IB Chemistry on Acid Base, pH Scale and Ionic Product Water, Kw
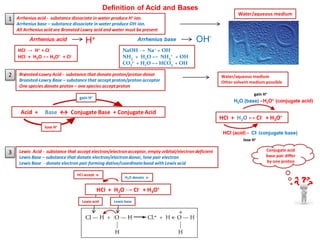
- 1. Brønsted-Lowry Acid - substance that donate proton/proton donor Bronsted-Lowry Base – substance that accept proton/proton acceptor One species donate proton – one species accept proton Arrhenius acid - substance dissociate in water produce H+ ion. Arrhenius base – substance dissociate in water produce OH-ion. All Arrhenius acid are Bronsted Lowry acid and water must be present HCI → H+ + CI- HCI + H2O ↔ H3O+ + CI- NaOH → Na+ + OH- NH3 + H2O ↔ NH4 + + OH- CO3 2- + H2O ↔ HCO3 - + OH- Water/aqueous medium Water/aqueous medium Other solvent medium possible Definition of Acid and Bases Arrhenius acid Arrhenius baseH+ OH- 2 1 gain H+ Acid + Base ↔ Conjugate Base + Conjugate Acid lose H+ HCI (acid) - CI- (conjugate base) lose H+ H2O (base) - H3O+ (conjugate acid) HCI + H2O ↔ CI- + H3O+ gain H+ Lewis Acid - substance that accept electron/electronacceptor, empty orbital/electrondeficient Lewis Base – substance that donate electron/electrondonor, lone pair electron Lewis Base - donate electron pair forming dative/coordinatebond with Lewis acid 3 HCI + H2O → CI- + H3O+ H2O donate e- HCI accept e- Lewis acid Lewis base Conjugate acid base pair differ by one proton
- 2. Physicalproperties of Acid • Substancedissolvesin water produce hydrogen ion/H+ or hydronium /H3O+ • HCI → H+ + CI- • Conduct electricity – free movingions • Sour, pH < 7 • Turn blue litmus red • Turn phenolphthaleincolourless • Turns methyl orange to red Properties of Acids and Bases Acid+ Metal (above H) → Salt + H2 gas 2HCI + Mg → MgCI2 + H2 Acid + Base → Salt + Water + product. Bases are - Metal Hydroxide,Metal Oxide, Metal Carbonates Acid + Metal Hydroxide → Salt + Water Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide Acid + Ammoniaaq and Amines → Salt + water HCI + NH4OH → NH4CI + H2O HCI + CH3NH2 → CH3NH3 + CI- Chemical properties of Acids / Bases Physical properties of Acid Physical properties of Bases • Substance dissolvesin water produce hydroxide/OH- ion • NaOH → Na+ + OH- • Conduct electricity– free moving ions • Bitter, pH > 7 • Turns red litmus blue • Turns phenolphthalein pink • Turns methyl orange to yellow Physical properties of Base Physical Properties Chemical Properties Physical Properties Chemical Properties Hydronium/Hydroxonium/Oxonium
- 3. Physicalproperties of Acid • Electrolytes,produce H3O+,hydronium ion • Conduct electricity • Sour, pH < 7 • Turn litmus red • Turn phenolphthaleincolourless • Turn methyl orange to red Physicalproperties of Base • Bitter,pH > 7 • Turn litmus blue • Turn phenolphthaleinpink • Turn methyl orange to yellow Physical/ChemicalProperties of Acids and Bases Chemical properties of Acid / BasePhysical properties of Acid/Base Bases Acid + Metal Hydroxide (Alkali) → Salt + Water LiOH + HCI → LiCI + H2O NaOH + HNO3 → NaNO3 + H2O KOH + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + H2O Acid + Metal Hydroxide (Insoluble) → Salt + Water Ca(OH)2 + 2HCI → CaCI2 + 2H2O Fe(OH)2 + 