This document provides an outline for deriving the Boltzmann equation in cosmology. It begins with a brief introduction to modern cosmology and thermal physics. It then discusses the Boltzmann equation, describing its development by Ludwig Boltzmann. It proceeds to derive the photon Boltzmann equation in an expanding universe, considering terms for the expansion of the universe, curvature, and gravitational potential. Finally, it discusses using the Boltzmann equation to study the evolution of cosmic structure and perturbations to the distribution function, including compton scattering terms.








![The Boltzmann Equation
df
dt
= C[f]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theboltzmannequationincosmology13-160904081546/85/The-Boltzmann-Equation-in-Cosmology-12-320.jpg)

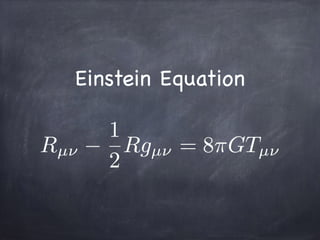





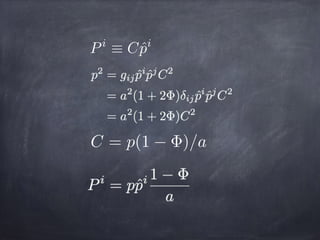
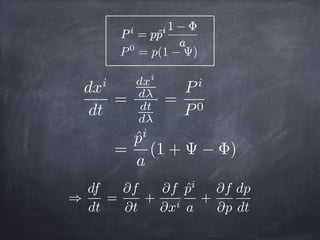

![We get Boltzmann equation
)
df
dt
=
@f
@t
+
@f
@xi
ˆpi
a
@f
@p
p[H +
@
@t
+
ˆpi
a
@
@xi
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theboltzmannequationincosmology13-160904081546/85/The-Boltzmann-Equation-in-Cosmology-23-320.jpg)
![Perturbed
Distribution Function
f = [exp{
p
T(1 + ⇥)
} 1] 1
'
1
ep/T 1
+ (
@
@T
[exp{
p
T
1}] 1
)T⇥
= f(0)
p
@f(0)
@p
⇥
Assume f = [exp{
p
T(1 + ⇥)
} 1] 1
f(0)
=
1
e
p
T 1
T
@f(0)
@T
= p
@f(0)
@p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theboltzmannequationincosmology13-160904081546/85/The-Boltzmann-Equation-in-Cosmology-24-320.jpg)
![Zero-Order
df
dt
=
@f(0)
@t
Hp
@f(0)
@p
= 0
@f(0)
@t
=
@f(0)
@T
dT
dt
=
dT/dt
T
p
@f(0)
@p
[
dT/dt
T
da/dt
a
]
@f(0)
@p
= 0
dT
T
=
da
a
) T /
1
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theboltzmannequationincosmology13-160904081546/85/The-Boltzmann-Equation-in-Cosmology-25-320.jpg)
![C[f] for Compton Scattering
e (!q ) + (!p ) $ e (!q 0
) + (!p 0
)
C[f(!p )] =
X
!q ,!p 0,!p
| Amplitude |2
{fe(!q 0
)f(!p 0
) fe(!q )f(!p )}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theboltzmannequationincosmology13-160904081546/85/The-Boltzmann-Equation-in-Cosmology-27-320.jpg)
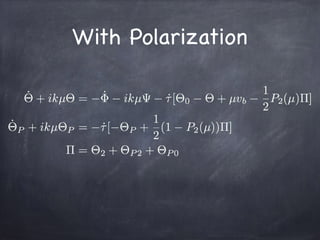
![First-Order
@⇥
@t
+
ˆpi
a
@⇥
@xi
+
@
@t
+
ˆpi
a
@
@xi
= ne T [⇥0 ⇥ + ˆp · !v b]
dt ⌘ ad⌘
µ ⌘
!
k · ˆp
k
˙⌧ ⌘
d⌧
d⌘
= ne T a
Fourier Transform
˙˜⇥ + ikµ˜⇥ + ˙˜ + ikµ˜ = ˙⌧[˜⇥0
˜⇥ + µ˜vb]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theboltzmannequationincosmology13-160904081546/85/The-Boltzmann-Equation-in-Cosmology-28-320.jpg)