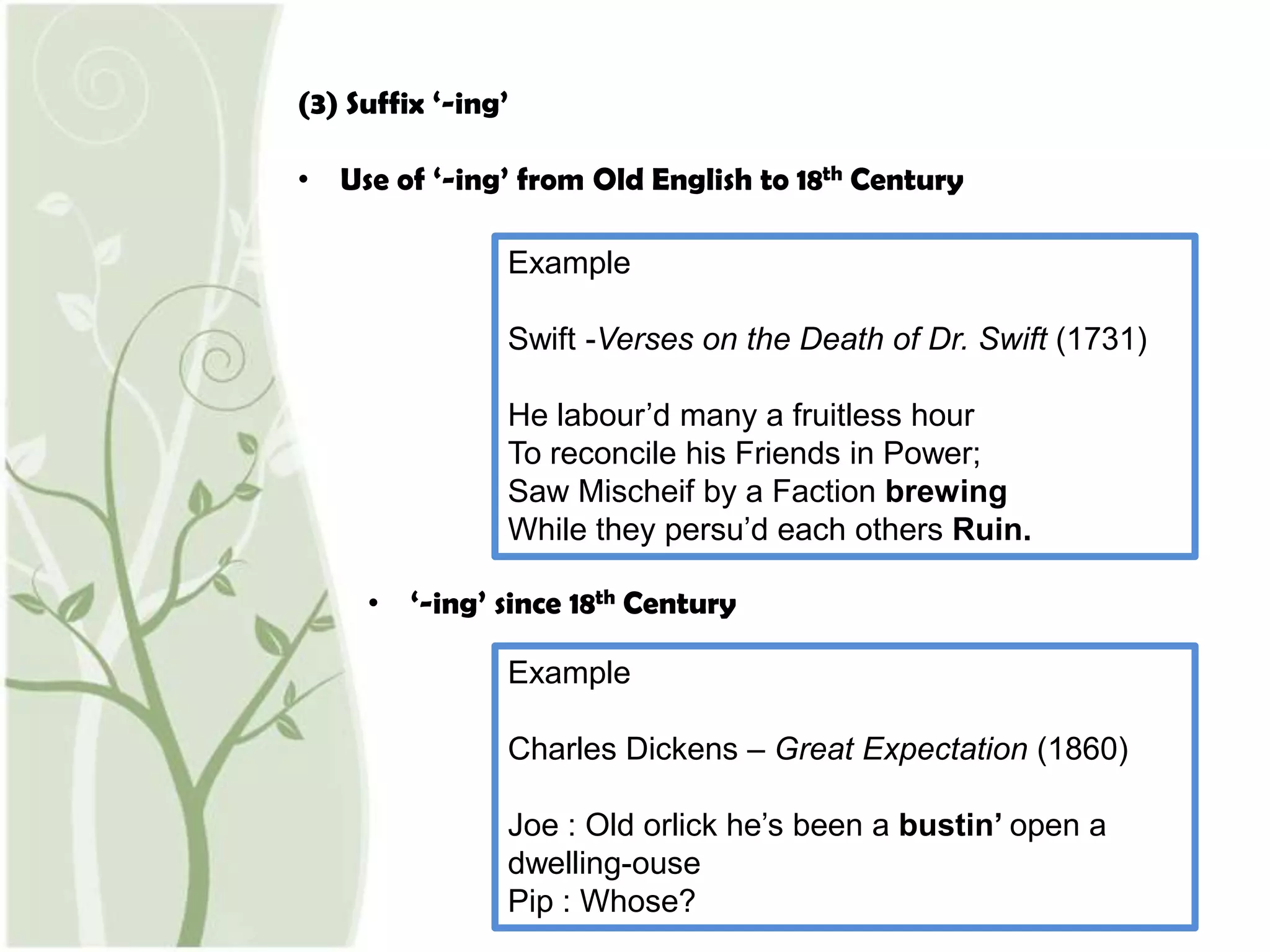
This document discusses social dialects in England. It defines a dialect as a variety of a language characteristic of a particular group. Social dialects are divided based on social class, while regional dialects differ based on geographic region. Examples of social dialects in England include pronouncing words beginning with "h" as either [h] or dropping the "h", pronouncing "r" after vowels as either [r] or dropping the "r", and pronouncing the "-ing" suffix as either [in] or [iŋ]. The background sections provide historical context on the evolution of these pronunciations from Old English to modern times. Studying social dialects provides insight into time periods, environments, literature, and social backgrounds.



