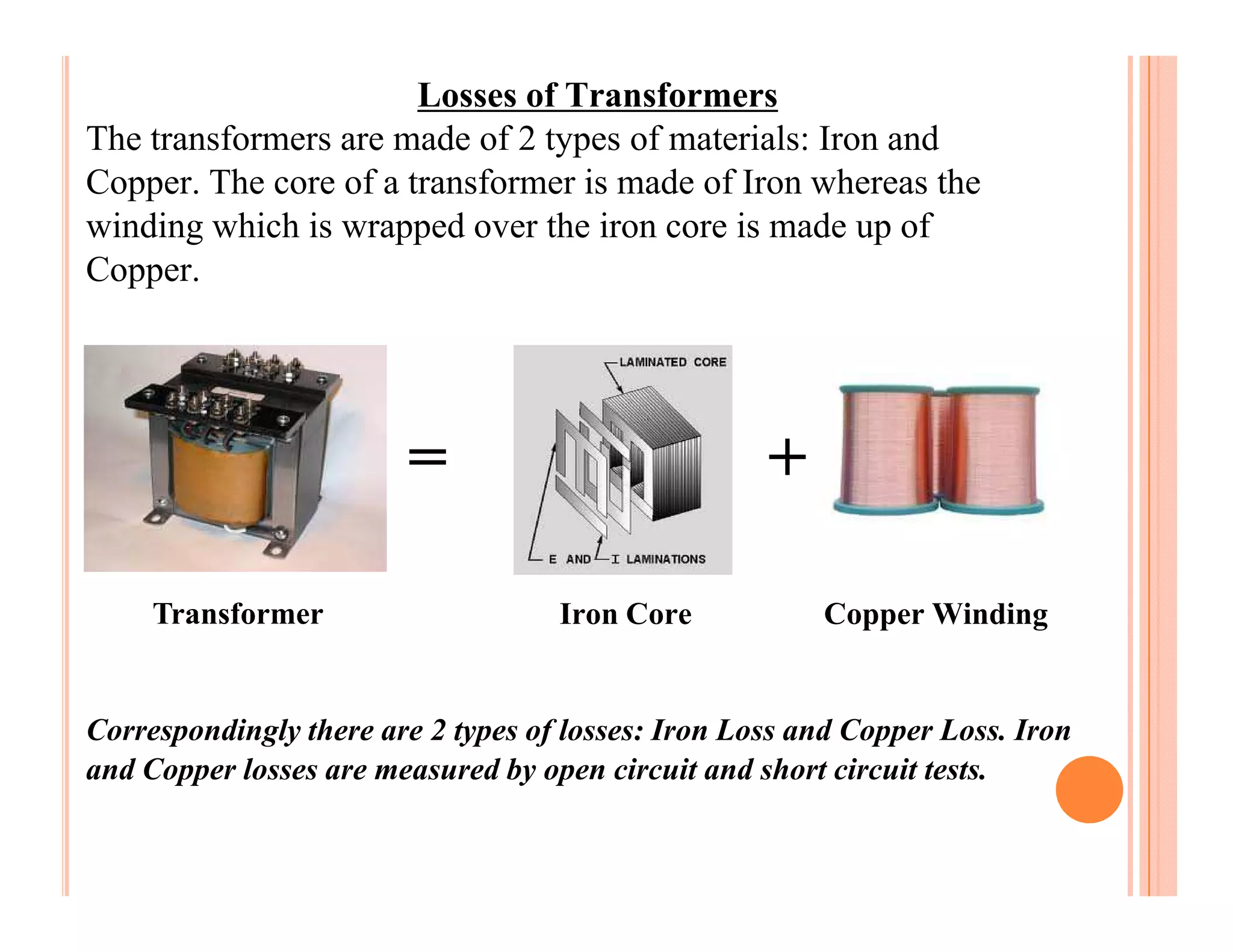
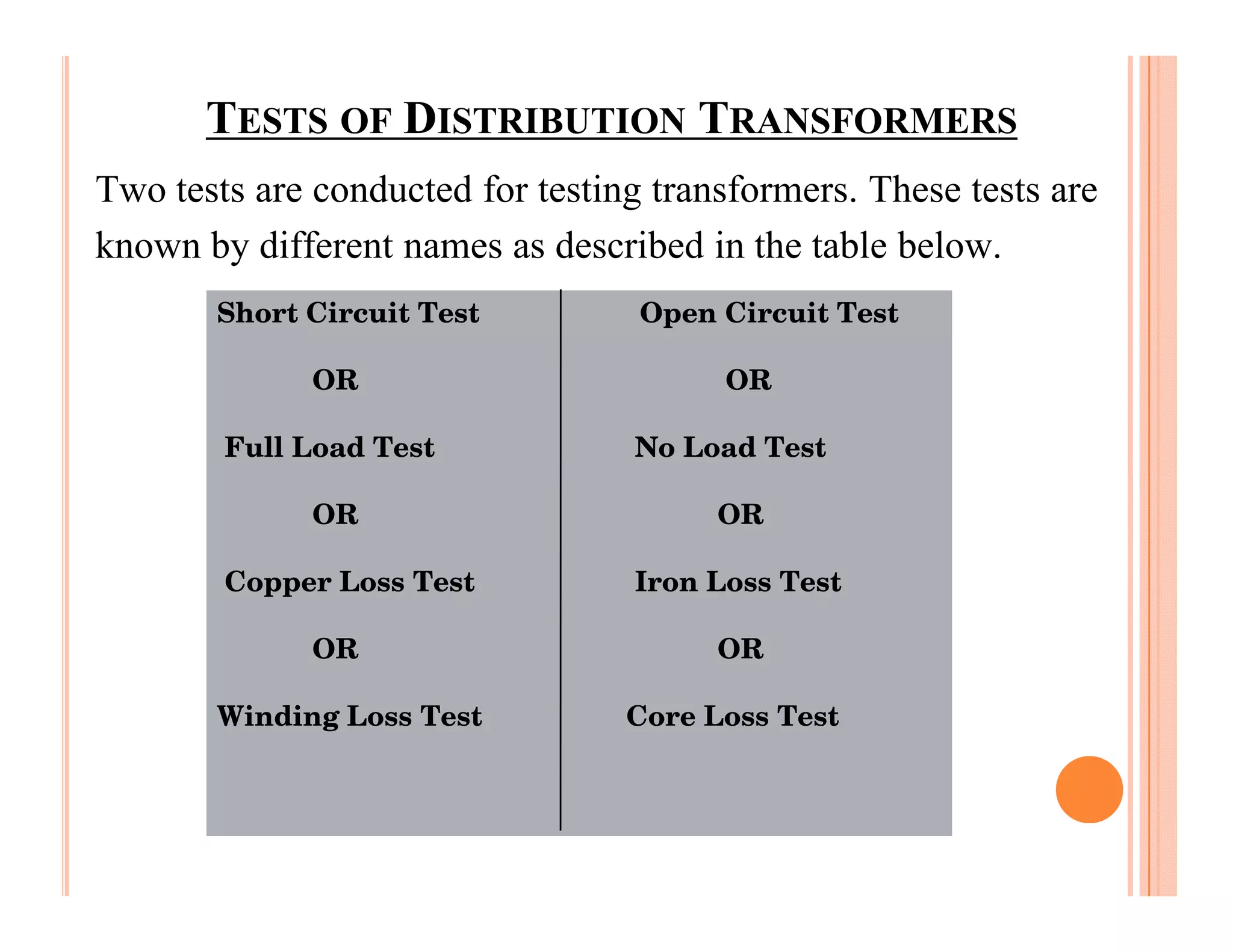
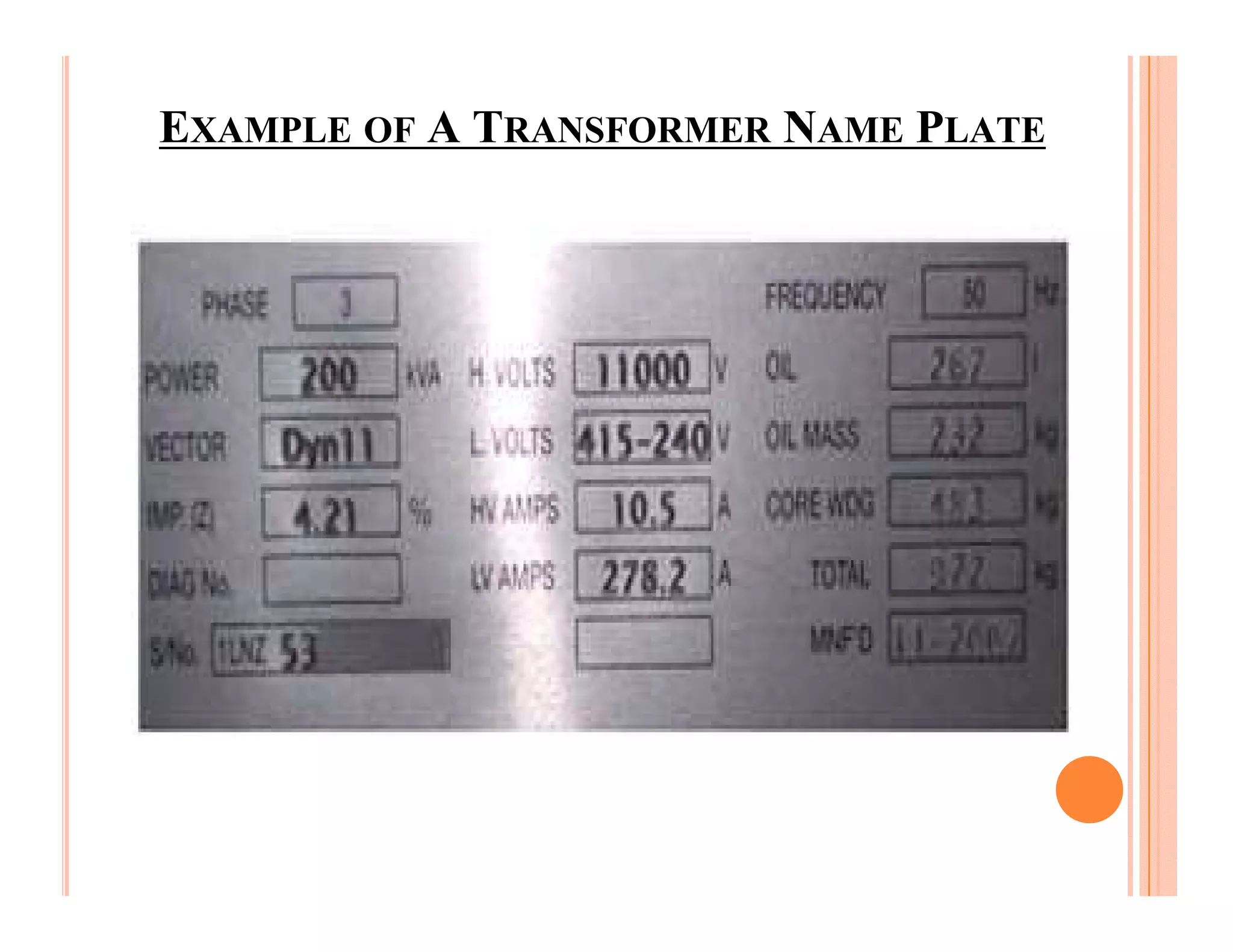
