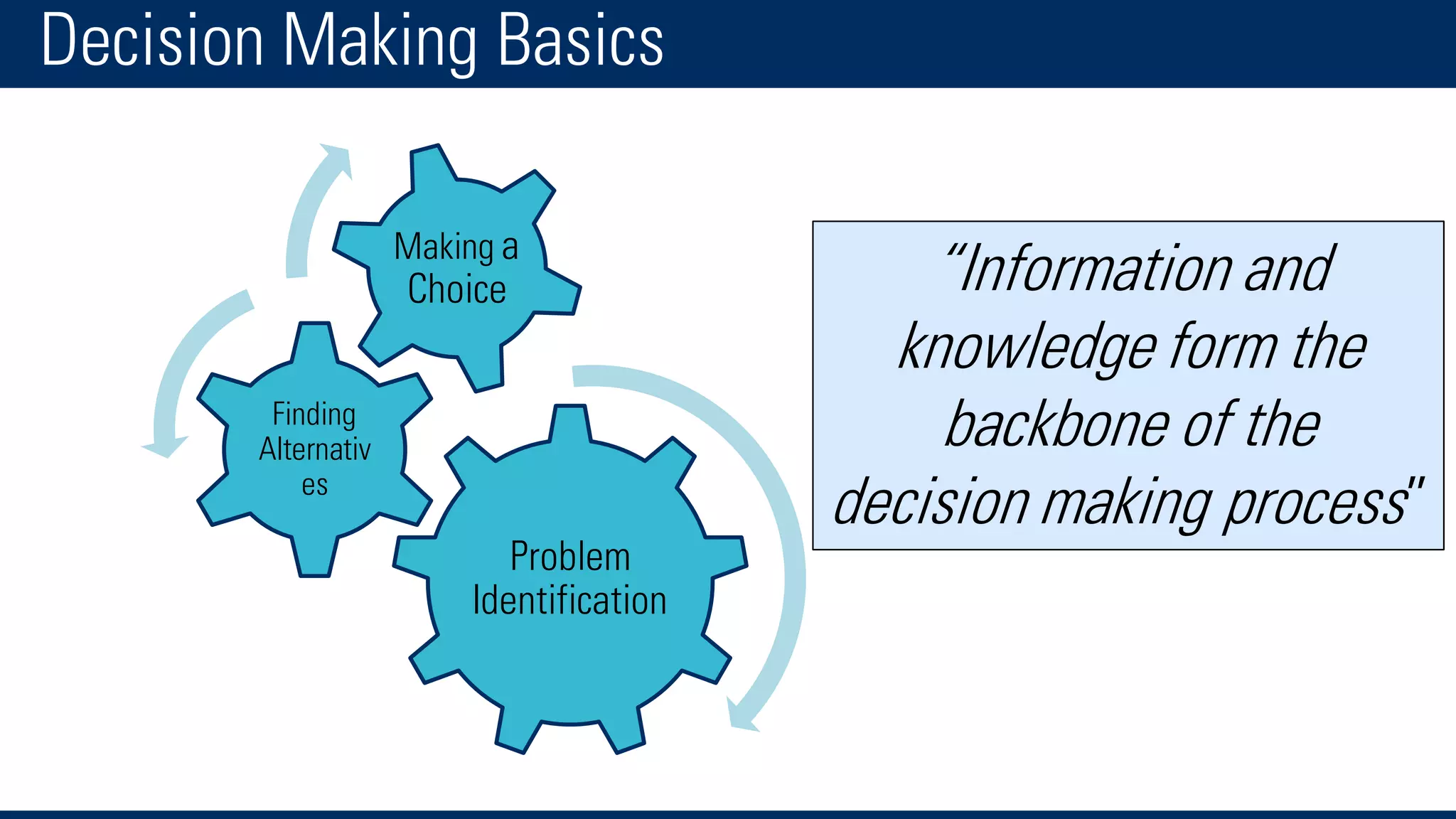
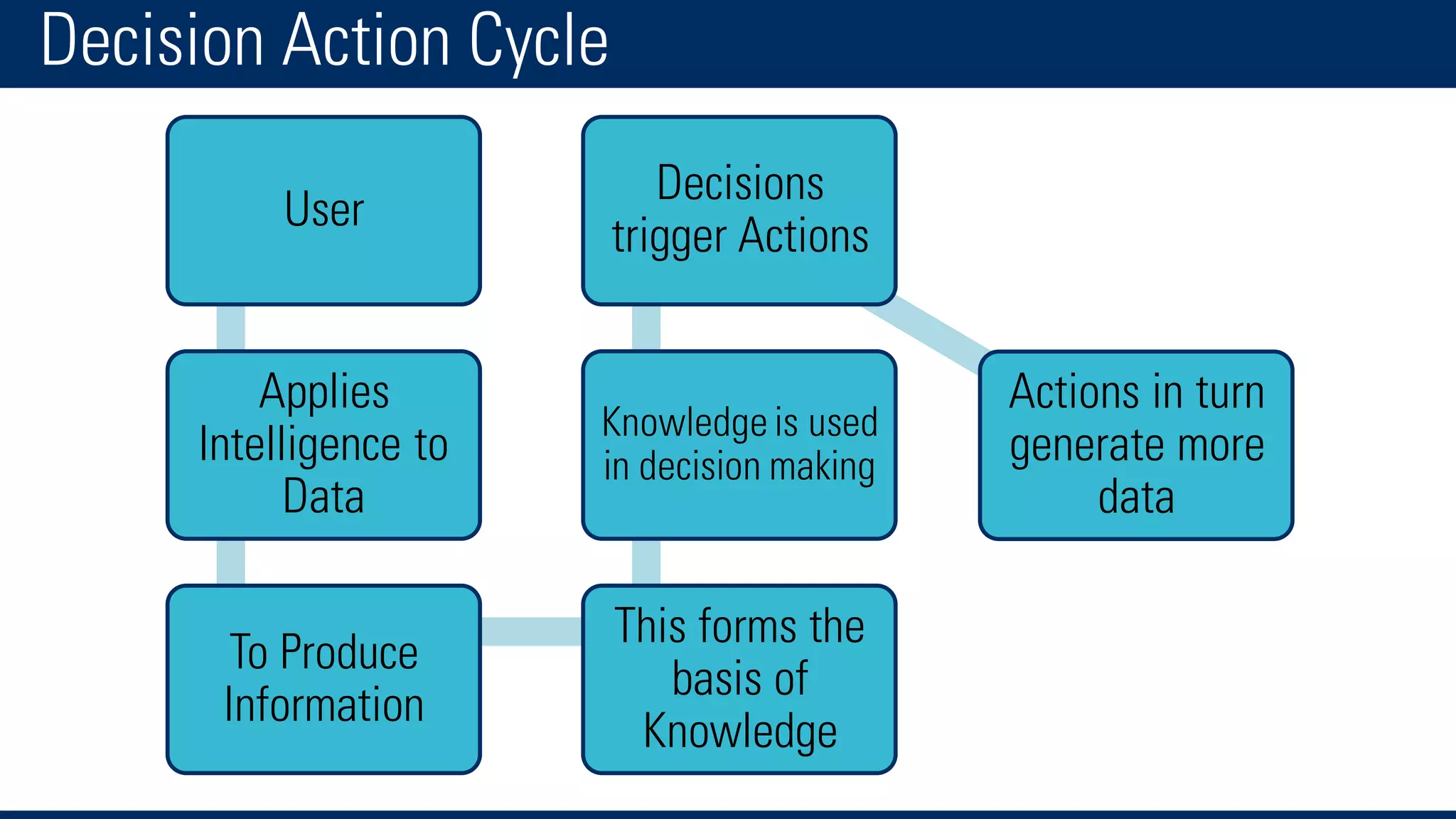
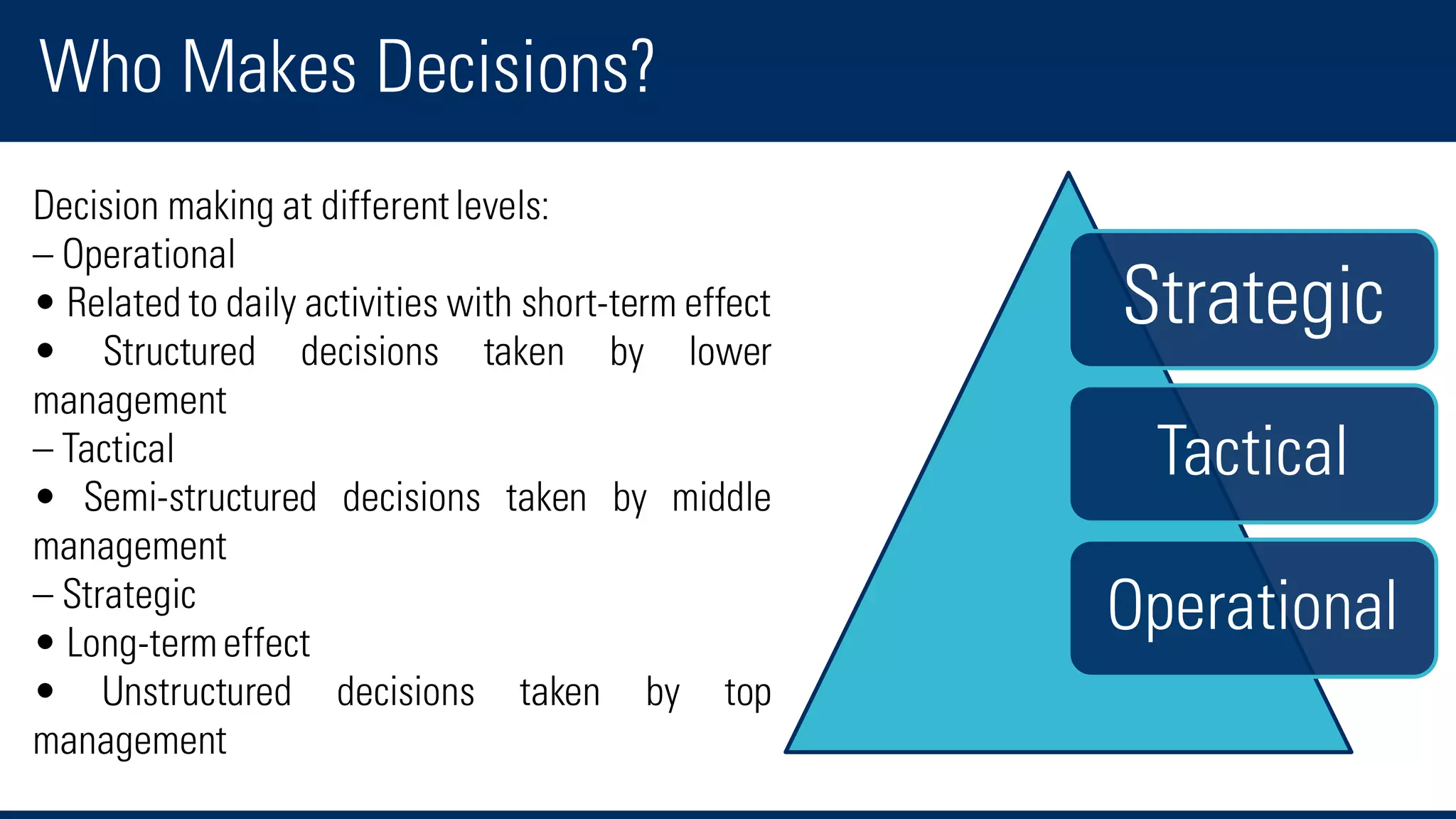
