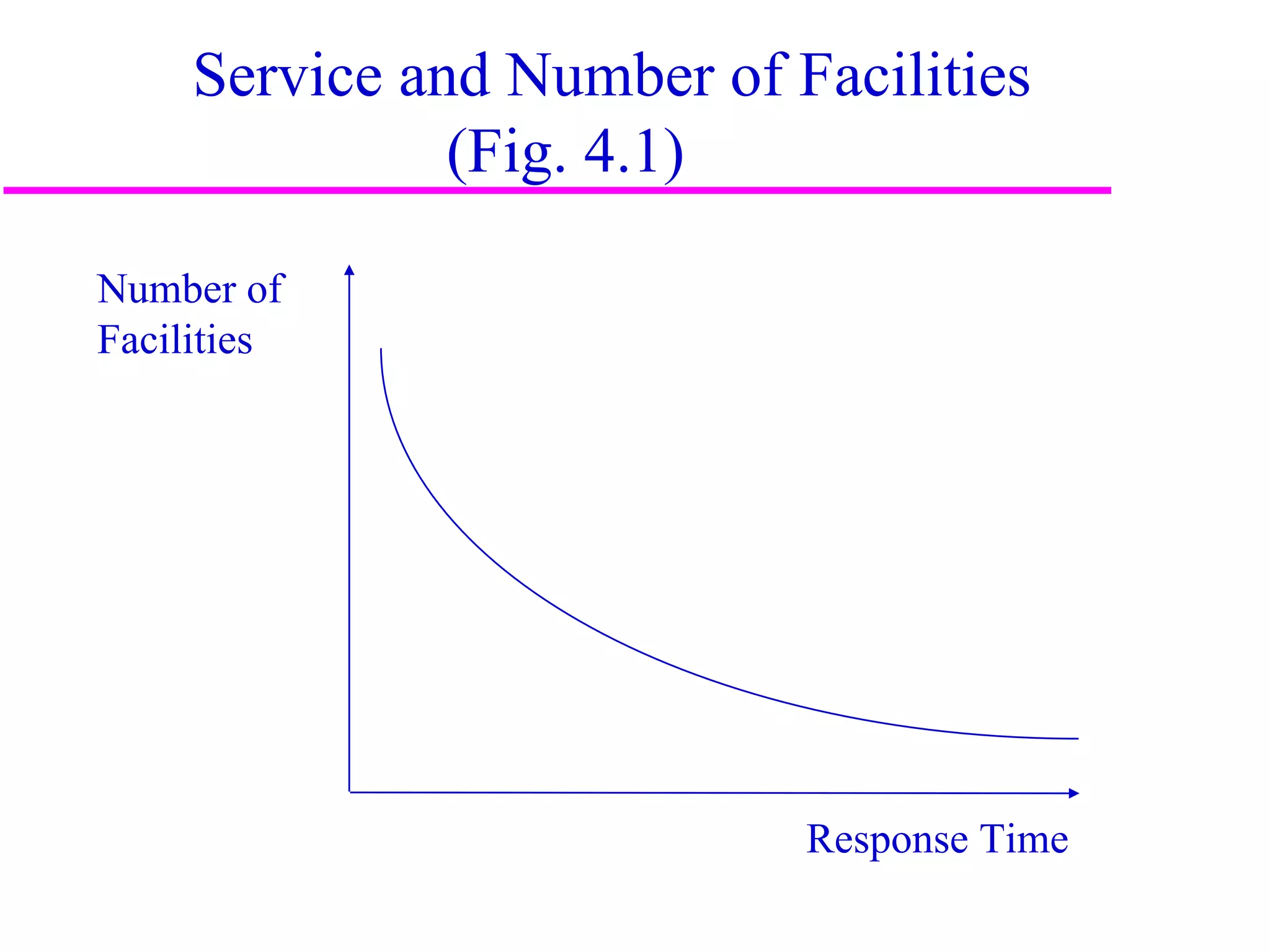
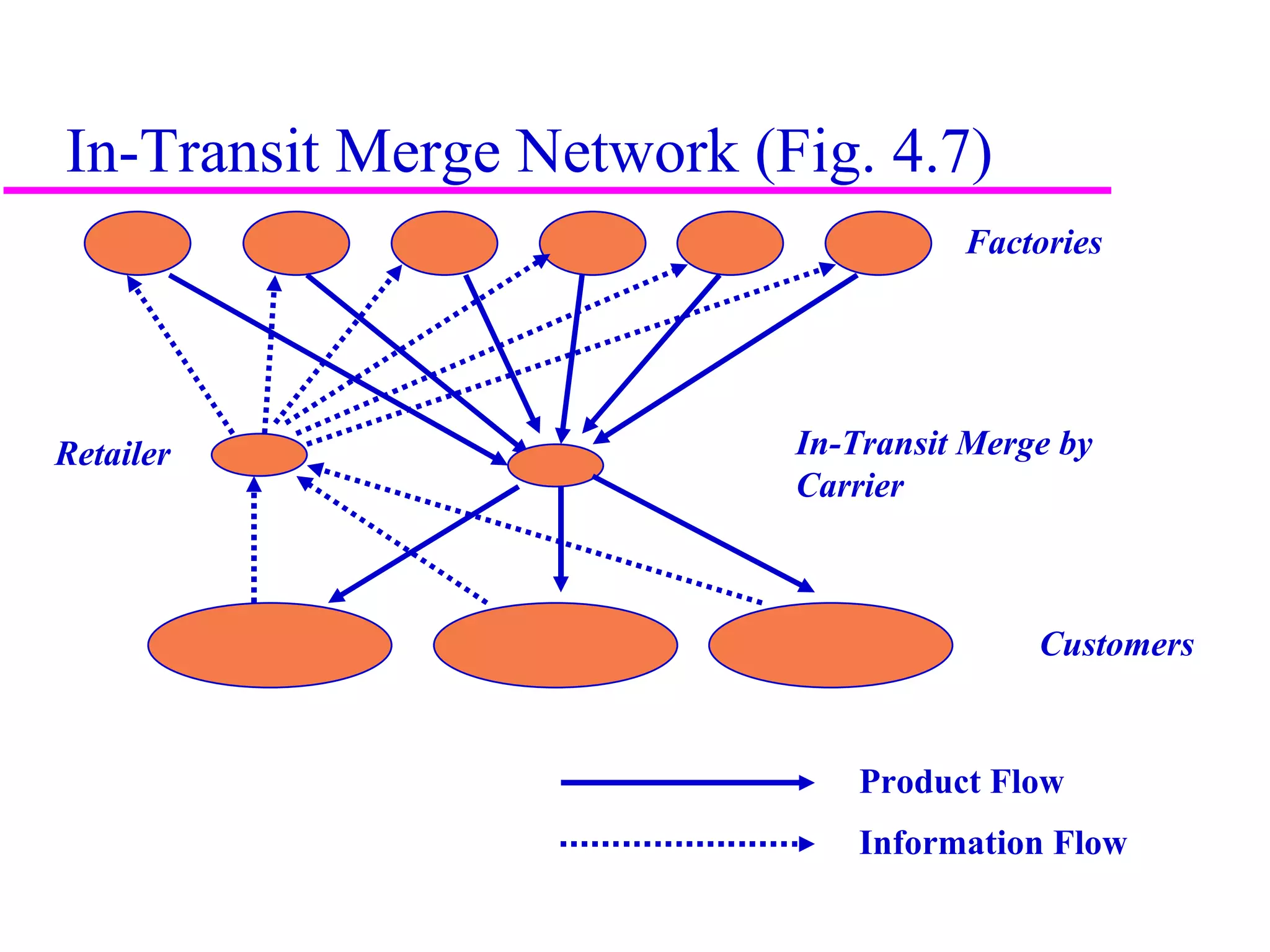
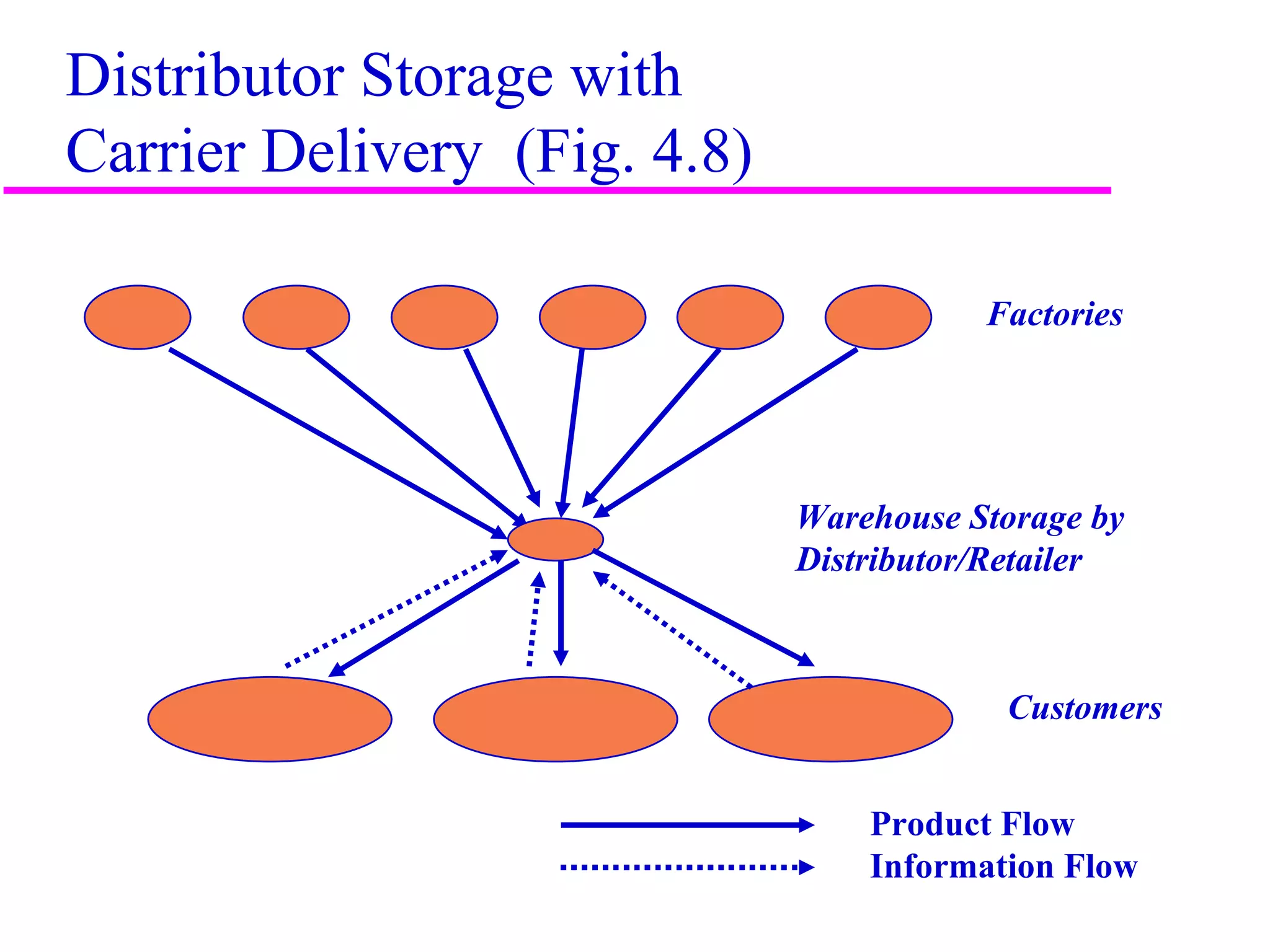
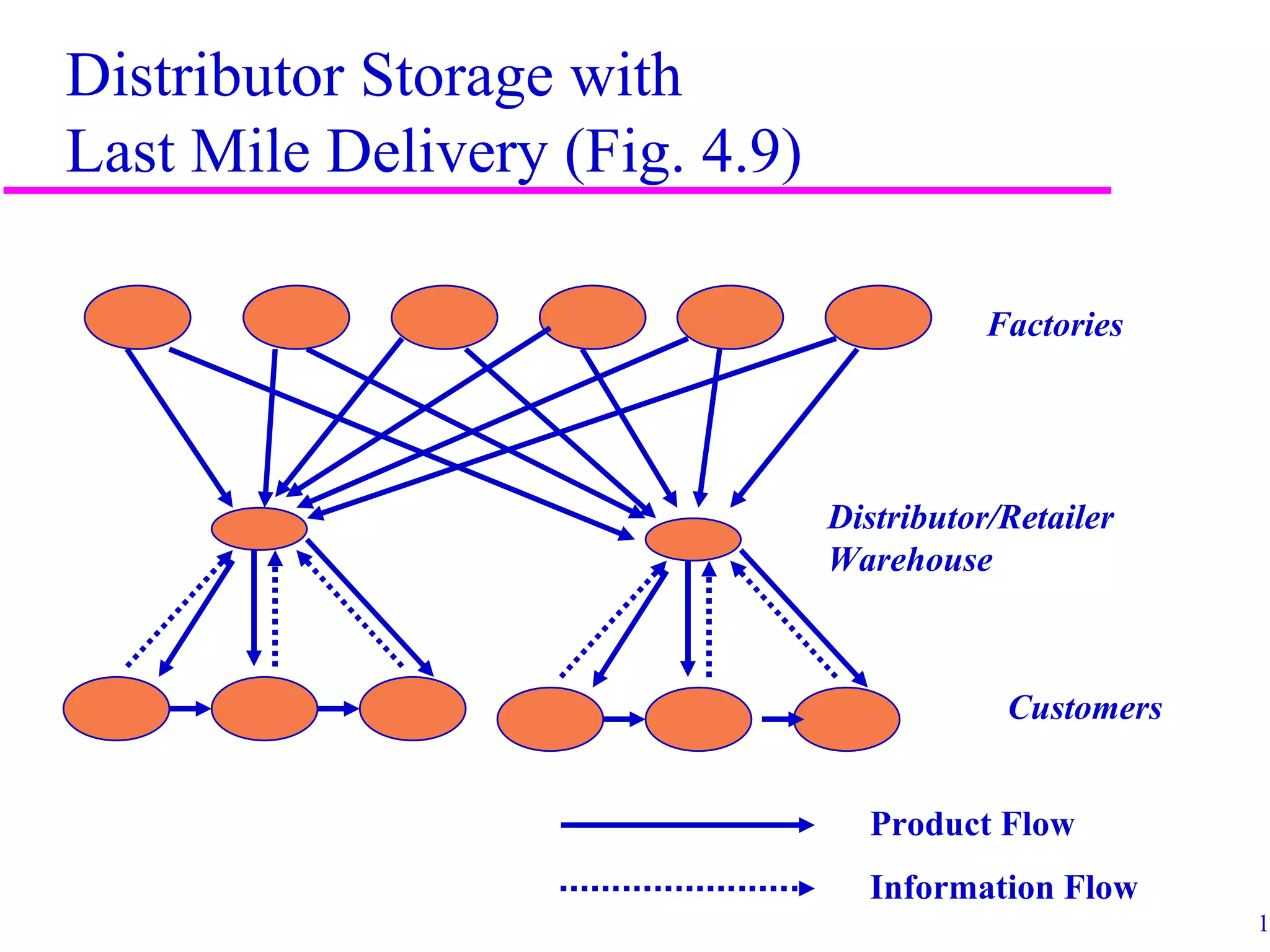
