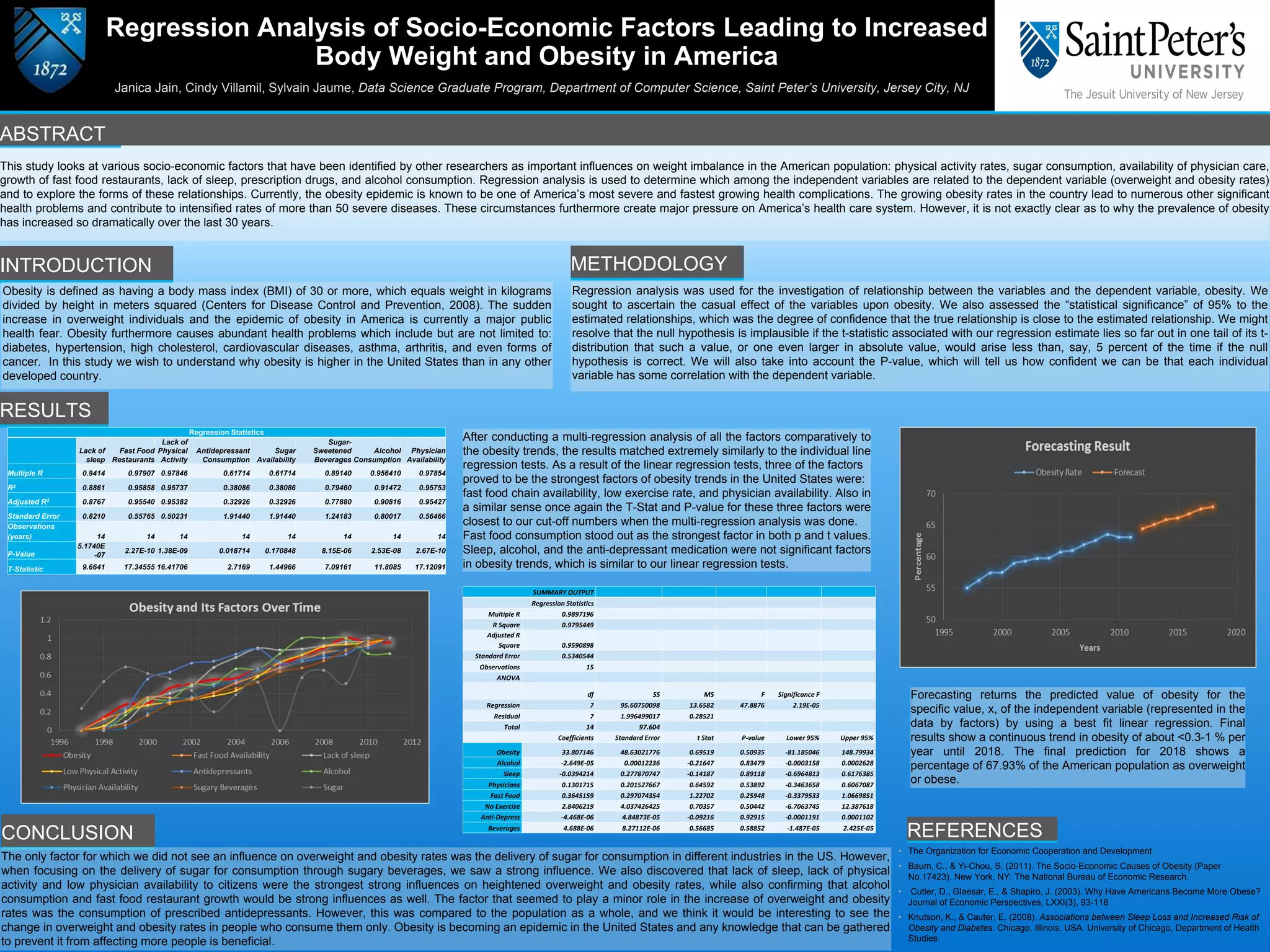
This study used regression analysis to examine the relationship between various socioeconomic factors and obesity rates in the United States. The regression results showed that lack of physical activity, increased availability of fast food restaurants, and lack of physician availability were the strongest influences on higher obesity rates. Fast food consumption had the strongest correlation to obesity based on the p-values and t-statistics. Lack of sleep, alcohol consumption, and antidepressant use did not significantly correlate to obesity trends. The final regression prediction estimated that the percentage of the American population that is overweight or obese will continue to increase by 0.3-1% per year until reaching 67.93% in 2018.