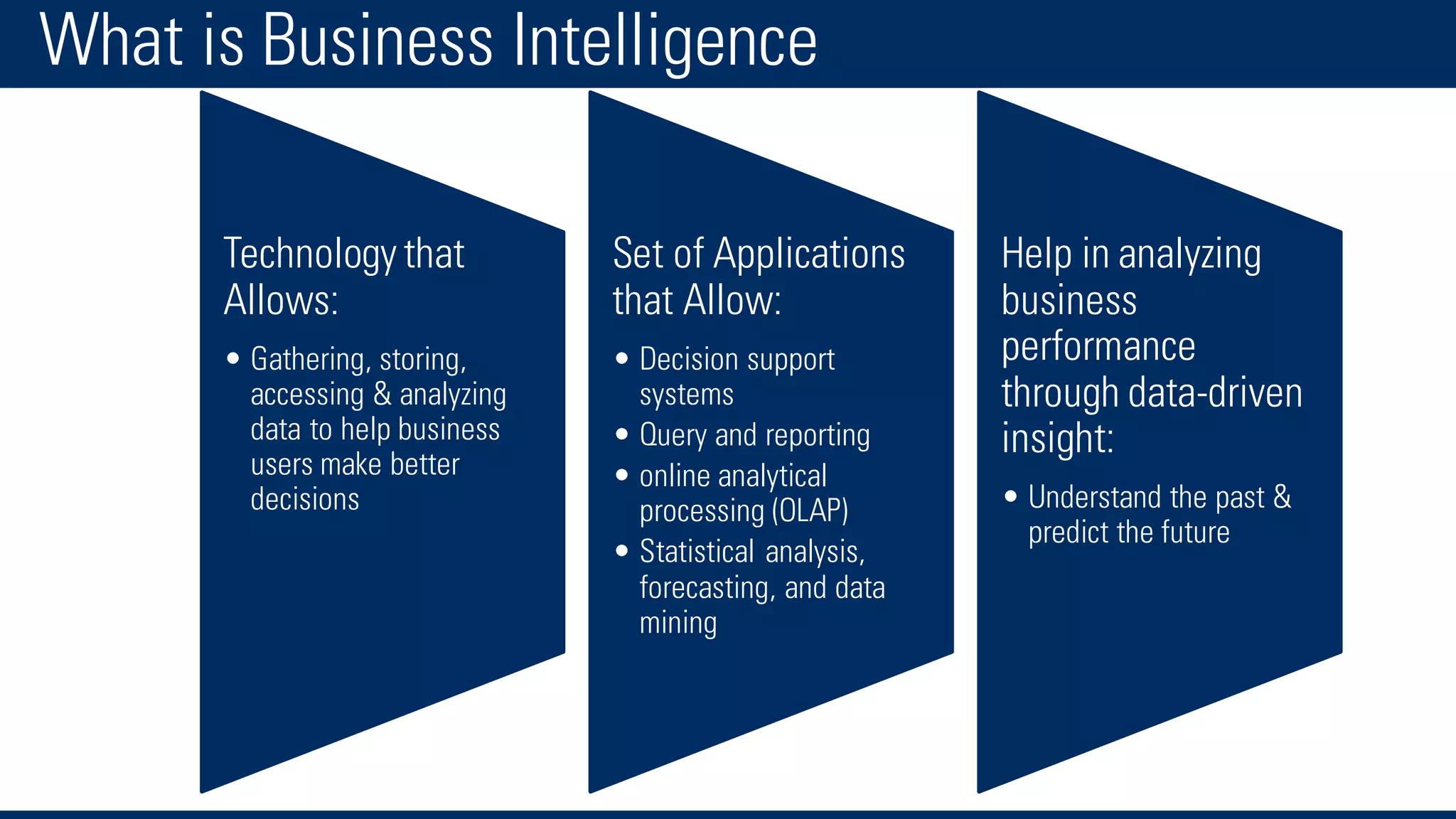
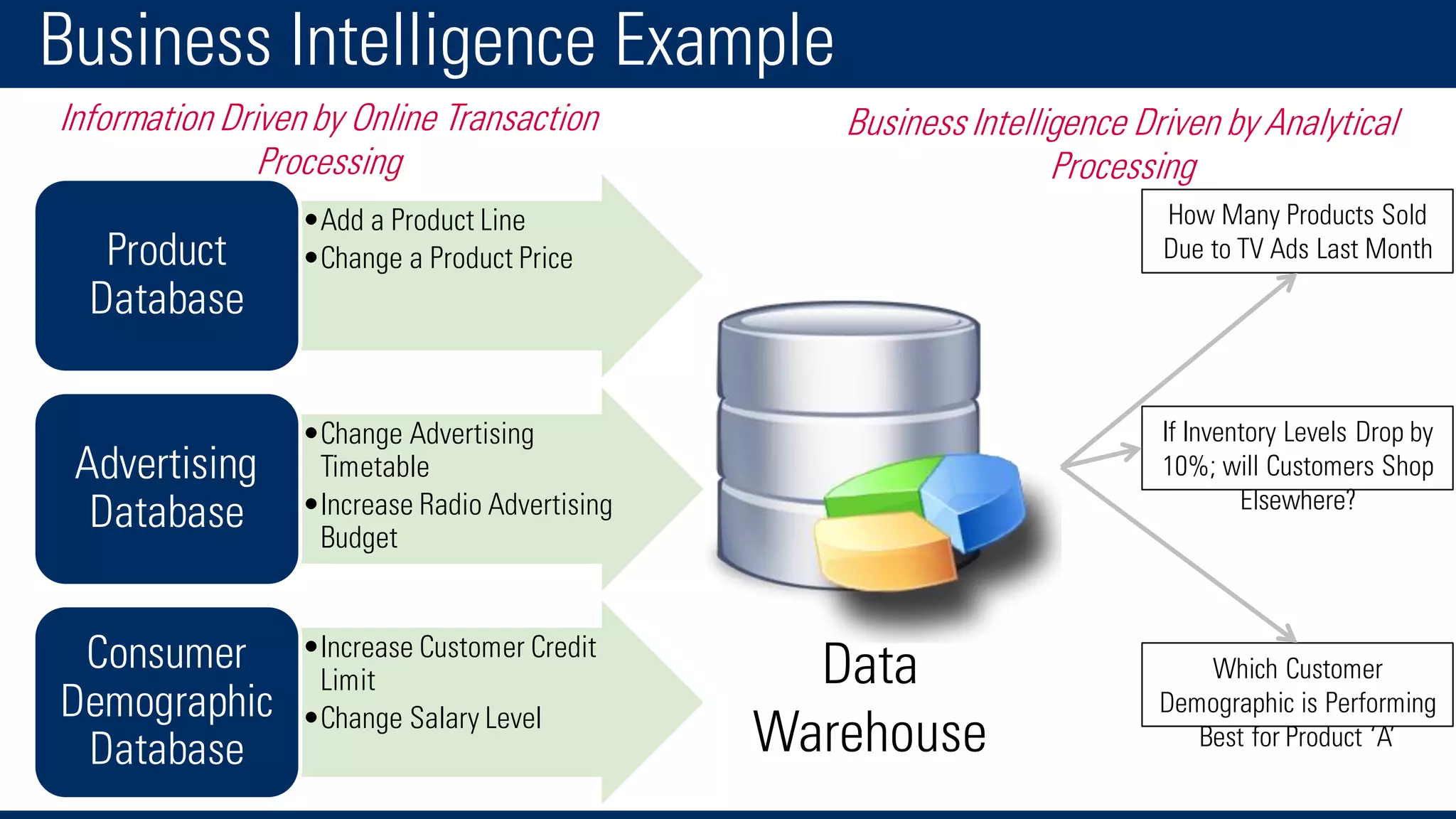
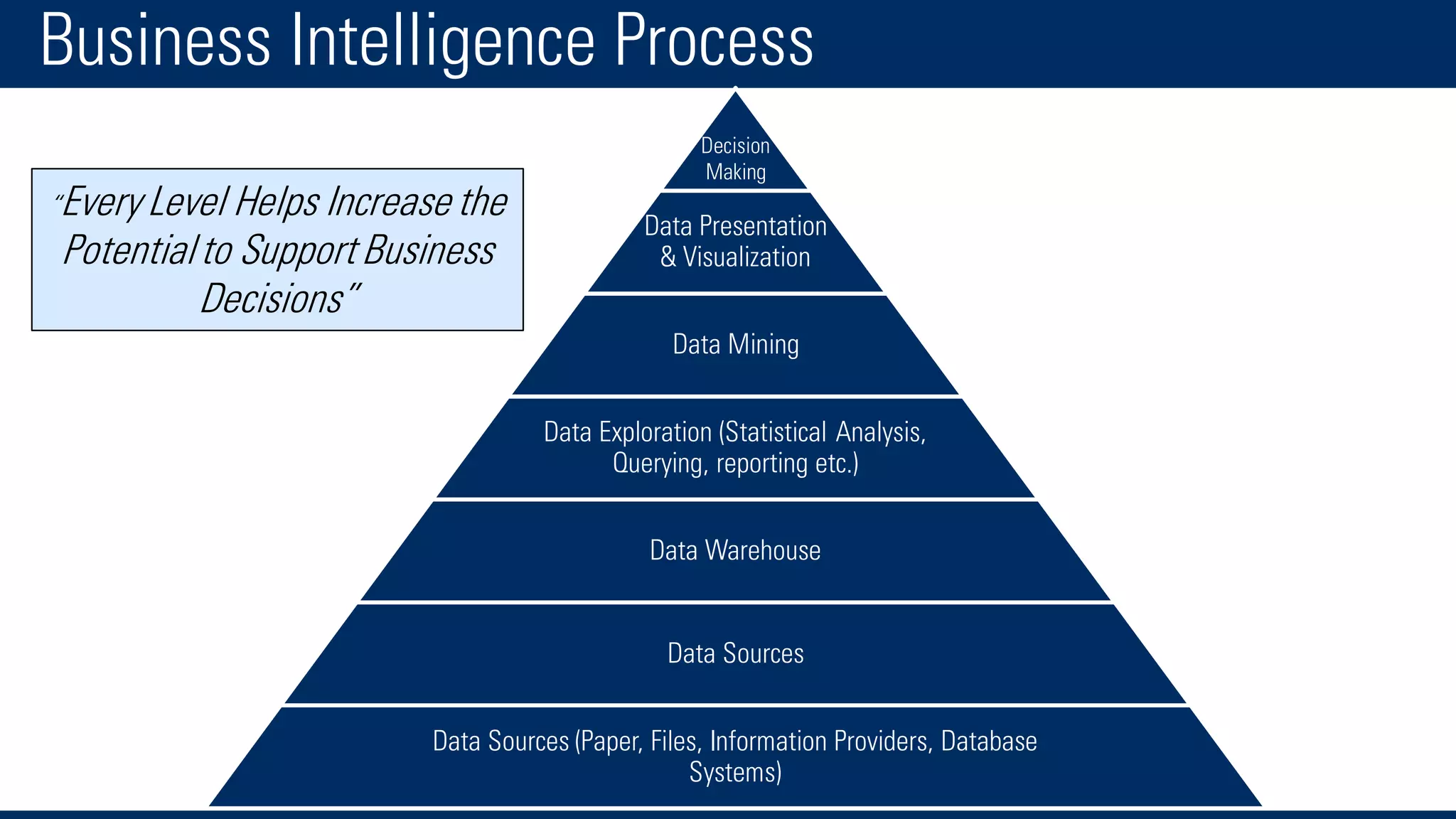
