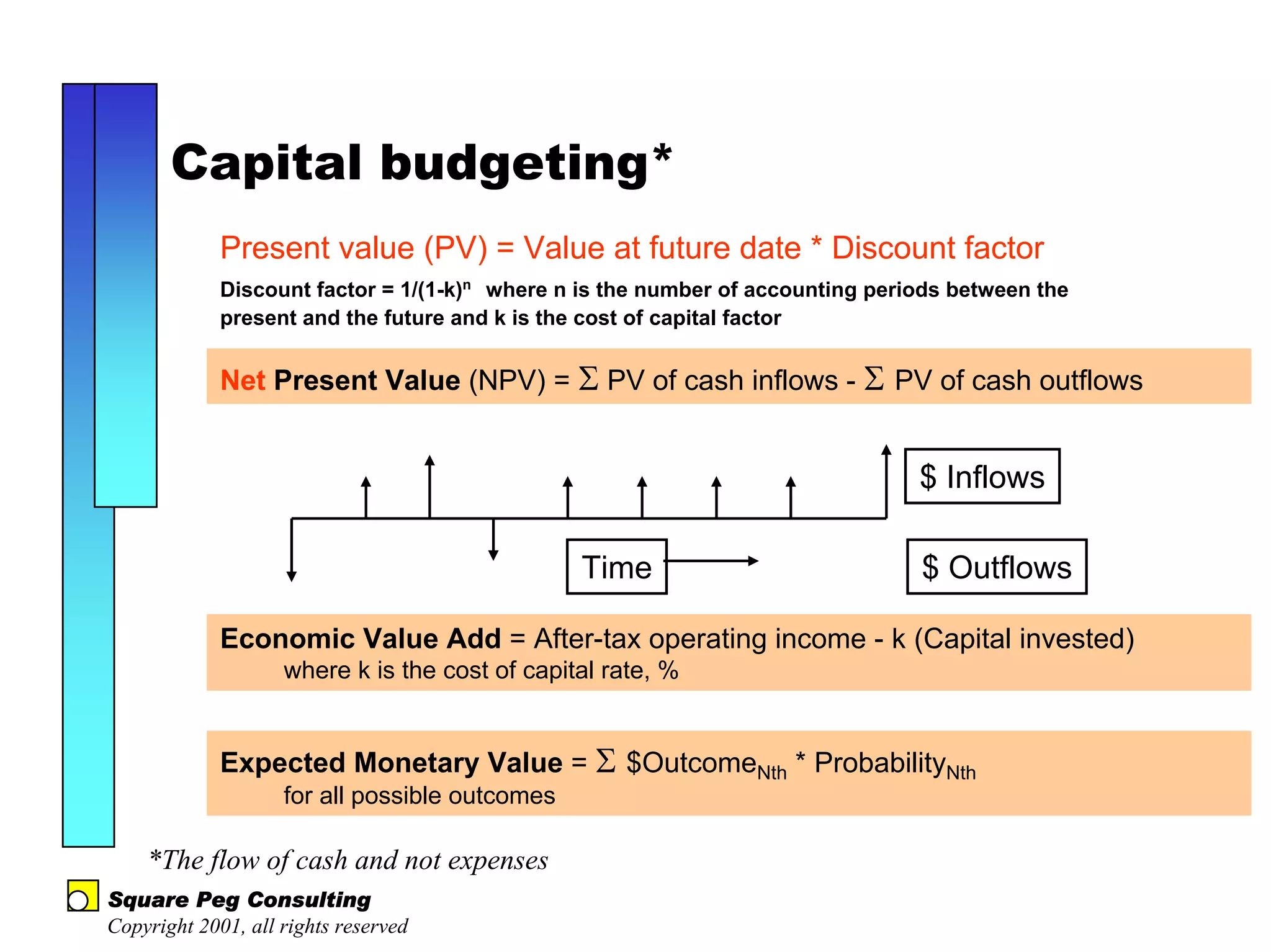
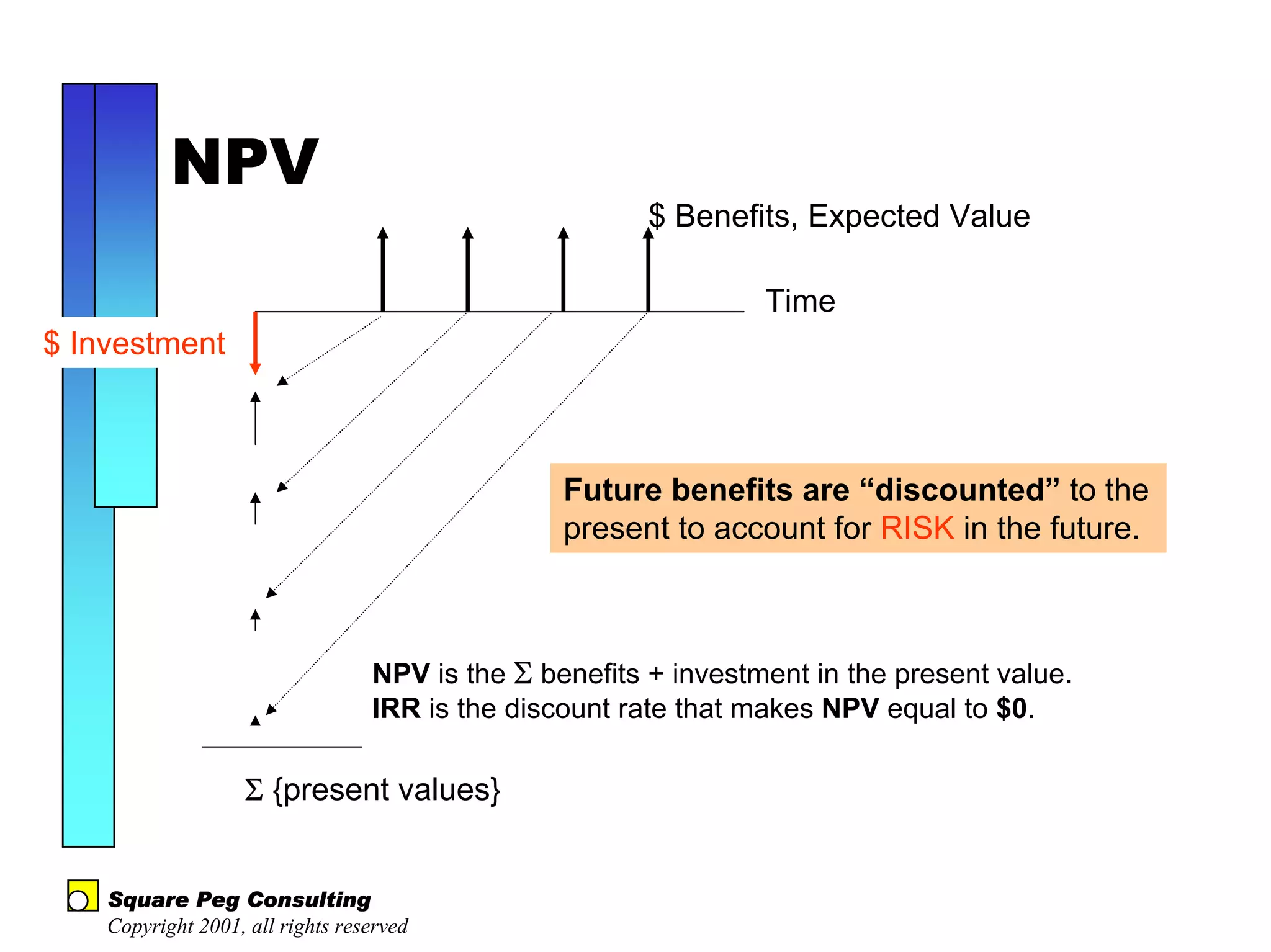
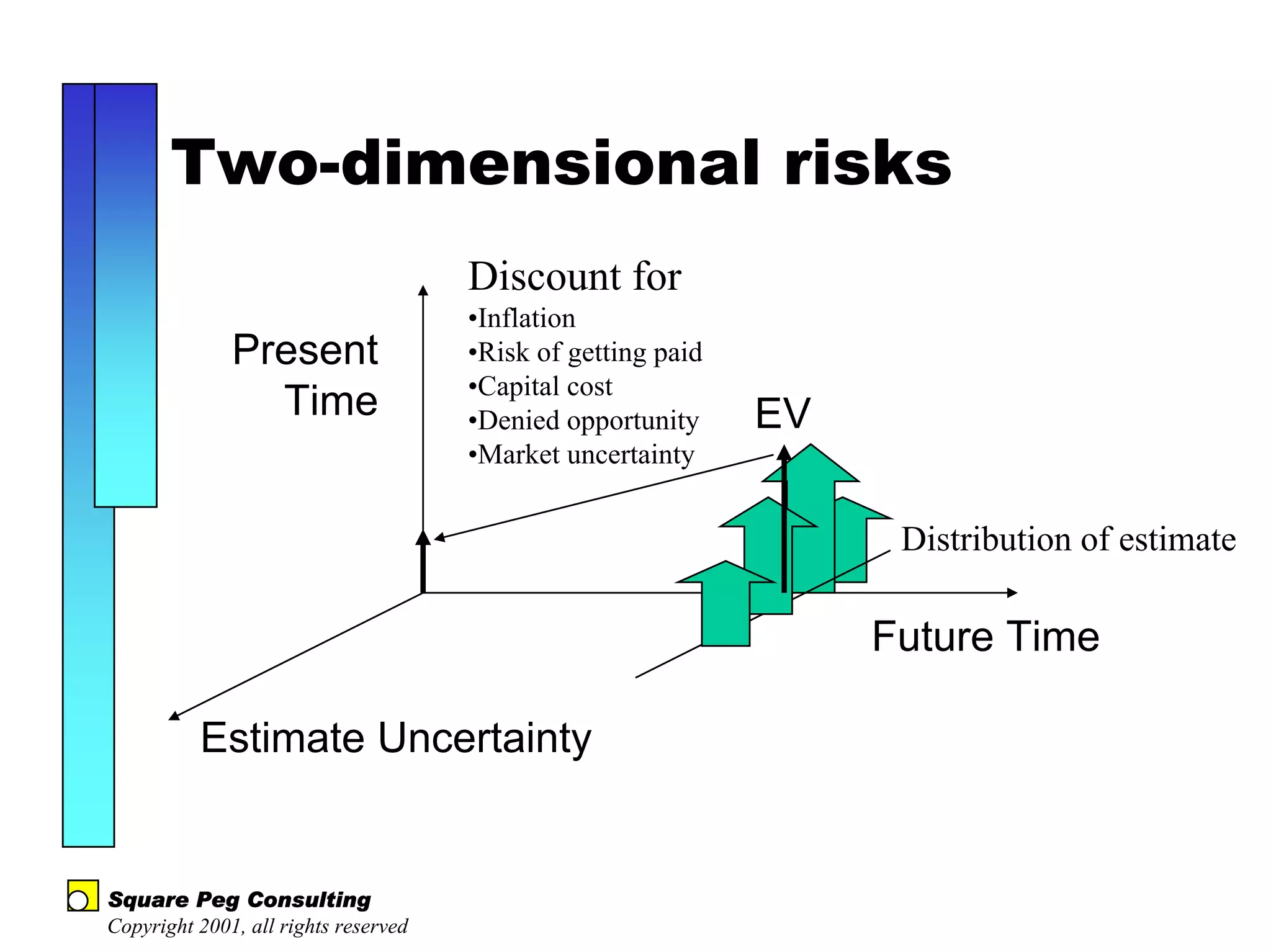
