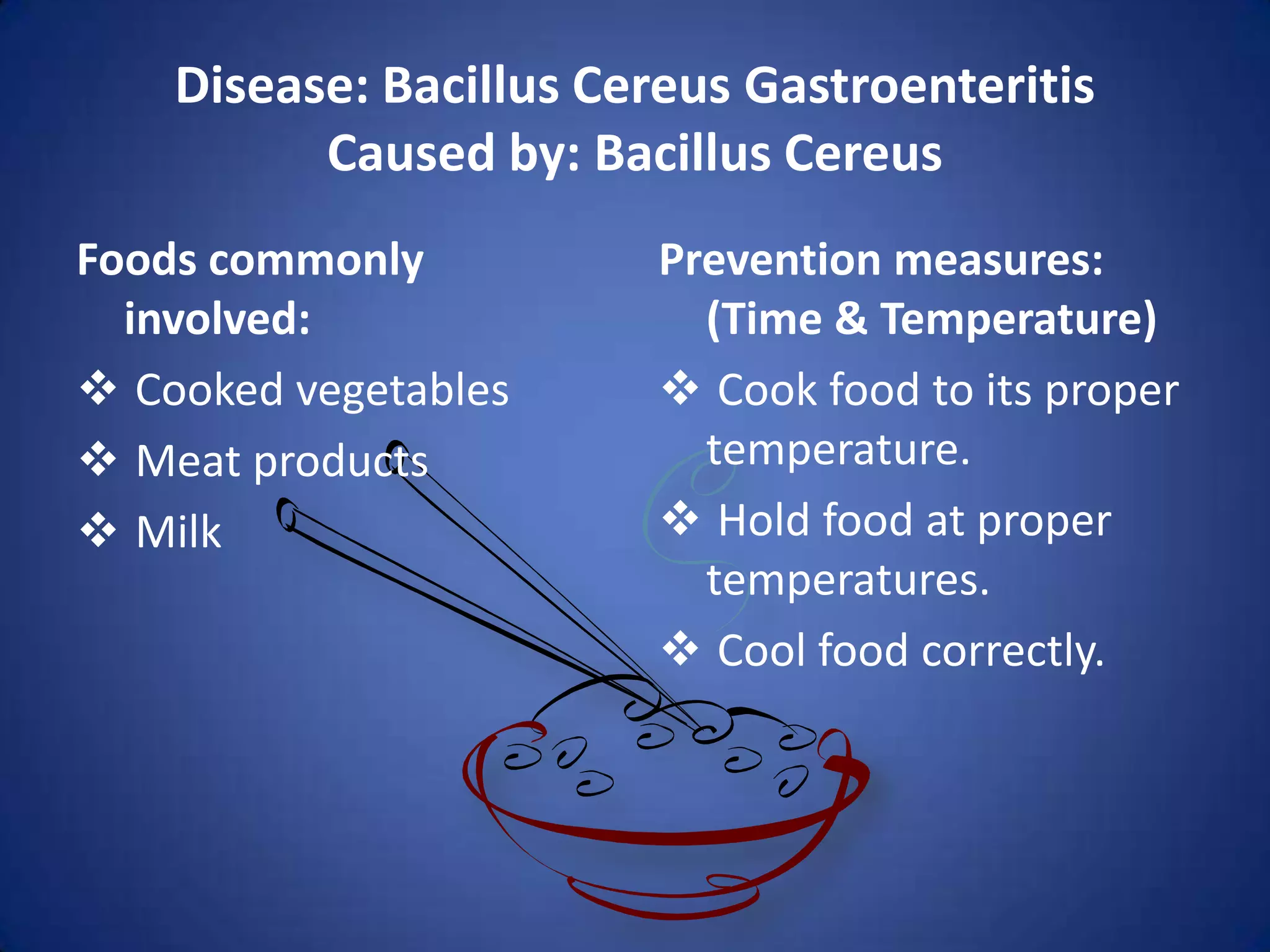
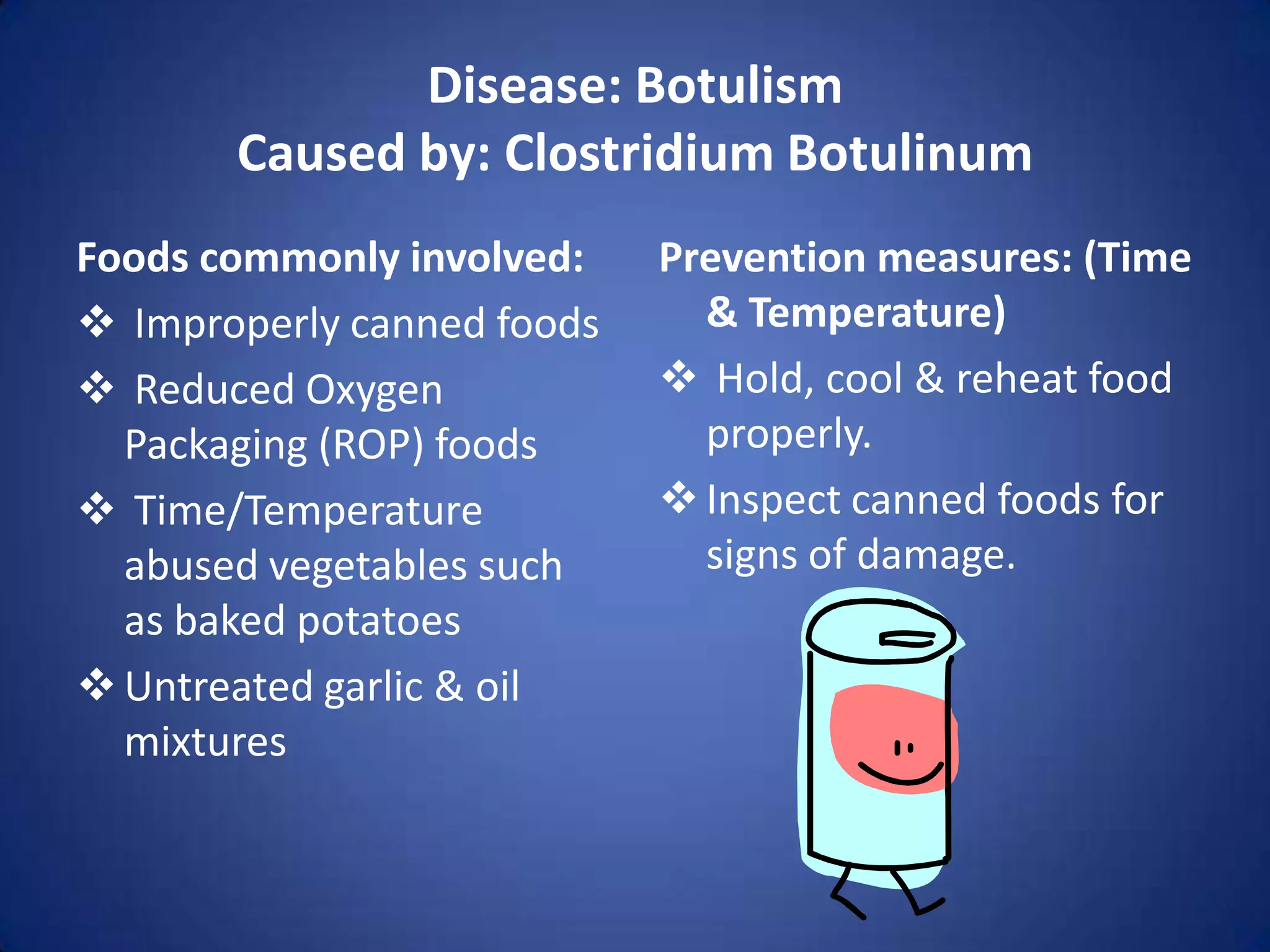
This document outlines various pathogens that can cause foodborne illness such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi, and toxins. It discusses the characteristics of these pathogens and the foods they are most likely to contaminate. Prevention methods are provided that focus on proper food handling and cooking to prevent pathogen growth and contamination.