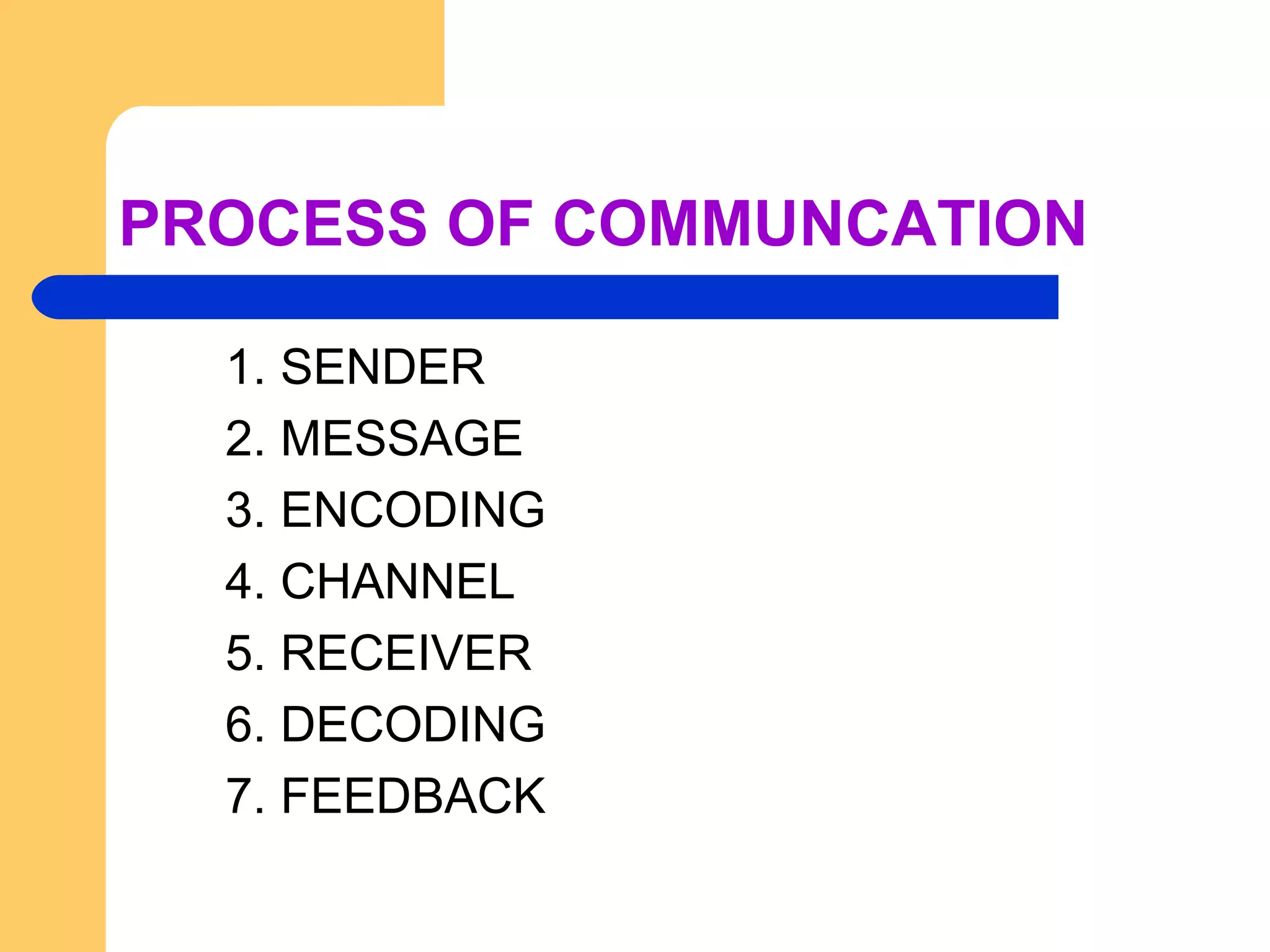
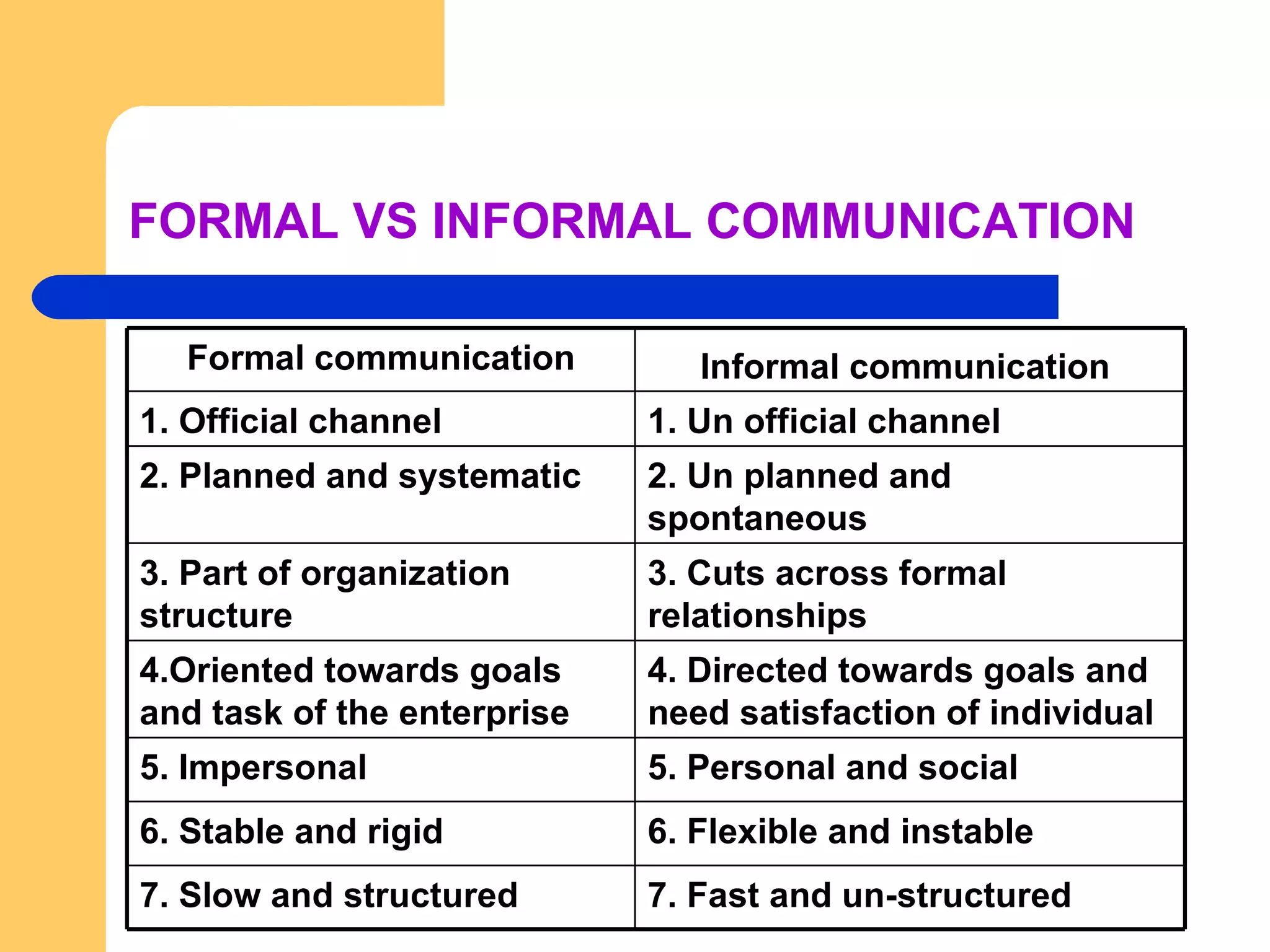
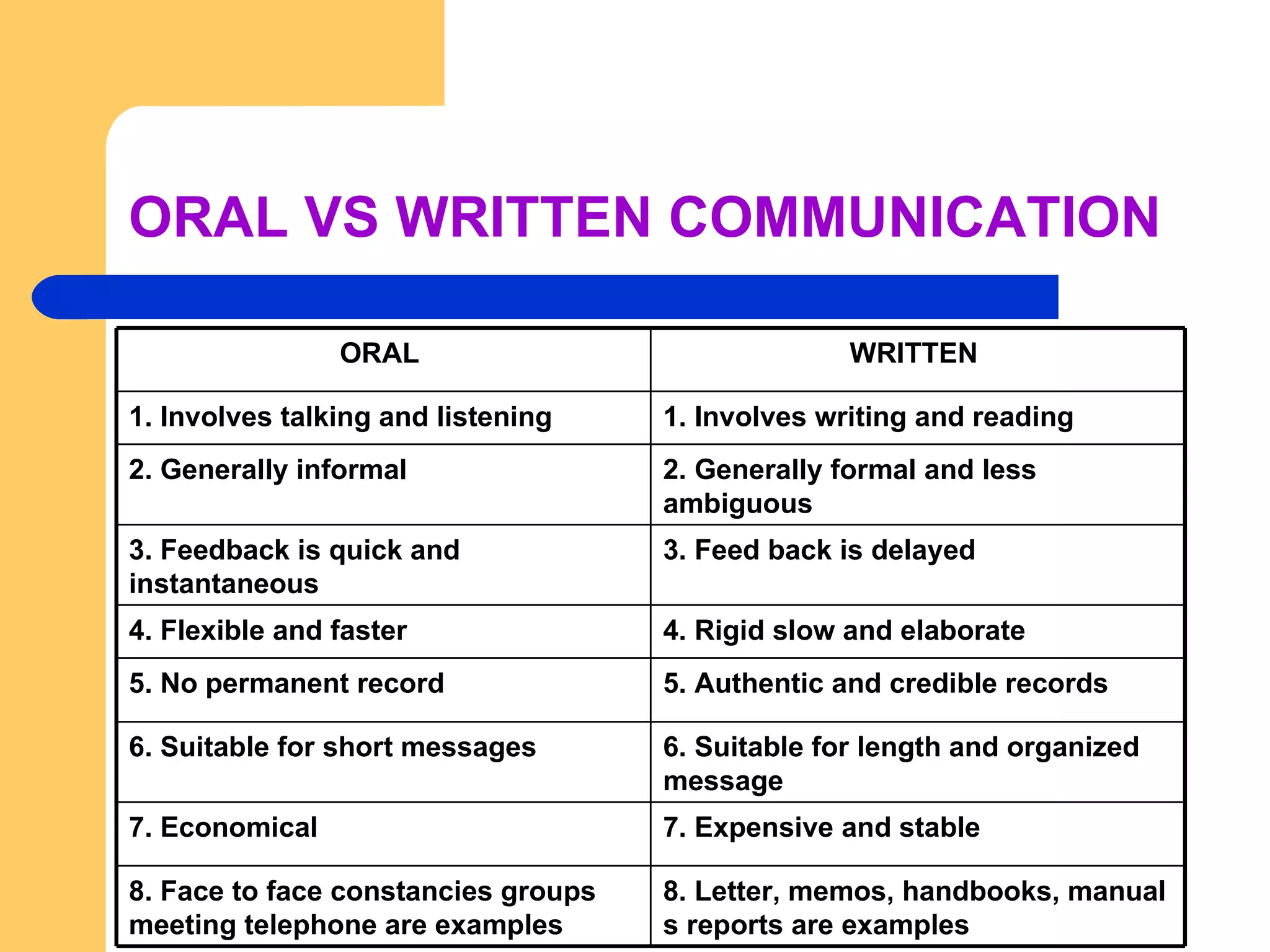
The document discusses communication in organizations. It defines communication as a continuous two-way process that creates understanding between people. The communication process involves a sender sending a message that gets encoded and transmitted through a channel to a receiver who decodes it. There are formal and informal channels of communication, and various barriers that can interfere with effective communication. Overcoming these barriers requires following principles like clarity, brevity, completeness and integrity.