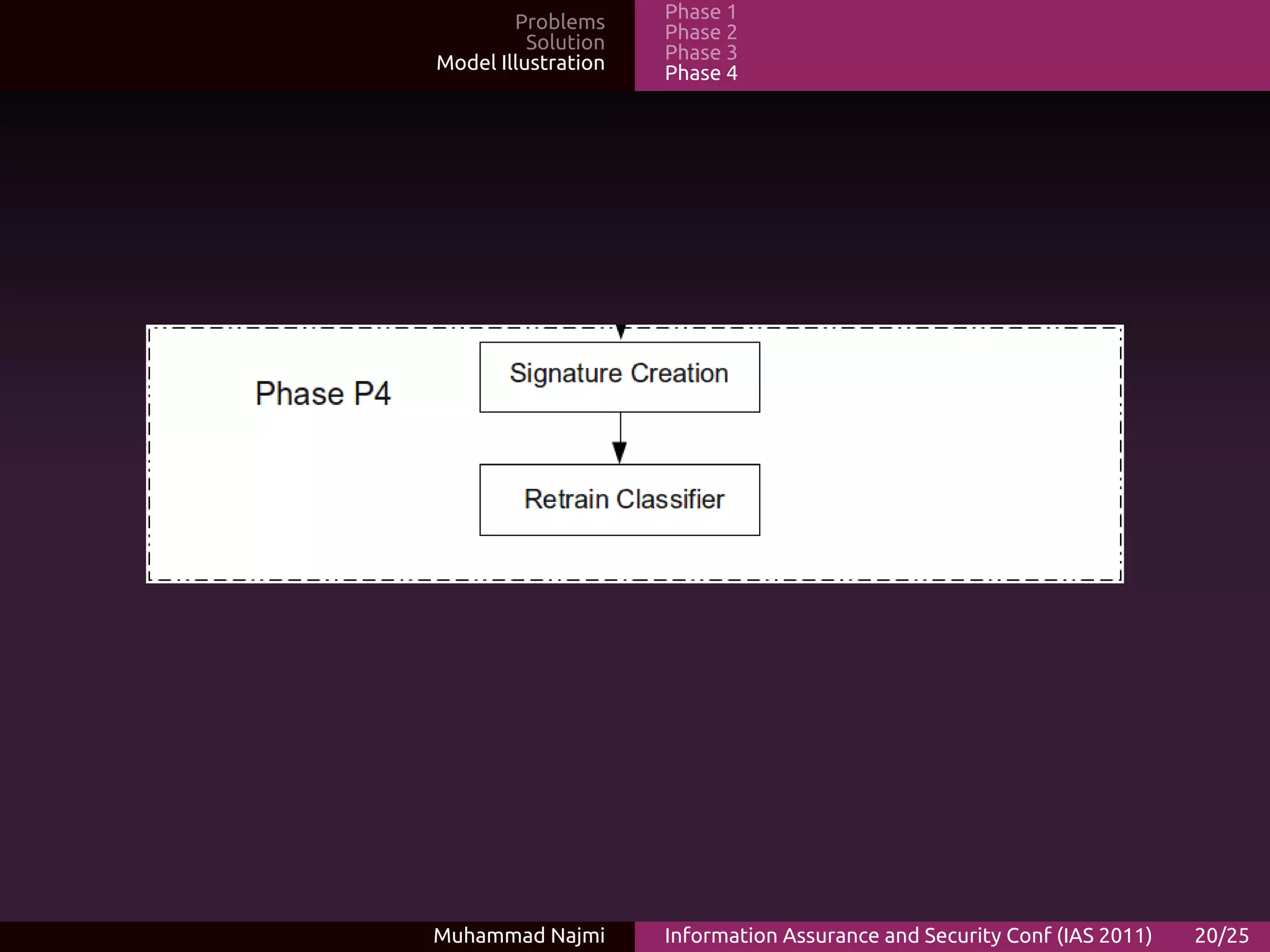
The document proposes an ensemble-based categorization and adaptive learning model for malware detection. The model consists of 4 phases: (1) feature selection and extraction from malware binaries, (2) categorization of malware into generic classes, (3) ensemble classification using weak learners, and (4) adaptive learning where new signatures are added for previously unknown malware. The goal is to improve malware detection accuracy and tackle new malware through adaptive learning.


![Problems
Solution
Model Illustration
Overview
• Malware detection is considered
‘‘undecidable’’[Cohen, 1986]
• Means 100 percent detection for all time is impossible
• But there’s still room for highest detection accuracy
Muhammad Najmi Information Assurance and Security Conf (IAS 2011) 3/25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ias-2011-najmi-120605105002-phpapp01/75/Ensembled-Based-Categorization-and-Adaptive-Learning-Model-for-Malware-Detection-3-2048.jpg)


![Problems
Solution
Model Illustration
Related works on malware detection
Statistical based:
• [Chouchane et al., 2007, Saudi et al., 2010,
Merkel et al., 2010]
Data mining and machine learning:
• [Sun et al., 2010, Komashinskiy and Kotenko, 2009,
Komashinskiy and Kotenko, 2010]
• [Elovici et al., 2007, Gavrilut et al., 2009,
Firdausi et al., 2010, Golovko et al., 2010]
Muhammad Najmi Information Assurance and Security Conf (IAS 2011) 7/25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ias-2011-najmi-120605105002-phpapp01/75/Ensembled-Based-Categorization-and-Adaptive-Learning-Model-for-Malware-Detection-7-2048.jpg)