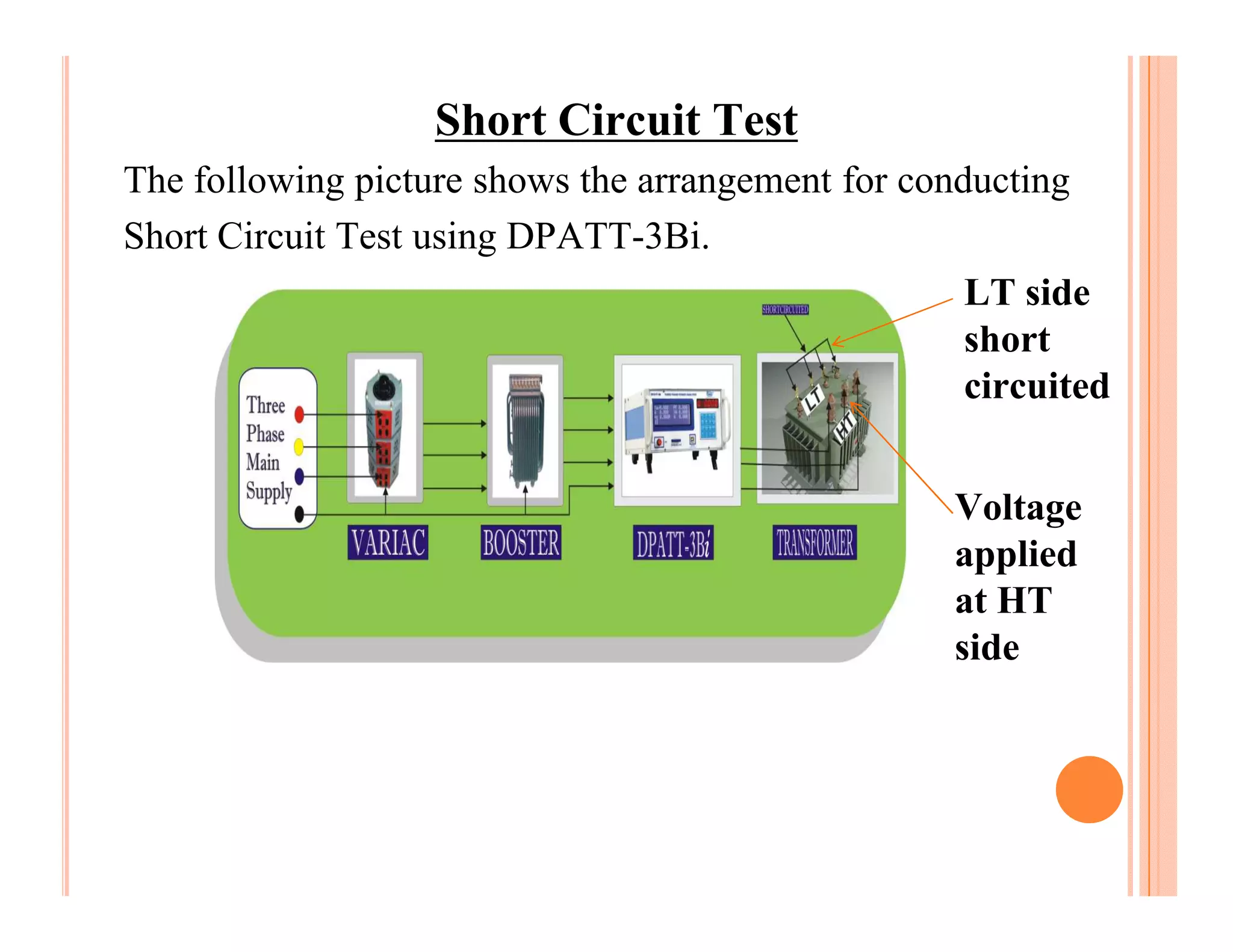
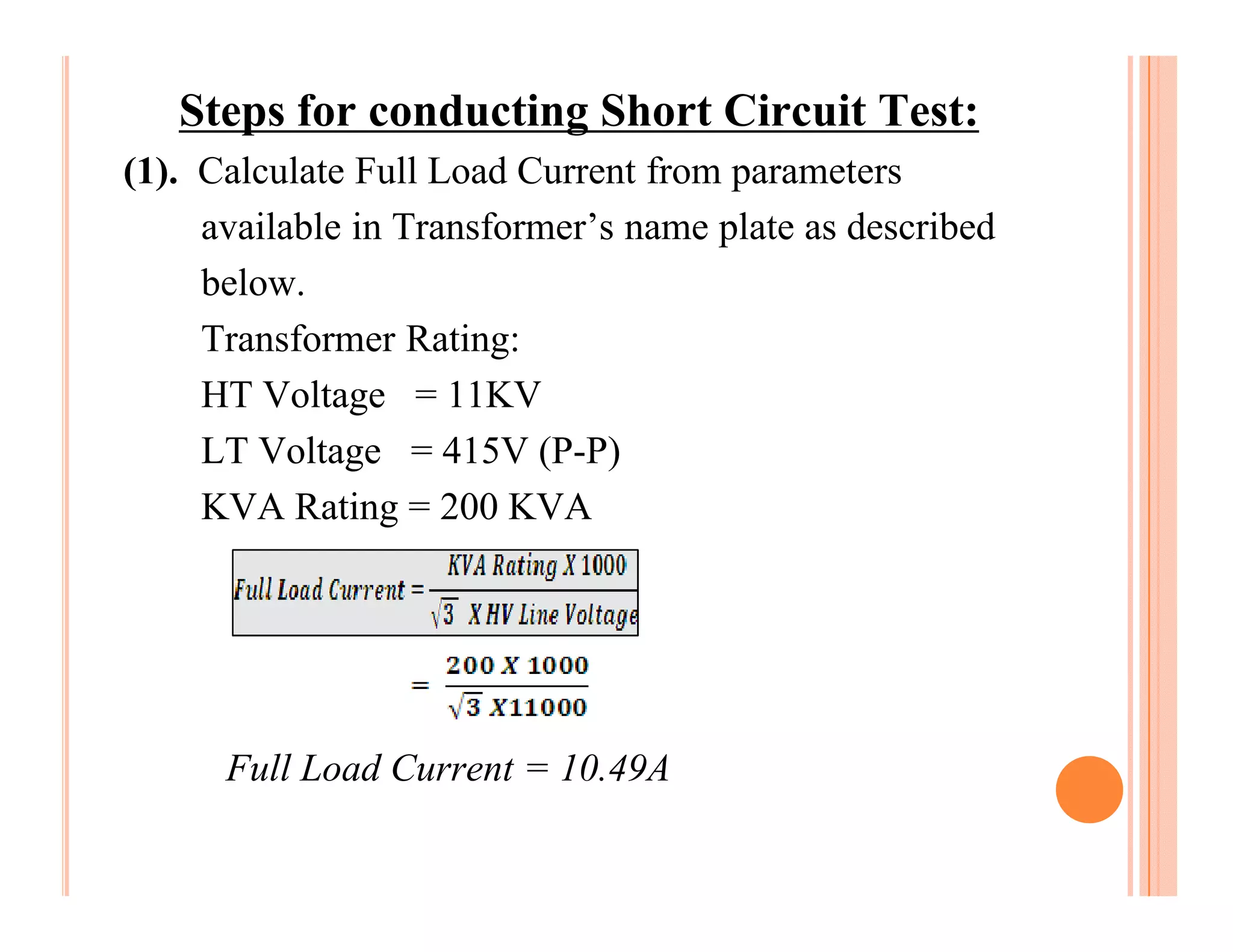
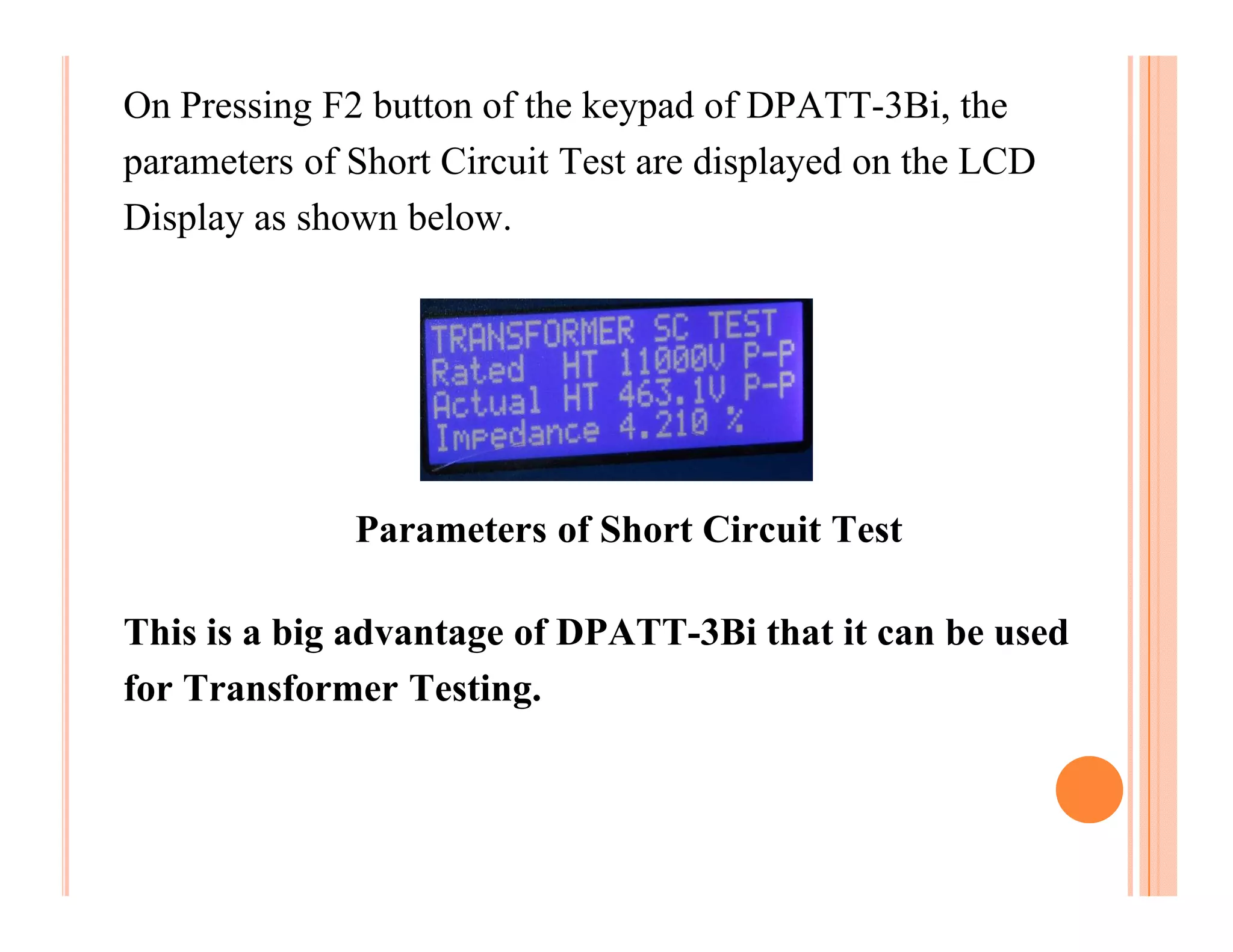
