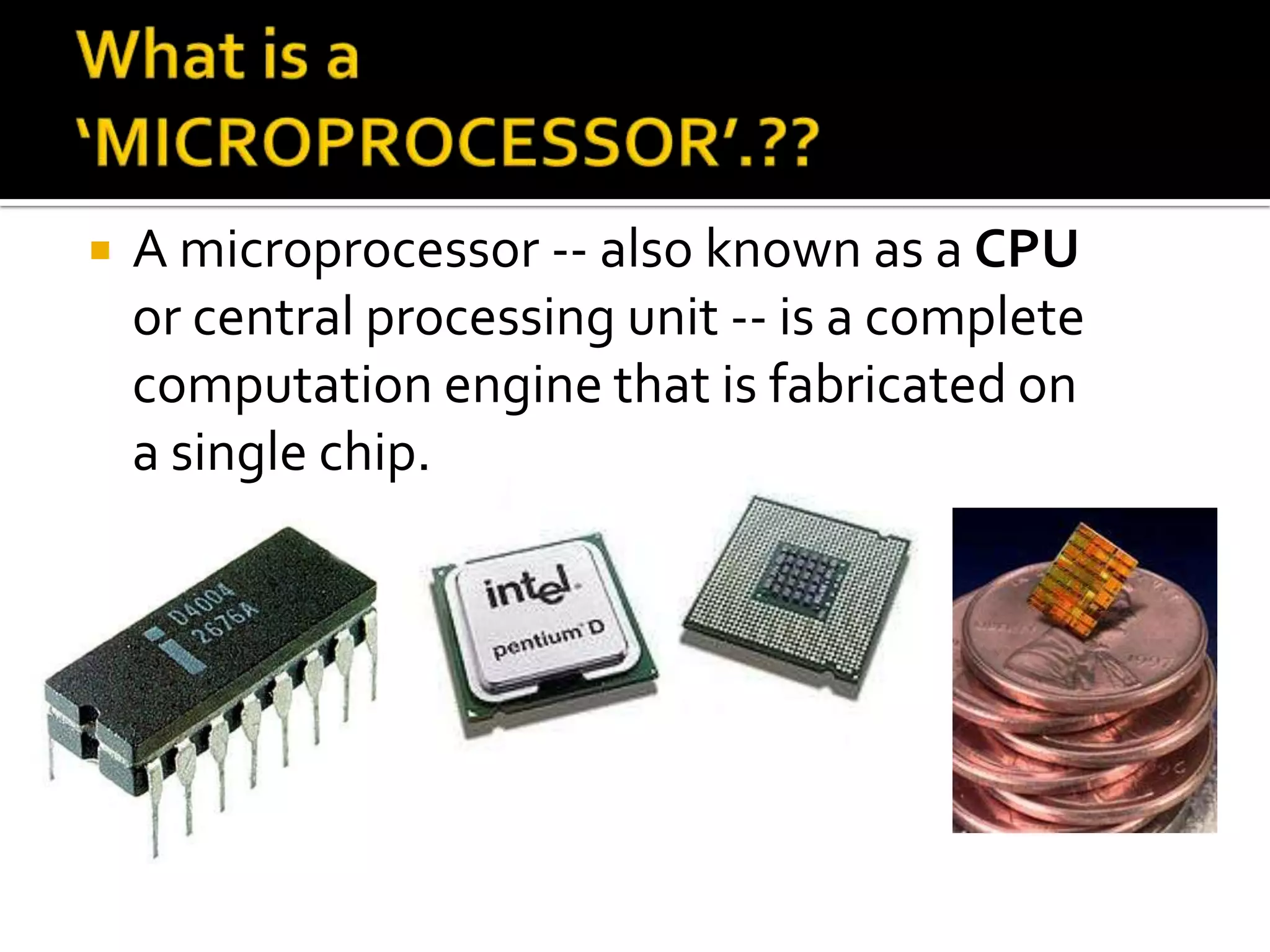
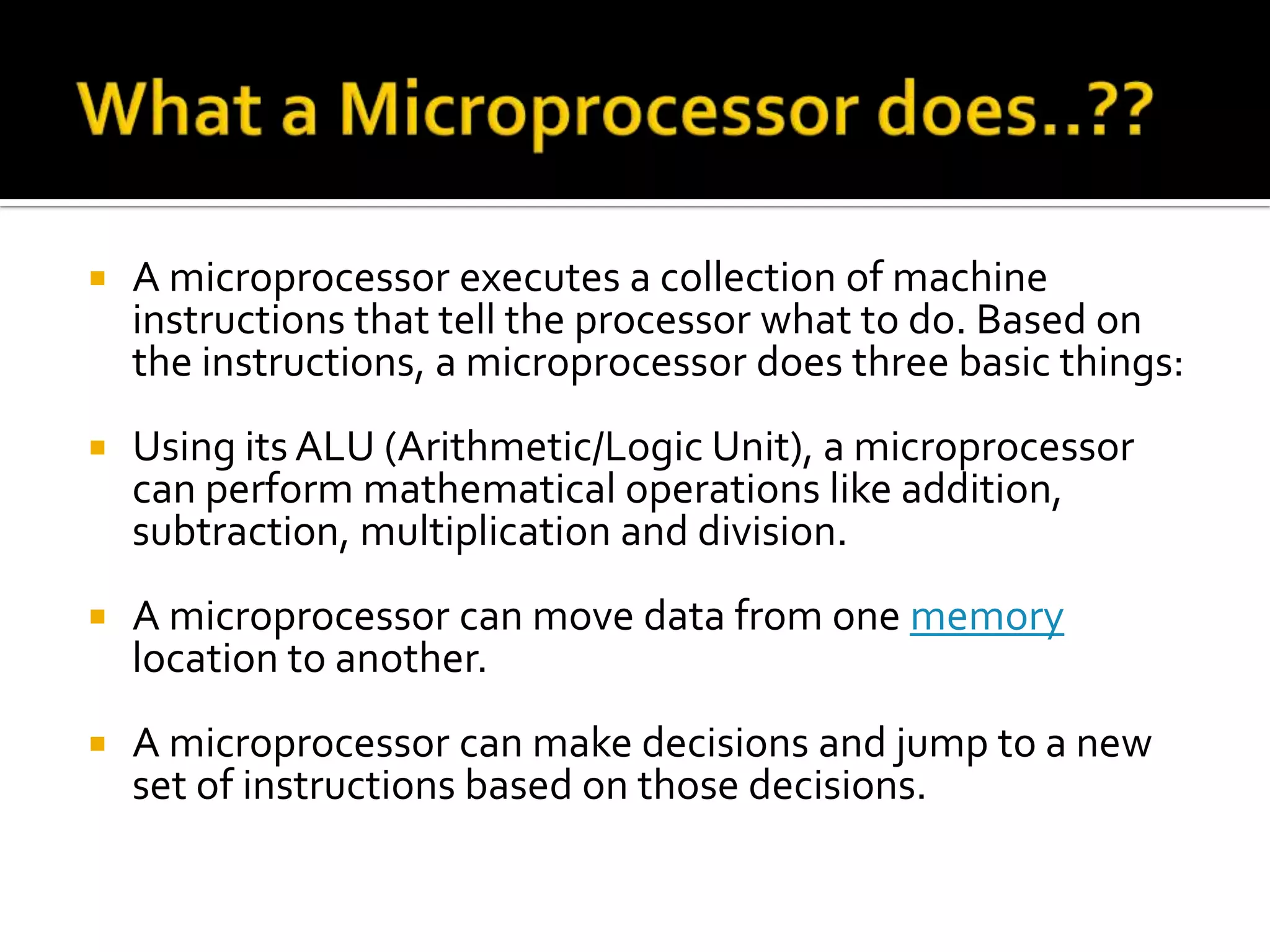
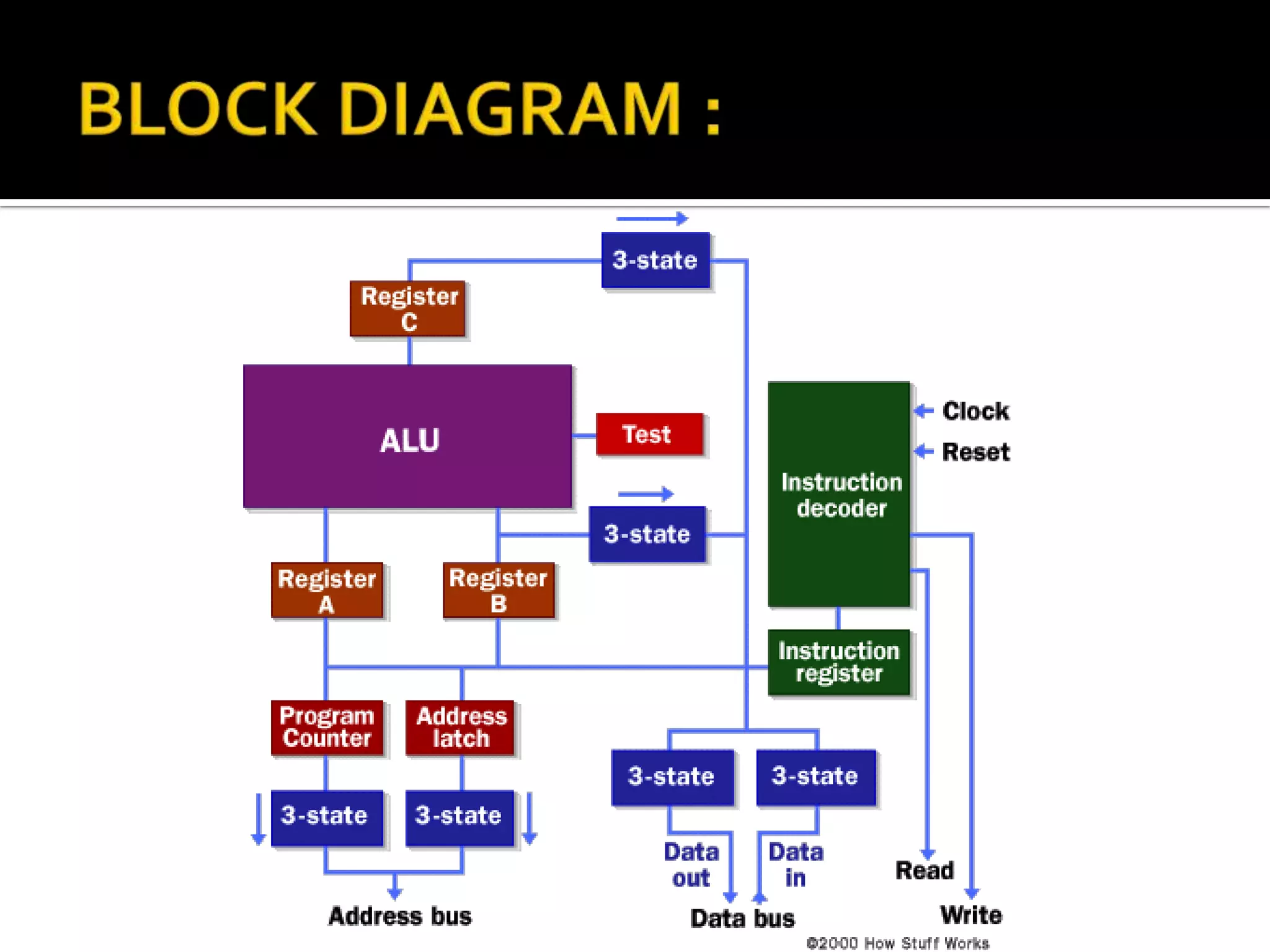
A microprocessor is a central processing unit that contains a complete computation engine on a single chip. It executes machine instructions to perform arithmetic operations, move data between memory locations, and make decisions by jumping to different instruction sets. A microprocessor contains registers for temporary storage of data, addresses, and processor status. There are different types of registers including general purpose, floating point, constant, vector, and special purpose registers that store program state information. Control and status registers include the program counter, instruction register, and program status word.