Acute kidney injury(AKI)
- 1. ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI) Abdulsalam Halboup M.Pharma (Clinical)
- 2. ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Acute kidney injury (AKI) is abrupt reduction in kidney functions as evidence by changed in laboratory values; serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen(BUN)and urine output. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is diagnosed if one of the following criteria is met : increase in serum creatinine (SCr) of at least 0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours, a 50% increase in baseline SCr within 7 days, or a urine output of less than 0.5 mL/kg/hour for at least 6 hours.
- 3. EPIDEMIOLOGY AND ETIOLOGY Between 5% and 7% of all hospitalized patients develop AKI. A greater prevalence of AKI is found in critically ill patients ( ICU-Acquired AKI). Despite improvements in the medical care of individuals with AKI, mortality generally exceeds 50%.
- 4. EPIDEMIOLOGY
- 5. CLASSIFICATION OF AKI Criteria used for AKI classification RIFLE: Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of Kidney Function and End Stage Renal Disease). AKIN: Acute Kidney Injury Network KDIGO: Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcome
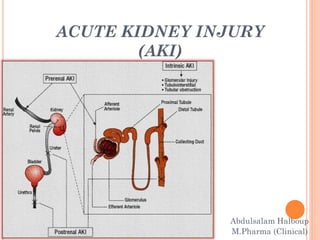
- 7. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY There are typically three categories of AKI: 1-prerenal AKI 2- intrinsic AKI 3- Postrenal AKI
- 9. PRERENAL AKI Prerenal AKI: is characterized by reduced blood delivery to the kidney. A common causes are: Volume depletion hemorrhage dehydration GI fluid losses. Decrease effective circulatory blood volume Decrease cardiac output (CHF, MI, hypotension Pulmonary hypertension Liver failure Sepsis Functional ACEIs, NSAIDs, ARBs, Cyclosporine and tacrolimus Prompt correction of volume depletion can restore kidney function to normal because no structural damage to the kidney has occurred.
- 10. INTRINSIC AKI Damage is within the kidney (structure of the nephron,); Vascular damage (renal thrombosis) Glomerular damage (nephrotic/nephritic glomerulonephritis Acute tubular necrosis(ATN)(it accounts for 50% of all cases of AKI) Ischemia (hypotension, sepsis Endogenous toxins(uric acid ,hemoglobin Exogenous toxin Aminoglycosides contrast induced nephropathy (CIN) amphotericin B Acute interstitial nephritis NSAIDs infections Prerenal AKI can progress to intrinsic AKI if the underlying condition is not promptly corrected
- 11. POSTRENAL AKI Postrenal AKI is due to obstruction of urinary outflow Bladder outlet obstruction Benign prostatic hypertrophy Prostate cancer Anticholinergic drug Ureteral obstruction Malignancy Pelvic / renal obstruction Postrenal AKI accounts for less than 10% of cases of AKI Rapid resolution of Postrenal AKI without structural damage restore kidney function
- 13. By monitoring Scr on a routine basis, it can be estimated whether kidney function is improving or worsening. Kidney function can also be evaluated based on urine output. Oliguria and anuria Oliguria is defined as urine outputs of less than 400 ml over 24 hours anuria is defined as urine output of less than 50 mL over 24 hours.
- 14. CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS OF AKI Peripheral edema Weight gain Nausea/vomiting/diarrhea/anorexia Mental status changes Fatigue Shortness of breath Pruritus
- 15. LABORATORY TESTS Elevated Scr (normal range approximately 0.6-1.2 mg/dL [53 to 106 μmol/L]) Elevated BUN concentration (normal range approximately 8 to 25 mg/dL [2.9-8.9 mmol/L]) Decreased CrCl (normal 90–120 mL/min) BUN: creatinine ratio greater than 20:1 in Prerenal AKI Less than 20:1 in intrinsic or Postrenal AKI Hyperkalemia Metabolic acidosis
- 16. PREVENTION APPROACHES Non-pharmacology for prevention Hydration to prevent contrast induced nephrotoxicity KDIGO guideline recommend using normal saline or sodium bicarbonate infusion Normal saline regimen: 1ml/kg/h for 12hours before and after procedure. Sodium bicarbonate regimen: 3ml/kg/hours for one hour before procedure and 1ml/kg/hours for 6 hours postcontrast.
- 17. PHARMACOLOGICAL THERAPY For prevention of CIN Ascorbic acid:3g orally pre and 2mg orally for two doses postprocedure and N-acetylcysteine(600-1200mg orally every 12 hours for 2-3 days, the first two doses precontrast Current KDIGO guideline suggest moderate control of blood glucose to level of 110-149 mg/dl with insulin prevent ICU-Acquired AKI
- 18. TREATMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
- 19. Goal of treatment: Minimize the degree of kidney insult Reduce extrarenal complication Restoration of renal function to pre AKI is the ultimate goal
- 20. TREATMENT APPROACHES Currently, there is no definitive therapy for AKI, supportive care is the mainstay of management regardless of etiology.
- 21. SUPPORTIVE CARE IN AKI Supportive care includes : Adequate nutrition, correction of electrolyte and acid-base abnormalities (particularly hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis) Fluid management, Correction of any hematologic abnormalities Medical management of infections, cardiovascular and GI conditions, and respiratory failure all drugs should be reviewed, and dosage adjustments made based on an estimate of the patient’s GFR.
- 22. NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL THERAPY Maintenance of adequate cardiac output and blood pressure to optimize tissue perfusion Discontinue medication associated with diminished renal blood flow Initiate appropriate fluid and electrolyte Renal replacement therapy RRT in sever AKI Hemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Absolute indications for dialysis usually include: BUN greater than 100 mg/dL (35.7 mmol/L) Potassium greater than 6 mEq/L (6 mmol/L) Magnesium greater than 9.7 mg/dL (4.0 mmol/L) Metabolic acidosis with a pH less than 7.15 Diuretic-resistant fluid overload.
- 24. PHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY Loop diuretics : are effective to reduce fluid overload. it can worsen AKI. Thiazide diuretics, when used as single agents, are generally not effective for fluid removal. Mannitol is also not recommended for treating volume overload associated with AK. Potassium sparing diuretics are not recommended. low dose dopamine LDD is not indicated in treating the AKI.
- 25. Equipotent dose of loop diuretics (Furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide and ethacrinic acid ) all have similar efficacy Ethacrynic acid is reserved for sulfa-allergic patient Continues infusion of loop diuretic overcome diuretic resistance associated with less adverse effect than intermittent bolus Dose: Initial iv loading dose equivalent to (40-60mg furosemide ) Continuous infusion equivalent to 10-20mg/h
- 26. STRATEGY TO OVERCOME DIURETIC RESISTANCE Administration of agents from different pharmacological classes, they act synergistically Thiazide (works on: distal convoluted tubule) loop diuretics (works on: ascending loop of Henle)
- 28. ELECTROLYTE MANAGEMENT Serum electrolyte should be monitored daily. Hyperkalemia is the most common and serious electrolyte abnormality in AKI Hypernatremia and fluid retention commonly occur …require daily calculation of sodium intake Phosphorus and magnesium should be monitored
- 29. PREVENTION OF ACUTE RENAL FAILURE Avoidance The best preventive measure for AKI, especially in individuals at high risk, is to avoid medications that are known to precipitate AKI. Nephrotoxicity is a significant side effect of aminoglycosides, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor antagonists(ARBs),(what are the risk factors?) Amphotericin B NSAIDs Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, Radiographic contrast agents GFR less than 60 mL/min , diabetes, dehydration, age more than 65 years, How to reduce CI-AK?