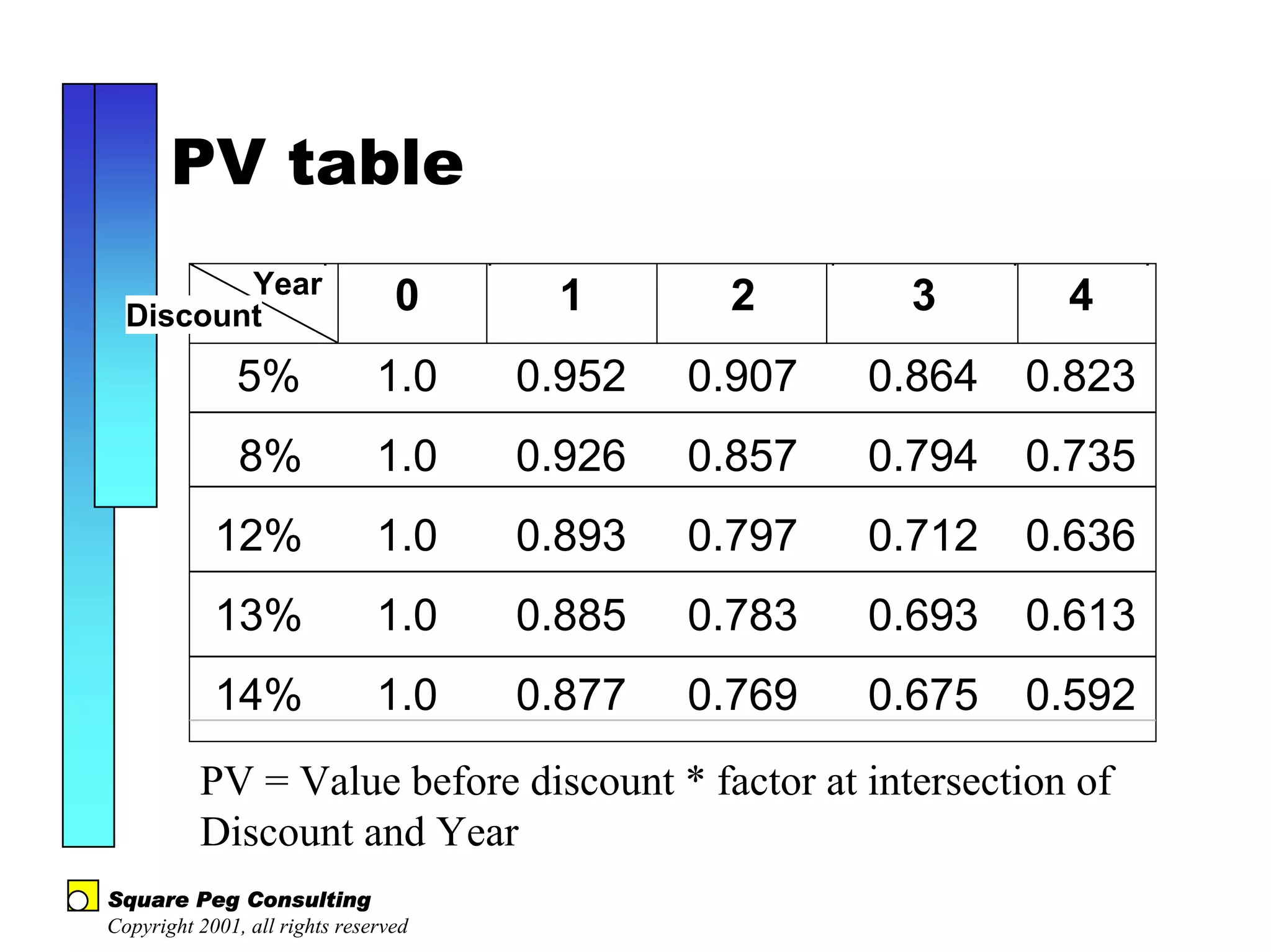
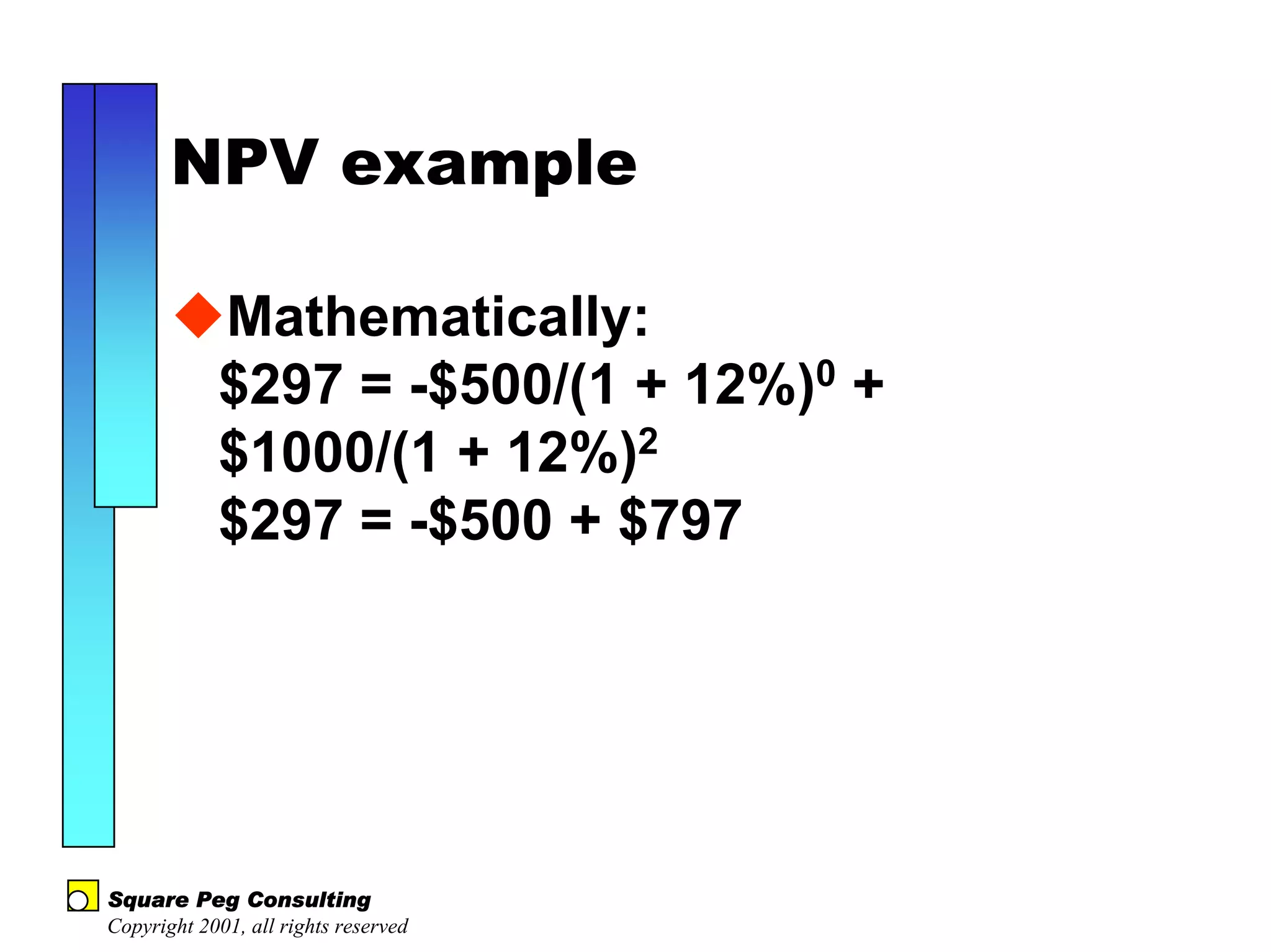
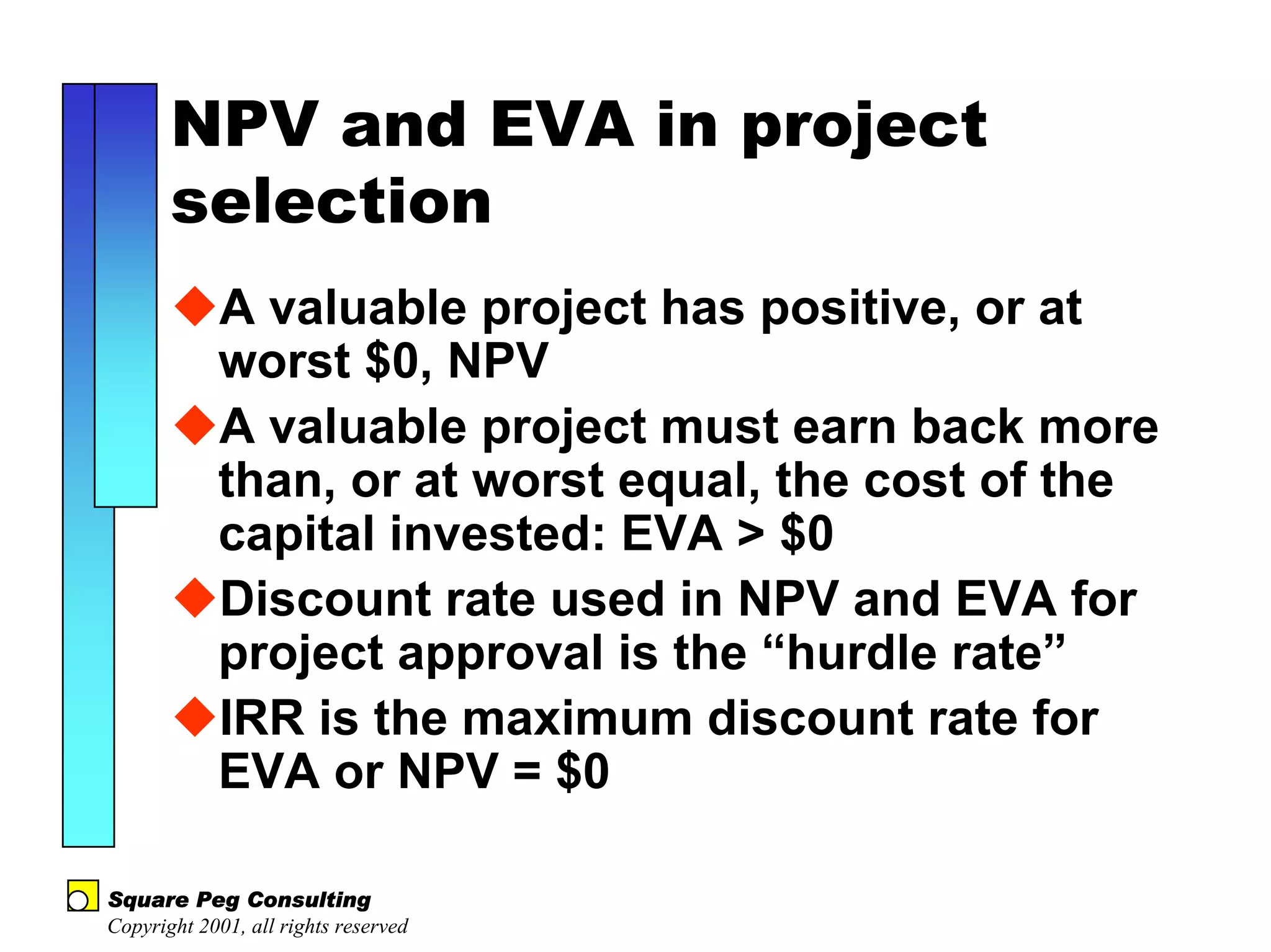
