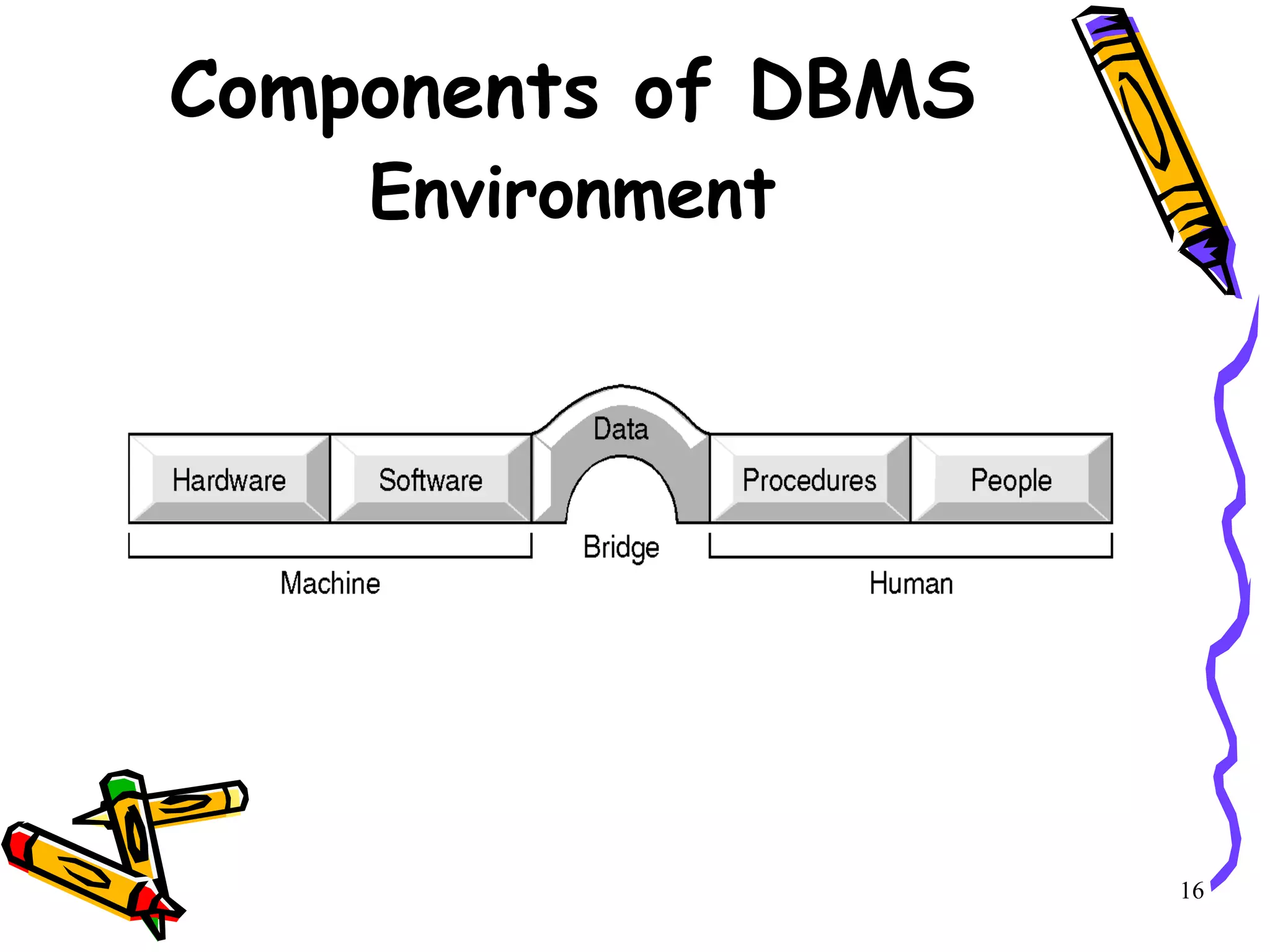
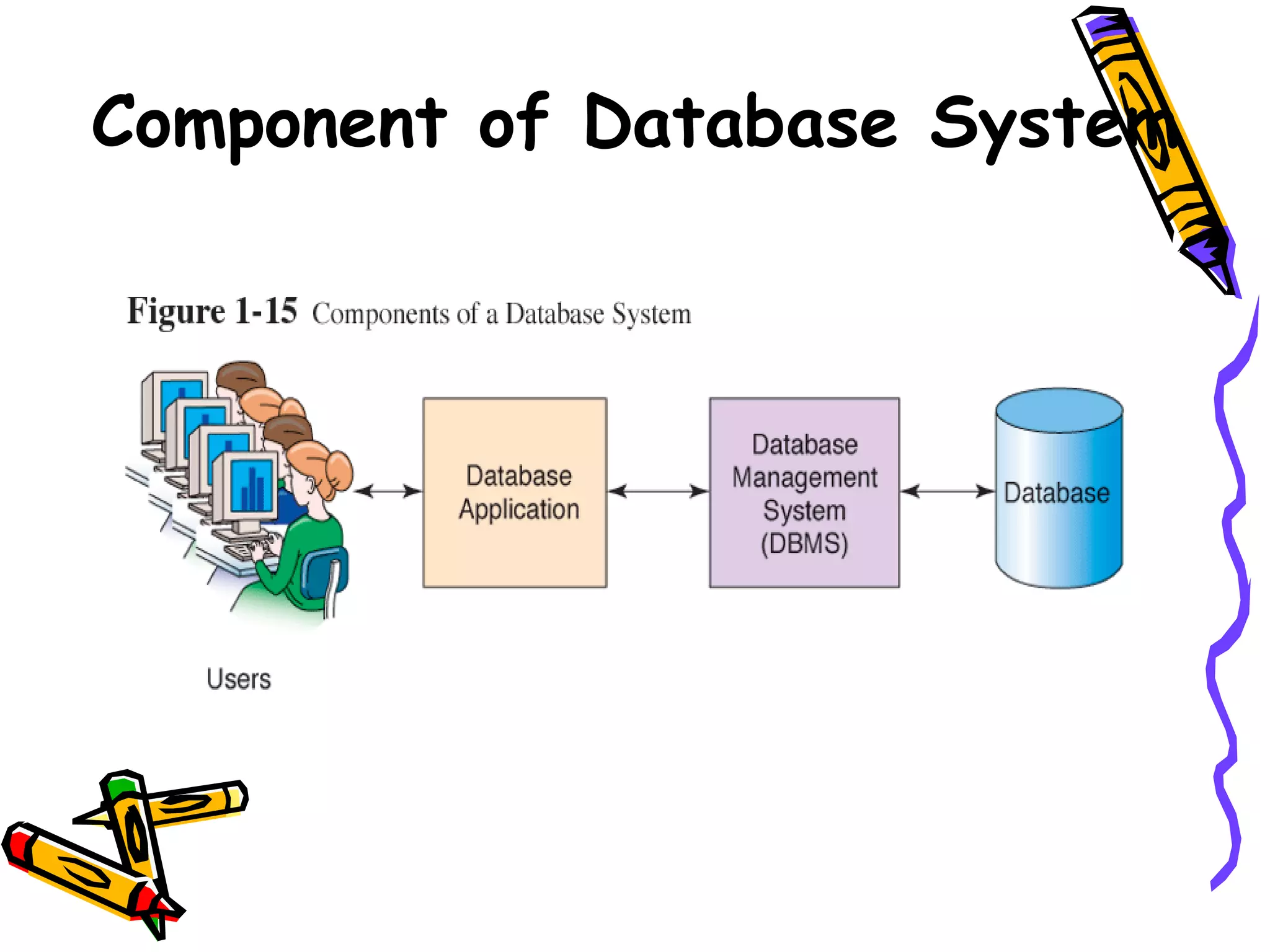
The document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS). It discusses the components of a DBMS environment including hardware, software, data, and procedures. It also outlines the roles in a database environment, the history of database systems, and the functions of a DBMS. Advantages include data control and consistency, while disadvantages include complexity, size, and costs.