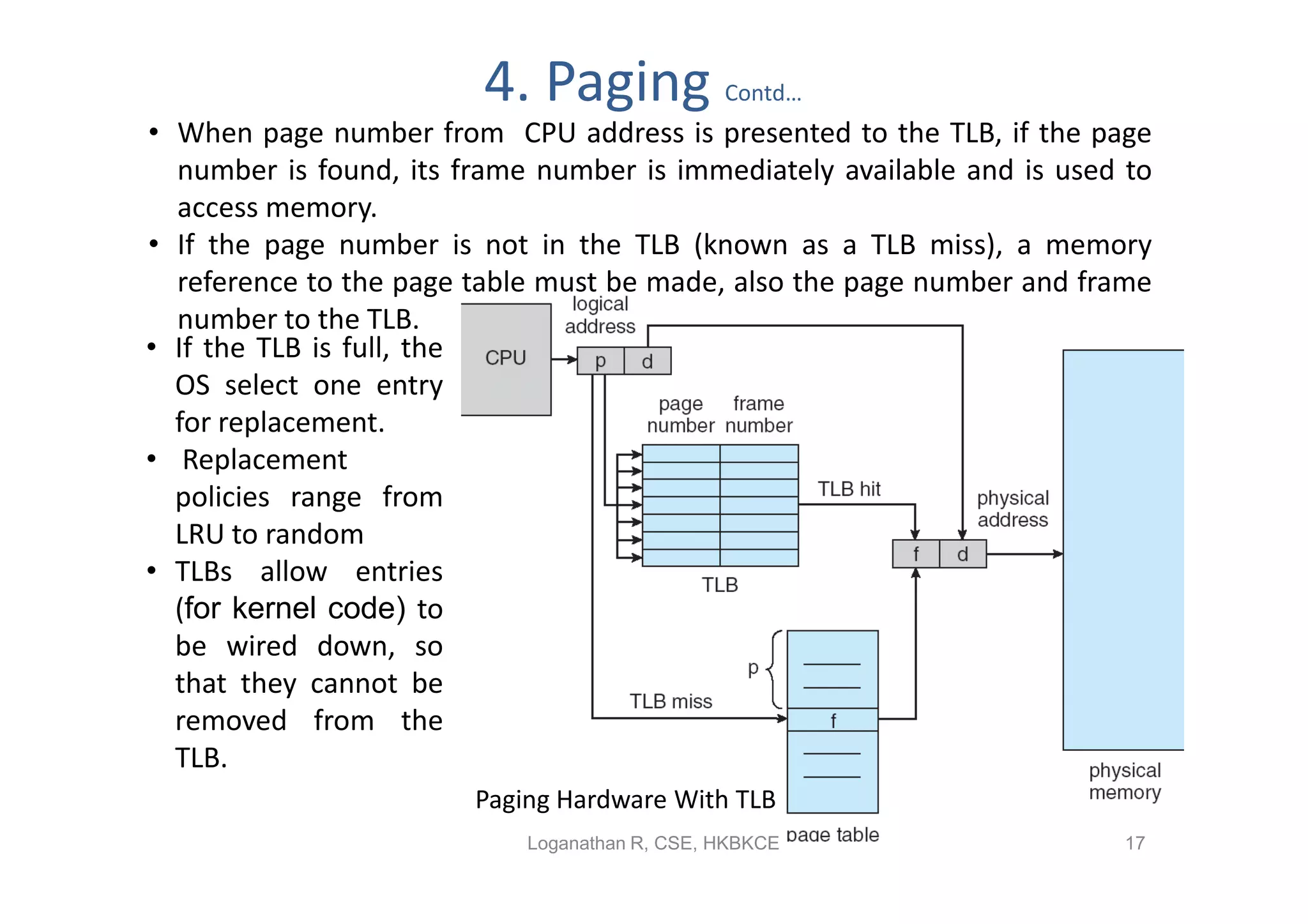
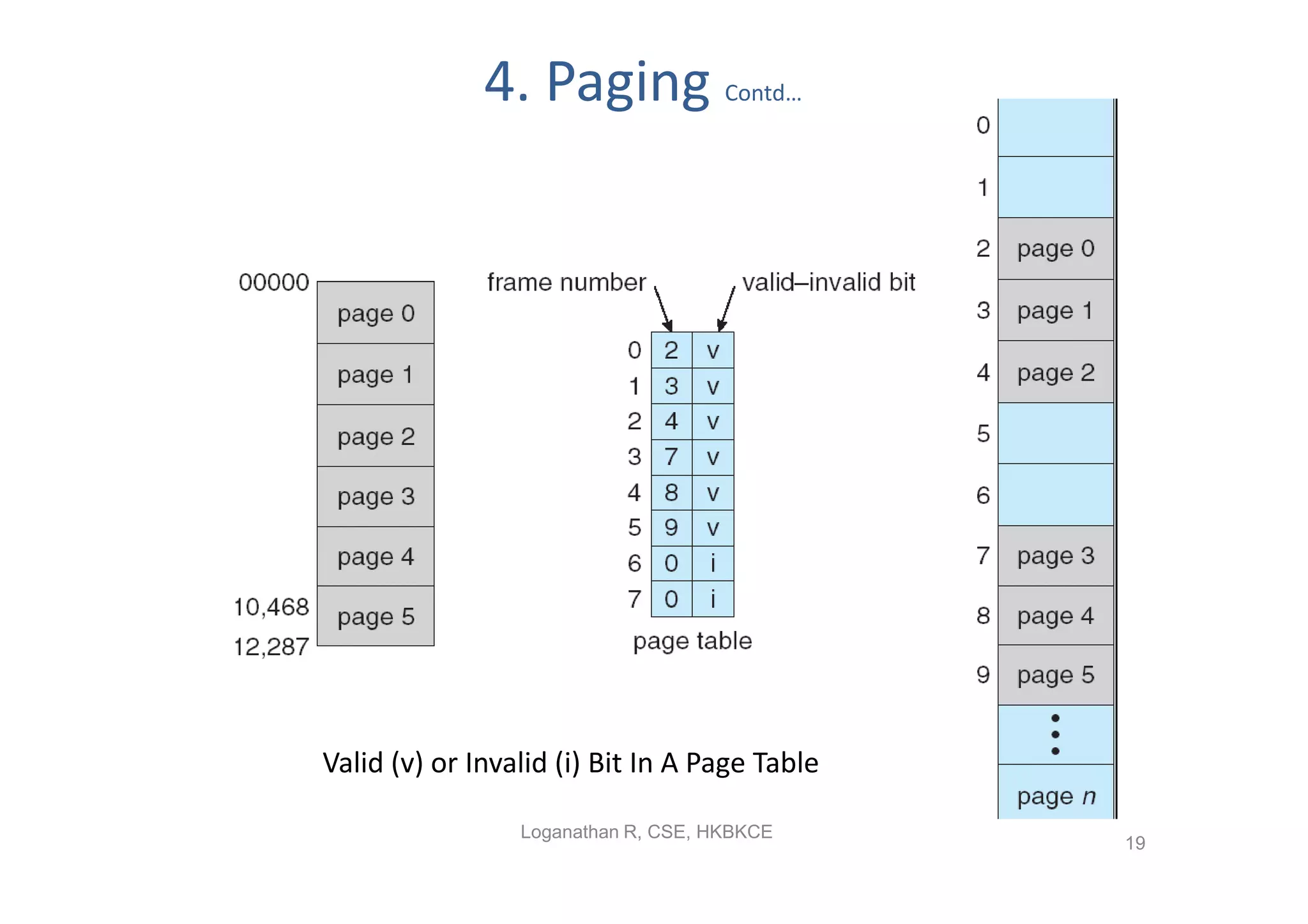
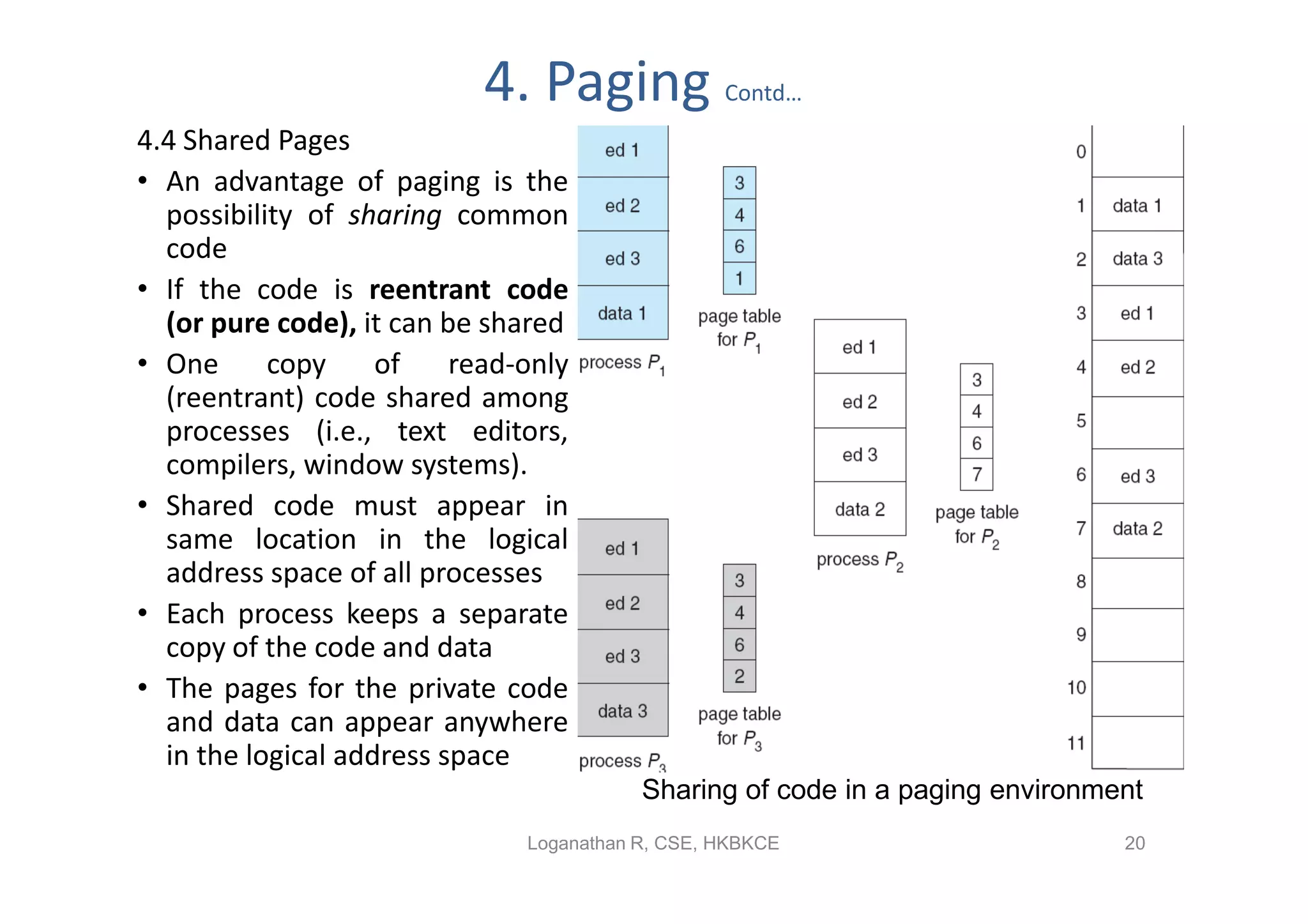
