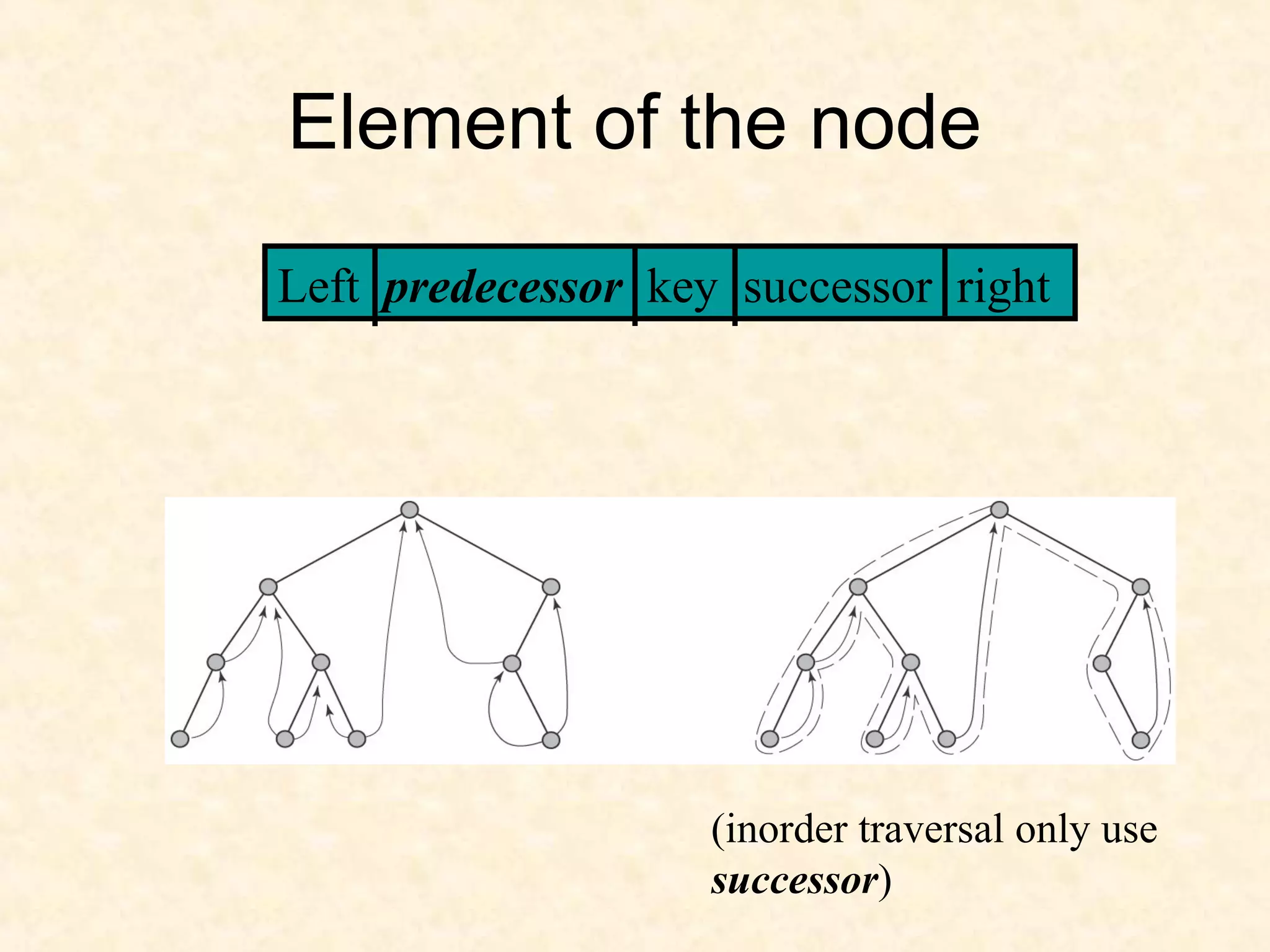
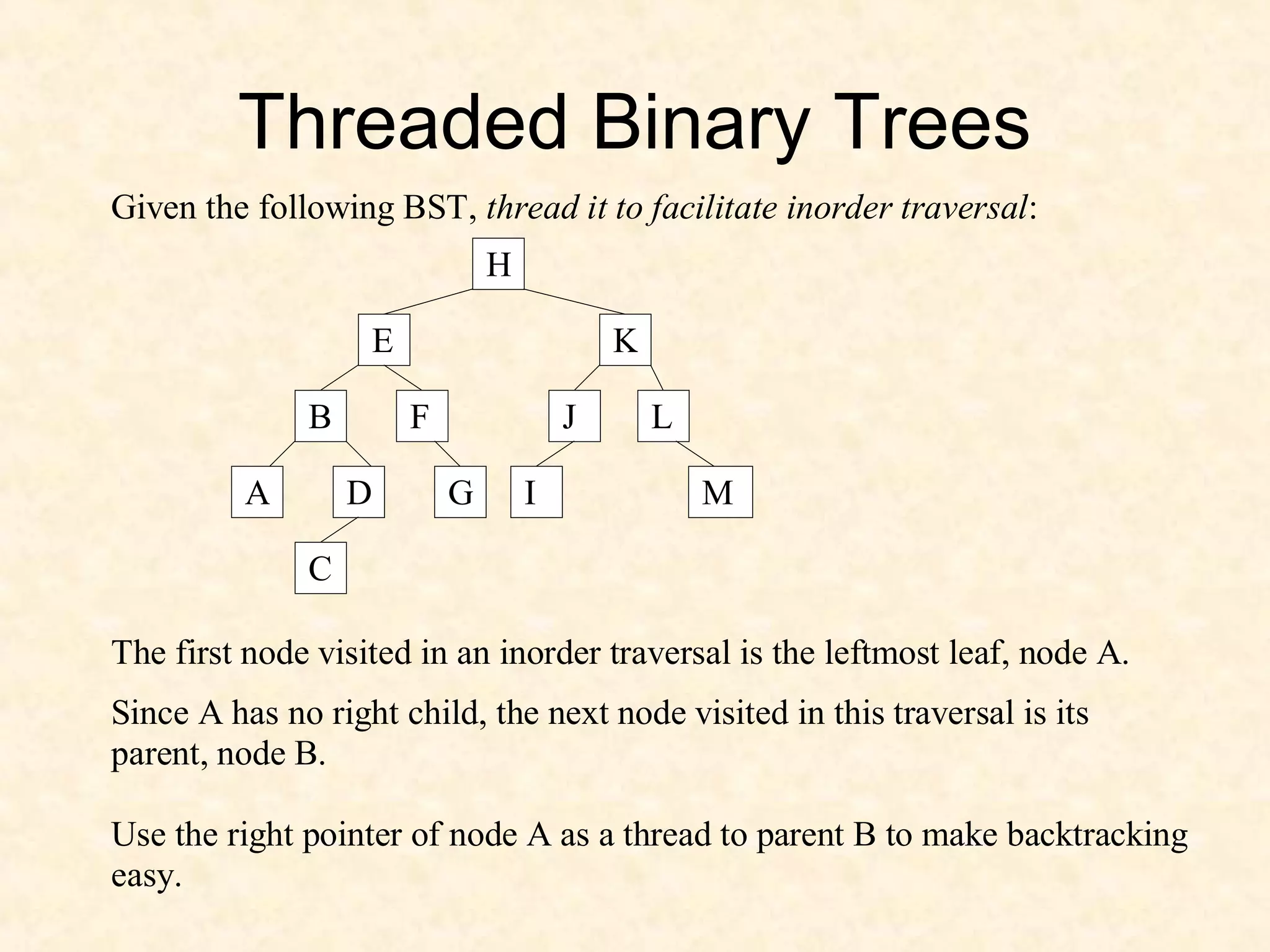
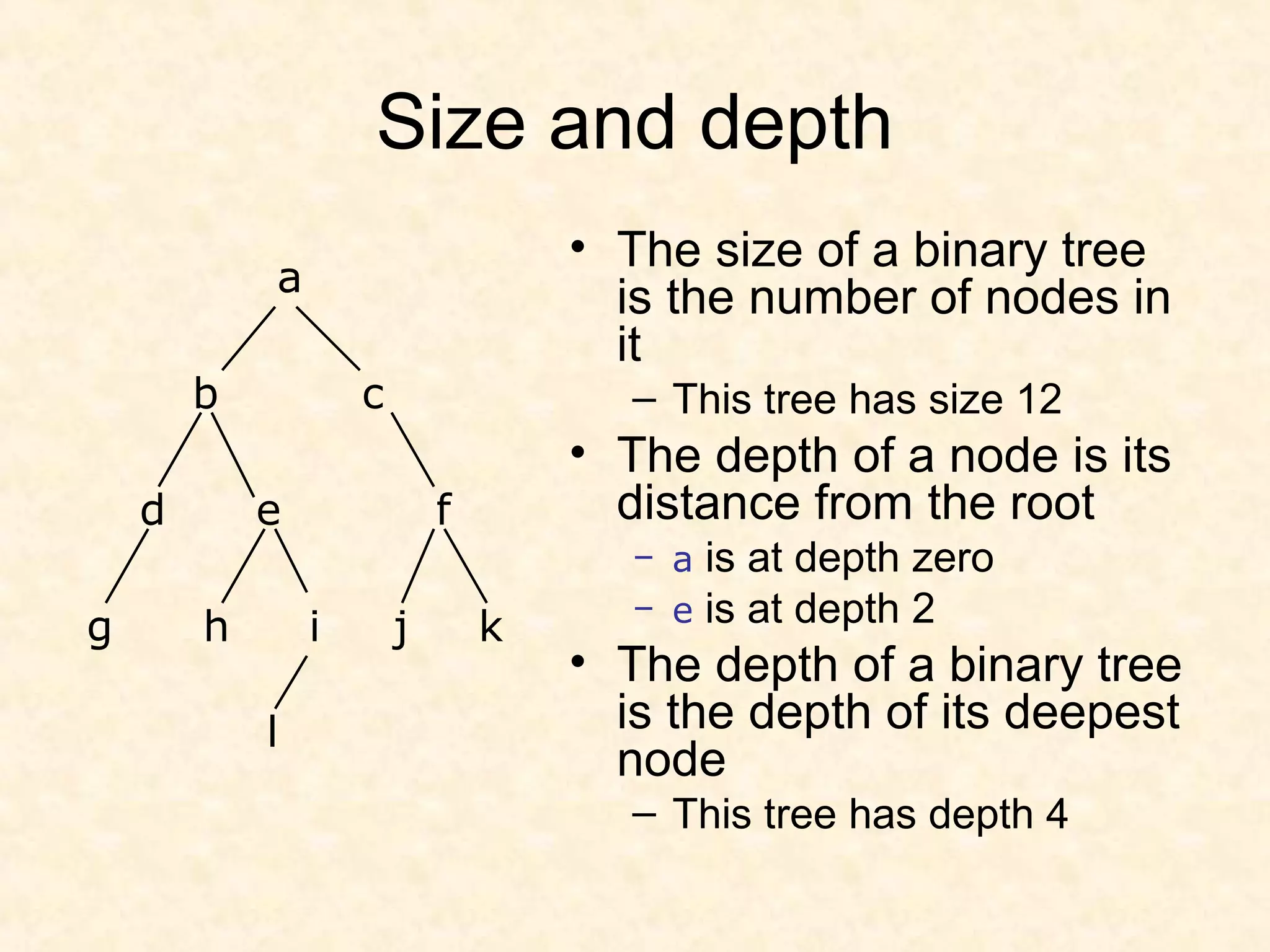
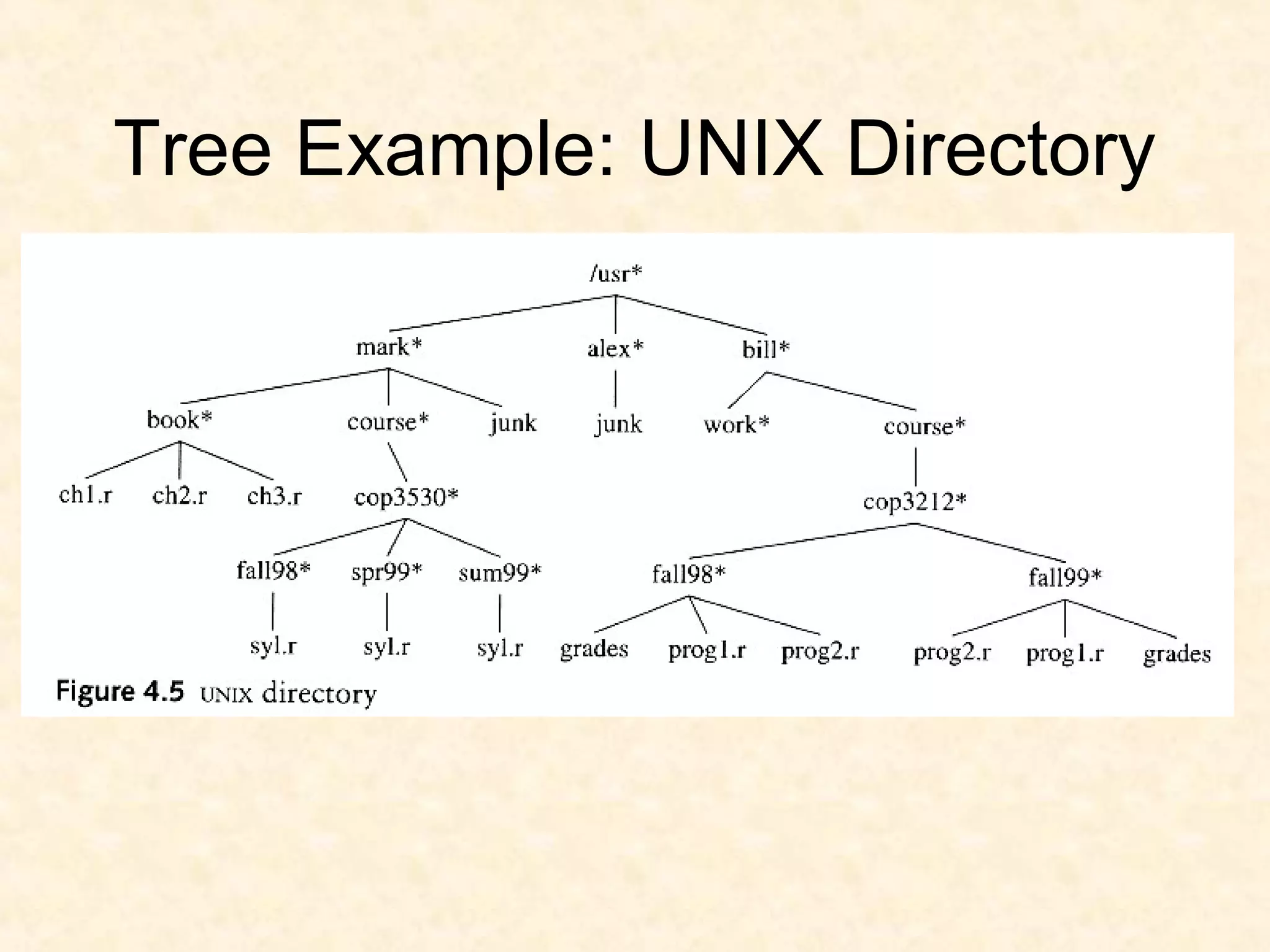
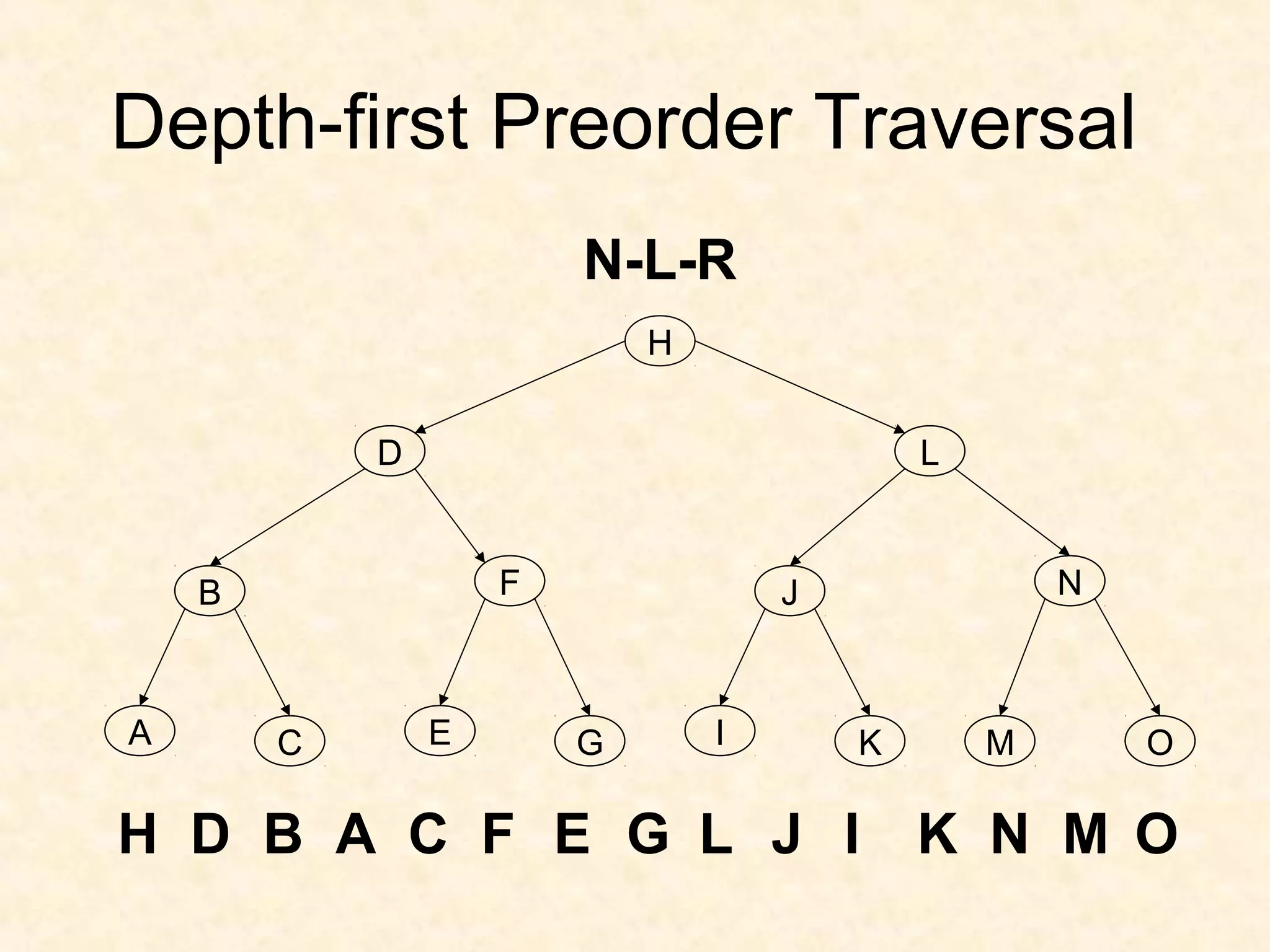
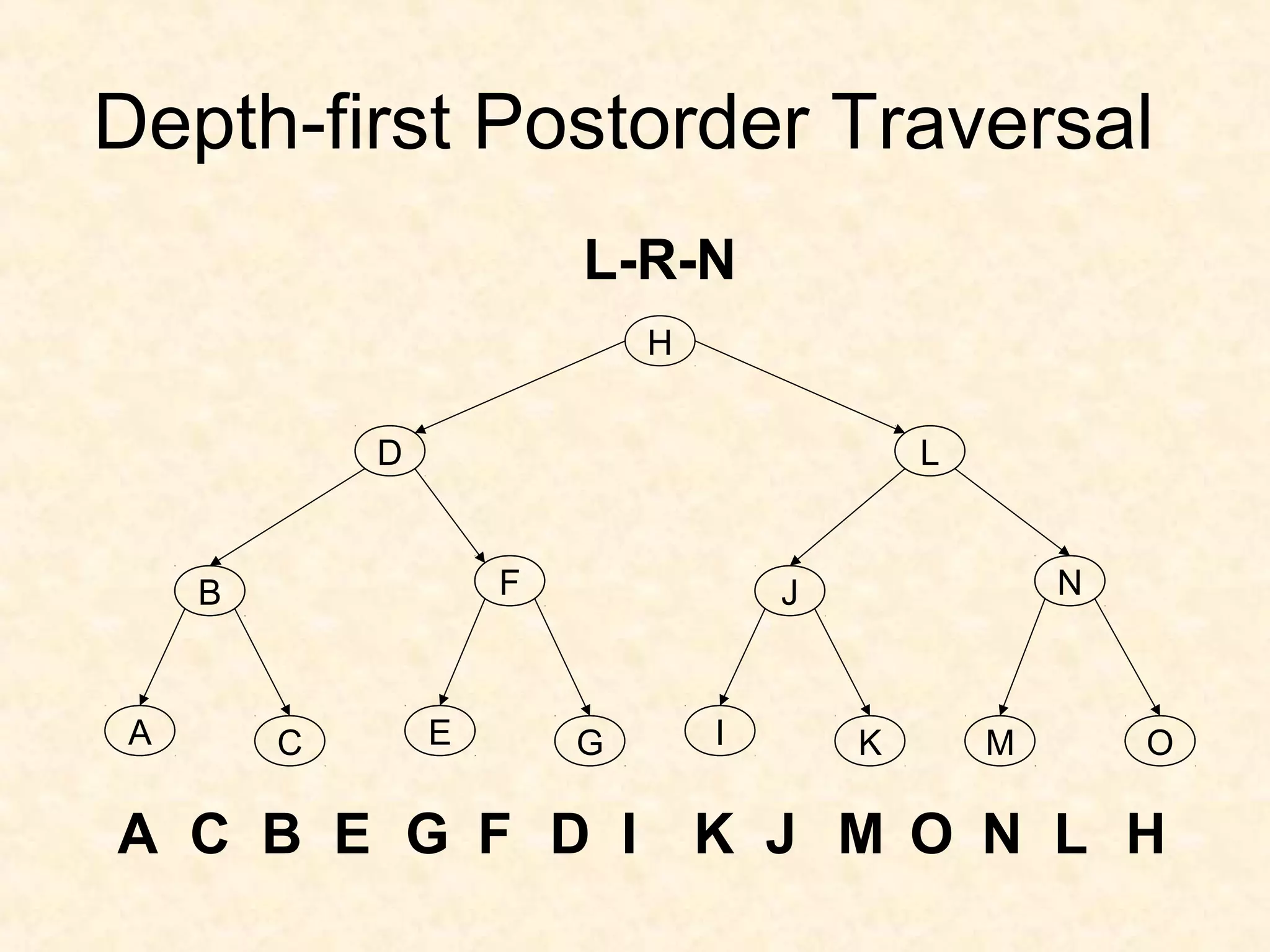
A binary tree is composed of nodes where each node contains a value and pointers to