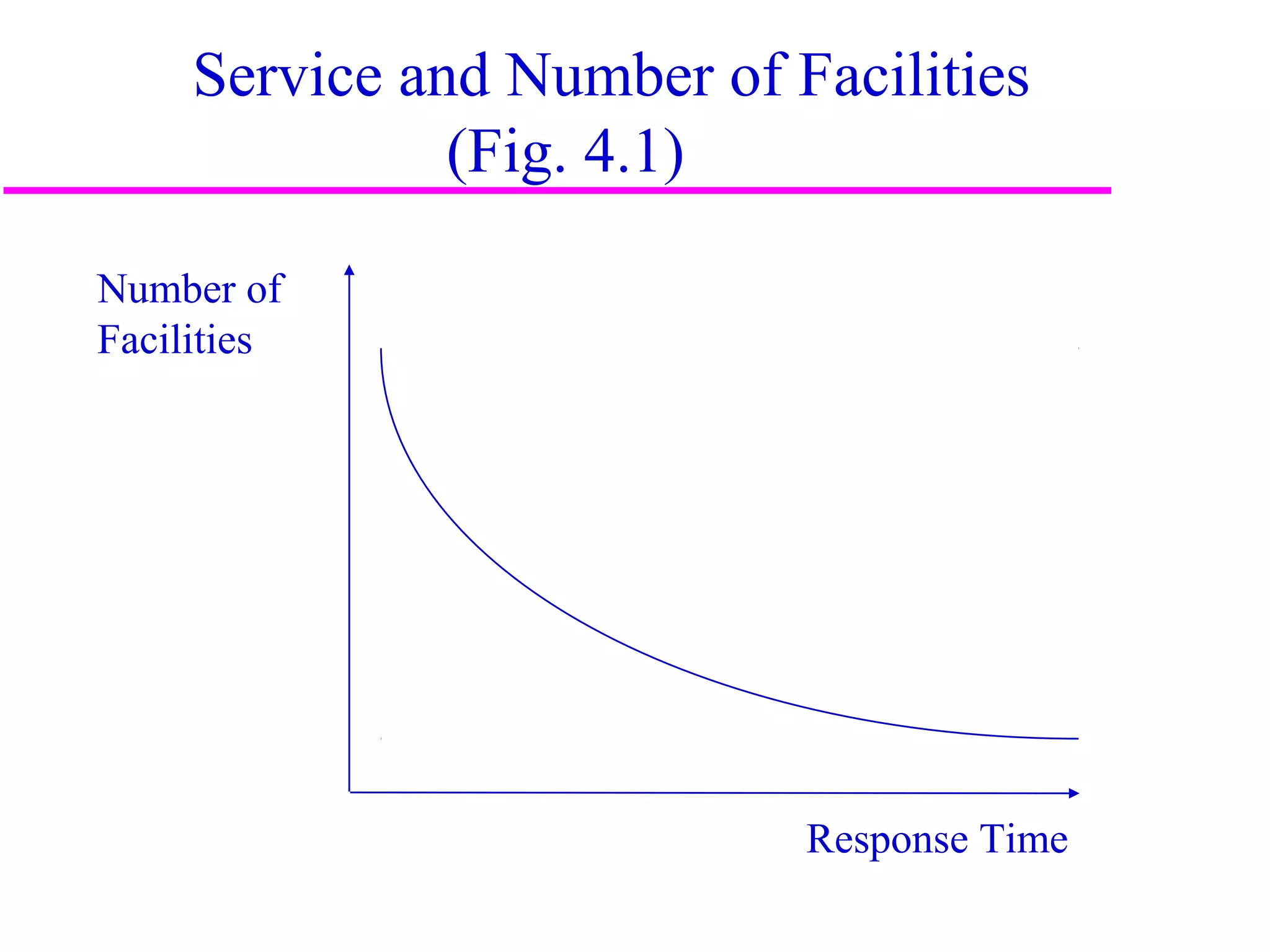
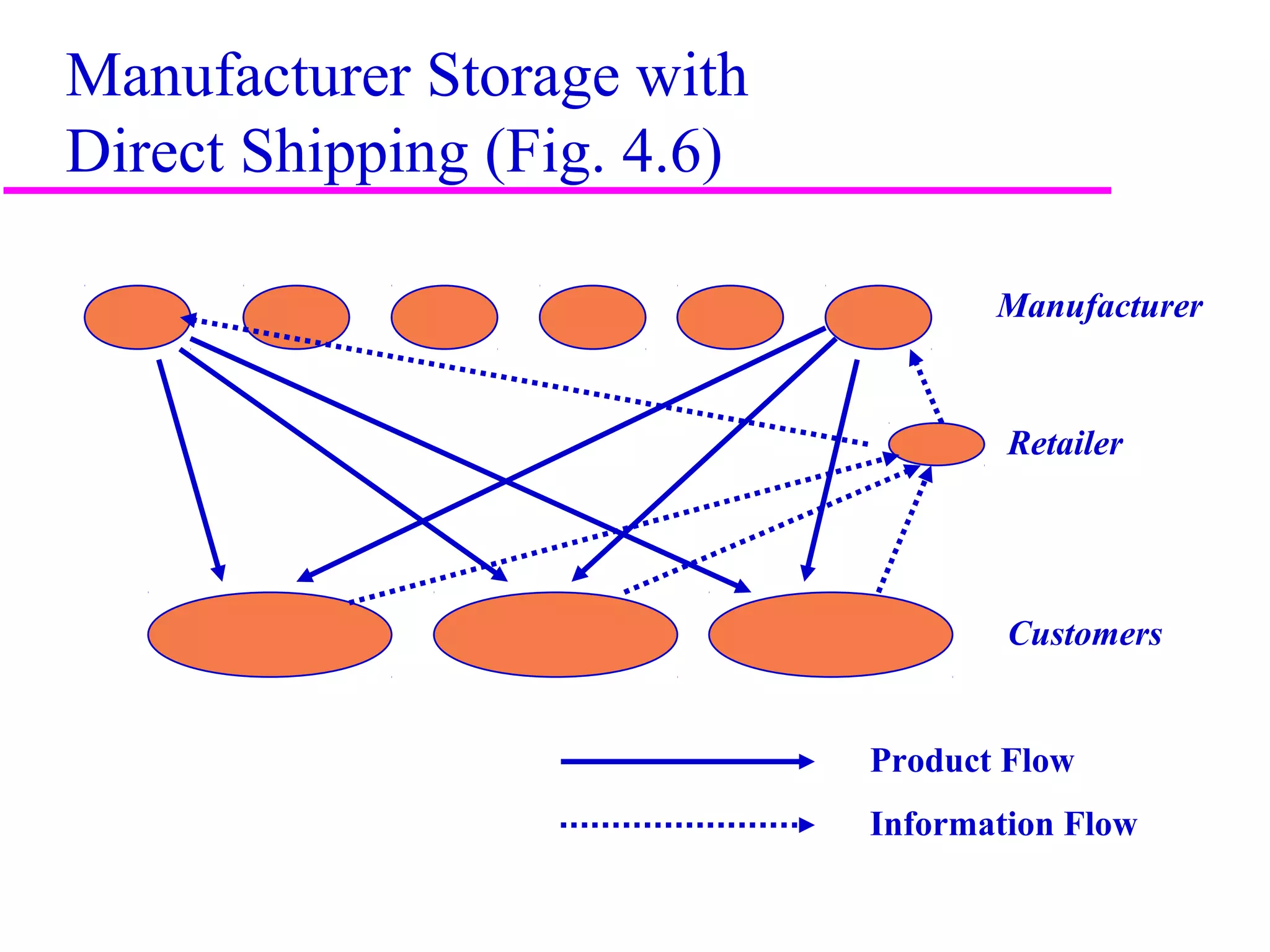
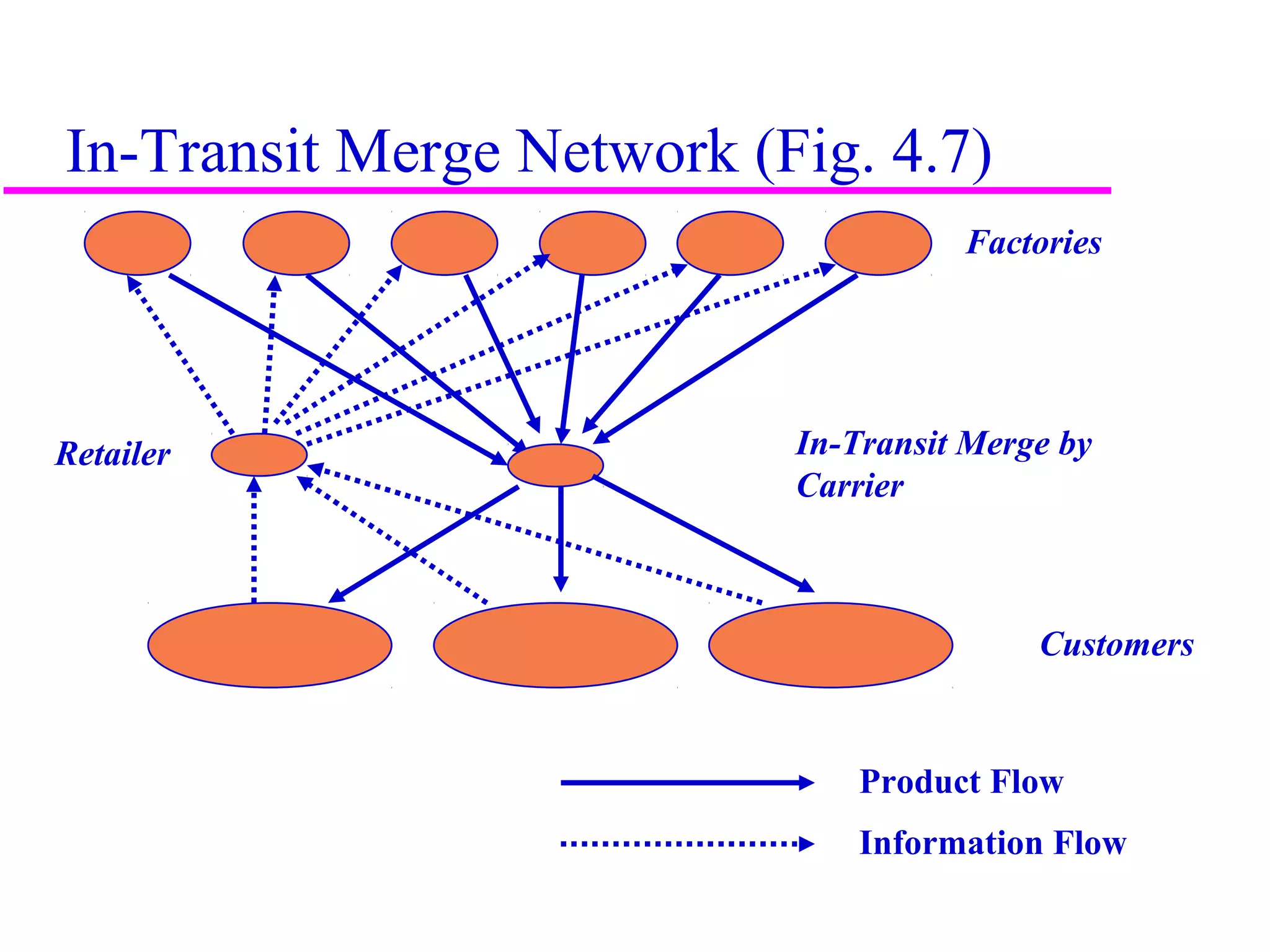
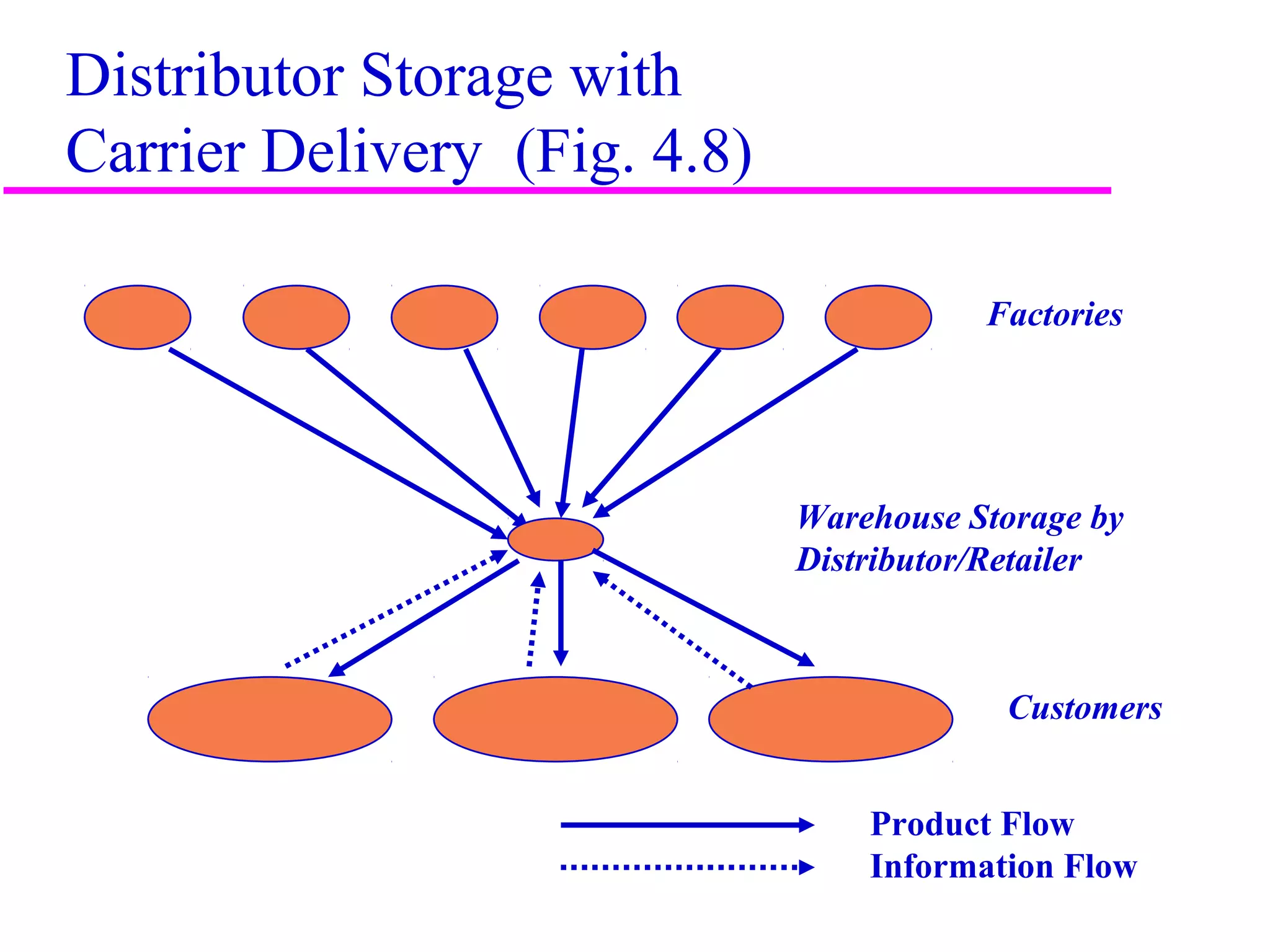