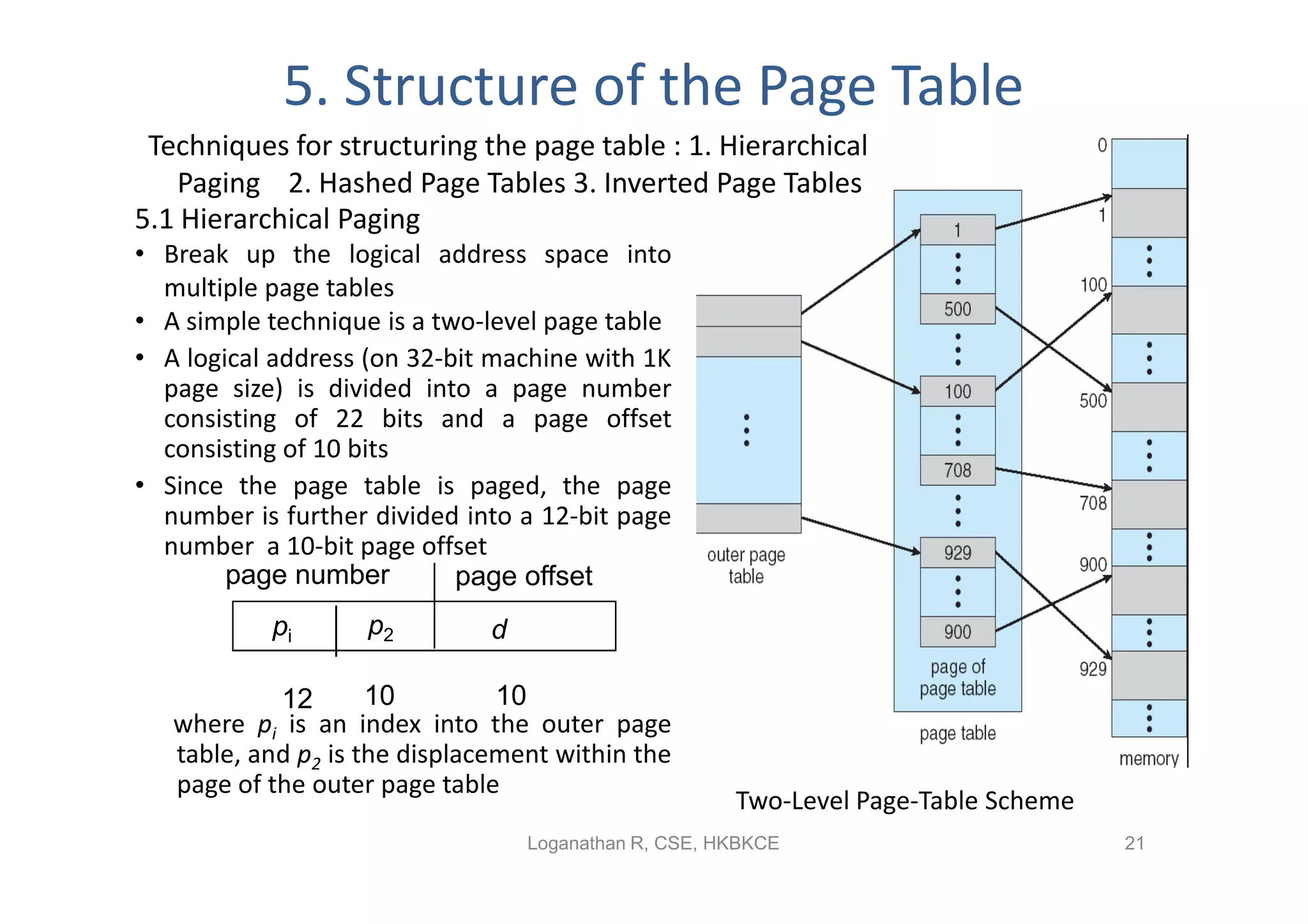
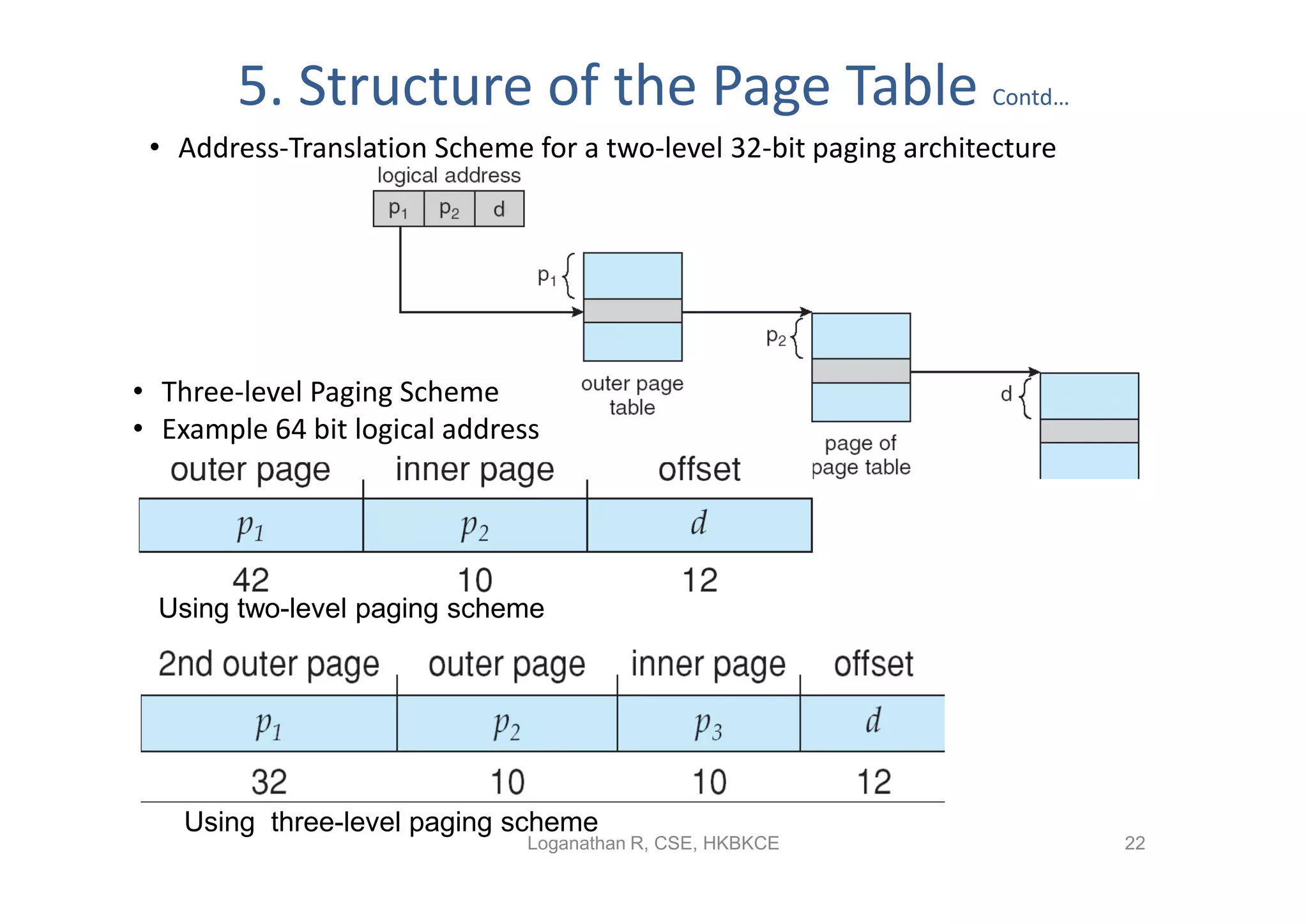
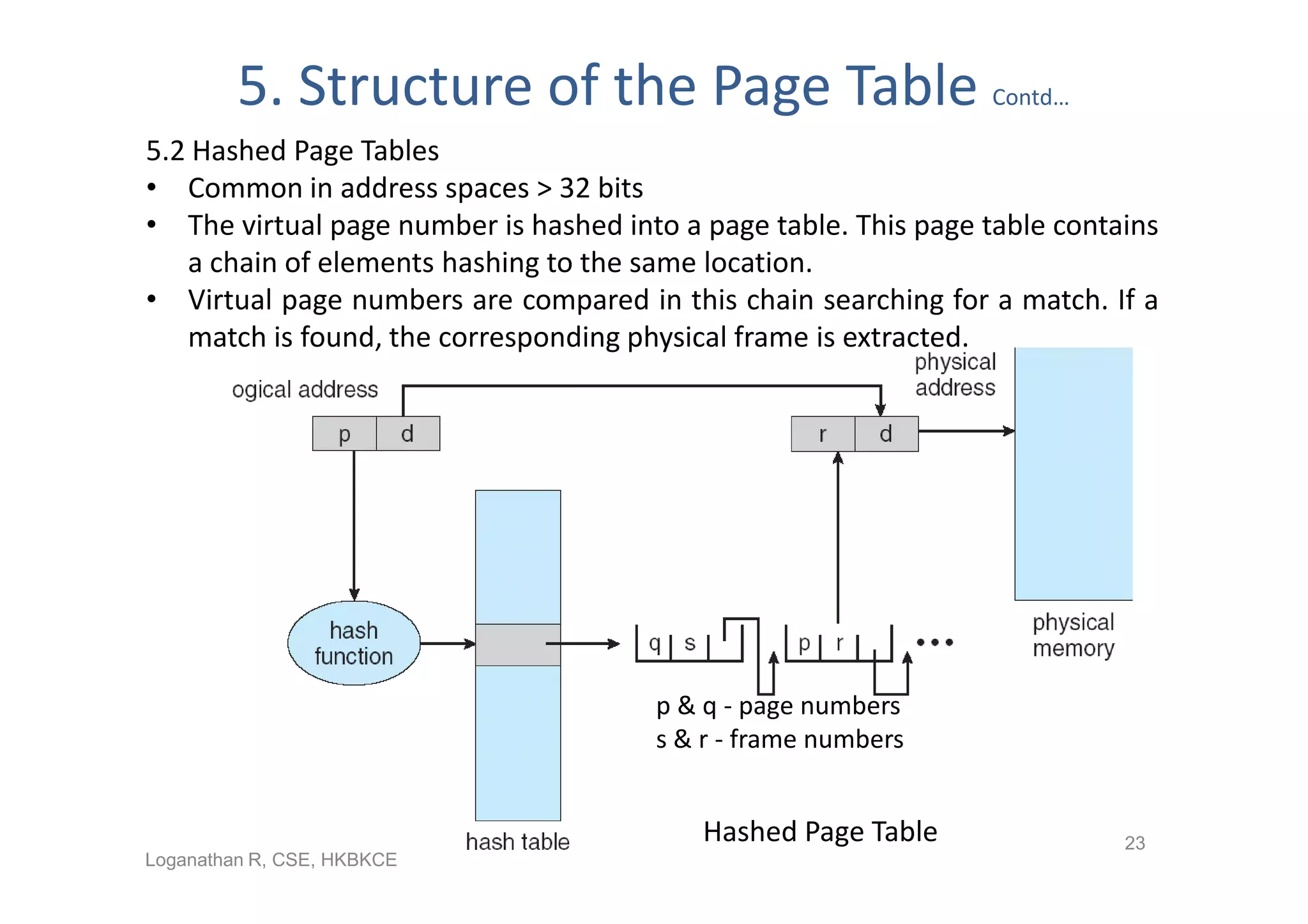
