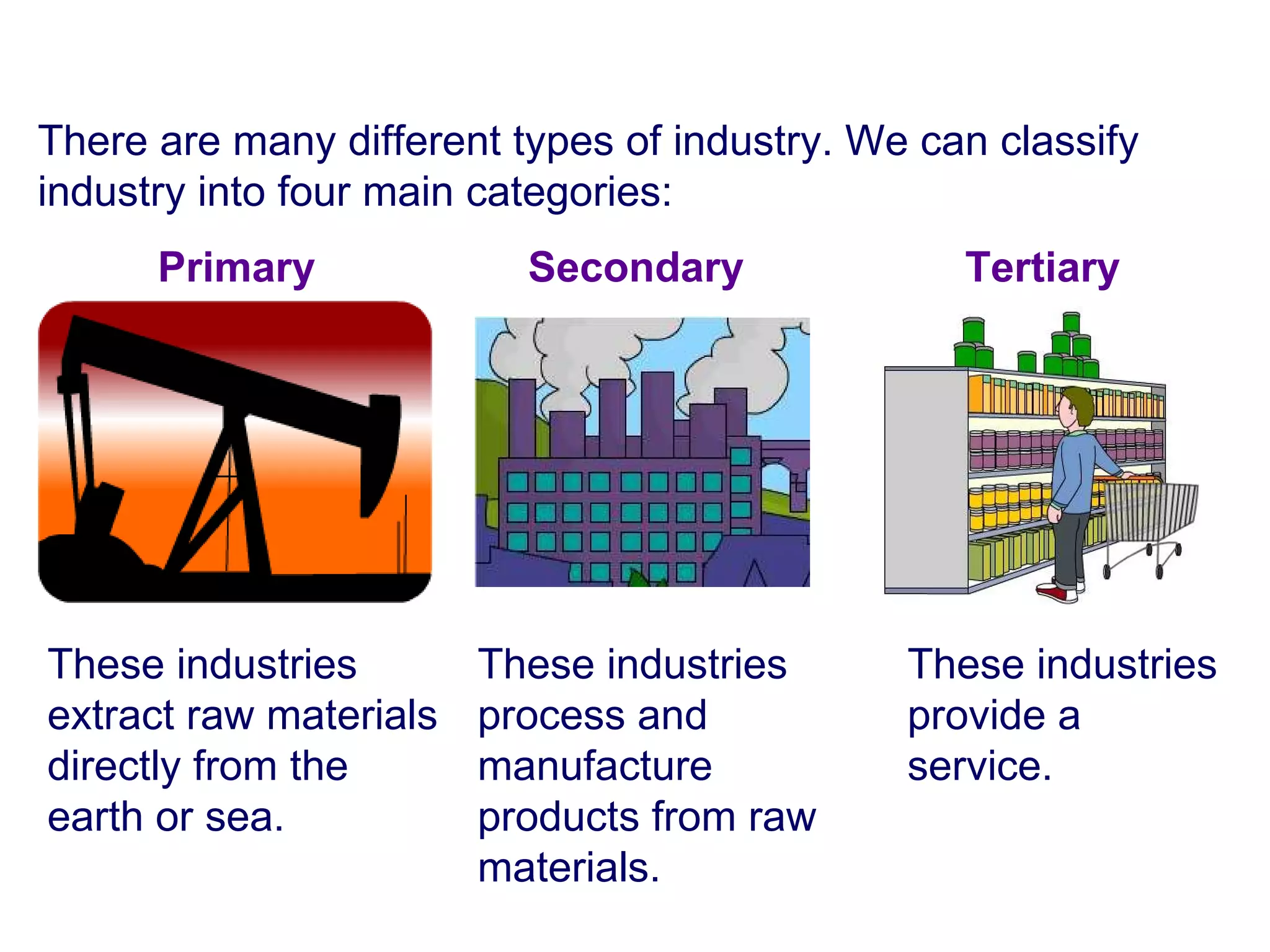