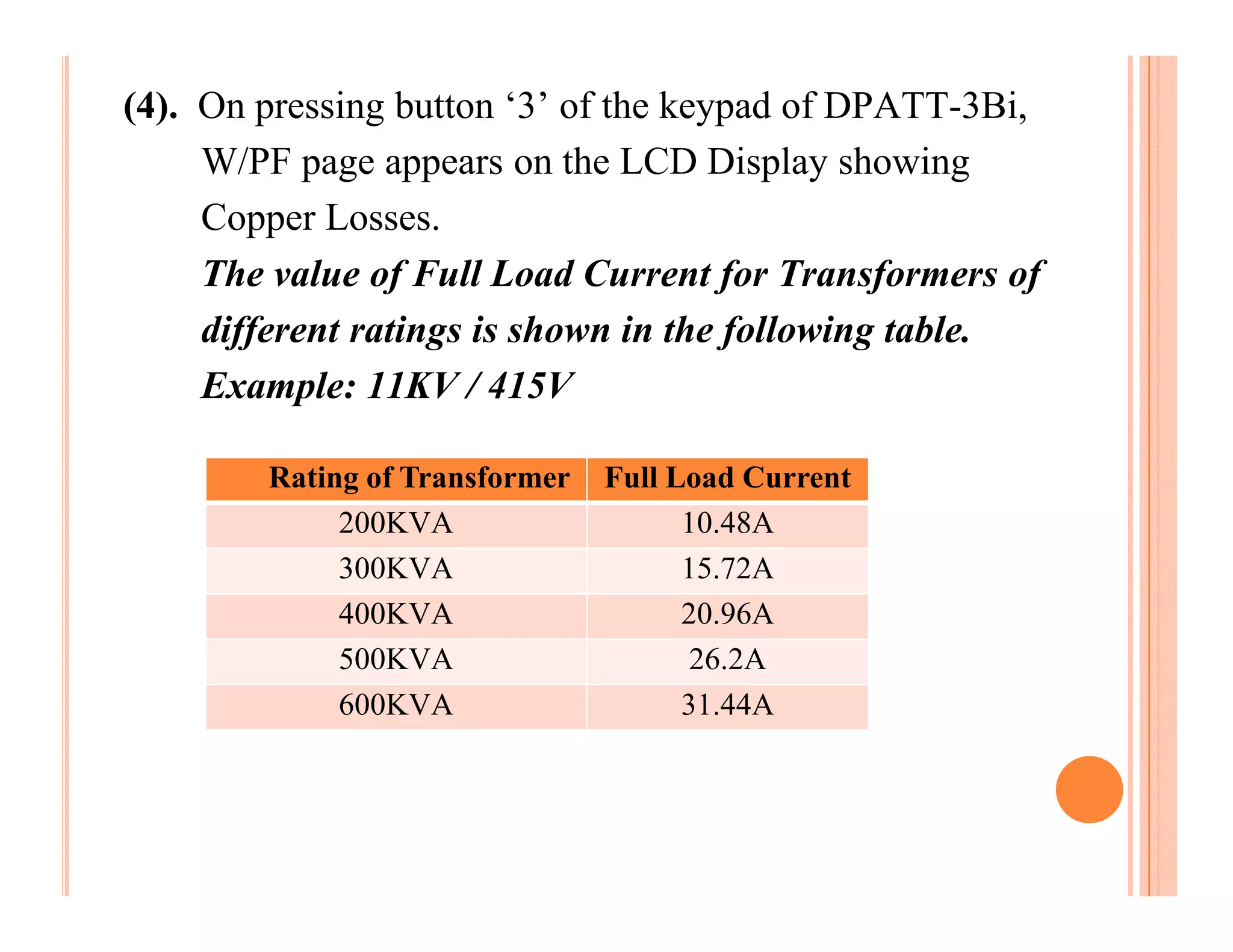
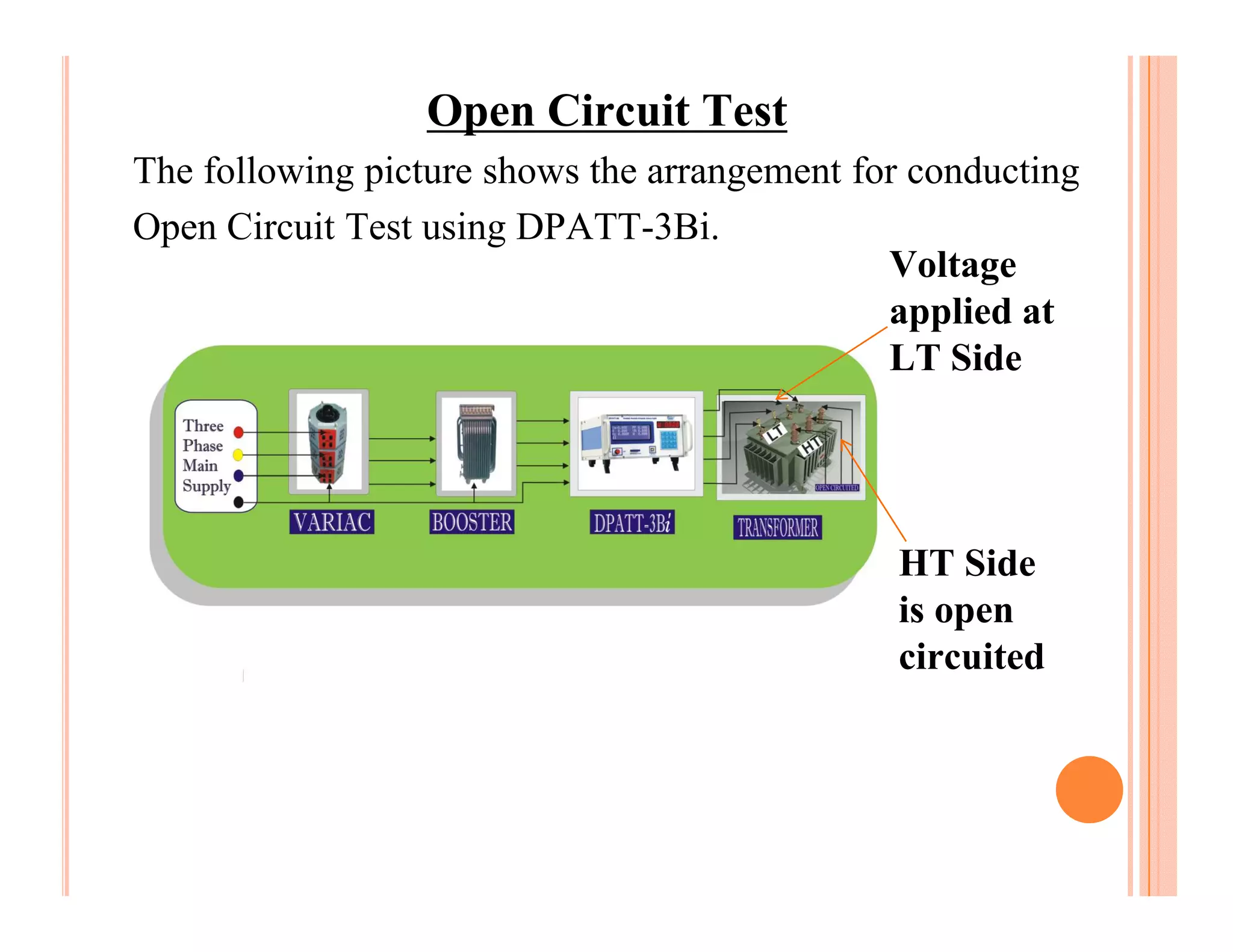
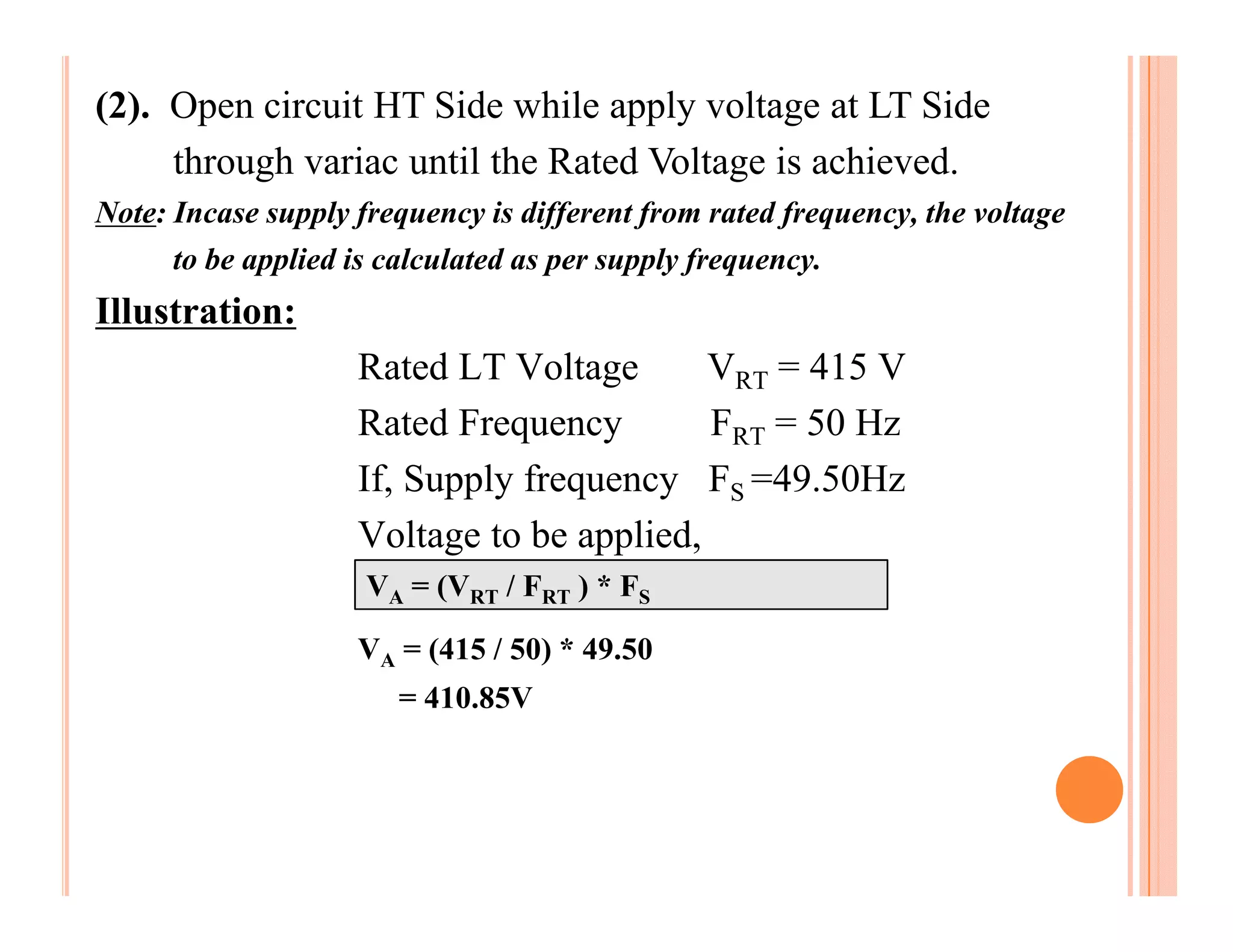