2HNO3 → Fe(NO3)2 + 2H2O Mg(OH)2 + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + 2H2O Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water CaO + 2HCI → CaCI2 + H2O CuO + 2HCI → CuCI2 + H2O Acid + Alkali Acids + Metal Oxide Acid + Metal Hydroxide Acid + Metal Carbonate Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt, Water + CO2 CaCO3 + 2HCI → CaCI2 + H2O + CO2 CuCO3 + 2HCI → CuCI2 + H2O + CO2 Acid+ Metal (above H) → Salt + H2 gas 2HCI + Mg → MgCI2 + H2 Acid + Base → Salt + Water + product. Bases are - Metal Hydroxide,Metal Oxide, Metal Carbonate Acid + Metal Hydroxide → Salt + Water Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide Acid + Ammoniaaq and Amines → Salt + water HCI + NH4OH → NH4CI + H2O HCI + CH3NH2 → CH3NH3 + CI-
- 4. CH3COOH ↔ H+ + CH3COO- (1 mole) (0.01 mole) Strong Acid / Base Weak Acid / Base Strong acid – ionise/dissociate completelyproducing H+ ion Strong base – ionise/dissociate completelyproducing OH- ion All are in ions state, NO molecule left Strong electrolytewith high conductivity ↑ Weak acid – ionise/dissociate partially producing H+ ion Weak base – ionise/dissociate partiallyproducing OH- ion Most in undissociated molecule form Poor electrolytewith low conductivity↓ HCI → H+ + CI- HBr → H+ + Br− Monoprotic acid - 1 mole H+ ion Diprotic acid - 2 mole H+ ion H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO4 2- (1 mole) (2 mole) Strong Acid - HI, HBr, HCI, HNO3, H2SO4, HCIO3, HCIO4 Strong Base - LiOH, KOH, NaOH, CsOH, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 Weak Acid - CH3COOH, HF, HCN, H2CO3, H3BO3, HNO2, H3PO4 Weak Base - NH3, C2H5NH2 , CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, C3H5O2NH2 Weak acid dissociate partially produce few H+ ion NH3 + H2O ↔ NH4 + + OH- C2H5NH2 + H2O ↔ C2H5NH3 + + OH- CO3 2- + H2O ↔ HCO3 - + OH- Weak base dissociate partially produce few OH- ion Vs Example of Strong Acid/Base Example of Weak Acid/Base Ba(OH)2 → Ba2+ + 2OH− (1 mole) (2 mole) (1 mole) (1 mole) Dissociatecompletely No moleculesleft All ion form Few ions form Dissociatepartially Molecules left Monoprotic base - Accept 1 mole H+ ions by 1mole OH- Na(OH) → Na+ + OH− (1 mole) (1 mole) All ion form Dissociatecompletely No moleculesleft Few ions form Dissociatepartially Molecules left H3PO4 ↔ H+ + H2PO4 - H2PO4 - ↔ H+ + HPO4 2- HPO4 2- ↔ H+ + PO4 3- H3PO4 ↔ 3H+ + PO4 3- Diprotic base - Accept 2 mole H+ ions by 2 mole OH- Weak triprotic acid dissociate partially produce few H+ ion One way reversible reversible One way One way reversible
- 5. CH3COOH ↔ H+ + CH3COO- (1 mole) (0.01 mole) Strong Acid / Base Weak Acid / Base Strong acid – ionise/dissociate completelyproducing H+ ion Strong base – ionise/dissociate completelyproducing OH- ion All are in ionic ions state Strong electrolytewith high conductivity ↑ Weak acid – ionise/dissociate partiallyproducing H+ ion Weak base – ionise/dissociate partiallyproducing OH- ion Most in undissociated molecule form Poor electrolytewith low conductivity↓ HCI → H+ + CI- HBr → H+ + Br− Monoprotic acid - produce 1 mole H+ ions Diprotic acid - 2 mole H+ H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO4 2- Strong acid - HI, HBr, HCI, HNO3, H2SO4, HCIO3, HCIO4 Strong base - LiOH, KOH, NaOH, CsOH, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 (1 mole) (2 mole) Weak Acid - CH3COOH, HF, HCN, H2CO3, H3BO3, H3PO4 Weak Base - NH3, C2H5NH2 , (CH3)2NH, C3H5O2NH2 Weak acid dissociate partially produce few H+ ion NH3 + H2O ↔ NH4 + + OH- C2H5NH2 + H2O ↔ C2H5NH3 + + OH- CO3 2- + H2O ↔ HCO3 - + OH- Weak bases dissociate partially produce few OH- ion Vs Example Strong Acid/Base Example Weak Acid/Base Concentrated Acid / Base Diluted Acid / Base Concentrated Acid – High number of mole/amt of solute per dm3 1 M HCI – 1 mole of HCI moleculesin 1 dm3 10 M HCI – 10 mole of HCI moleculesin 1 dm3 Diluted Acid – Low number of mole/amt of solute per dm3 0.1M HCI – 0.1 mole of HCI molecule in 1 dm3 0.01M HCI – 0.01 mole of HCI molecule in 1 dm3 ConcentratedAcid may NOT be a Strong Acid 10M CH3COOH – Concentrated Acid ↑ but Weak Acid ↓ DilutedAcid may be a Strong Acid 0.01M HCI – DilutedAcid ↓ but Strong Acid ↑ 10M CH3COOH - CONCENTRATED WEAK acid because 10M acid molecule will dissociate partially forming few H+ ions 0.01M HCI - DILUTED STRONG acid because all 0.01M acid molecule dissociate fully forming H+ ions Vs Diprotic base - 2 mole OH- Ba(OH)2 → Ba2+ + 2OH− (1 mole) (2 mole) (1 mole) (1 mole)
- 6. Strong/Weak Acid and Base Strong Acid/Weak Acid Strong acid - HI, HBr, HCI, HNO3, H2SO4, HCIO3, HCIO4 Weak Acid - CH3COOH, HF, HCN, H2CO3, H3BO3, H3PO4 Strong Base/ Weak Base Strong base - LiOH, KOH, NaOH, CsOH, Ca(OH)2 Weak Base - NH3, C2H5NH2, (CH3)2NH, C3H5O2NH2 Distinguishbet strong and weak acid ElectricalconductivityRate of rxn pH Strongacid Strong acid → High ionization → High conc H+ → High conductivity→ High rate rxn → Lower pH Strong acid Oxoacid O atom > number ionizable proton HNO3, H2SO4, HCIO3,HCIO4 Hydrohalicacid HI, HBr, HCI Weak acid Hydrohalicacid HF Oxoacid O atom ≥ number ionizable protonby 1 HCIO, HNO2, H3PO4 Carboxylicacid COOH Strong base – containOH- or O2- LiOH, NaOH, CaO, K2O Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 Weak base – contain electronrich nitrogen, N NH3, C2H5NH2, (CH3)2NH, C3H5O2NH2 Strong base Weak base 1 2 3 Weak acid 0.1 M HCI 0.1 M CH3COOH H+ 0.1 mole 0.0013 mole pH 1 (Low) 2.87 (High) Electrical conductivity High (Ionize completely) Low (Ionize partially) Rate with magnesium Fast Slow Rate with calcium carbonate Fast Slow Weaker acid → Low ionization → Low conc H+ → Low conductivity→ Low rate rxn → High pH Strong acid HA A-H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+A- A- A- A- A- A- Ionizes completely Weak acid HA HA H+ A- H+ H+ A- A- HA HA HA HA HA HA Ionizes partially
