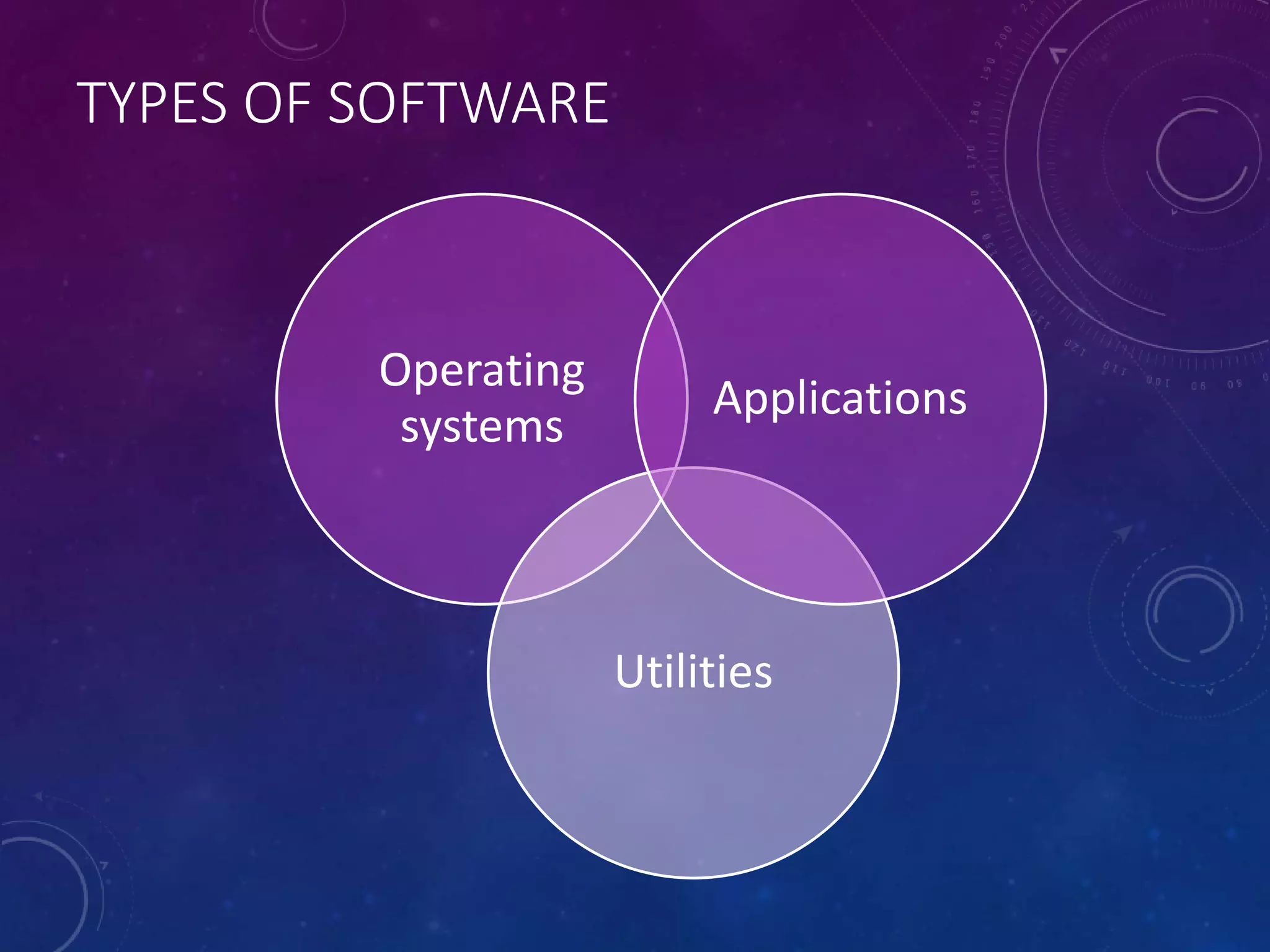
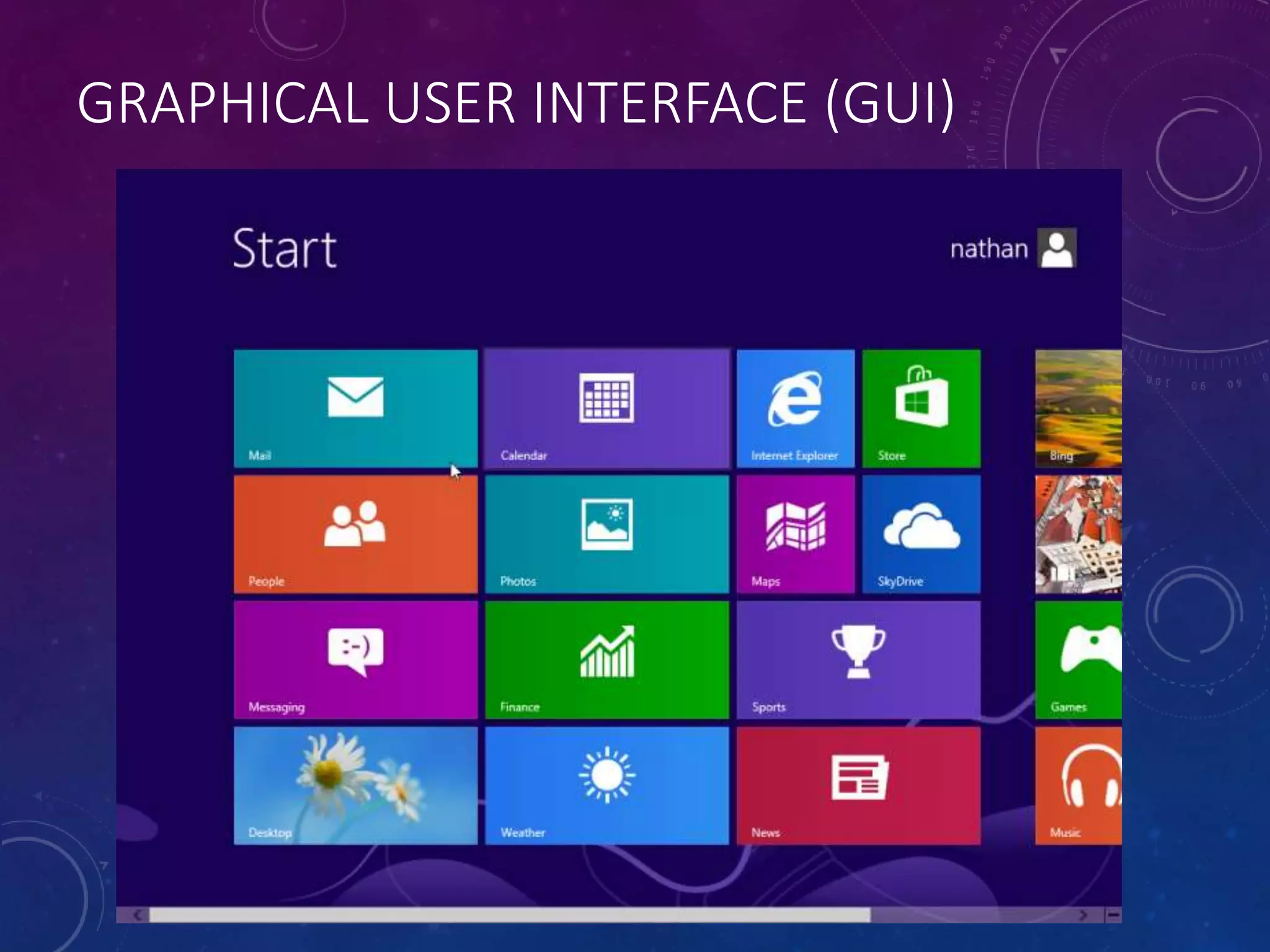
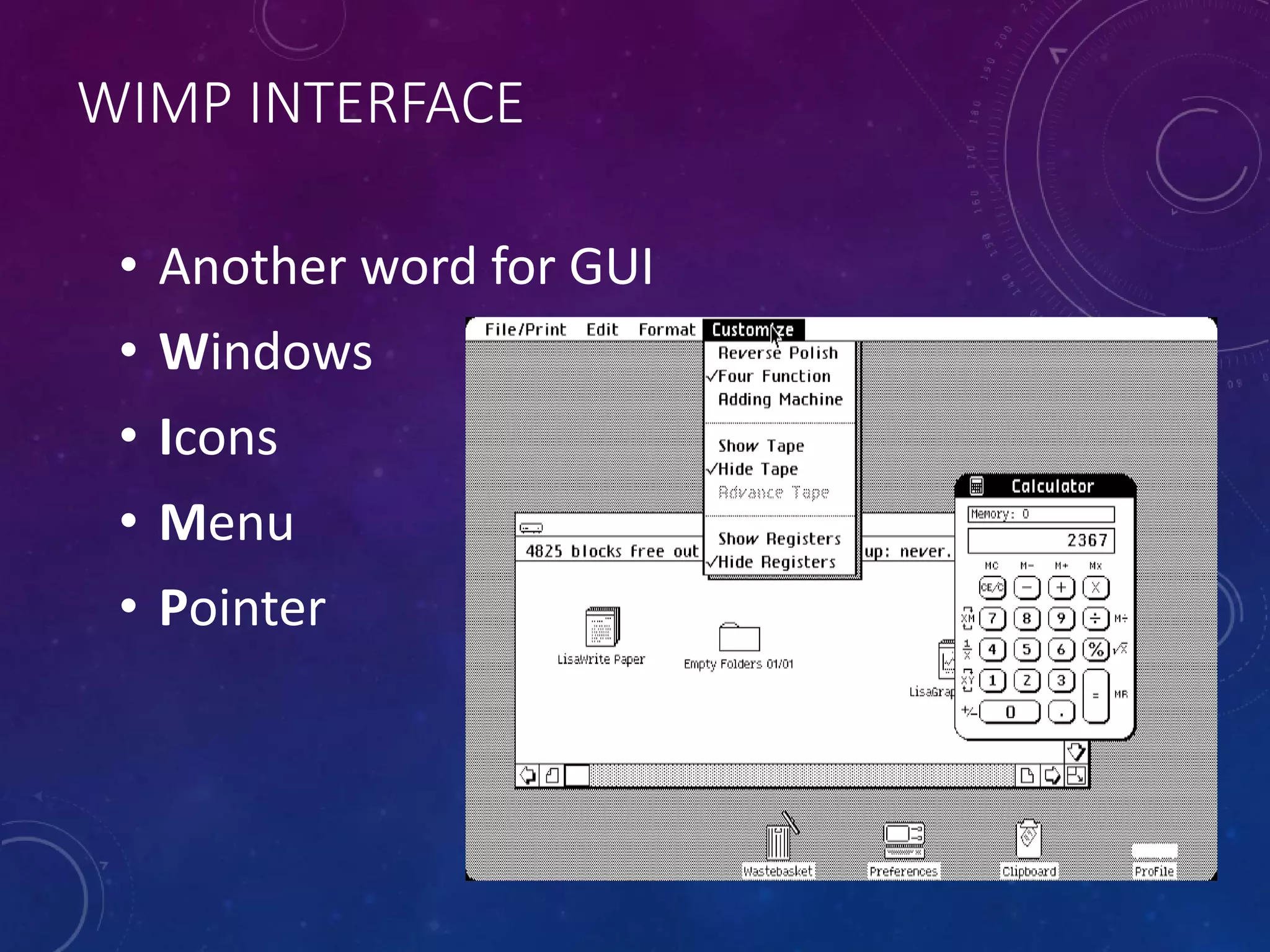
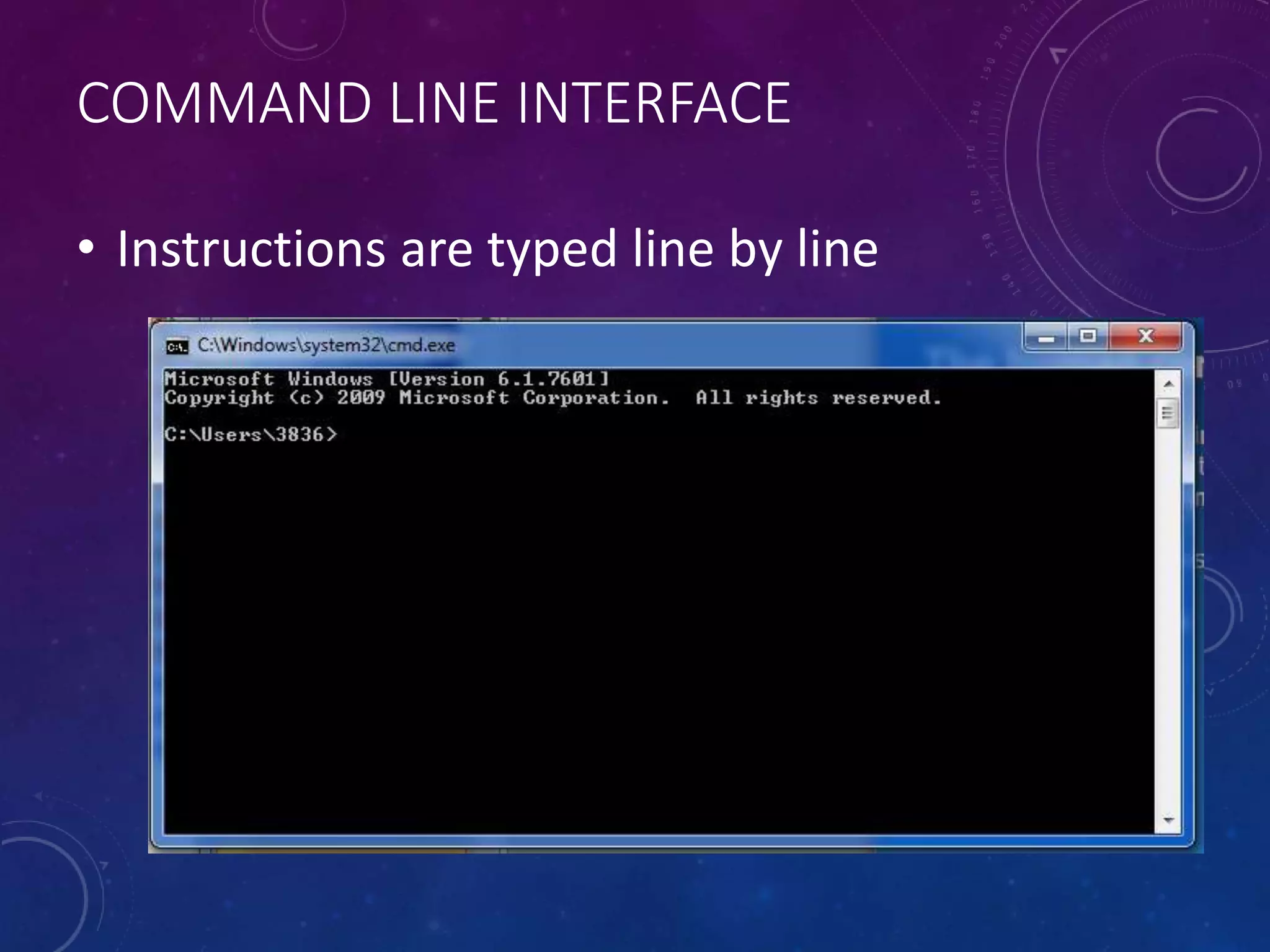