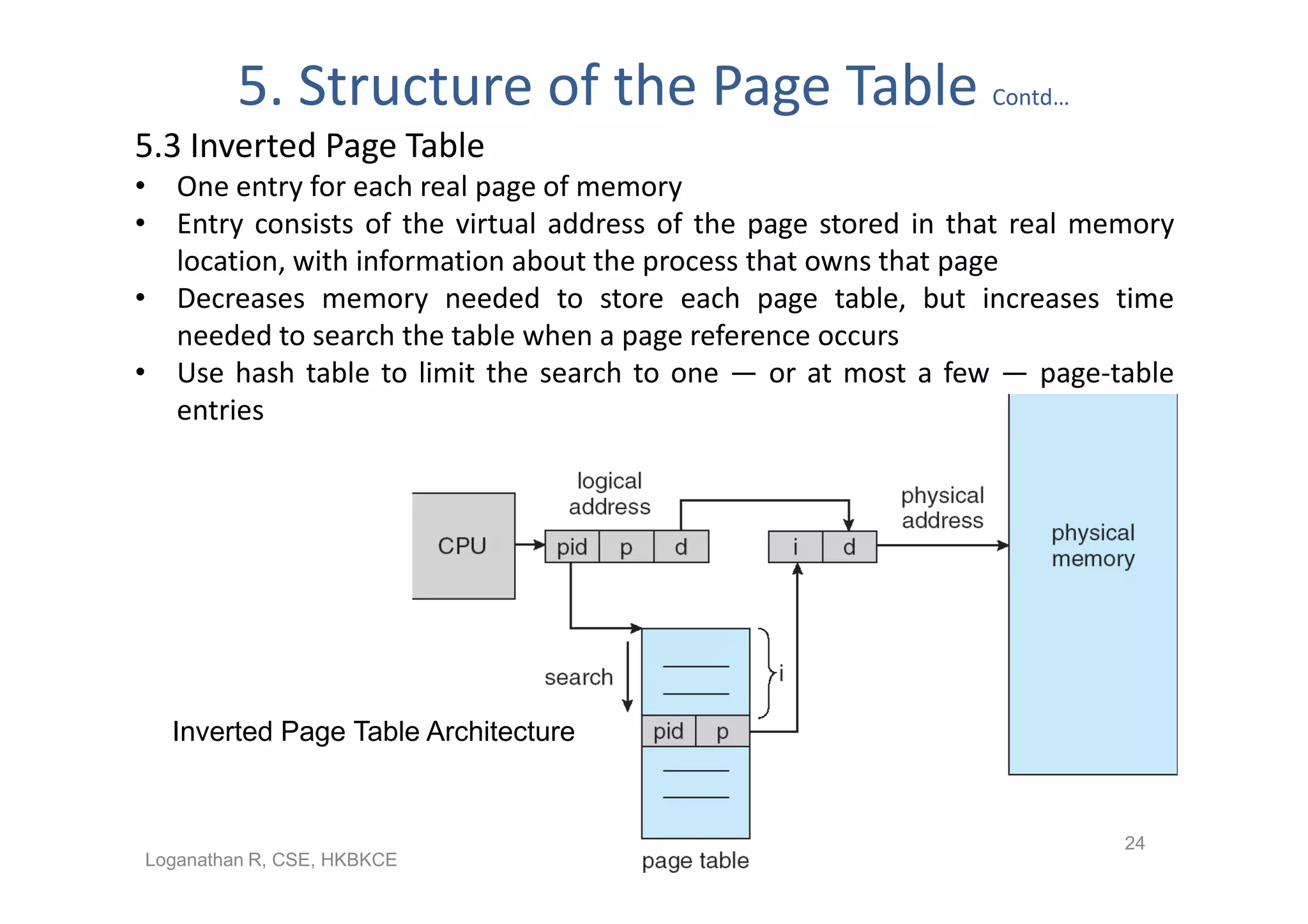
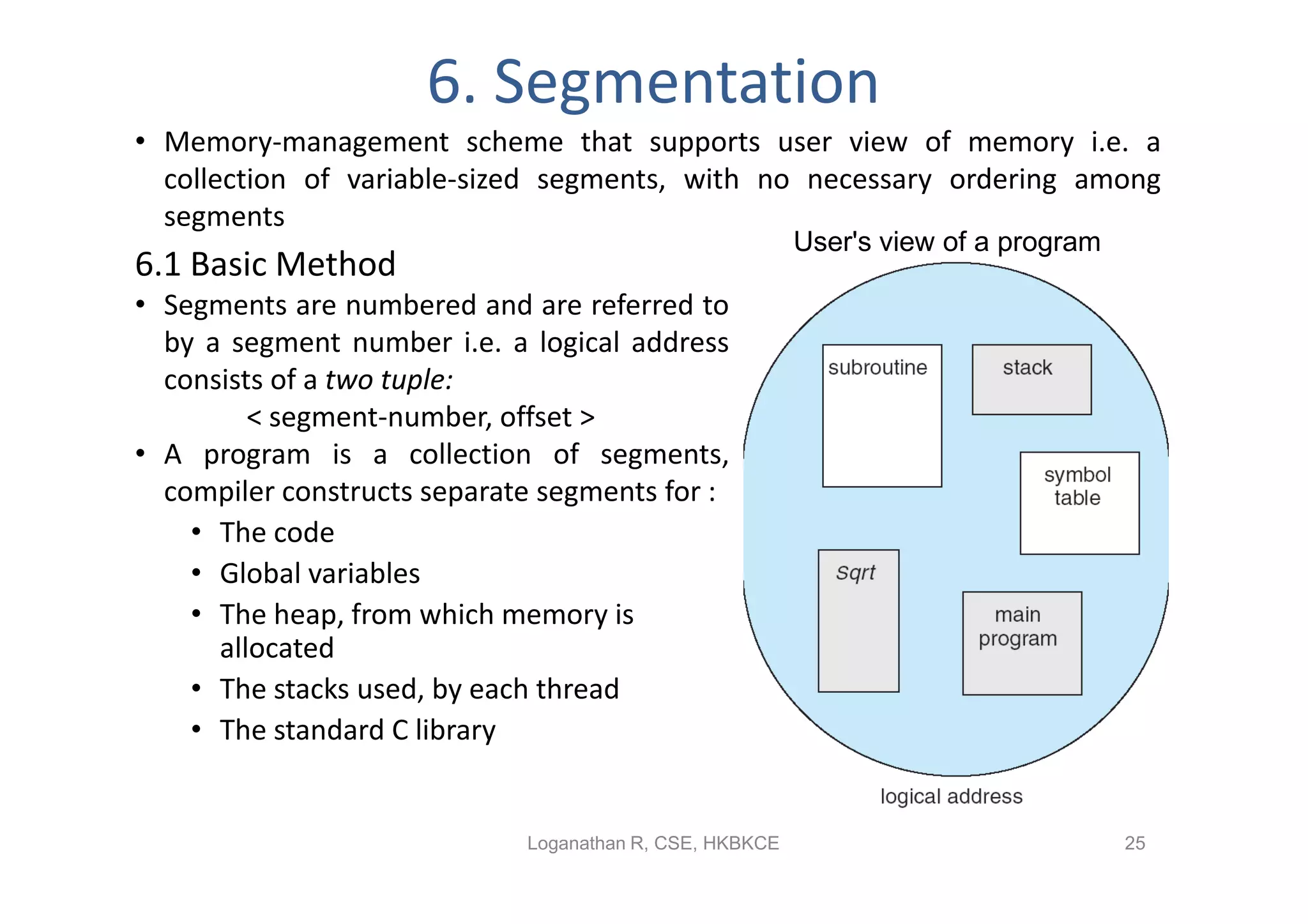
The document discusses different memory