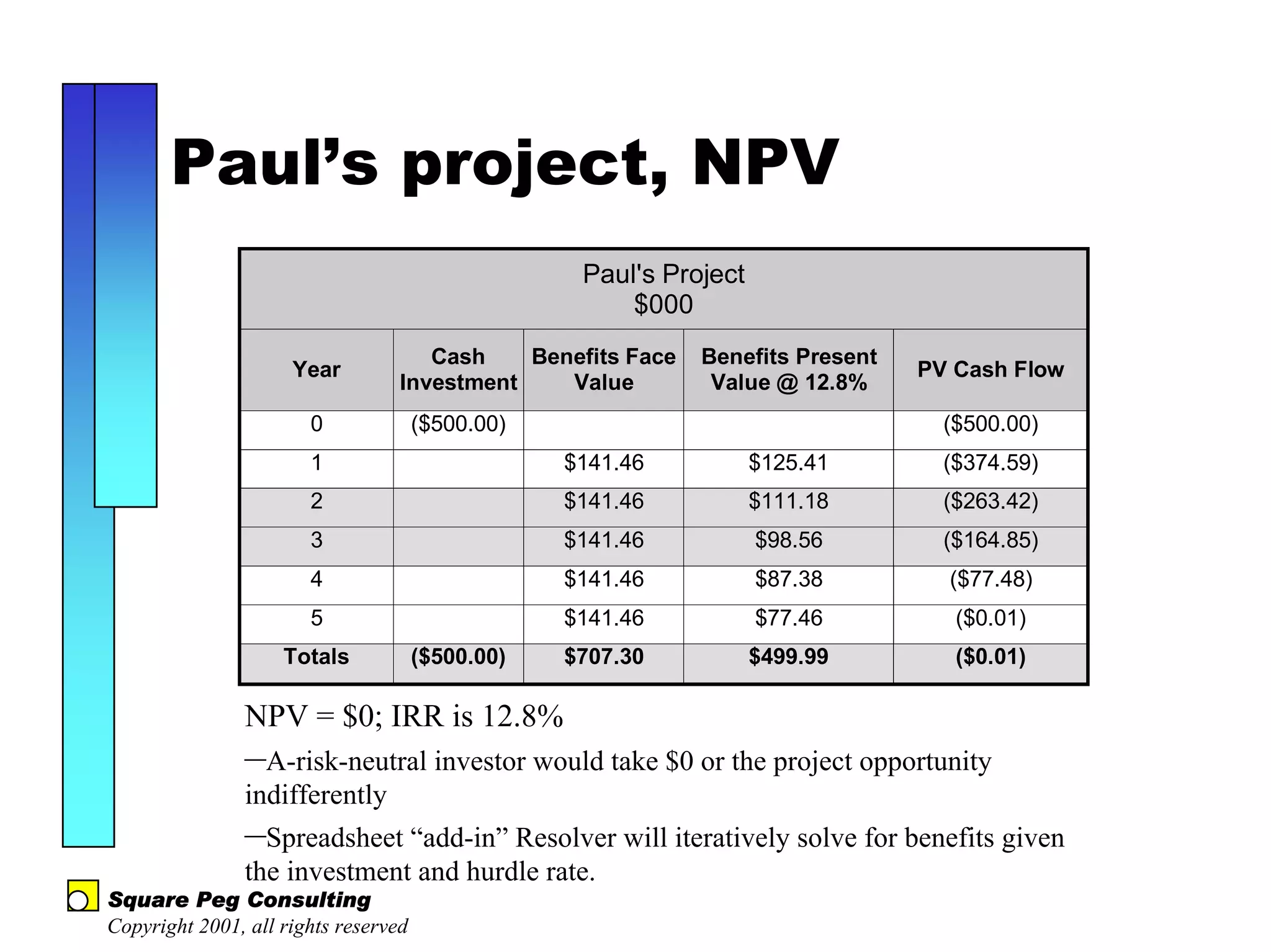
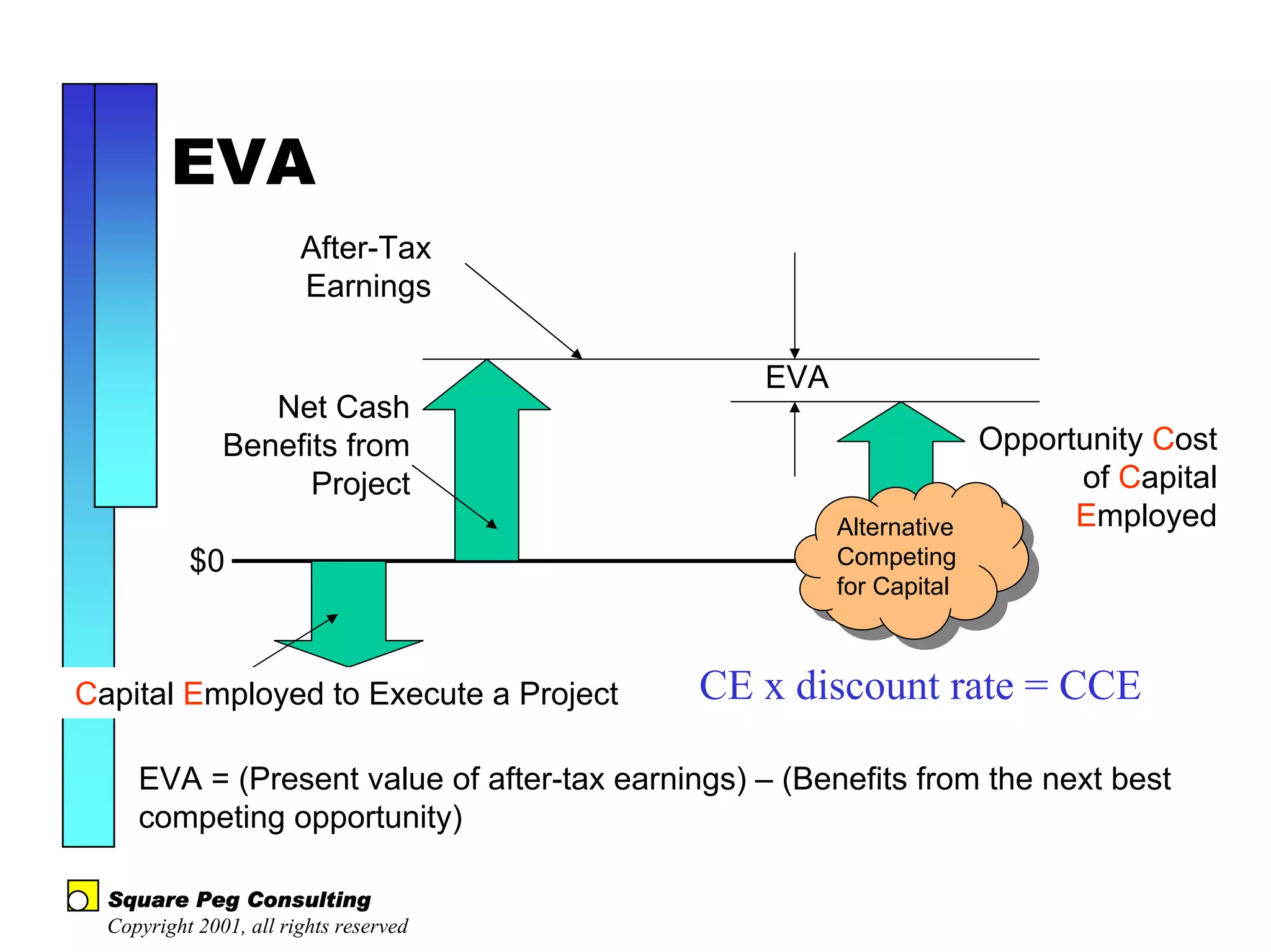
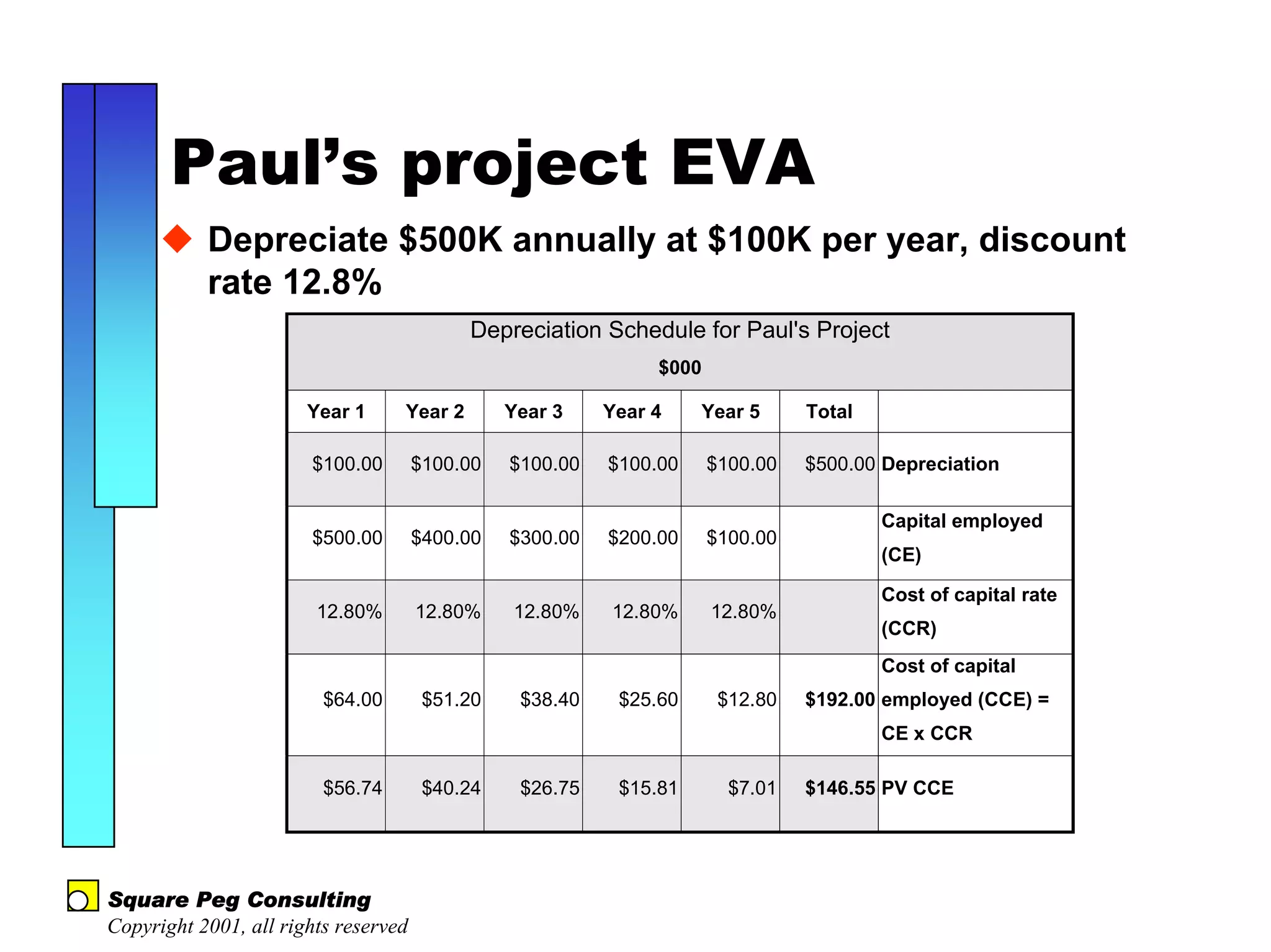