- 7. Easier using pH scale than Conc [H+] • Conc H+ increase 10x from 0.0001(10-4) to 0.001(10-3) - pH change by 1 unit from pH 4 to 3 • pH 3 is (10x) more acidic than pH 4 • 1 unit change in pH is 10 fold change in Conc [H+] Conc OH- increase ↑ by 10x pH increase ↑ by 1 unit pOH with Conc OH- pOH = -log [OH- ] [OH- ] = 0.0000001M pOH = -log [0.0000001] pOH = -log1010-7 pOH = 7 pH + pOH = 14 pH + 7 = 14 pH = 7 (Neutral) pH with Conc H+ pH = -log [H+ ] [H+ ] = 0.0000001M pH = -log [0.0000001] pH = -log1010-7 pH = 7 (Neutral) Conc H+ increase ↑ by 10x pH decrease ↓ by 1 unit pH measurement of Acidity of solution • pH is the measureof acidity of solutionin logarithmicscale • pH = powerof hydrogenor minuslogarithmto base ten of hydrogenion concentration ← Acidic – pH < 7 Alkaline – pH > 7 → pOH with Conc OH- pOH = -log [OH- ] [OH- ] = 0.1M pOH = -log[0.1] pOH = 1 pH + pOH = 14 pH + 1 = 14 pH = 13 (Alkaline) pH with Conc H+ pH = -log [H+ ] [H+ ] = 0.01M pH = -log [0.01] pH = -log1010-2 pH = 2 (Acidic) Easier pH scaleConc H+
- 8. Conc [H+ ] = 1 x 10-12 pH = -lg[H+ ] pH = -lg[10-12 ] pH = 12 Conc [OH- ]= 1 x 10-2 pOH = -log10[OH-] pOH = -log1010-2 = pOH = 2 pH + pOH = 14 pH + 2 = 14 pH = 12 Conc [H+ ] = 1 x 10-2 pH = -lg[H+ ] pH = -lg[10-2 ] pH = 2 Alkaline Alkaline Acidic Acidic Kw - Ionic product constant water Using conc [H+] pH = -log10[H+] pH = -log10[H+] pOH = -log10[OH-] pH + pOH = 14 Kw = [H+][OH-] Using conc [OH-] pOH = -log10[OH-] Conc[OH- ]= 1 x 10-12 pOH = -log10[OH-] pOH= -log1010-12 =pOH = 12 pH + pOH = 14 pH + 12 = 14 pH = 2 Formula for acid/basecalculation 22 3 OH OHOH Kc OHOHOHKc 3 2 2 OHOHKw 3 OHOH3 14 100.1 7714 101101100.1 7 101 OH OHOHOHOH 322 H2O dissociateforming H3O+ and OH- (equilibriumexist) 14 100.1 wK Dissociation water small [H2O] is constant Kw = 1.0 x 10-14 Ionic Product constantwater at -25C Kc - Dissociation constant water 7 3 101 OH
- 9. 0.2 01.0log log 10 10 pH pH HpH 22 3 OH OHOH Kc OHOHKOHK wc 3 2 2 OHOH3 14 100.1 7714 101101100.1 OHOHOHOH 322 H2O dissociateforming H3O+ and OH- (equilibriumexist) 14 100.1 wK Dissociation water small [H2O] is constant Kw - Ionic product constant water Kw = 1.0 x 10-14 Ionic Product constant water at -25C Kc - Dissociation constant water Cal conc of H+ ,OH- and pH of water Cal conc of H+ ,OH- and pH of 0.01M HCI OHHOH2 OHHKw OHH14 100.1 7714 101101100.1 7 101 H H2O H2O HCI OHHOH2 H2O OHHKw OHH14 100.1 Assuming H+ all from HCI = 0.01 )()( 2OHHHCIHH H+ = 0.01 + 1.0x10-12 = 0.01 + 0.000000000001 ≈ 0.01 OHHOH2 H+ = 1x10-12 OH- = 1x10-12 CIHHCI 0.01 mol 0.01 mol0.01 1 mol ↔ 1 mol 1mol 0.000000000001 0.000000000001 H+ OH- = 0.01 = 0.000000000001 or 0.7 101log 7 10 pH pH 0.21214 12 100.1 01.0 100.1 01.0100.1 12 14 14 pH pOH OH OH
- 10. 22 3 OH OHOH Kc OHOHKOHK wc 3 2 2 OHOH3 14 100.1 7714 101101100.1 OHOHOHOH 322 H2O dissociate forming H3O+ and OH- (equilibrium exist) 14 100.1 wK Dissociation water small [H2O] is constant Kw - Ionic product constant water Kw = 1.0 x 10-14 Ionic Product constant water at -25C Kc - Dissociation constant water Cal conc of H+ ,OH- and pH of 0.01M KOH Cal conc of H+ ,OH- and pH of 0.1M H2SO4 7.0 2.0log log 10 10 pH pH HpH H2O KOH H2SO4 OHHOH2 H2O OHHKw OHH14 100.1 Assuming H+ all from H2SO4 = 0.2 7.03.1314 3.13 100.5 2.0 100.1 2.0100.1 14 14 14 pH pOH OH OH )()( 242 OHHSOHHH H+ = 0.2 + 5 x 10-14 = 0.2 + 0.000000000000005 ≈ 0.2 OHHOH2 H+ = 5x10-14 OH- = 5x10-14 2 442 2 SOHSOH 0.1 mol 0.2 mol 0.2 1 mol ↔ 1 mol 1 mol 0.00000000000005 0.0000000000005 H+ OH- = 0.2 = 0.00000000000005 OHHOH2 1 mol ↔ 1 mol 1 mol OHHOH2 OHHKw OHKKOH 0.01 mol 0.01 mol 0.01 Assuming OH- all from KOH = 0.01 )()( 2OHOHKOHOHOH = 0.01 = 0.000000000001 12 10log log 101 01.0 100.1 01.0100.1 12 10 10 12 14 14 pH pH HpH H H or H+ = 1x10-12 OH- = 1x10-12
