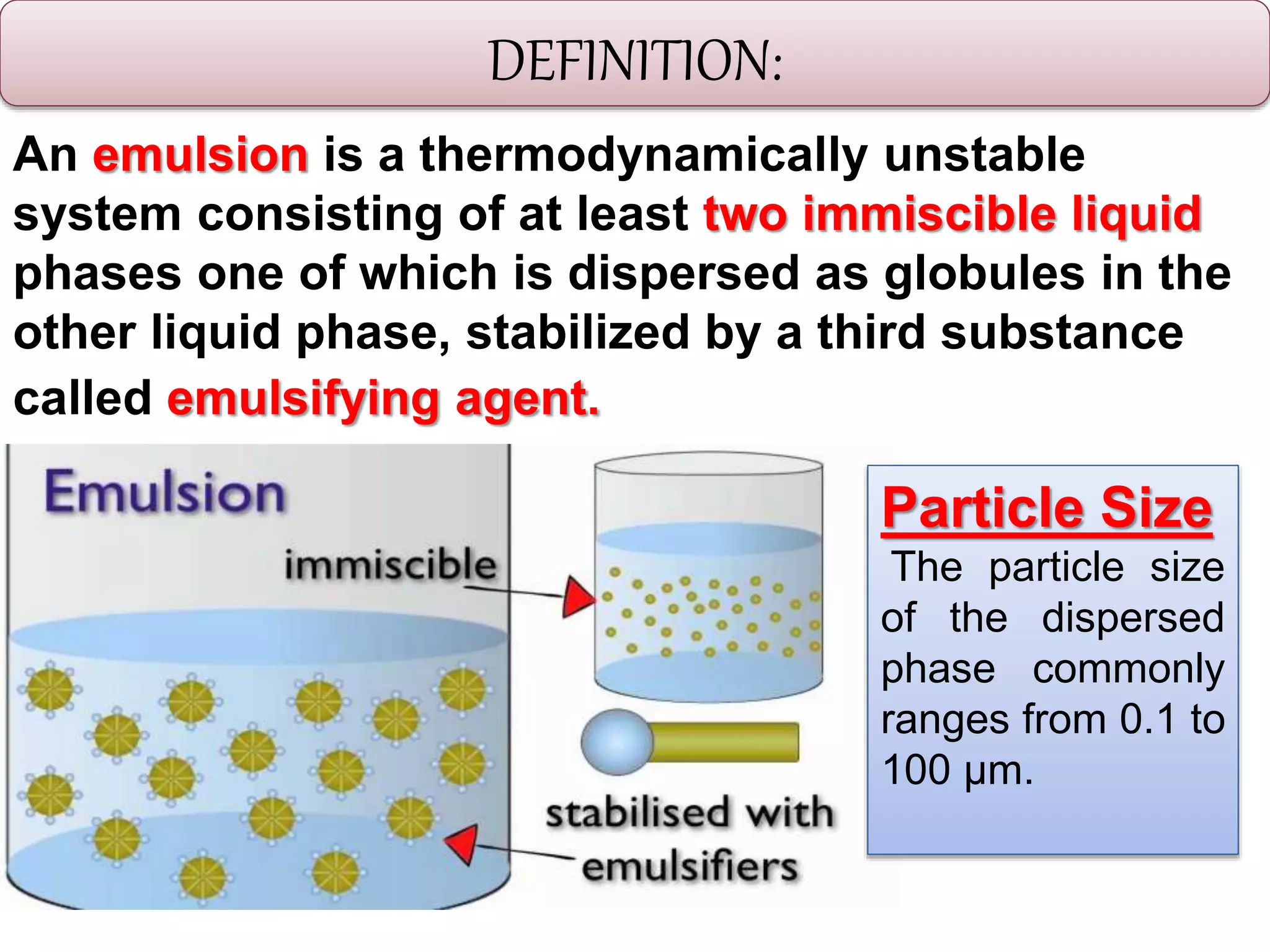
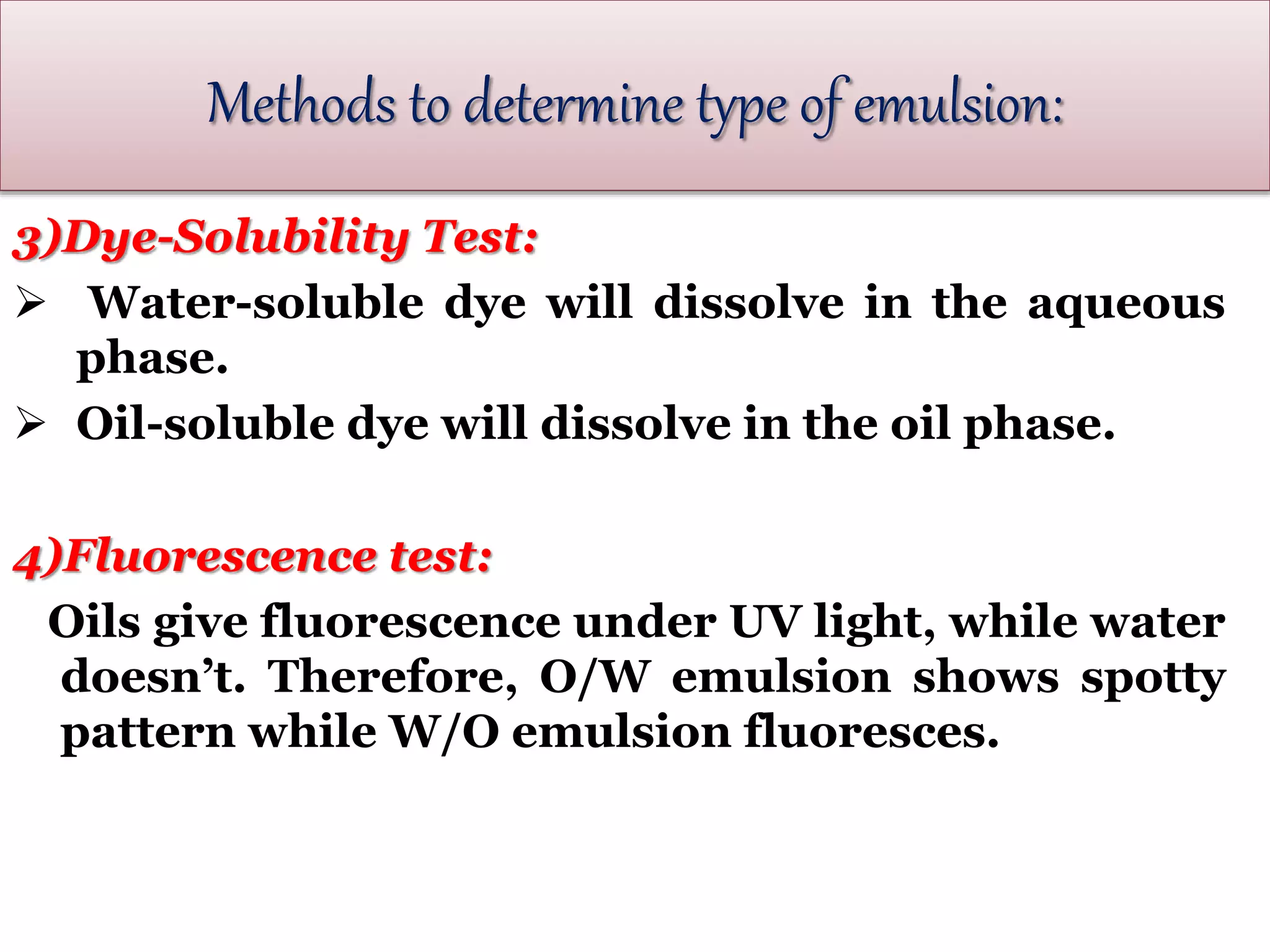
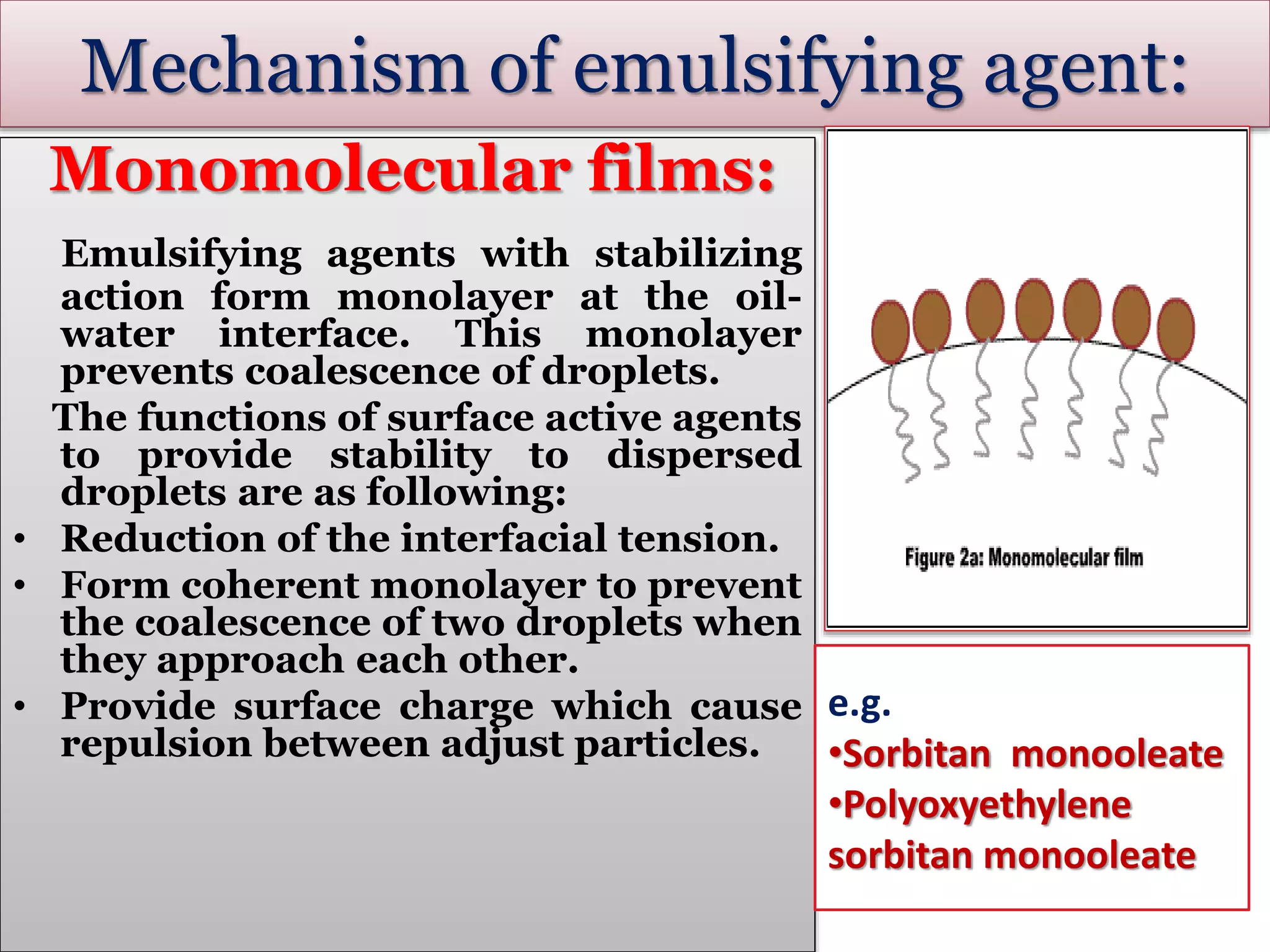
This document defines an emulsion as an unstable system consisting of at least two immiscible liquid phases, one dispersed as globules in the other. Emulsions can be oil-in-water or water-in-oil, with particle sizes typically ranging from 0.1 to 100 μm. Emulsifying agents help stabilize emulsions by forming monomolecular or multi-molecular films at the oil-water interface to prevent globule coalescence. Common emulsifying agents include surface-active agents, hydrophilic colloids, and finely divided solids. The HLB system assists in selecting emulsifying agents based on their hydrophilic-lipophilic balance. Pharmaceutical applications of emulsions include