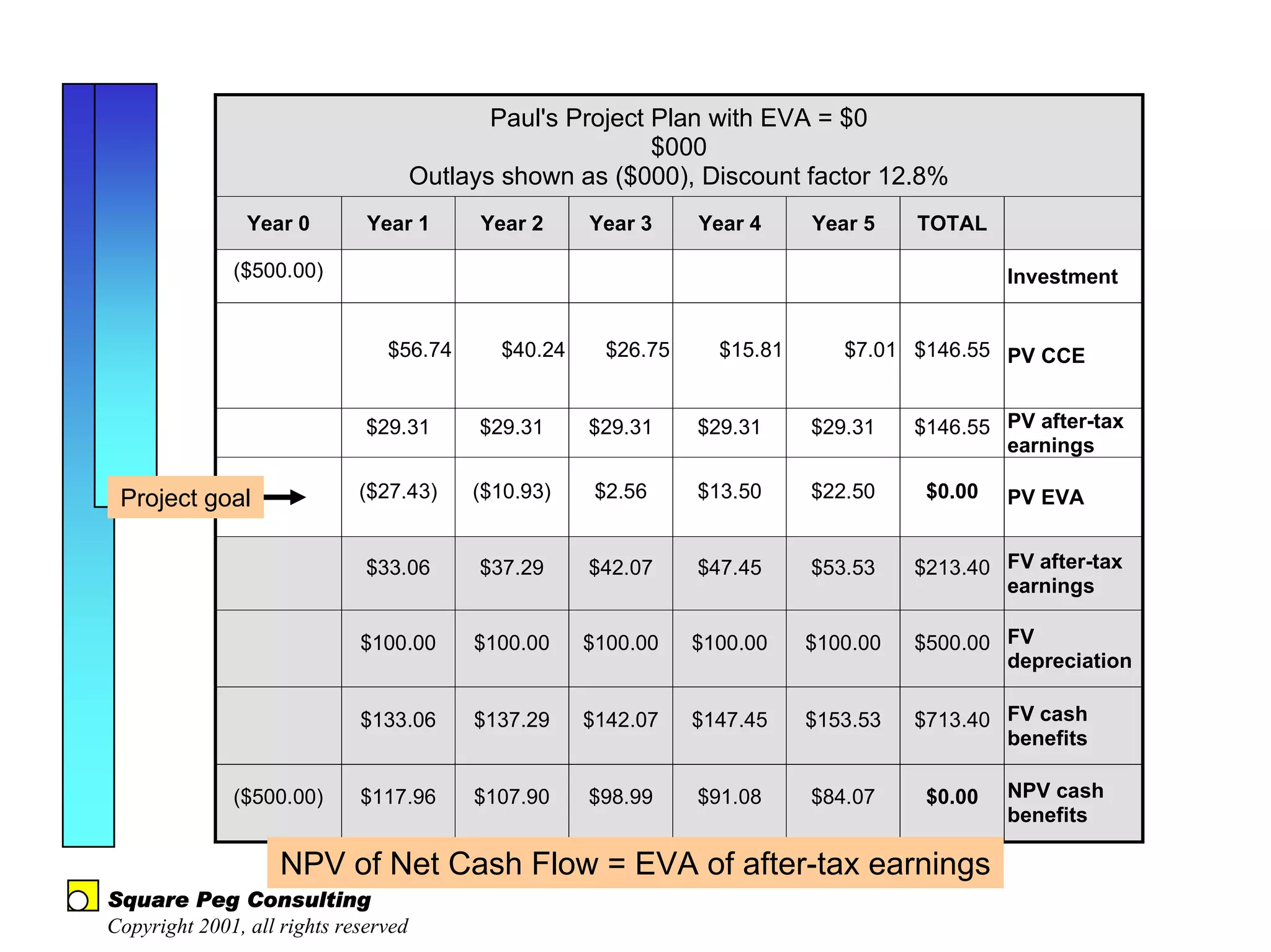
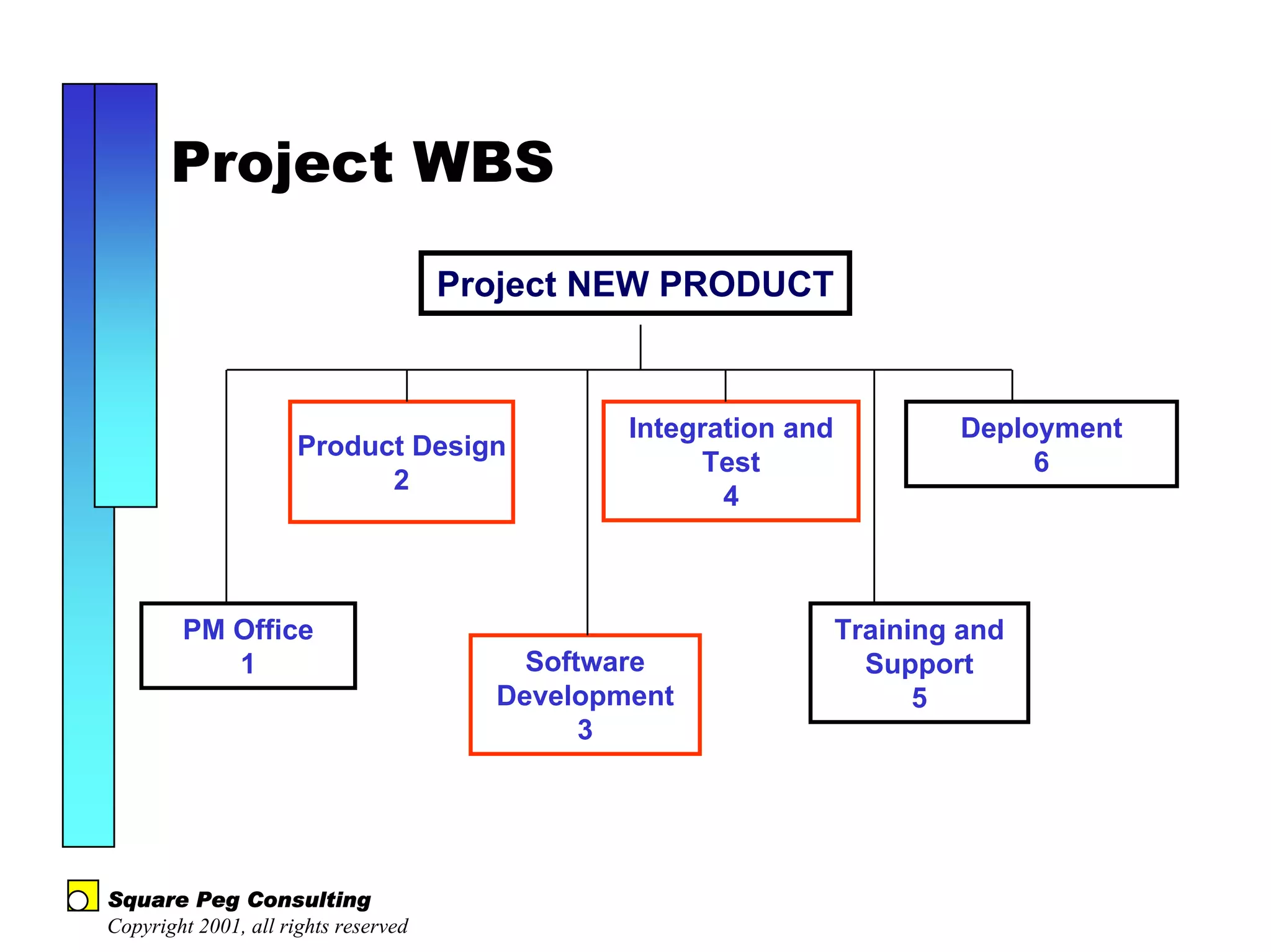
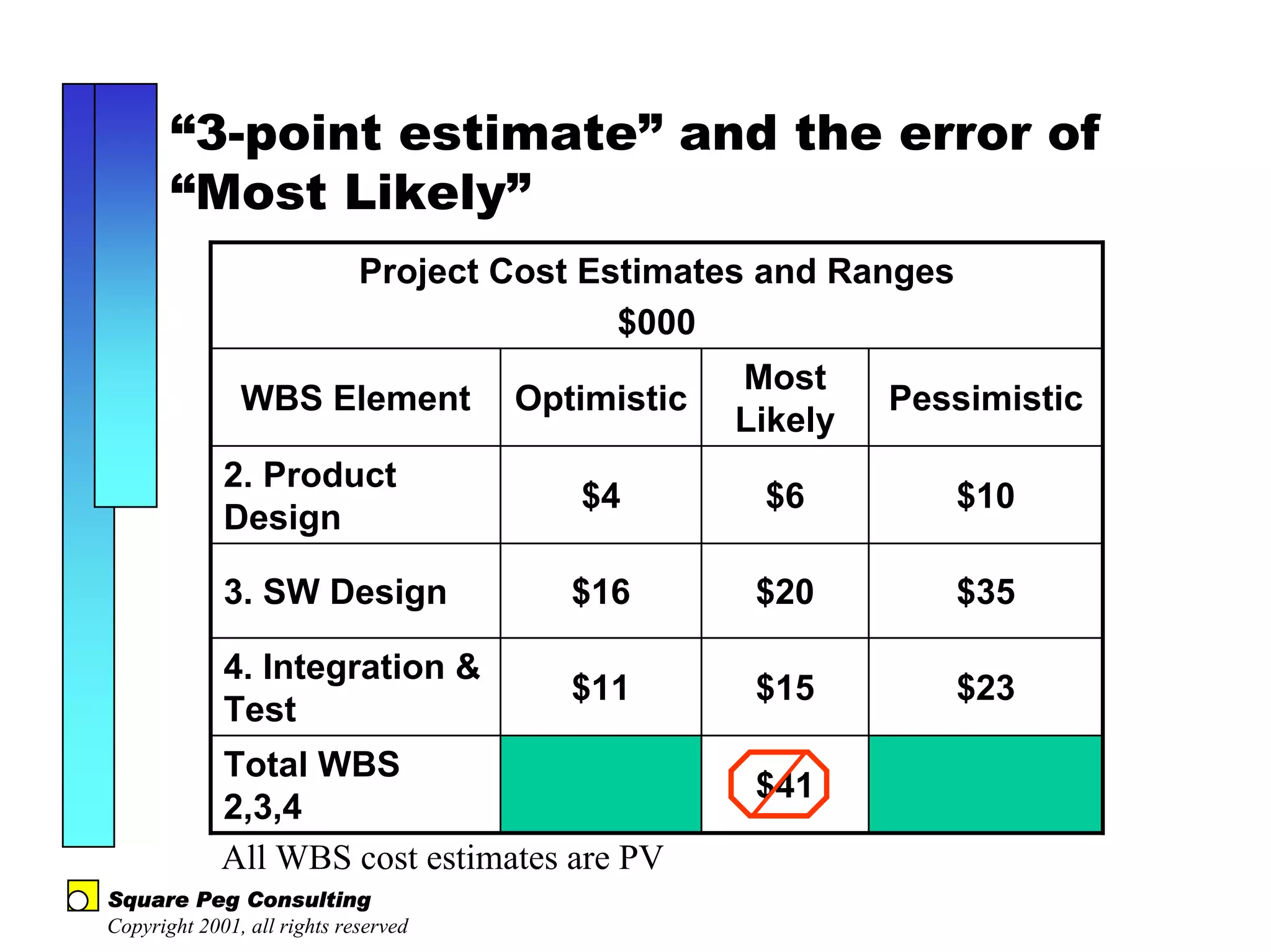