- 11. Number sig fig in log calculation Significant number in log calculation log10(3575)=3.55327 = 3.5532 log10(3.000x104) = 4.477121 = 4.4771 log10(3.3 x 104) = 4.5185 = 4.51 Calculation involve pH = -log10[H+] Conc H+ = 1.9 x 10-4 pH= -log10[1.9 x 10-4] = 3.721 = 3.72 Measurement scale not linear • Simple average CANNOT be used • Average of pH 7, pH 8, pH 9 pH scale is logarithmic, pH = -log[H+] Correct average = convert to H+ conc pH 7 = -log10[H+] → H+ = 10-7 pH 8 = -log10[H+] → H+ = 10-8 pH 9 = -log10[H+] → H+ = 10-9 pH pH= -lg10H+ Conc H+ 0 0 = -lg10100 1.0 1 1 = -lg1010-1 0.1 2 2 = -lg1010-2 0.01 3 3 = -lg1010-3 0.001 4 4 = -lg1010-4 0.0001 5 5 = -lg1010-5 0.00001 6 6 = -lg1010-6 0.000001 7 7 = -lg1010-7 0.0000001 8 8 = -lg1010-8 0.00000001 9 9 = -lg1010-9 0.000000001 10 10= -lg1010-10 0.0000000001 11 11= -lg1010-11 0.00000000001 12 12= -lg1010-12 0.000000000001 13 13= -lg1010-13 0.0000000000001 14 14= -lg1010-14 0.00000000000001 Easier using pH scale than Conc [H+] • Low pH – High H+ conc – More acidic • High pH – Low H+ conc – Less acidic • pH 3 (10x) more acidic > than pH 4 • 1 unit change in pH is 10 fold change in Conc [H+] Relationship between pH and Conc H+ Uncertainty involving pH 8 3 987 Average Uncertainty involving pH 4 sig fig 5 sig fig/4 decimal place 4 sig fig 5 sig fig/4 decimal place Conc H+ = 3.2 x 10-5 M pH = - log10[3.2 x 10-5]= 4.4948 = 4.49 2 sig fig 3 sig fig/2 decimal place 2 sig fig3sig fig/2 decimal place 2 sig fig3sig fig/2 decimal place 2 sig fig 3sig fig 2 sig fig3 sig fig 2 sig fig 3 sig fig pH solution = 7.40. Cal conc of H+ ions 7.40 = -log10 [H+] [H+] = 10-7.40 = 4.0 x 10-8 3 sig fig 2 sig fig 2 sig fig 4.7 ]107.3lg[ 107.3 3 101010 8 8 987 pH pH Average Average
- 12. What is pH for [H+ ] = 1 x 10-12 M pH = -lg [10-12 ] pH = 12 What is conc of H+ of pH 3.20? 3.20 = -lg [H+ ] [H+ ] = 10 –2.20 [H+ ] = 6.3 x 10-4 pH = -log10[H+] pOH = -log10[OH-] pH + pOH = 14 Kw = [H+][OH-] Formula acid/basecalculation 2 sig fig 1 sig fig 3 sig fig 2 sig fig What is pH for [OH- ] = 0.15M pOH = -lg [0.15] pOH = 0.823 pH + pOH = 14 pH = 14 – 0.823 = 13.2 pOH = -log[OH-] 3 sig fig 2 sig fig Calculate conc of H+, OH- and pH for 0.0010M HCI. 1 2 3 4 CIHHCI 0.001 ↔ 0.001 0.001 OHHOH2 HCIH2O OHHKw Assuming H+ all from HCI = 0.0010 )()( 2OHHHCIHH = 0.001 Negligible / too little OHH14 100.1 0.3 001.0log log 10 10 pH pH HpH 0.31114 11 101 001.0 100.1 001.0100.1 11 14 14 pH pOH OH OH or Cal conc OH- /pH when3.o x 10-4 H+ add water HCI H2O CIHHCI OHHOH2 OHHKw OHH14 100.1 11 4 14 414 103.3 100.3 100.1 100.3100.1 OH OH 3x10-4 ↔ 3x10-4 52.3 100.3log log 4 10 10 pH pH HpH