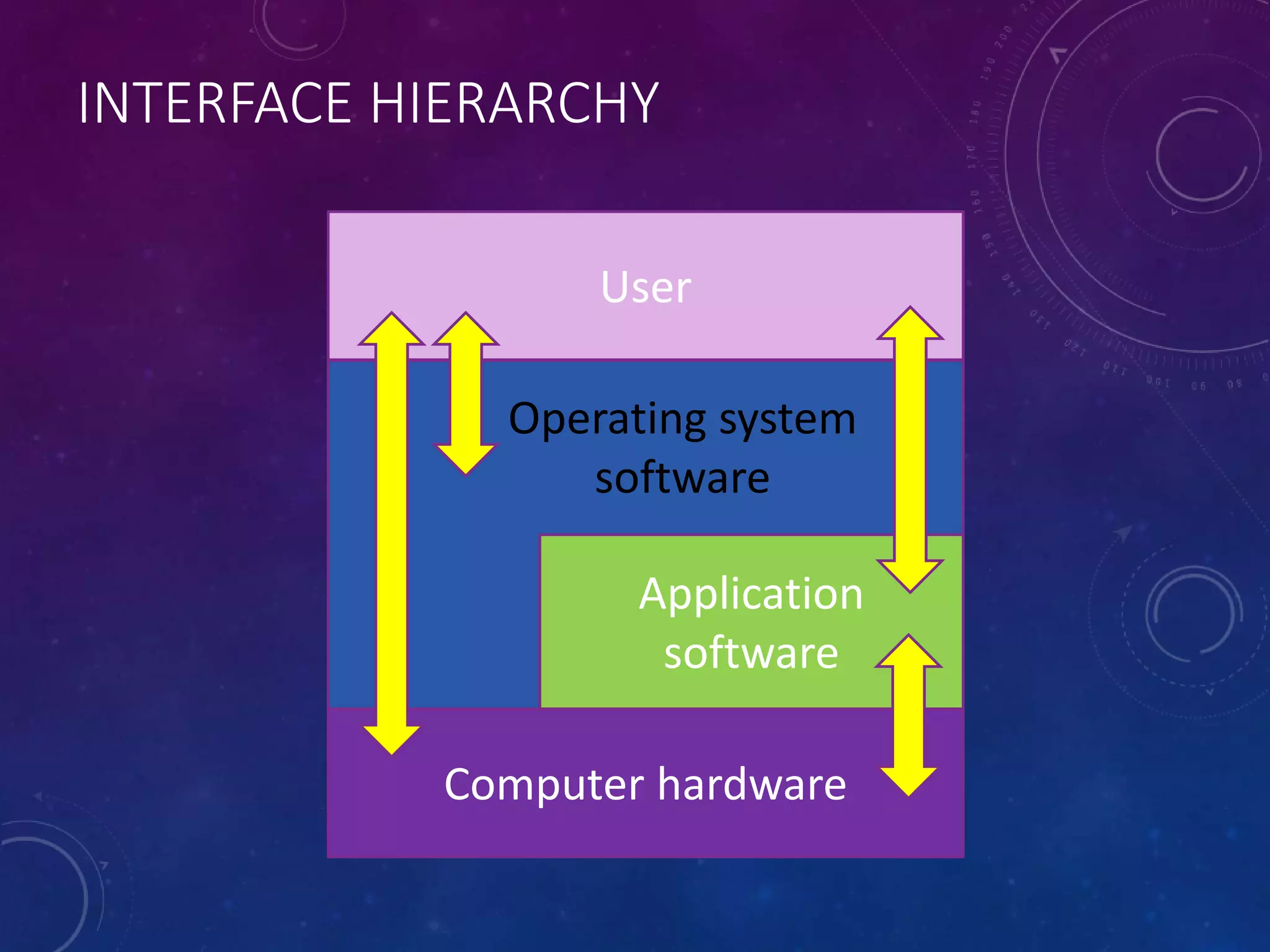
This document discusses different types of software, including operating systems, utilities, and applications. It describes operating systems as software that controls how computer hardware works and provides communication between the user and computer. Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are the most widely used type of interface today, allowing for easy use through windows, icons, menus, and pointers. Command line interfaces require users to type commands, and were more common in the past. The document also outlines various functions of operating systems and examples of utility and application software.