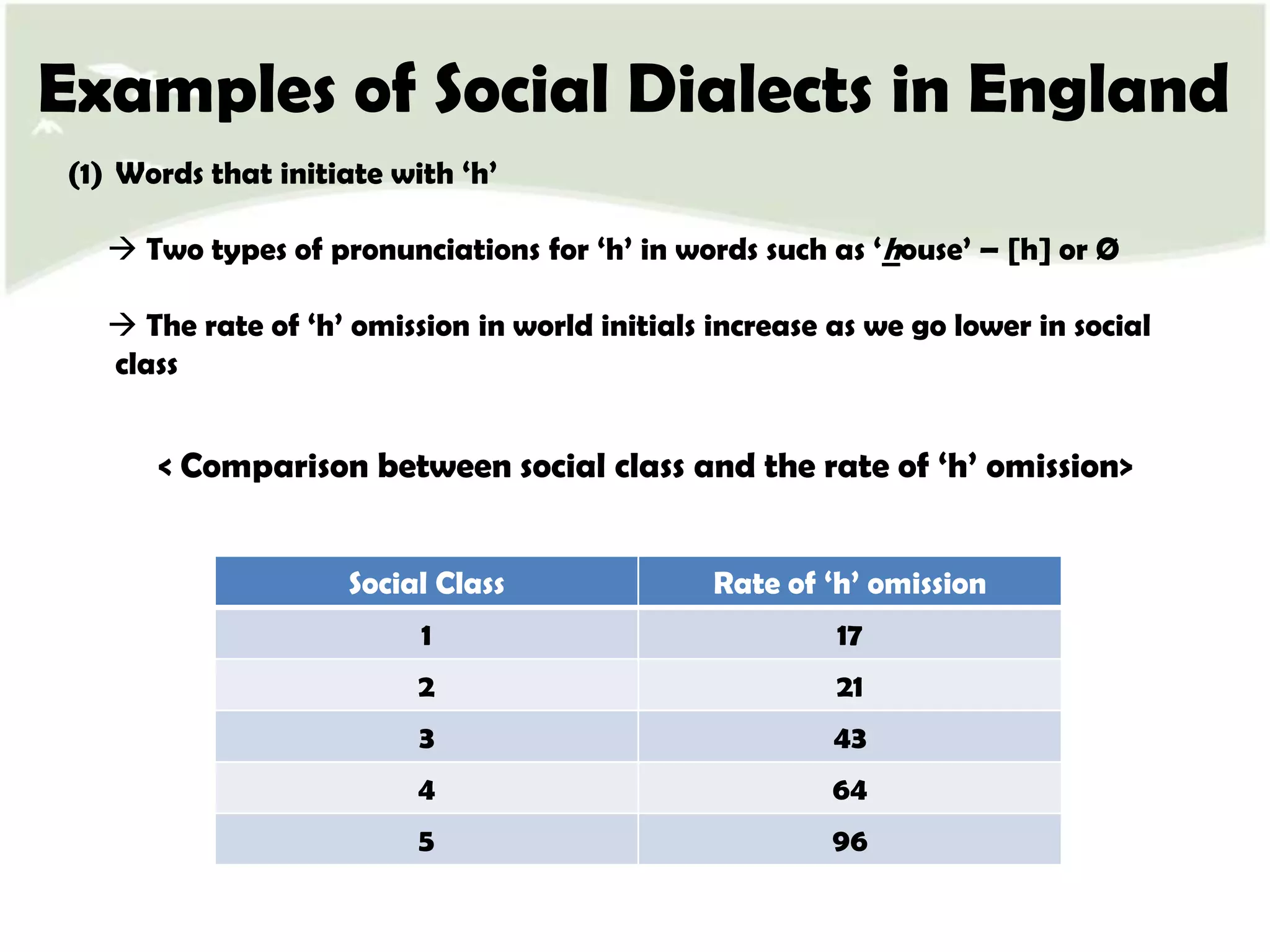

![Examples of Social Dialects in EnglandWords that initiate with ‘h’ Two types of pronunciations for ‘h’ in words such as ‘house’ – [h] or Ø The rate of ‘h’ omission in world initials increase as we go lower in social class< Comparison between social class and the rate of ‘h’ omission>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-110605201516-phpapp01/75/Social-Dialects-in-English-7-2048.jpg)
![(2) ‘r’ that comes behind a vowelTwo types of pronunciations in ‘r’ in worlds such as ‘car’ or ‘cart’ – [r] or Ø People of high social class have the tendency to omit the sound ‘r’ behind a vowel< The realization of [r] in words >](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-110605201516-phpapp01/75/Social-Dialects-in-English-8-2048.jpg)
![(3) Suffix ‘-ing’ Two types of pronunciation in ‘-ing’ in words such as ‘swimming’ and ‘sleeping’ – [in] or [iŋ] Higher social classes use more [in] compared to [iŋ]< Use of pronunciation [iŋ] for suffix ‘-ing’>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-110605201516-phpapp01/75/Social-Dialects-in-English-9-2048.jpg)