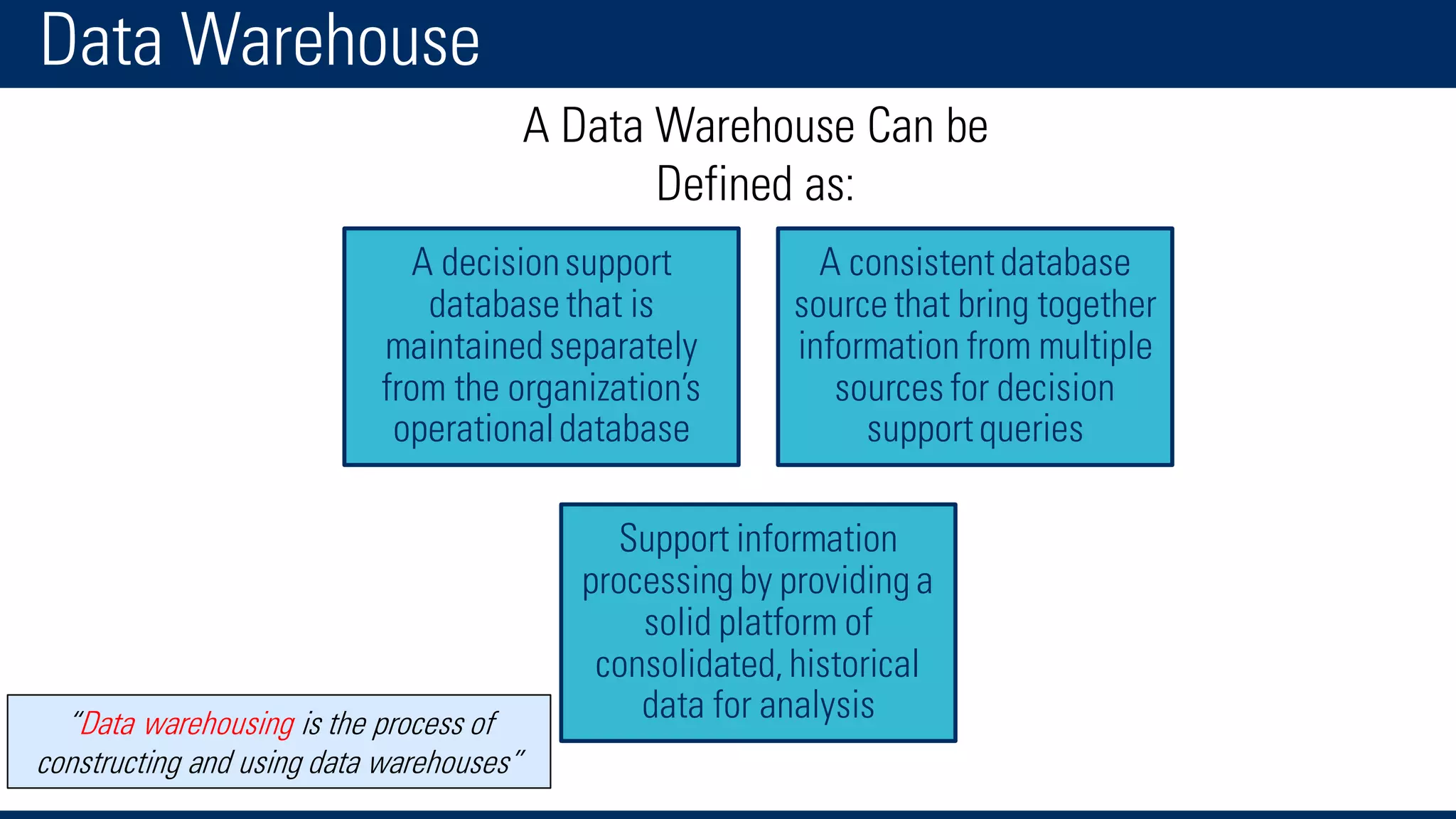
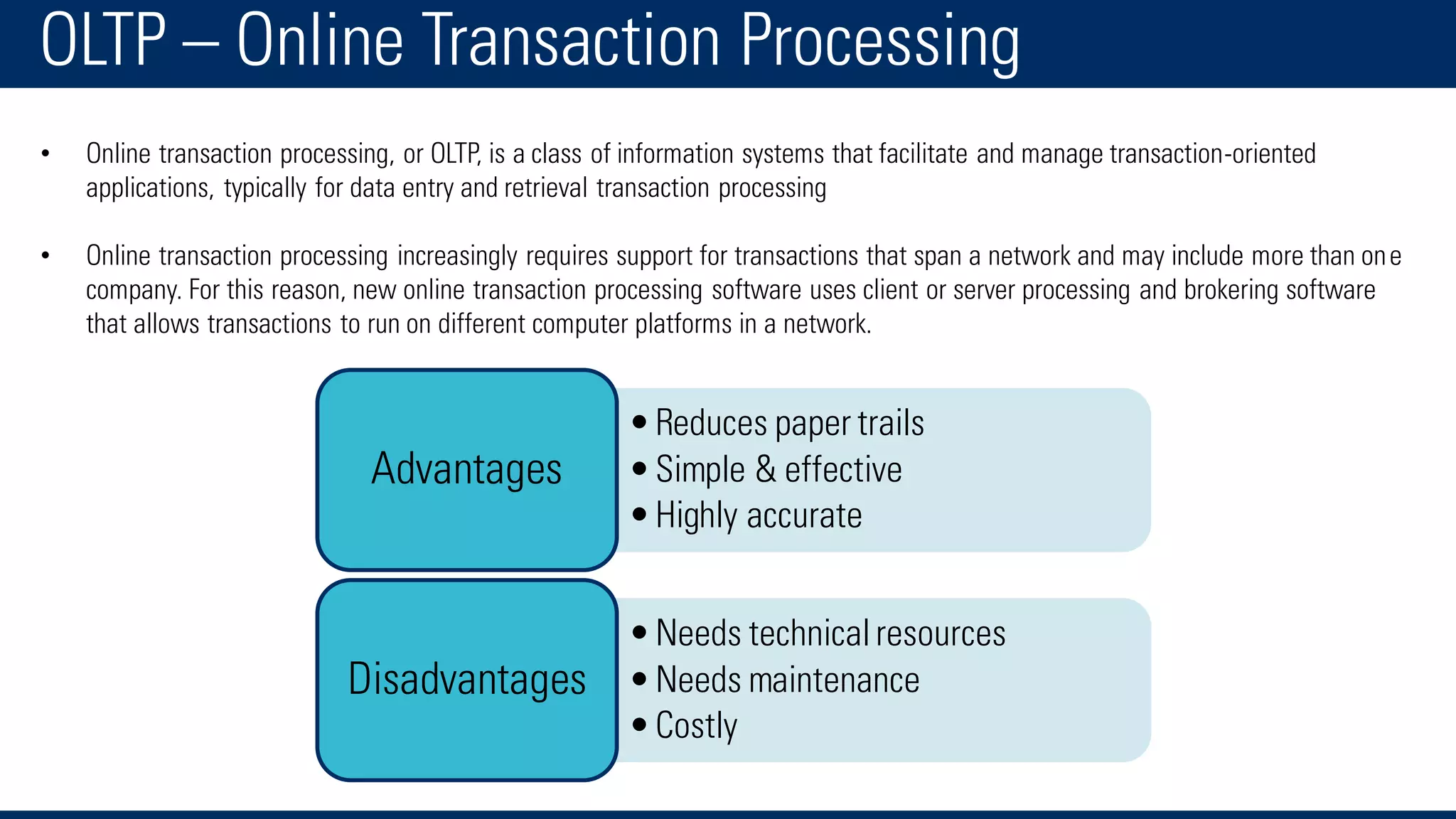
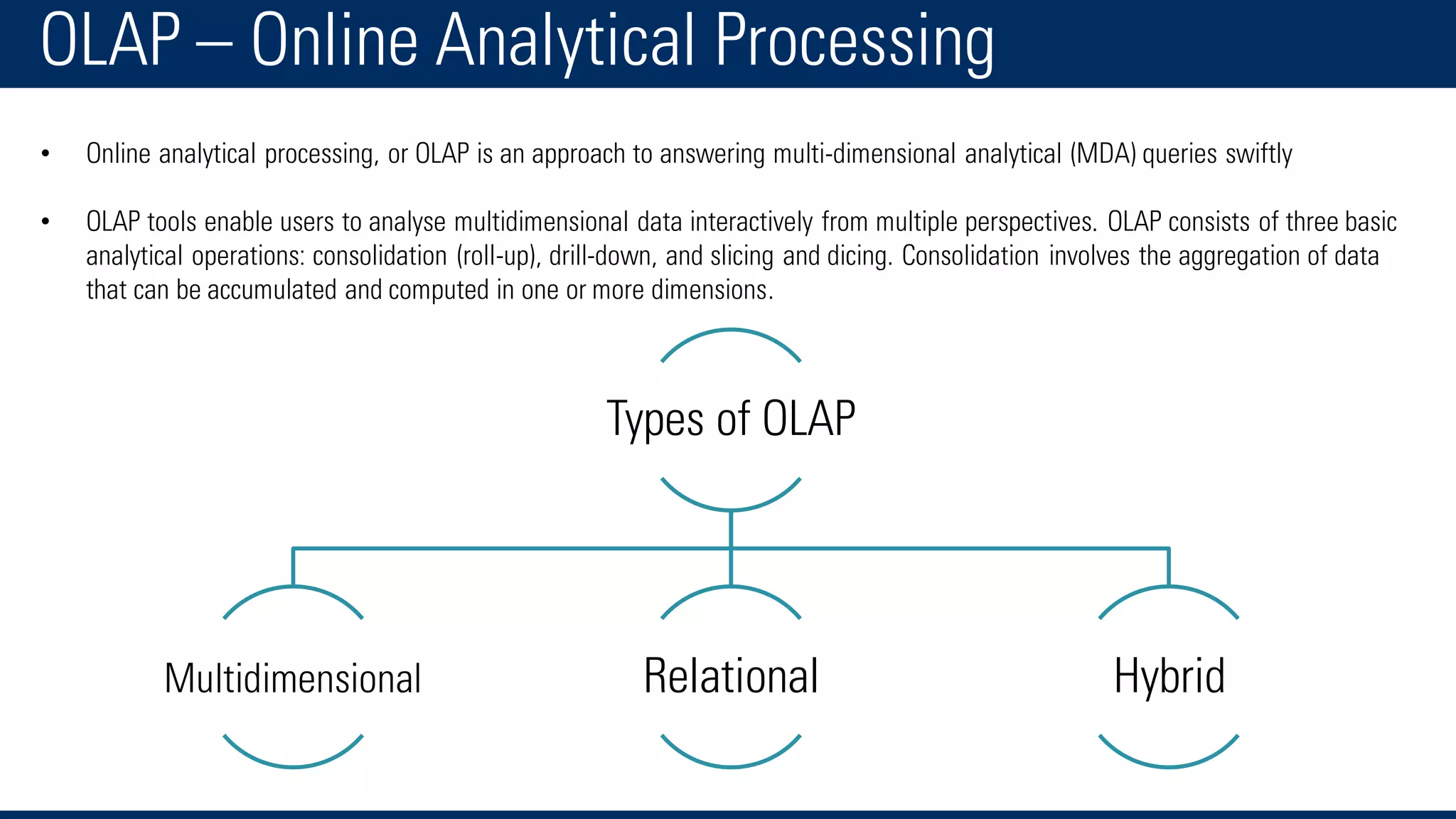