- 13. pH weak acid at variousconcentration HCOOCHOHCOOHCH 2323 Extendof dissociationdependon initialconcentrationacid Conc of acid Observed pH CH3COOH CalculatedpH HCI 0.10 2.7 1.0 0.010 3.0 2.0 0.0010 3.5 3.0 0.00010 4.2 4.0 CIHHCI Weak acid Strong acid Dissociate partially Dissociate completely At same acid concentration • HCI has HIGHER[H+] > CH3COOH • HCI has LOWER pH < CH3COOH • HCI dissociate completely - Strong acid • CH3COOH dissociatepartially - Weak acid At decreasing acid concentration • Extend of dissociation for CH3COOH increase • pH weak acid closer to strong acid • Dilution increase the extend of dissociation Conc decrease HCOOCHOHCOOHCH 2323 Trends Addition Water Dilution shift equilibrium to right Decreaseconc of CH3COOH,CH3COO- andH+ Conc on left side is more effecteddue to CH3COO- and H+ Equilibrium shift to right to increase conc of CH3COO- and H+ again Extend of dissociation for acid increase (shift to right) О О Concept Map [H+] [OH-] pH pOH Kw = [H+] x [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 pH + pOH = 14 pH = -lg [H+] [H+] = 10-pH pOH = -lg [OH-] [OH-] = 10-pOH
- 14. Question on Acid and Base Which list contains only strong acids ? A. CH3COOH, H2CO3, H3PO4 B. HCI, HNO3, H2CO3 C. CH3COOH, HNO3, H2SO4 D. HCI, HNO3, H2SO4 When equal volume of four 1M solutions are arranged in order of increasing pH (lowest pH first), what is the correct order? A. CH3COOH < HNO3 < CH3CH2NH2 < KOH B. HNO3 < CH3COOH < CH3CH2NH2 < KOH C. CH3CH2NH2 < HNO3 < CH3COOH < KOH D. KOH < CH3CH2NH2 < CH3COOH < HNO3 pH of a solution changes from pH =2 to pH =5. What happens to the concentrationof H+ ions during this pH change? A. Decrease by factor of 1000 B. Increase by factor of 1000 C. Decrease by factor of 100 D. Increase by a factor of 100 Solution of acid A has a pH of 1 and a solution of acid B has a pH of 2. Which statement is correct ? A. AcidA is stronger than acid B B. [A] > [B] C. Concentrationof H+ ions in A is higher than B D. Concentrationof H+ ions in B is twice the concentrationof H+ in A 100ml of NaOH solution of pH 12 is mixed with 900ml of water. What is the pH of resulting solution? A. 1 B. 3 C. 11 D. 13 1 2 3 4 5 О О О О О List two ways to distinguish between strong and weak acid/base6 By Conductivitymeasurement 1M StrongAcid – Ionise completely– More H+ ion – pH lower ↓ 1M Weak Acid – Ionise partially – Less H+ ion – pH higher ↑ 1M StrongAcid – Ionise completely– More H+ ion – Conductivityhigher ↑ 1M Weak Acid – Ionise partially – Less H+ ion – Conductivitylower ↓ By pH measurement Which methodwill distinguishbet equimolarstrong base and strong acid? i) Add magnesiumto each solutionand observeformationbubbles ii) Add aqueoussodium hydroxideto each solutionand measuretemp change iii) Use each solutionin circuit with battery/lampto see brightnesslamp 7 О О
- 15. Click here on pH calculation Click here on Bronsted Lowry/ Lewis Acid/Base Video on Acid/ Base Click here on Lewis Acid/Base Click here on pH varies with temperature Click here on pKa and pKb calculation