management strategies:
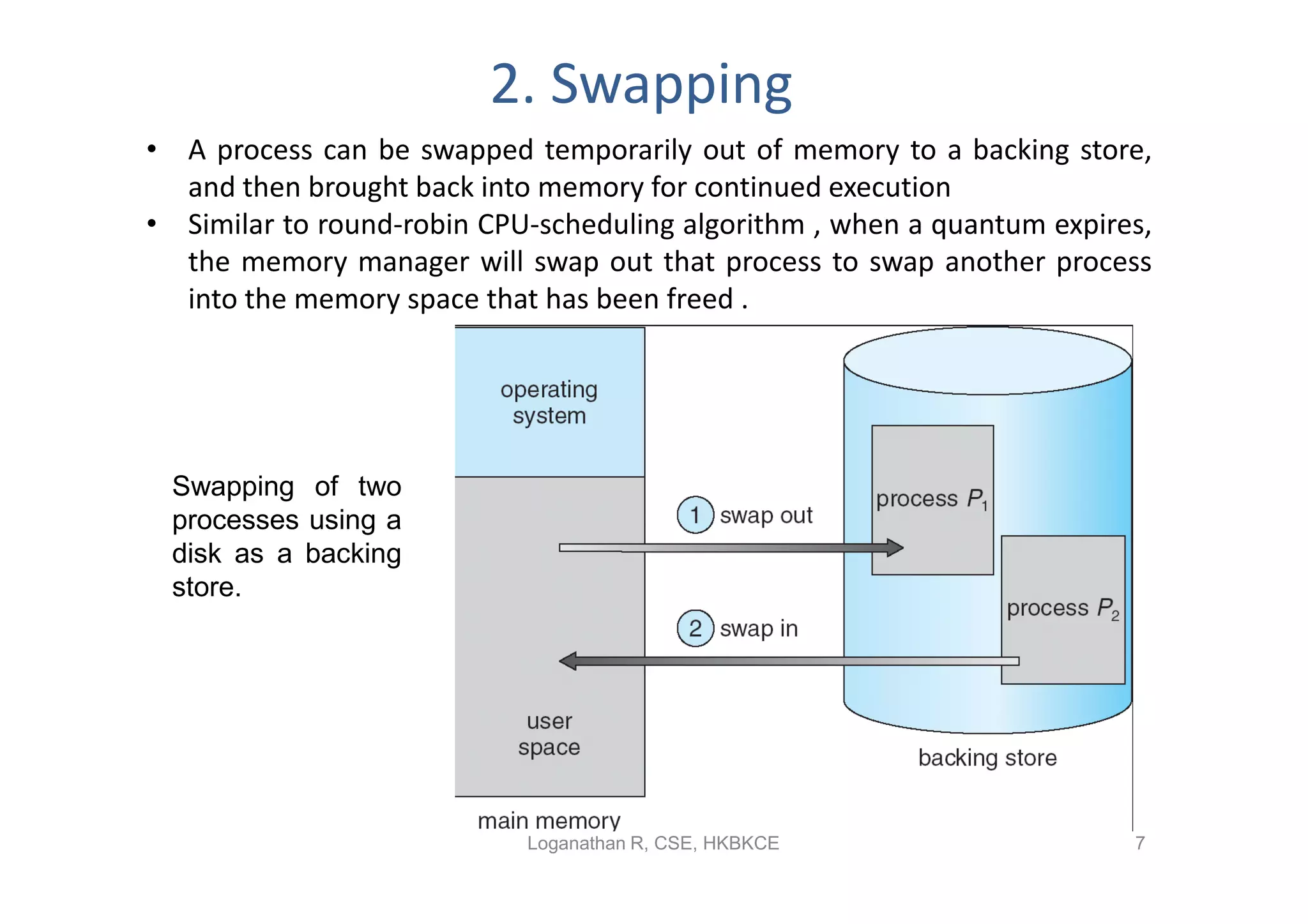
- Swapping allows processes to be swapped temporarily out of memory to disk, then back into memory for continued execution. This improves memory utilization but incurs long swap times.