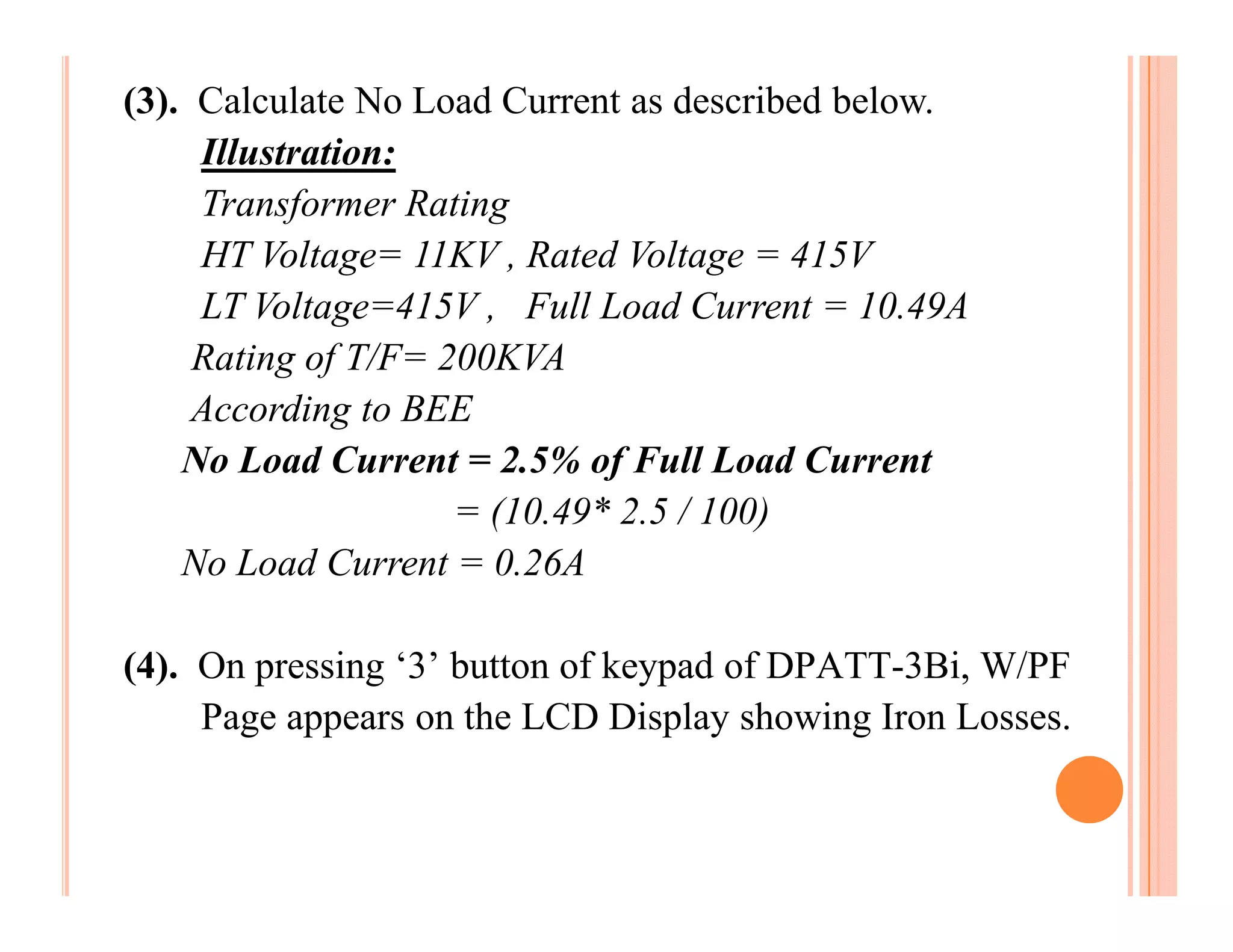
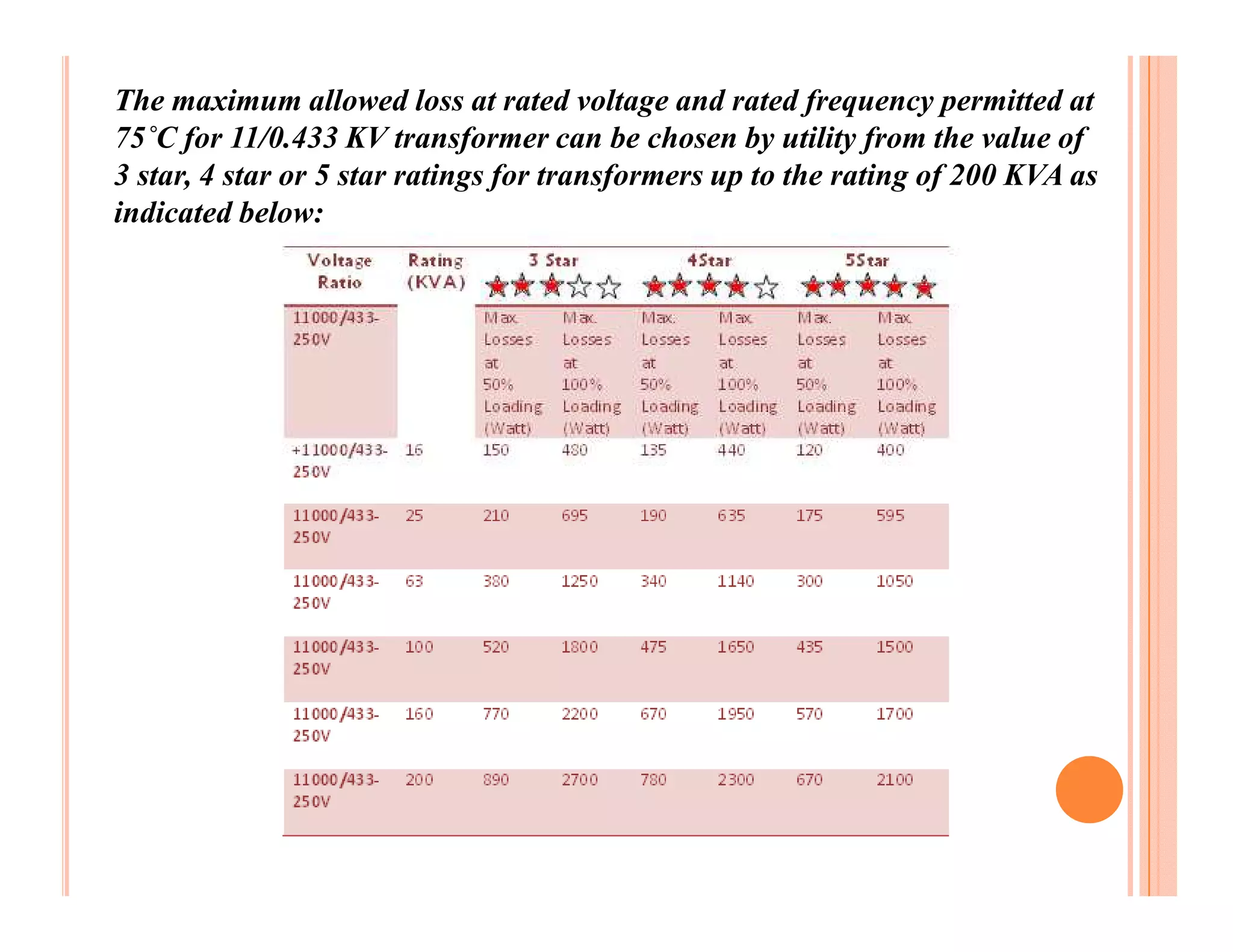
