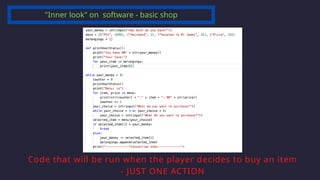
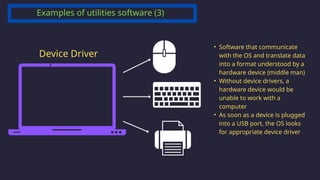
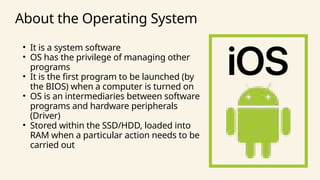
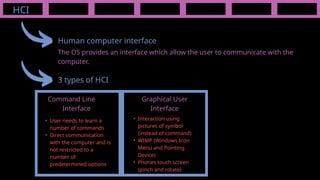
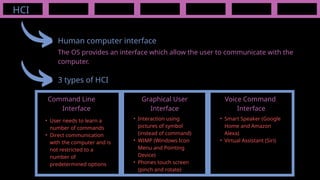
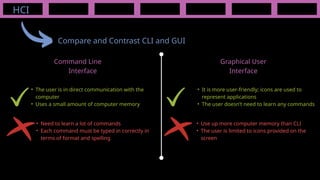
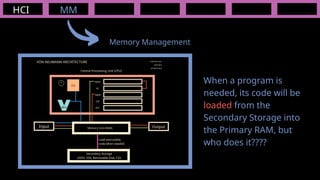
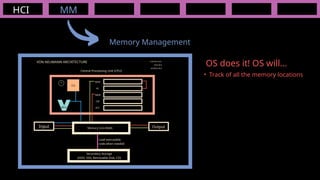
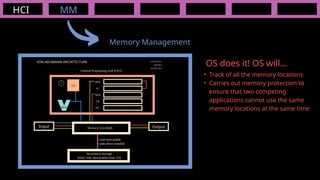
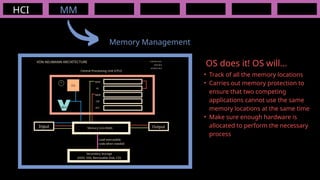
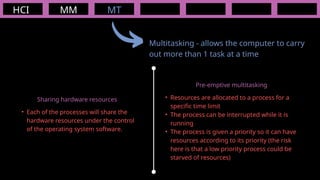
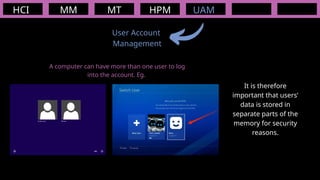
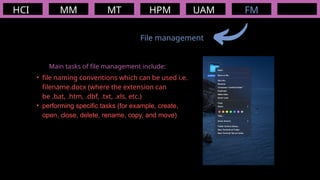
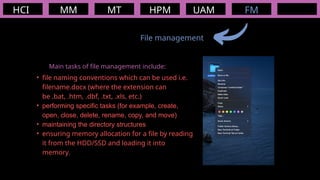
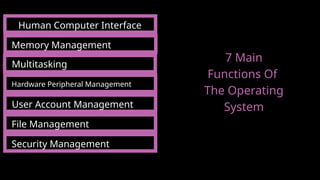
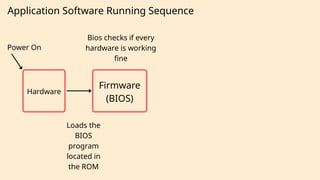
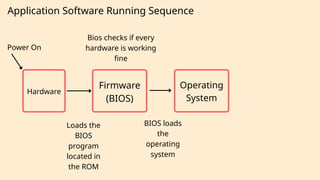
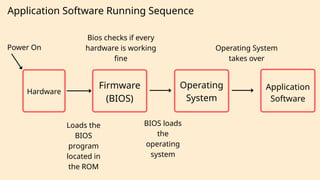
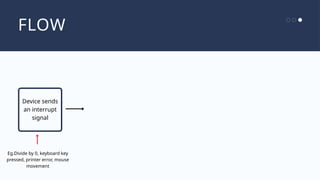
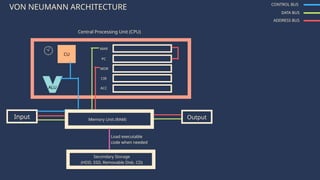
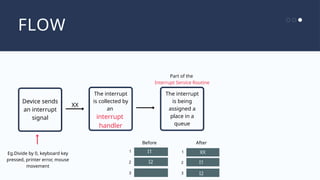
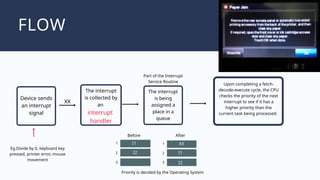
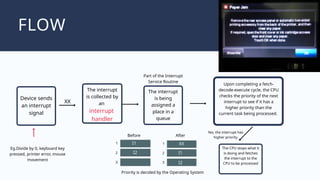
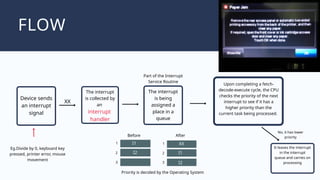
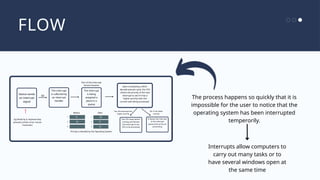
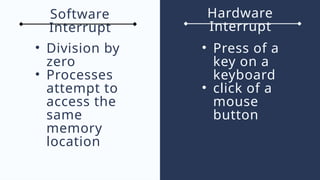
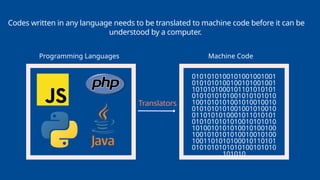
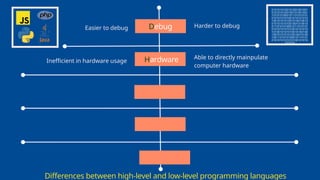