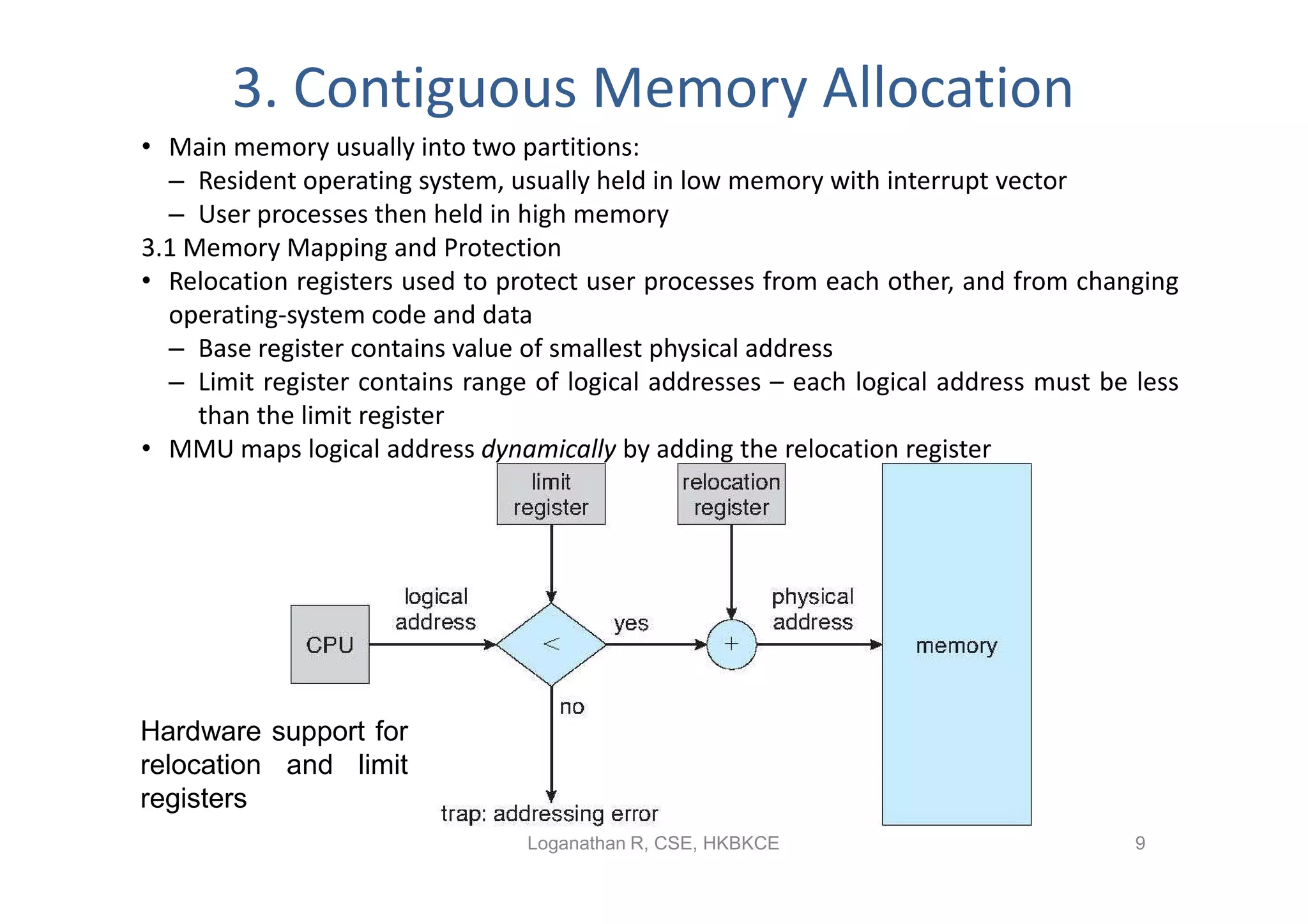
- Contiguous memory allocation allocates processes into contiguous regions of physical memory using techniques like memory mapping and dynamic storage allocation with first-fit or best-fit. This can cause external and internal fragmentation over time.