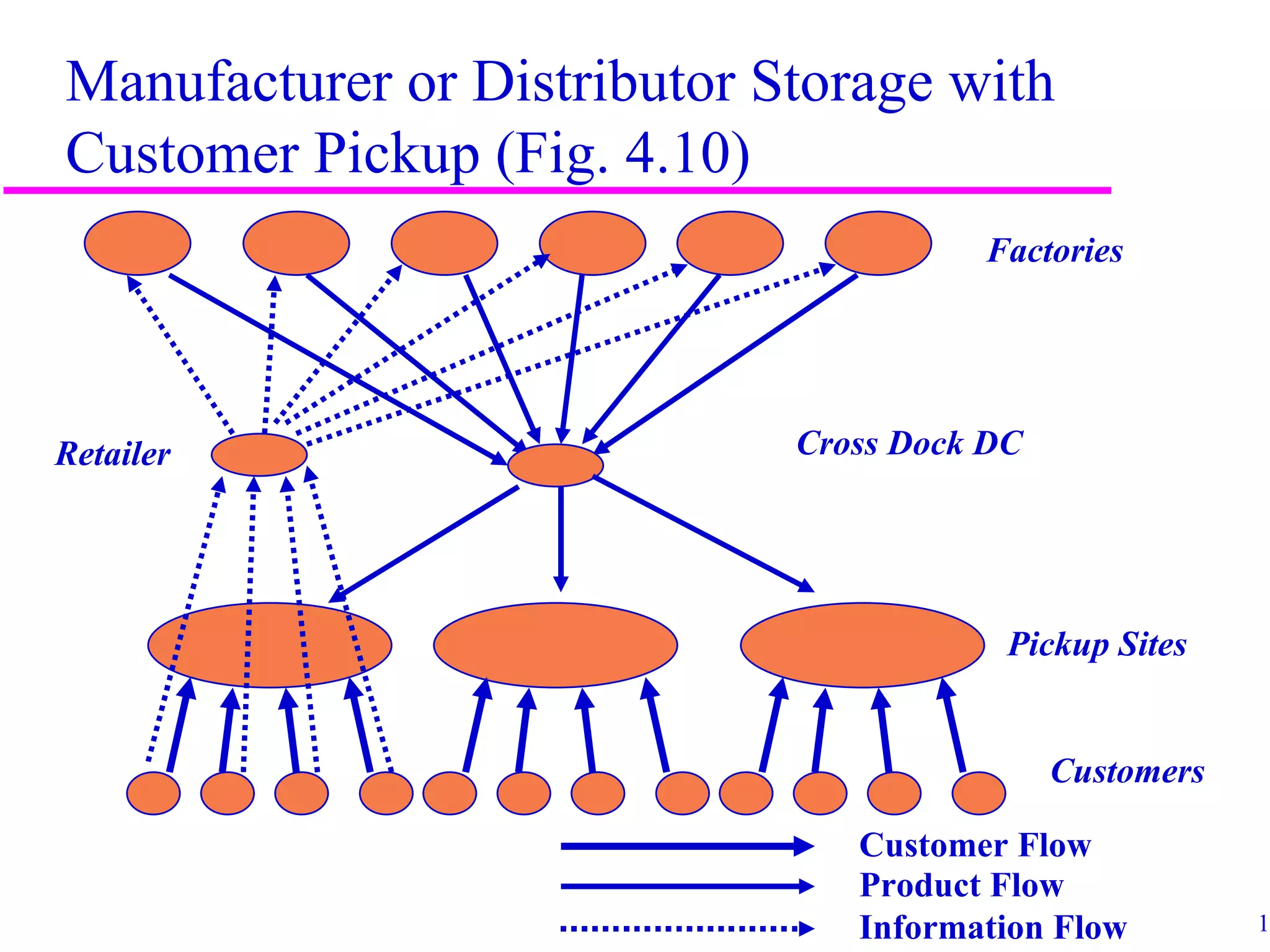
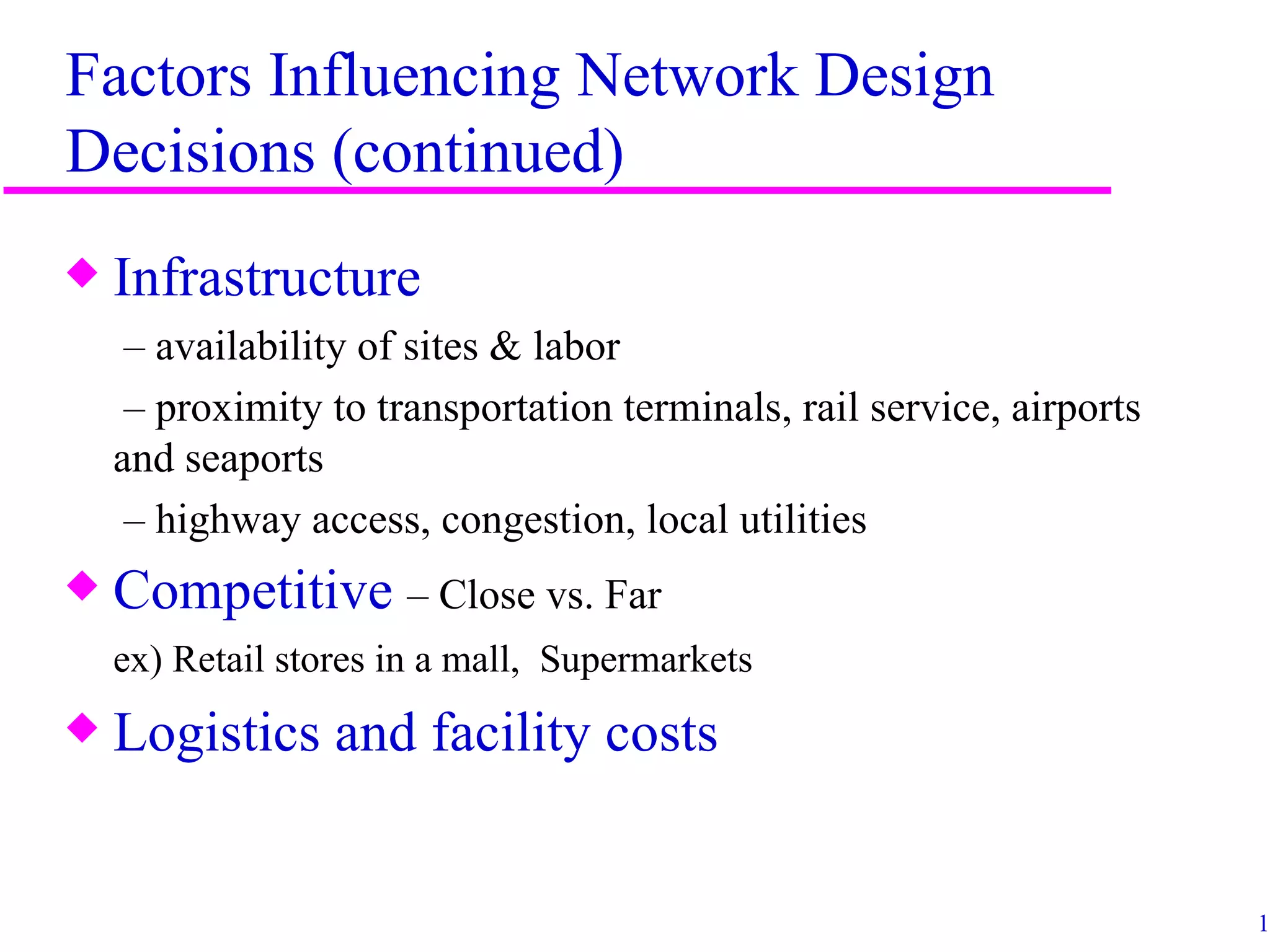
The document discusses factors that influence distribution network design for supply chains. It describes how distribution affects costs and customer experience. Distribution network design must balance customer needs like response time and product availability with supply chain costs like inventory and transportation. The document outlines different distribution network design options and provides examples of how companies implement various designs. It also discusses factors like strategic objectives, technology, infrastructure, competition and costs that influence decisions around facility roles, locations, capacity and market allocation.