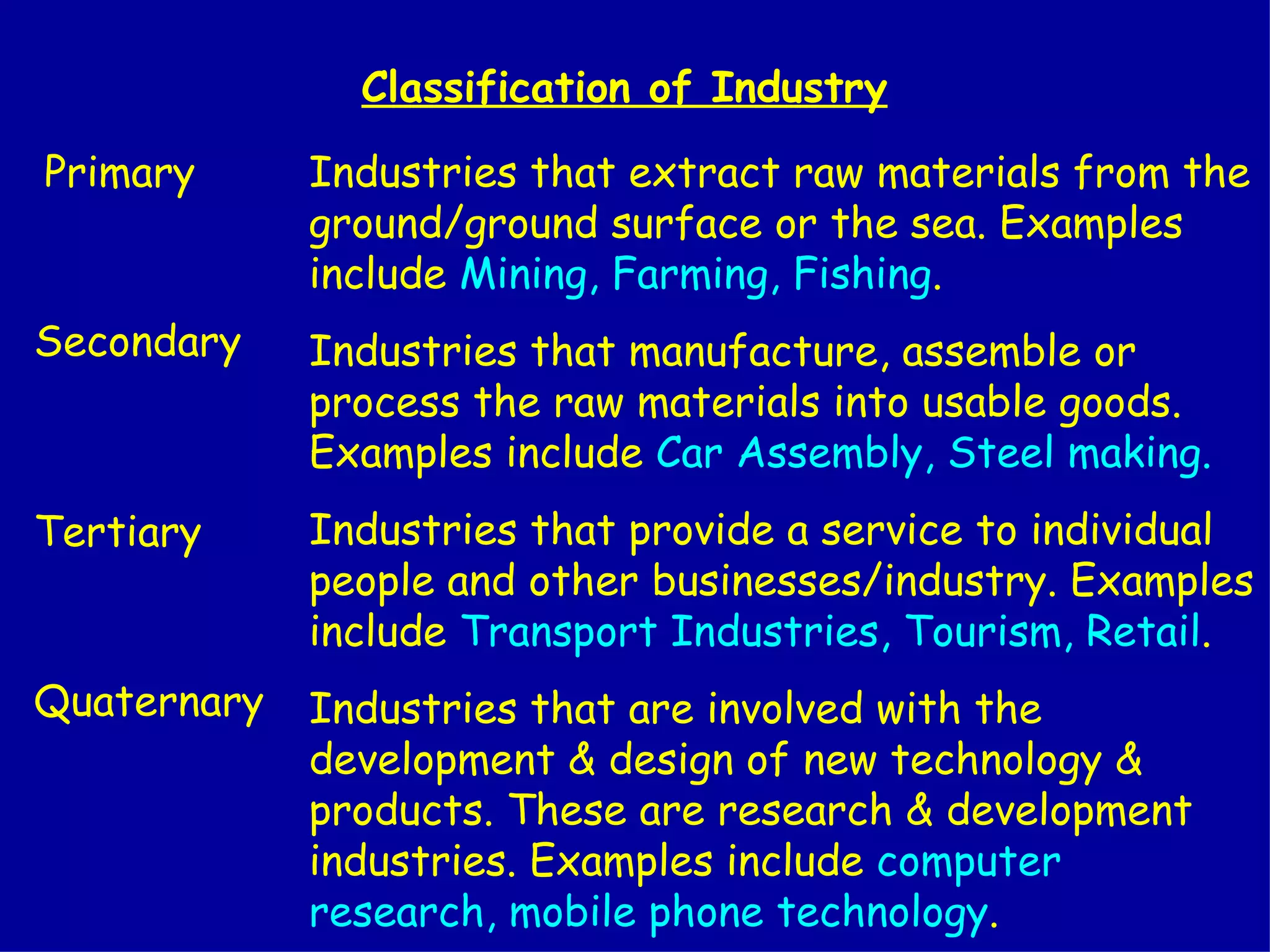