its left and right children. A binary tree traversal involves systematically visiting each node by traversing either breadth-first or depth-first. Breadth-first traversal visits nodes by level while depth-first traversal can be pre-order, in-order, or post-order depending on when the node is visited. Threaded binary trees reduce the number of null pointers by using them to point to other nodes for more efficient traversals.

















![INORDER-TREE-WALK(x)
if x != NIL
INORDER-TREE-WALK(left[x])
print key[x]
INORDER-TREE-WALK(right[x])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-24-2048.jpg)

![TREE-SEARCH (x, k)
if (x== NIL) || (k == key[x])
return x
if (k < key[x])
return TREE-SEARCH(left[x], k)
else
return TREE-SEARCH(right[x], k)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-26-2048.jpg)
![ITERATIVE-TREE-SEARCH(x, k)
while (x != NIL) && (k != key[x])
if k < key[x]
x = left[x]
else x = right[x]
return x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-27-2048.jpg)
![TREE-MINIMUM (x)
while left[x] != NIL
x = left[x]
return x
TREE-MAXIMUM(x)
while right[x] != NIL
x = right[x]
return x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-28-2048.jpg)
![TREE-SUCCESSOR(x)
if (right[x] != NIL)
return TREE-MINIMUM (right[x])
y = p[x]
while (y != NIL) && (x == right[y])
x = y