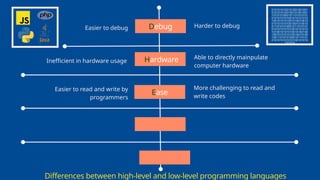
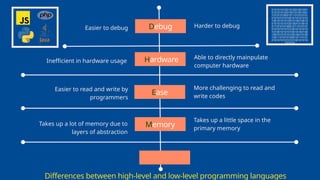
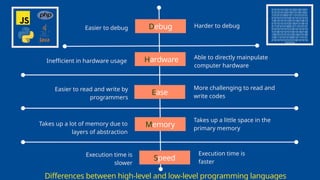
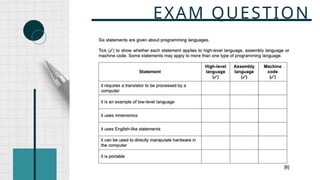
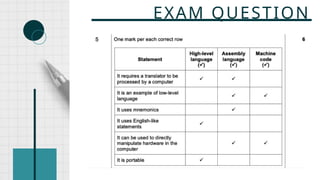
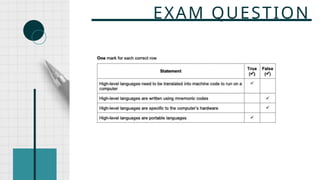
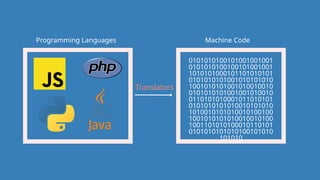
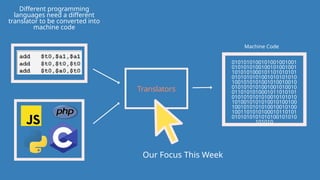
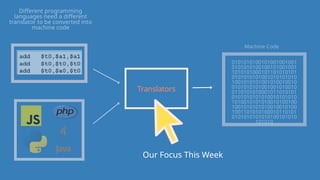
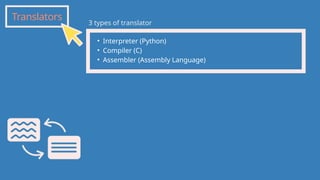
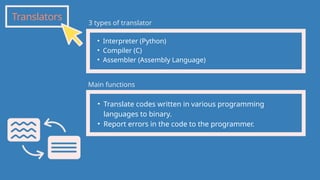
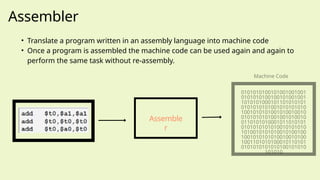
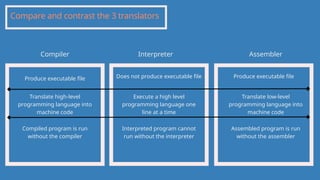
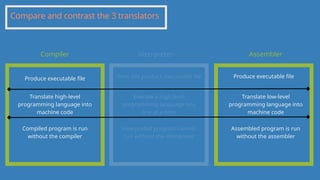
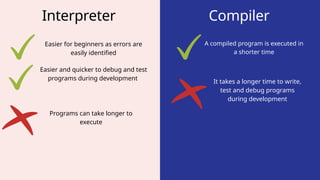
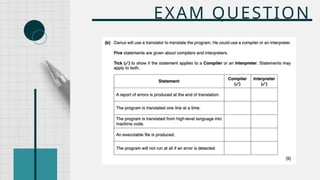
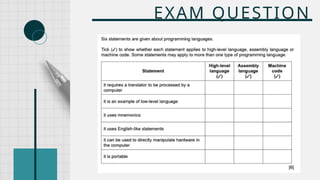
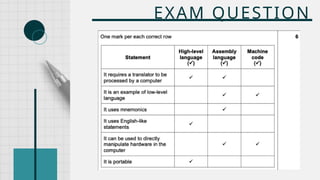
The document outlines the definitions and classifications of software, including system and application software. It describes the role of the operating system in managing hardware and executing software, as well as various functions such as memory management, multitasking, and user account management. Additionally, it discusses interrupts and their role in handling multiple processes efficiently within a computer system.