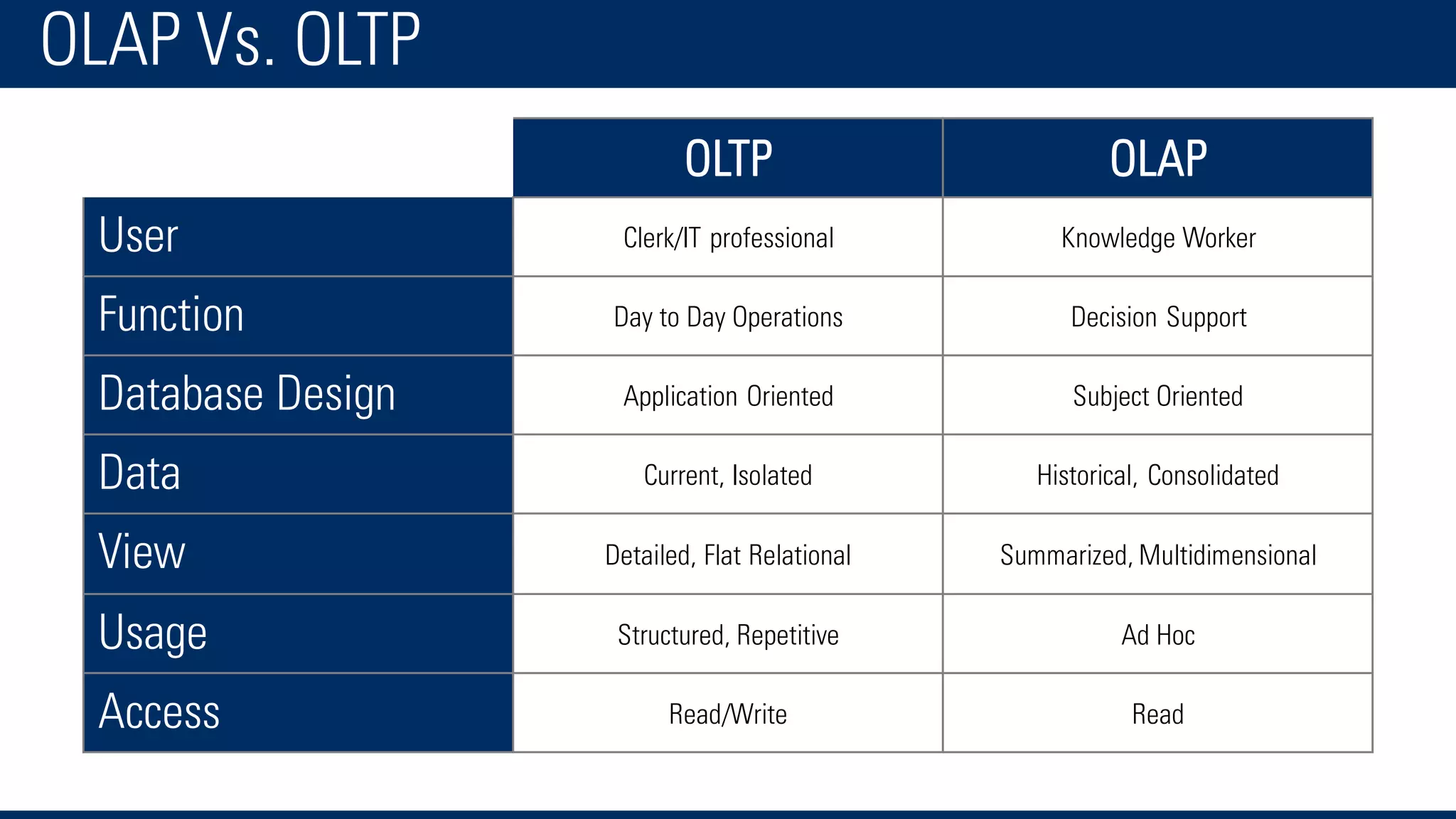
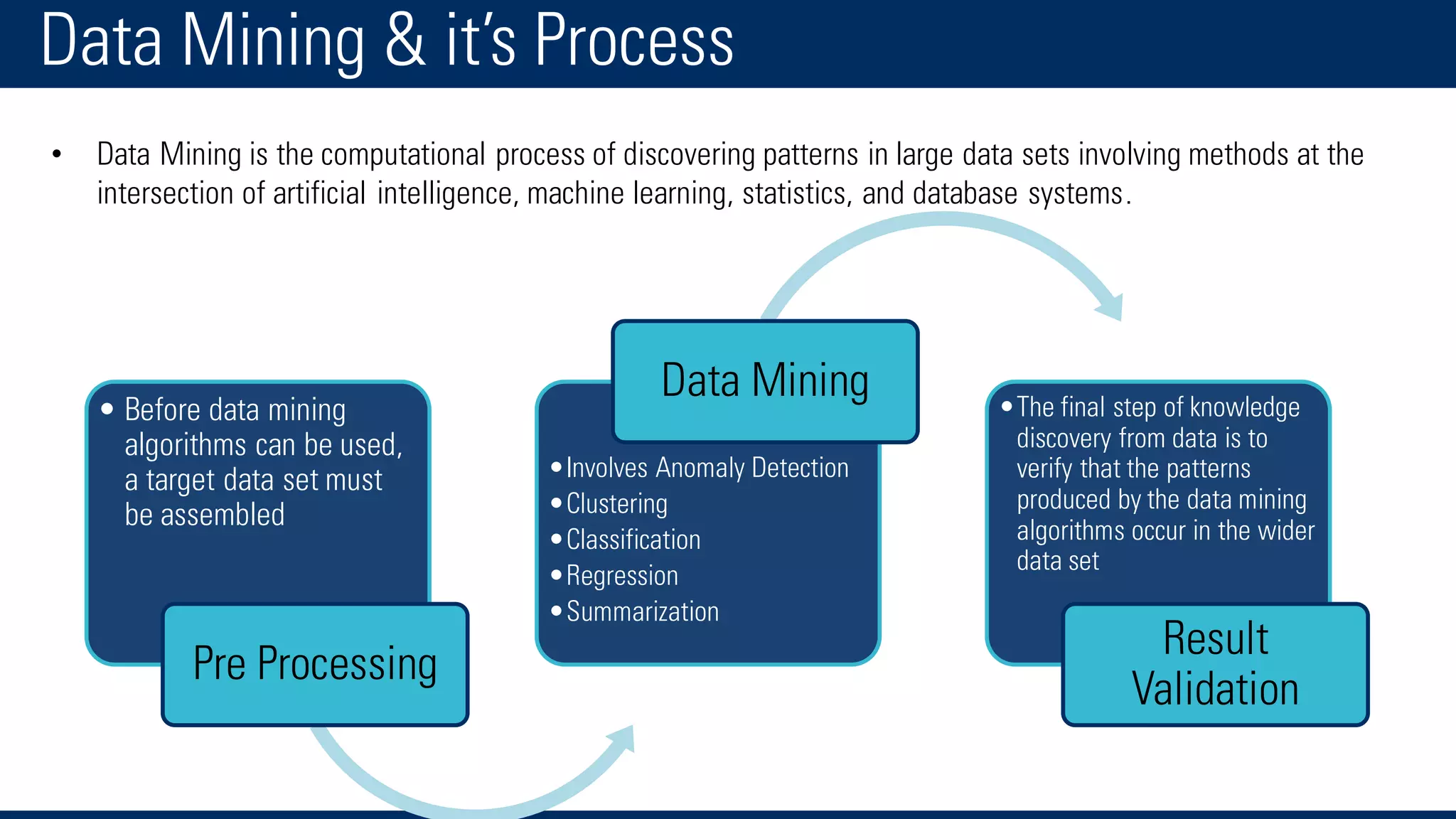
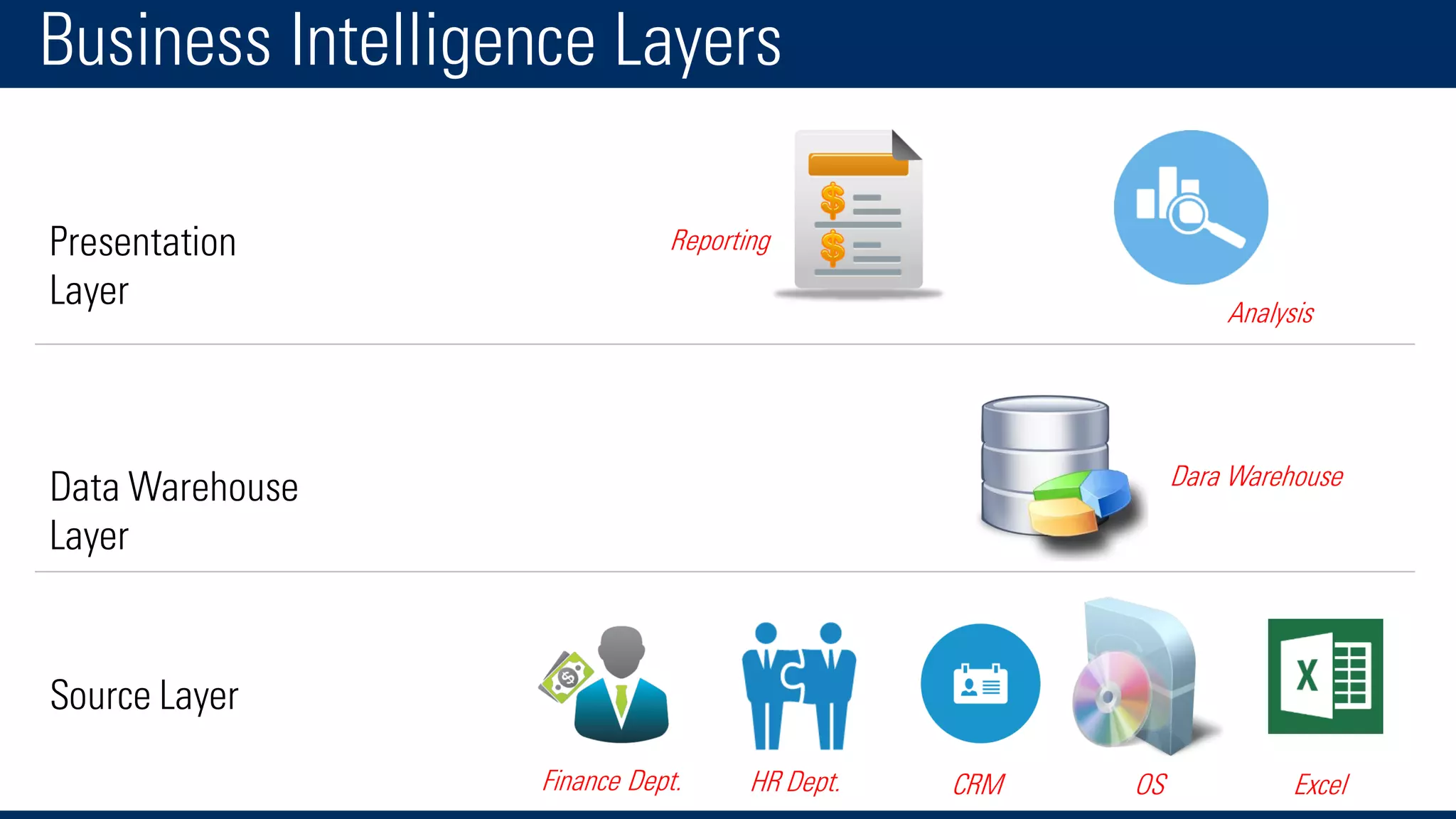
The document discusses business intelligence and the decision making process. It defines business intelligence as using technology to gather, store, access and analyze data to help users make better decisions. This includes applications like decision support systems, reporting, online analytical processing, and data mining. It also discusses key concepts like data warehousing, OLTP vs OLAP, and the different layers of business intelligence including the presentation, data warehouse, and source layers.