y = p[y]
return y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-29-2048.jpg)
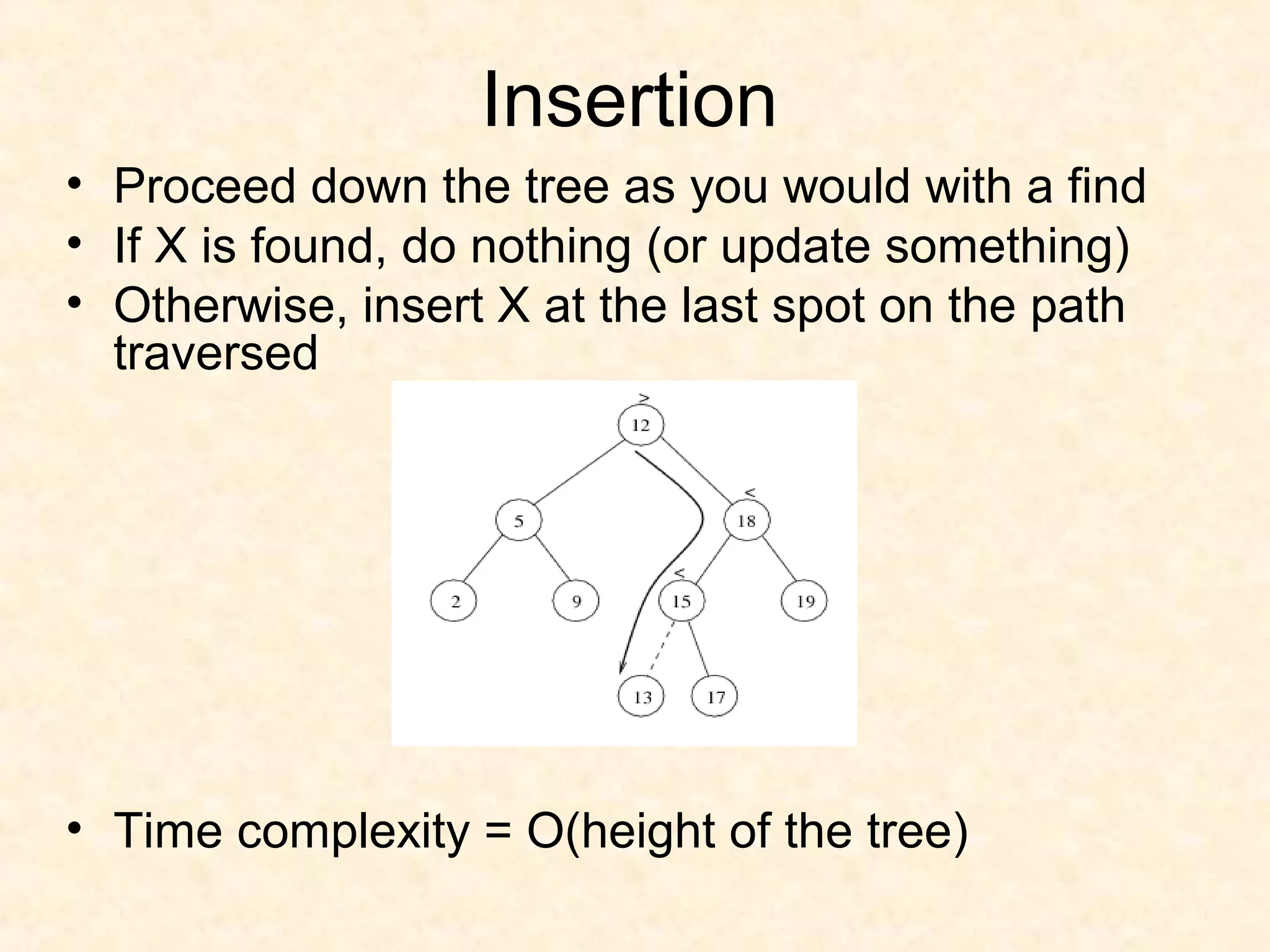
![TREE-INSERT(T, z)
y = NIL
x = root[T]
while (x != NIL)
y = x
if (key[z] < key[x])
x = left[x]
else x = right[x]
p[z] = y
if (y == NIL)
root[T] = z // Tree T was empty
else if (key[z] < key[y])
left[y] = z