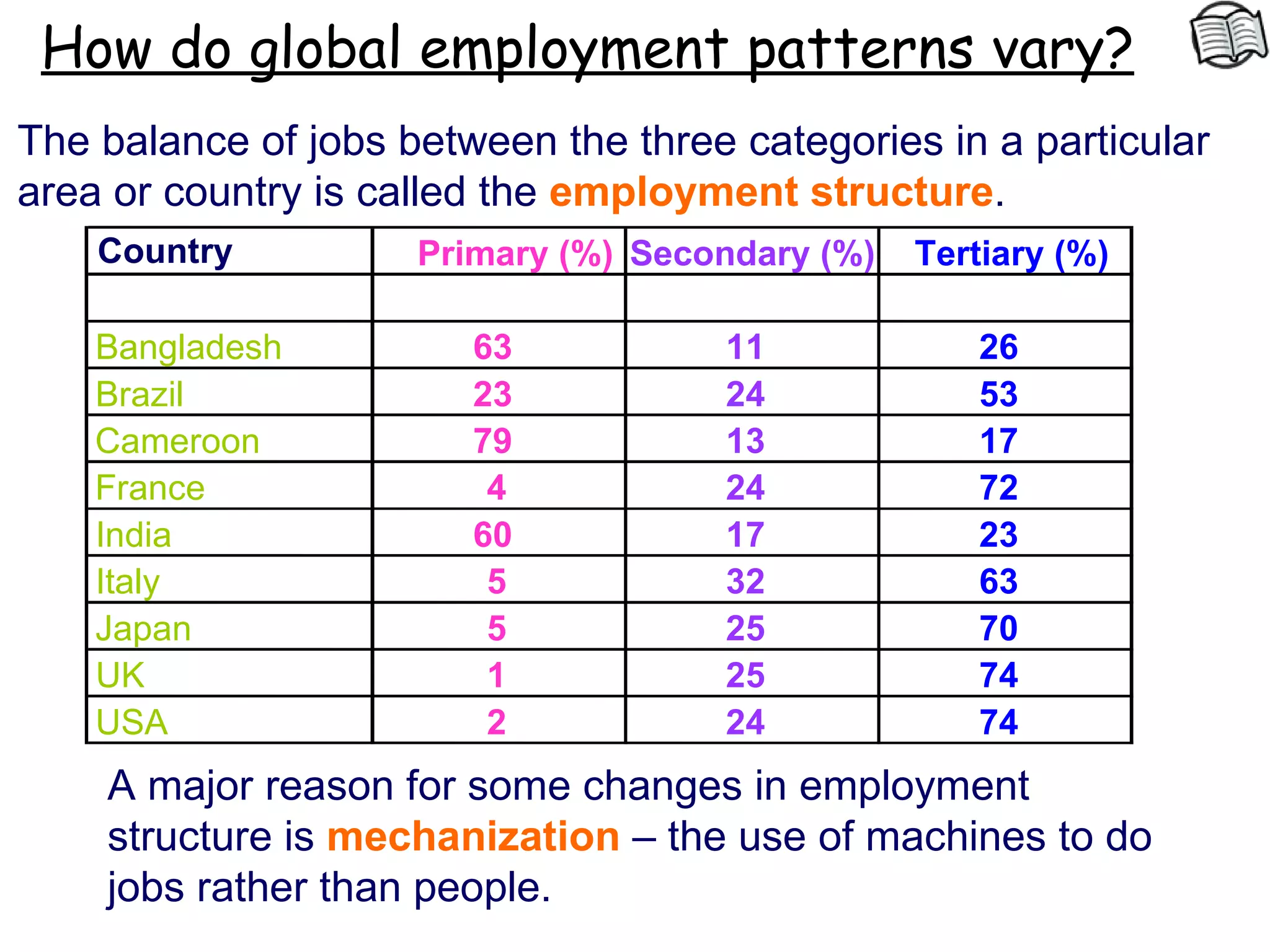