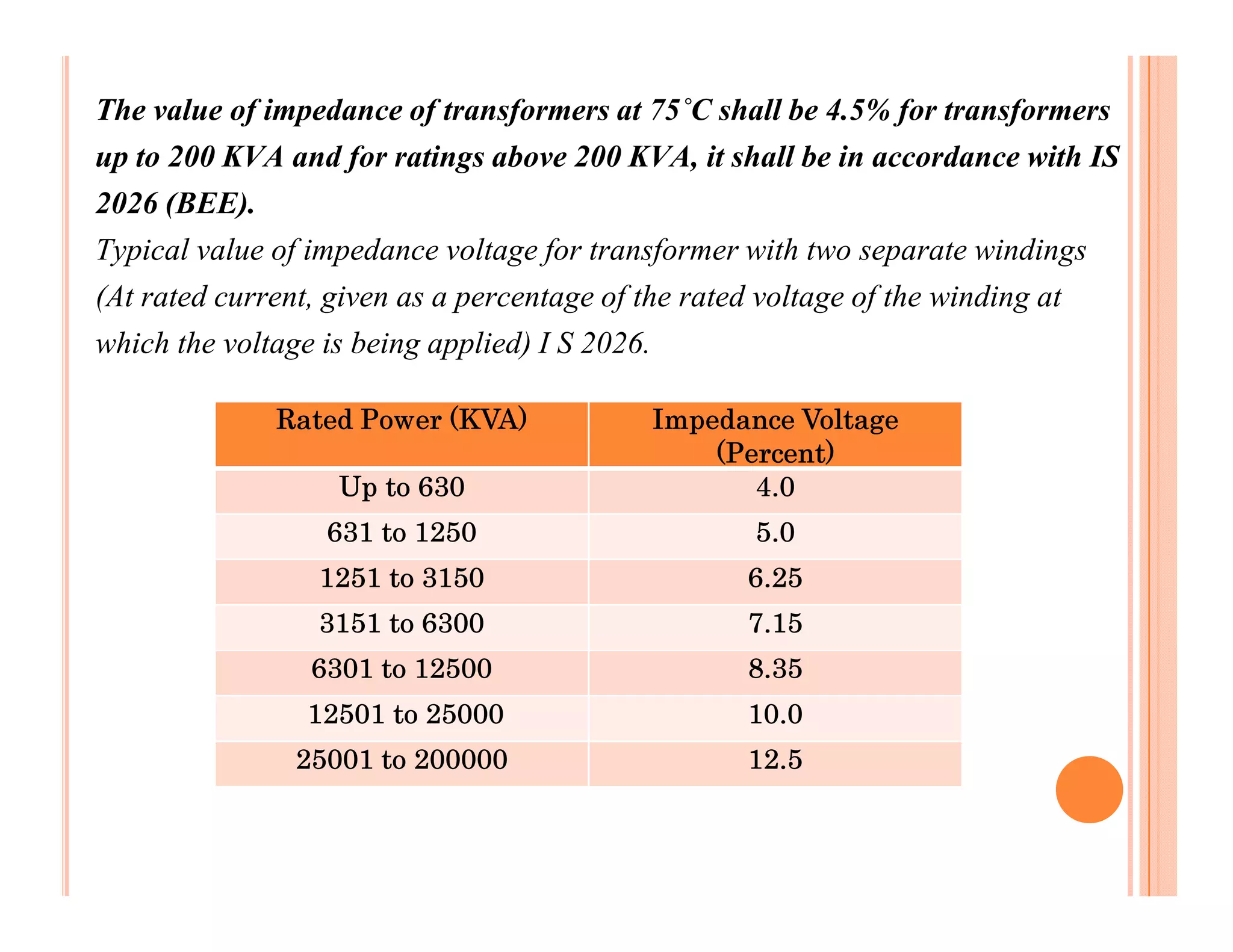
The document describes how to conduct short circuit and open circuit tests on transformers using a DPATT-3Bi device to measure copper and iron losses, respectively. It provides details on the test setups, calculations for full load current and no load current, and how to interpret the results displayed on the DPATT-3Bi screen. The document also lists standard limits for transformer impedance voltages and losses according to Indian standards.