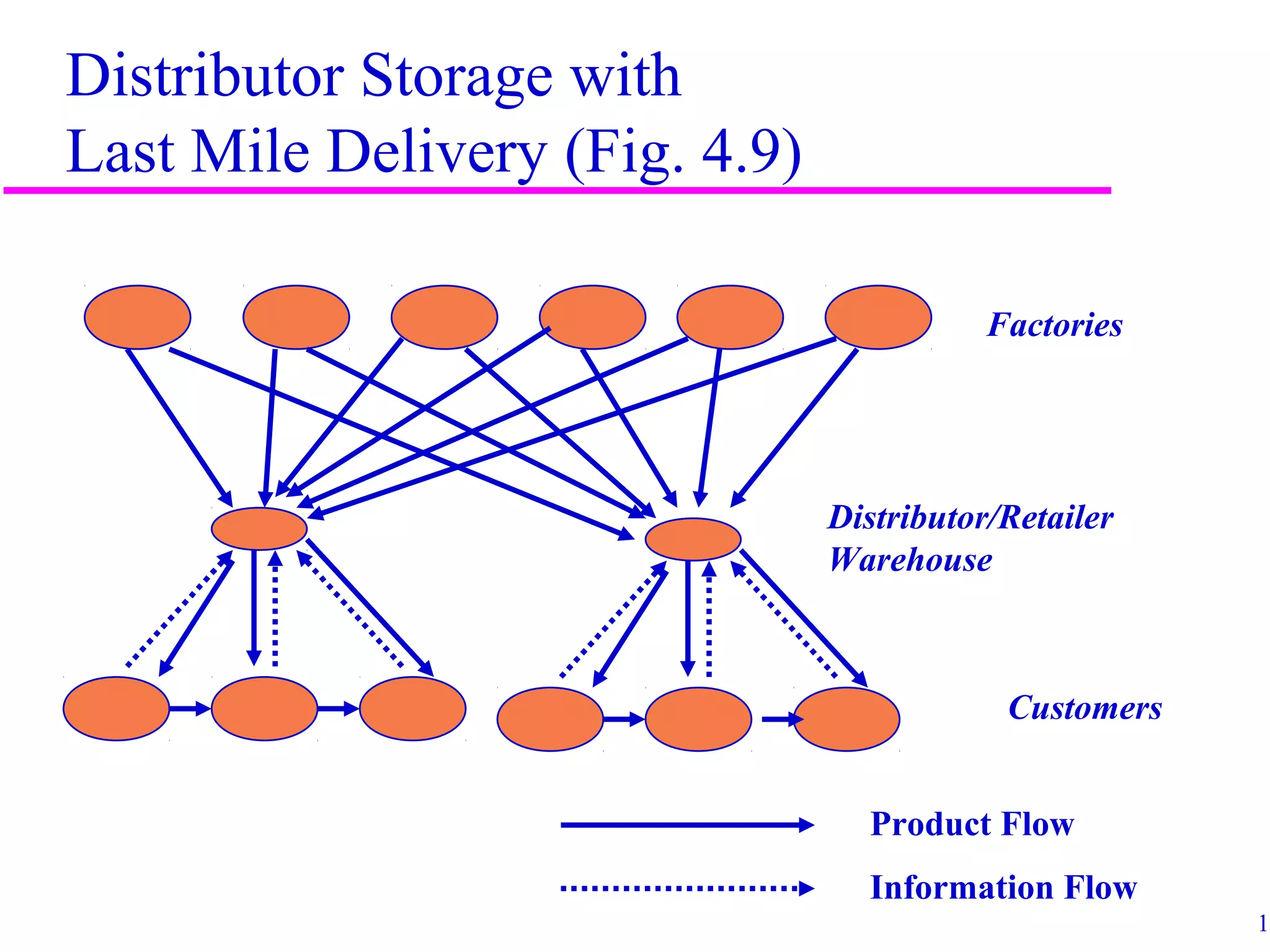
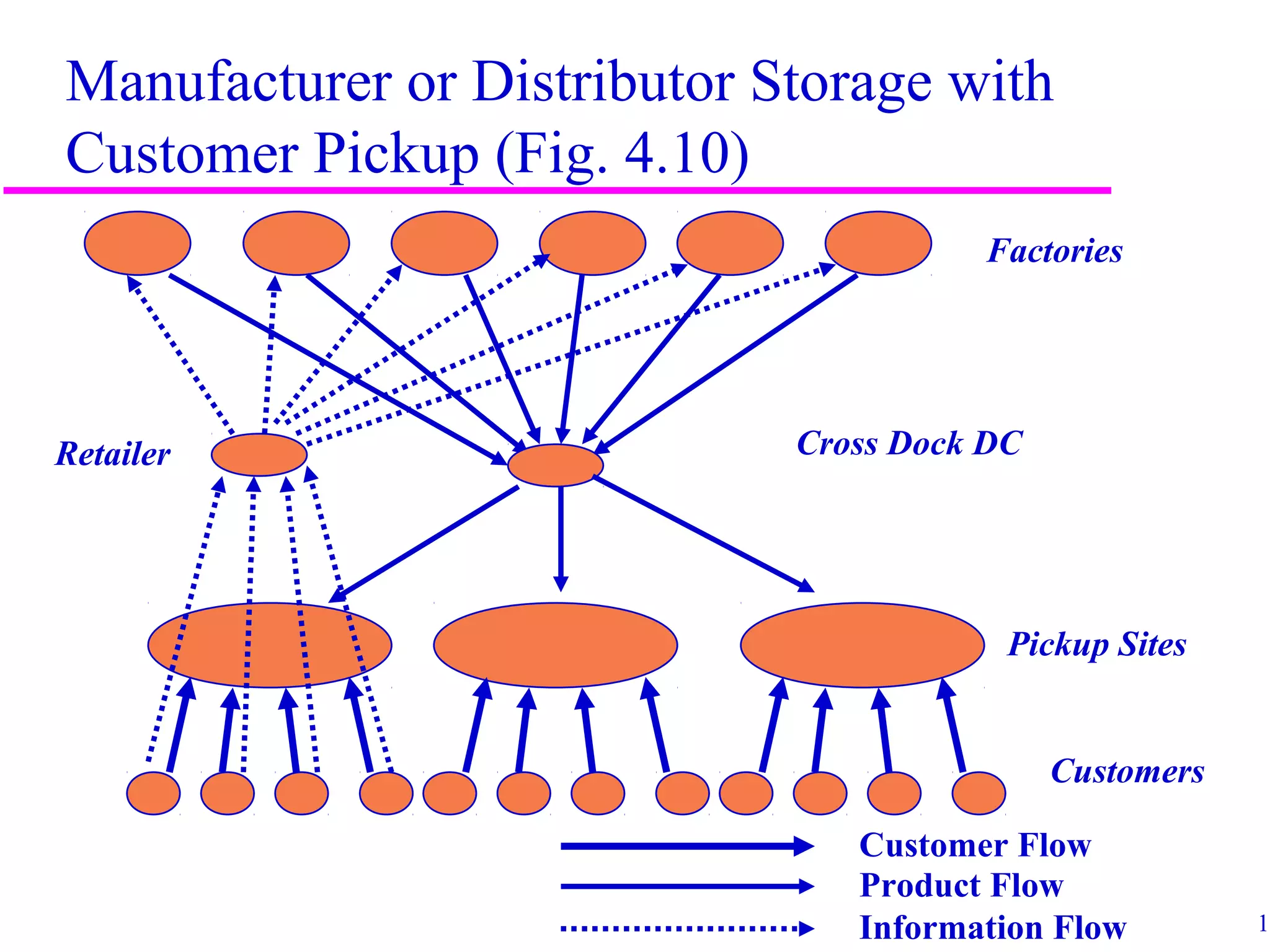
The document discusses factors that influence distribution network design for supply chains. It describes how distribution moves products from suppliers to customers and affects costs and customer experience. Distribution network performance is evaluated based on customer needs met and costs. The design must balance customer service metrics like response time, availability and order visibility with supply chain costs like inventory, transportation and facilities. Key distribution network options include direct shipping from manufacturers, distributor warehouses, and customer pickup locations. The choice of network has long-term consequences and is influenced by strategic, technological, economic and infrastructure considerations.