else right[y] = z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-31-2048.jpg)

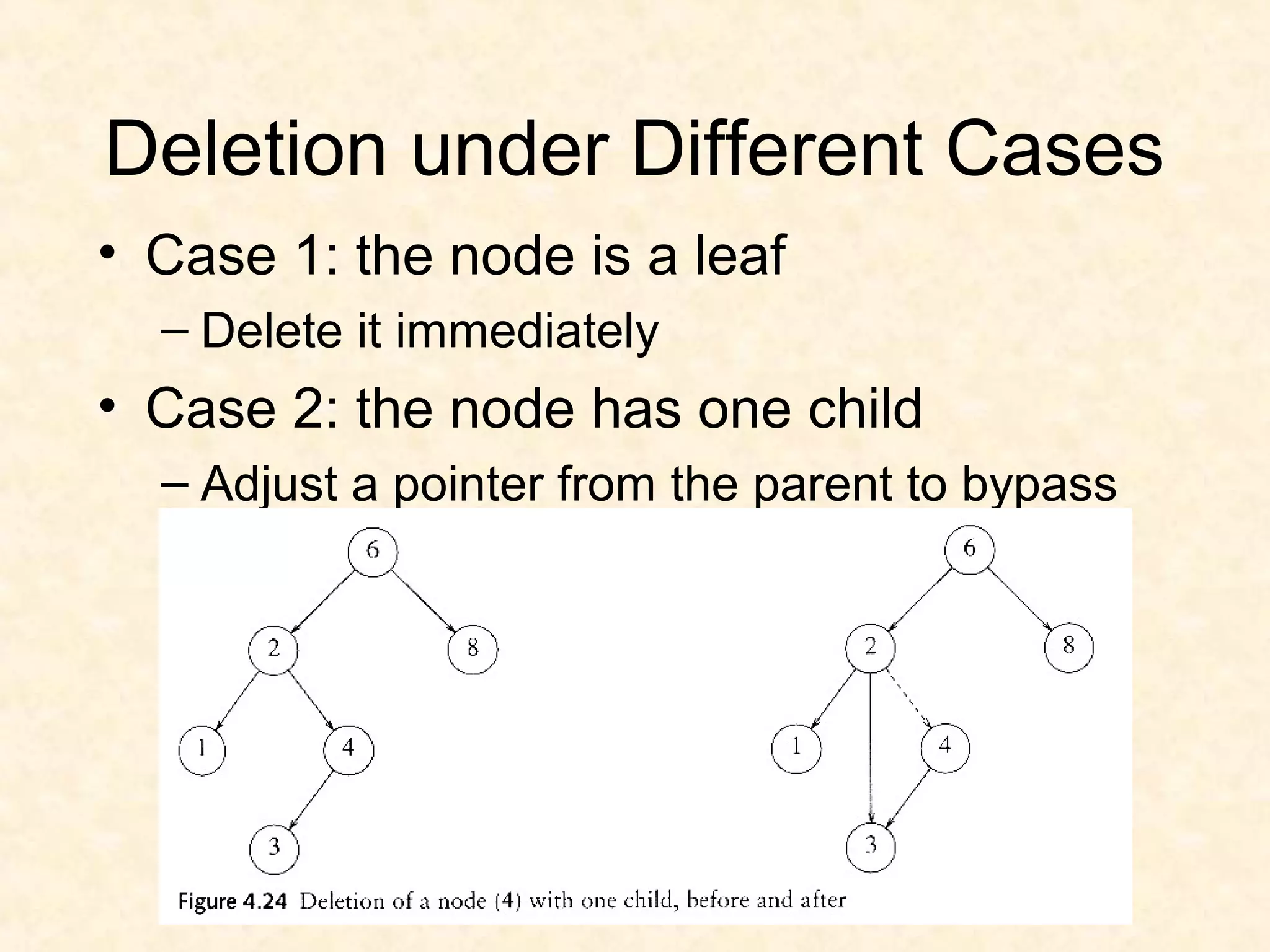
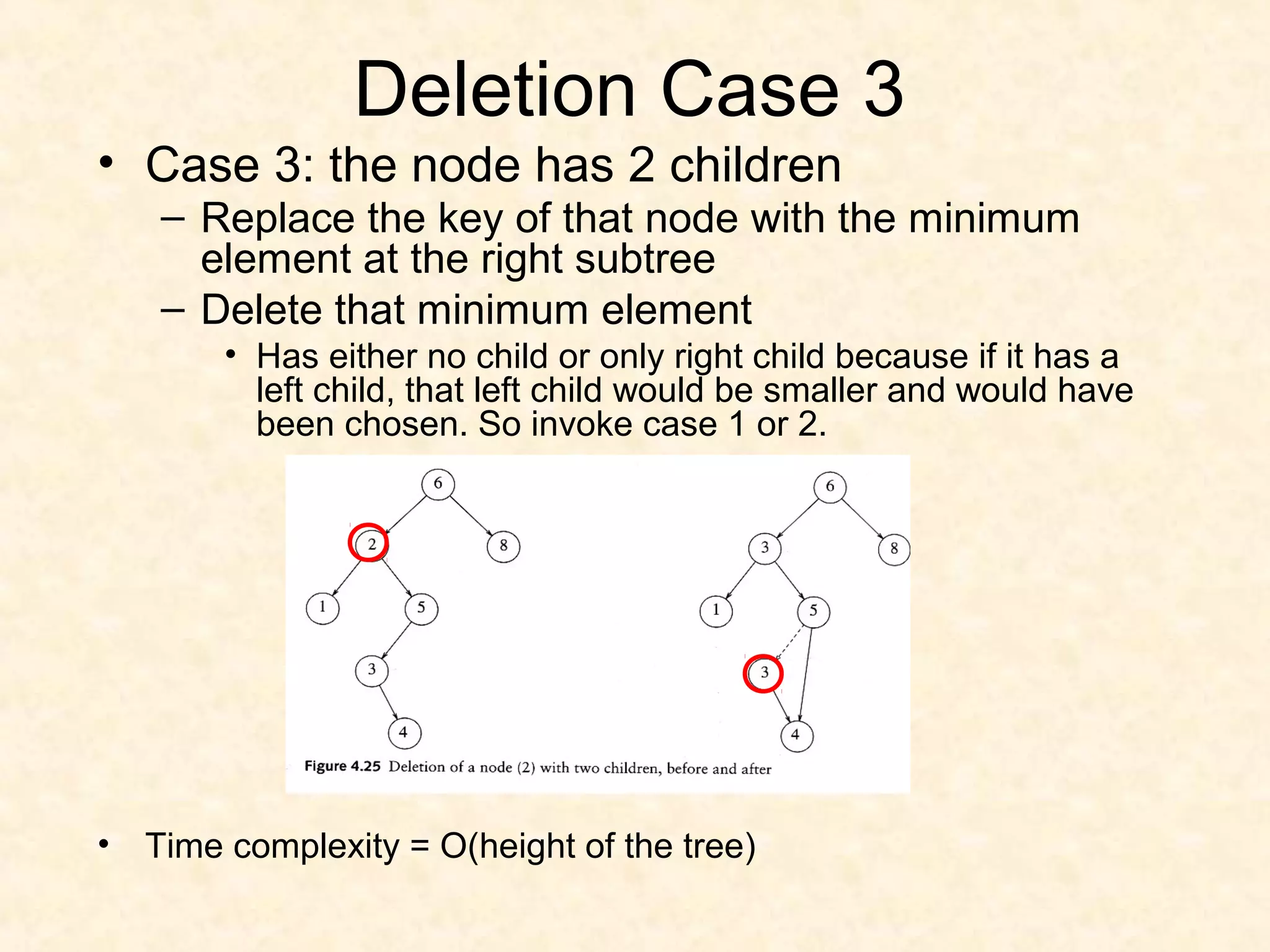
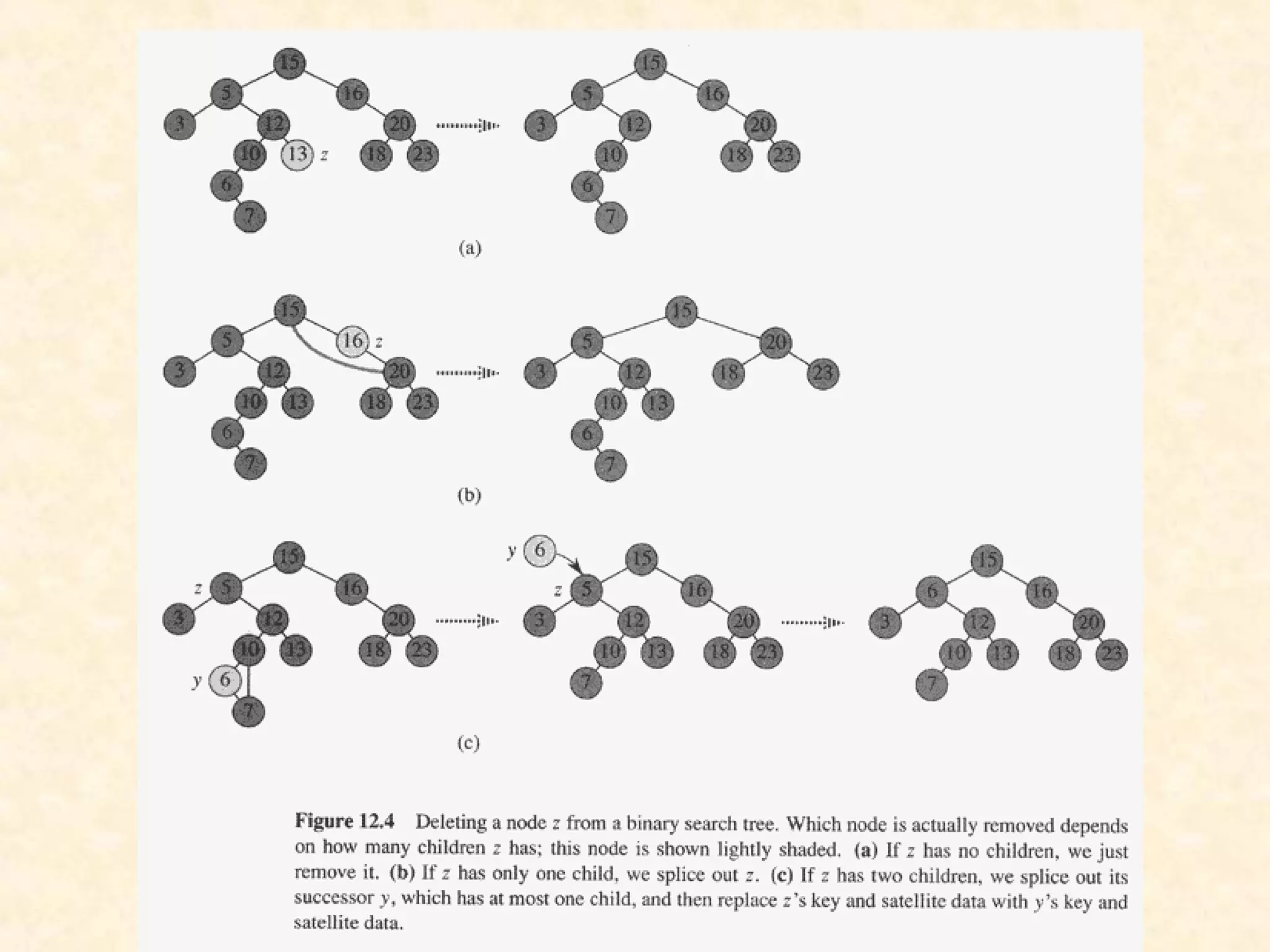
![TREE-DELETE(T, z)
if (left[z] == NIL) || (right[z] == NIL)
y = z
else y = TREE-SUCCESSOR(z)
if (left[y] != NIL)
x = left[y]
else x = right[y]
if (x != NIL)
p[x] = p[y]
if (p[y] == NIL)
root[T] = x
else if (y == left[p[y]])
left[p[y]] = x
else right[p[y]] = x
if (y != z)
key[z] = key[y]
copy y's satellite data into z
return y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-150422084019-conversion-gate02/75/BINARY-SEARCH-TREE-35-2048.jpg)