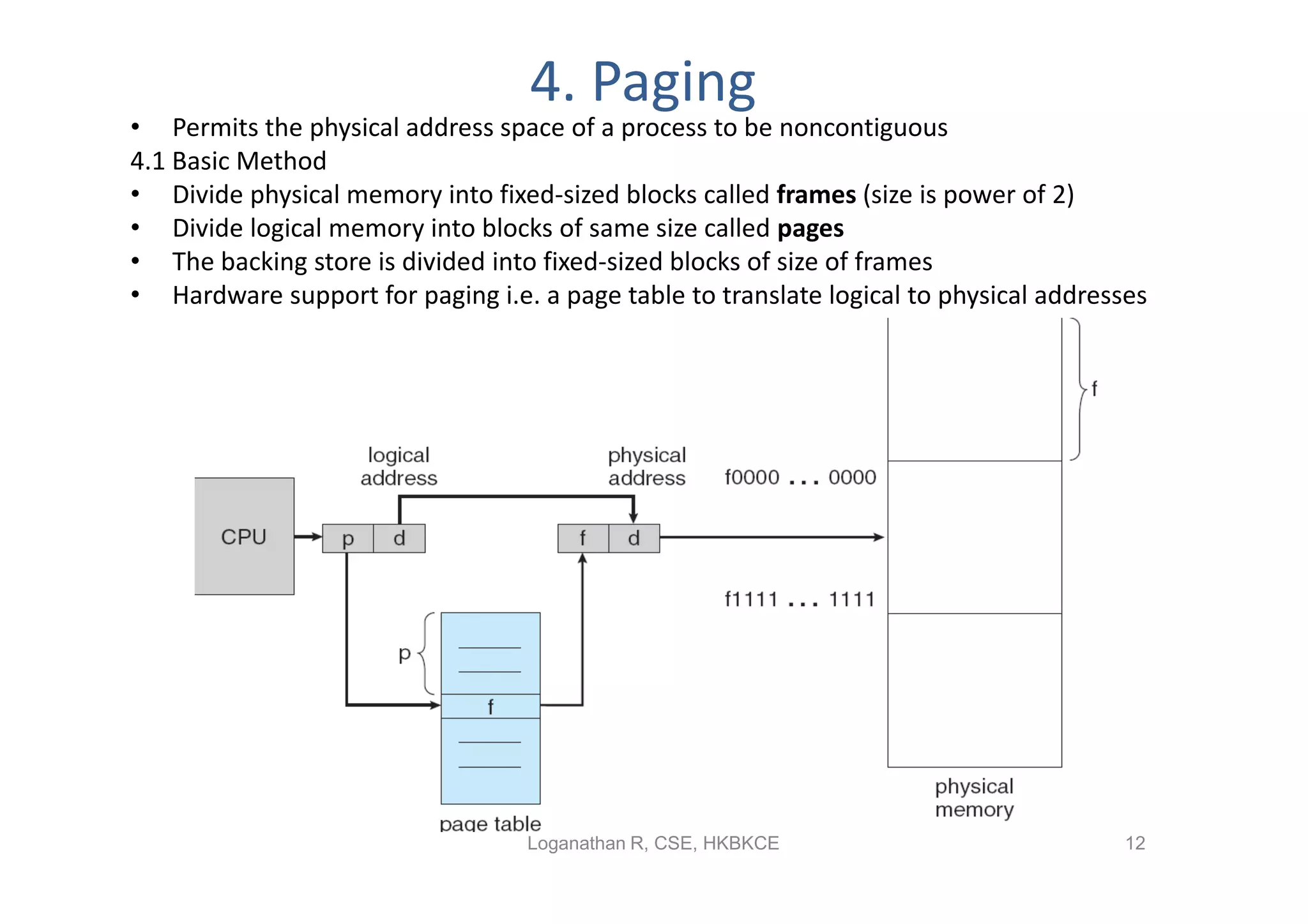
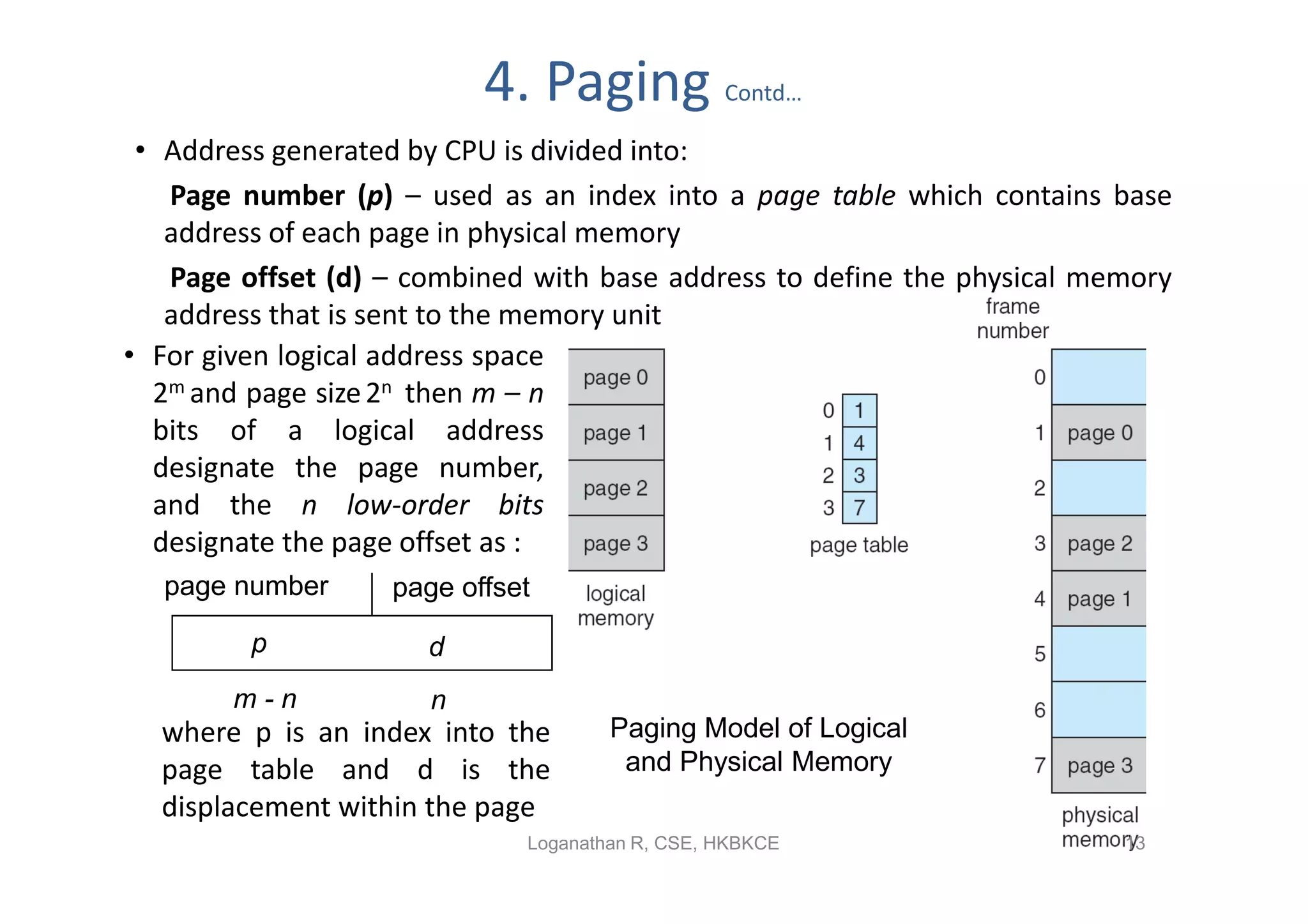
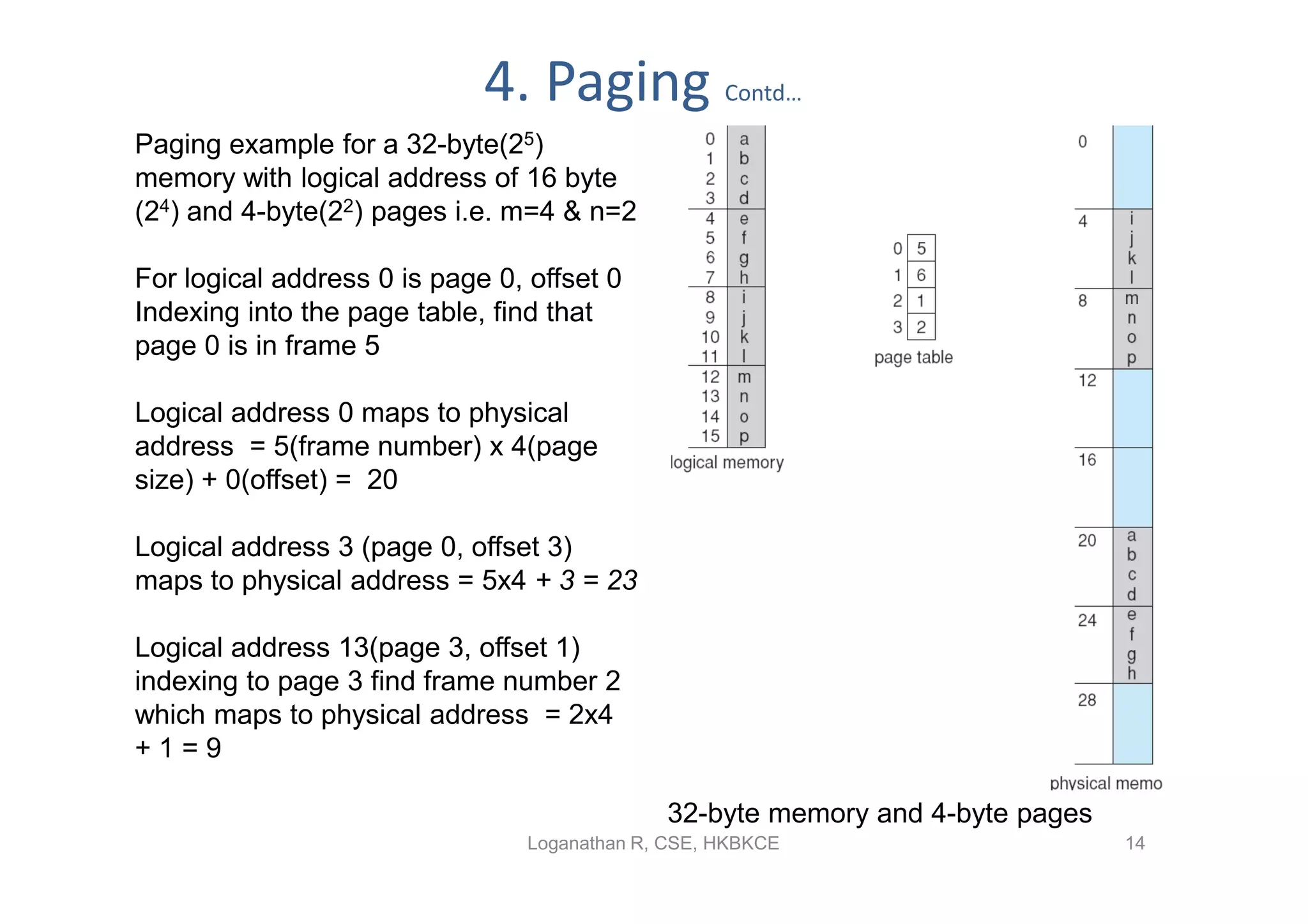
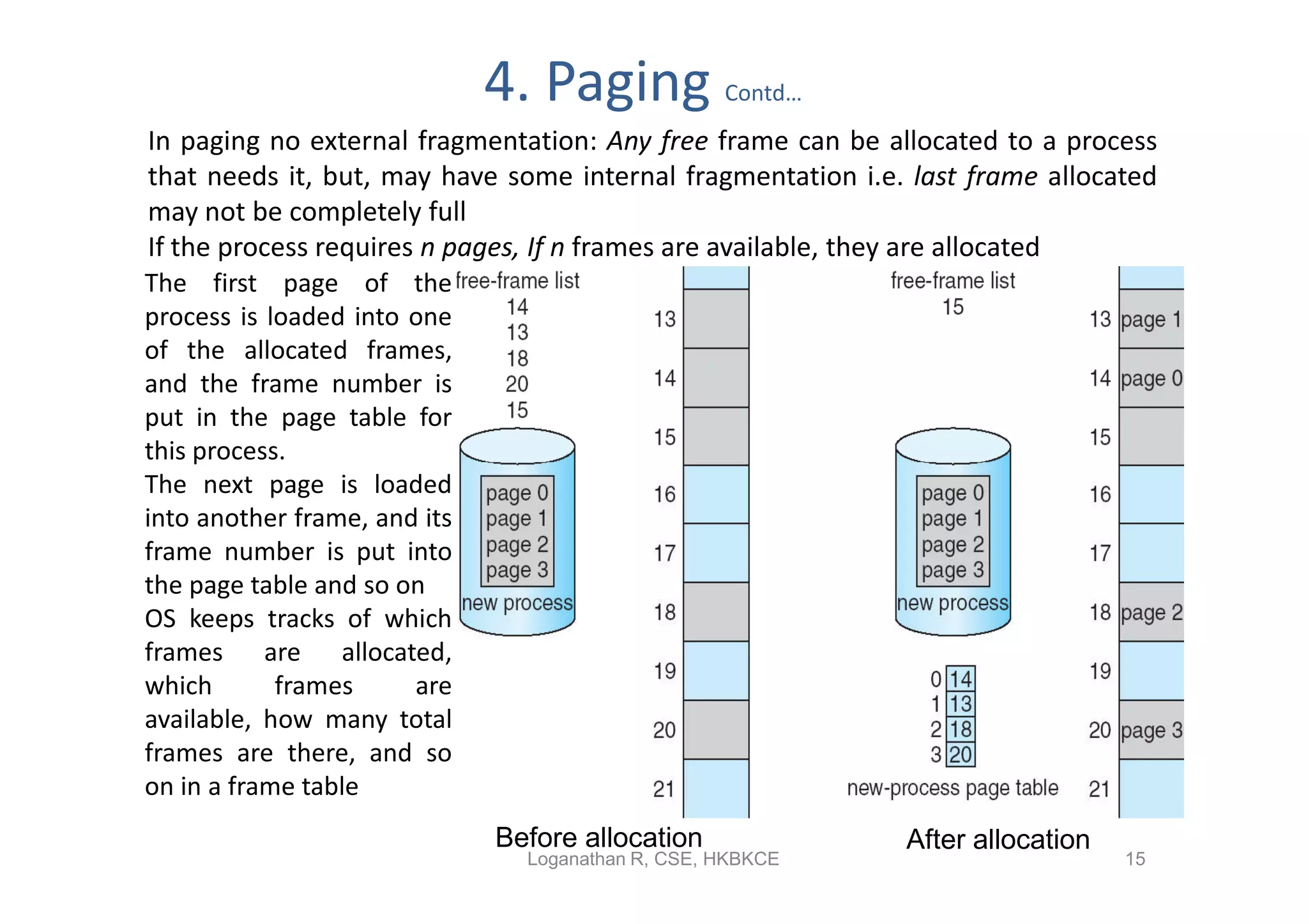
- Paging permits the physical memory used by a process to be noncontiguous by dividing memory into pages and mapping virtual addresses to physical frames, allowing more efficient use of memory but requiring page tables for translation.