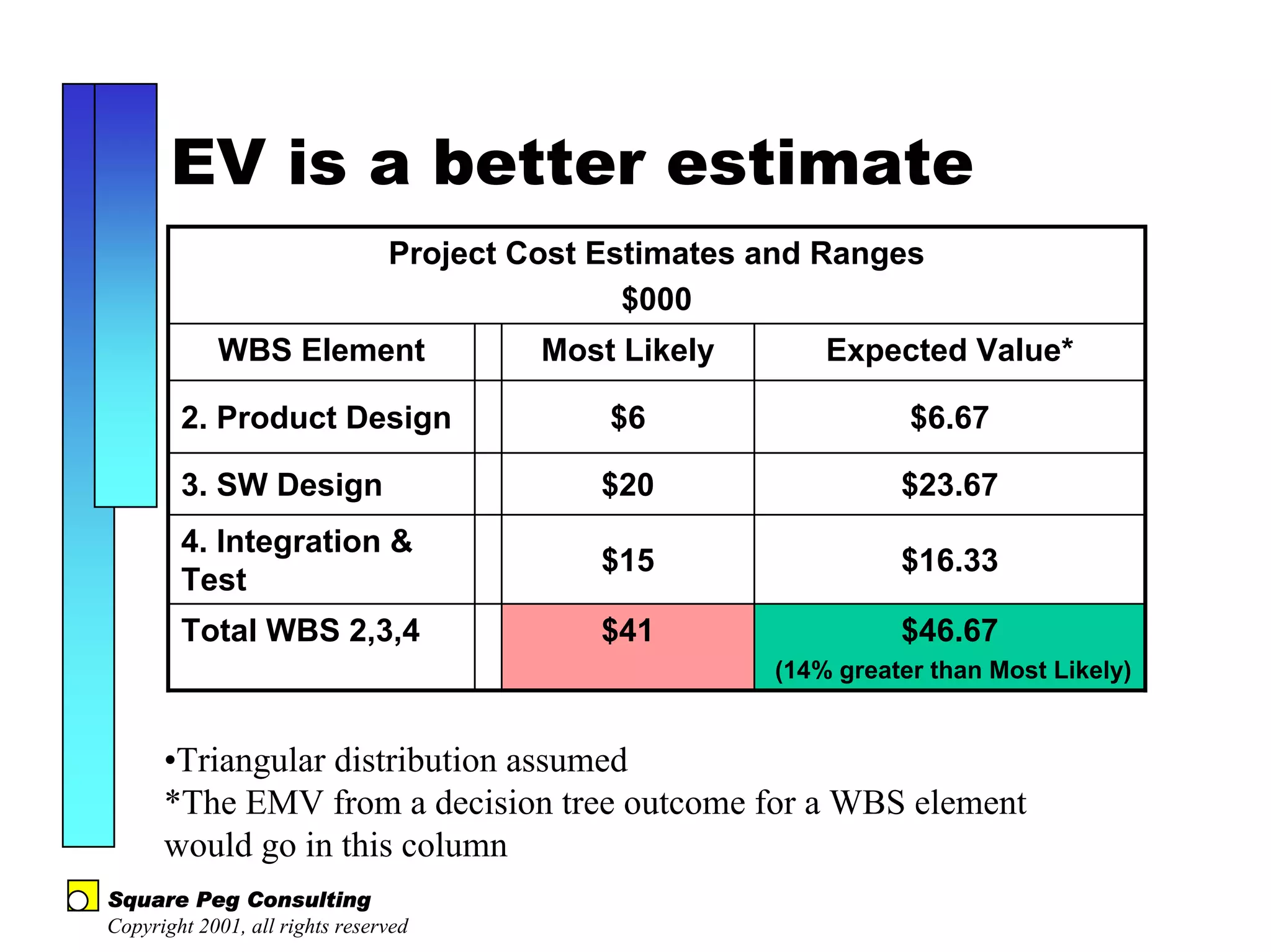
The document discusses quantitative risk analysis in budgeting, emphasizing the necessity of accounting for risk in financial estimates and cash flow projections. It covers key concepts like net present value (NPV), expected monetary value (EMV), and economic value added (EVA) to evaluate project investments and their associated risks. Additionally, it presents practical examples and methodologies for risk-managed budgeting and expense forecasting.