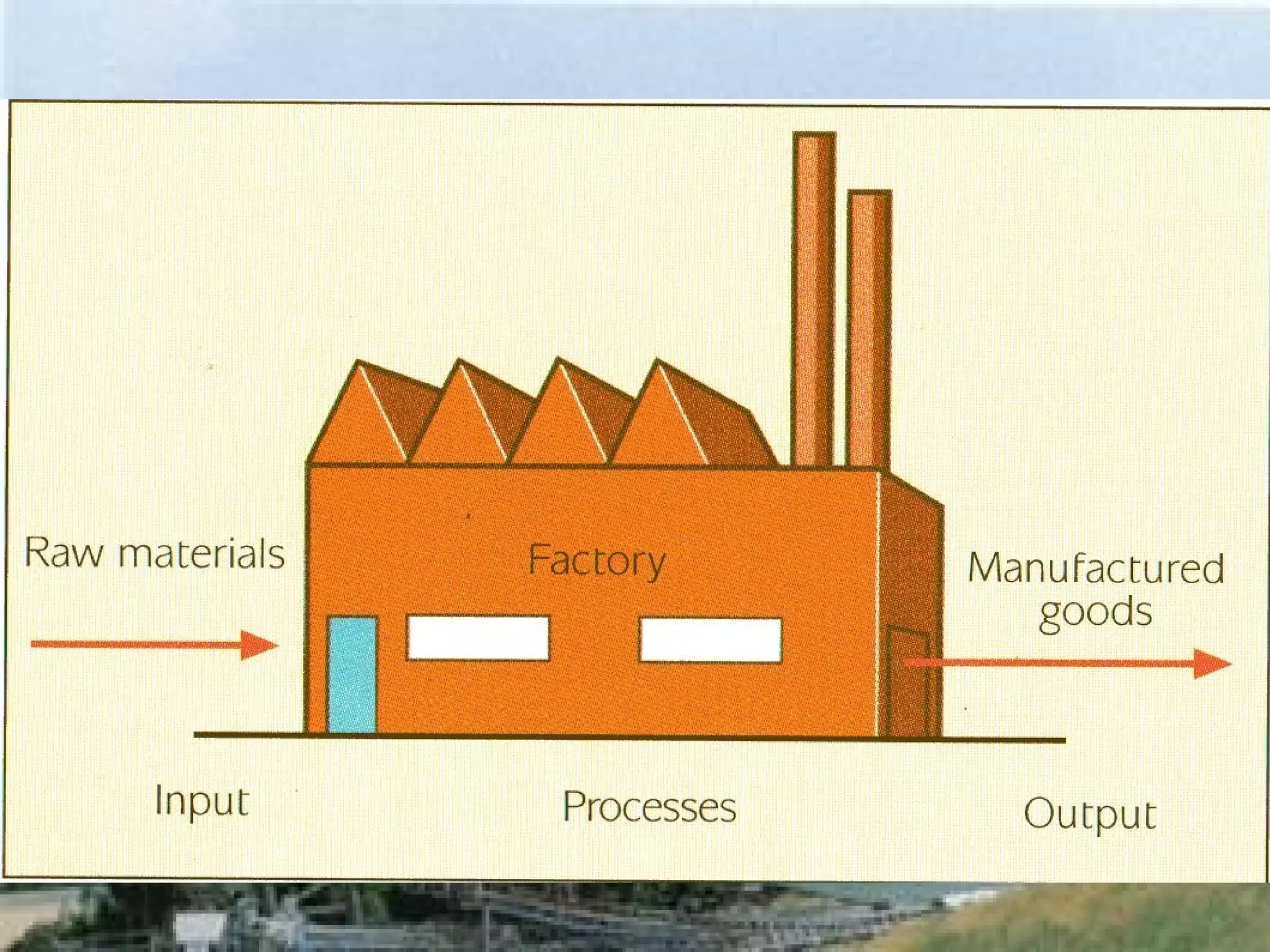
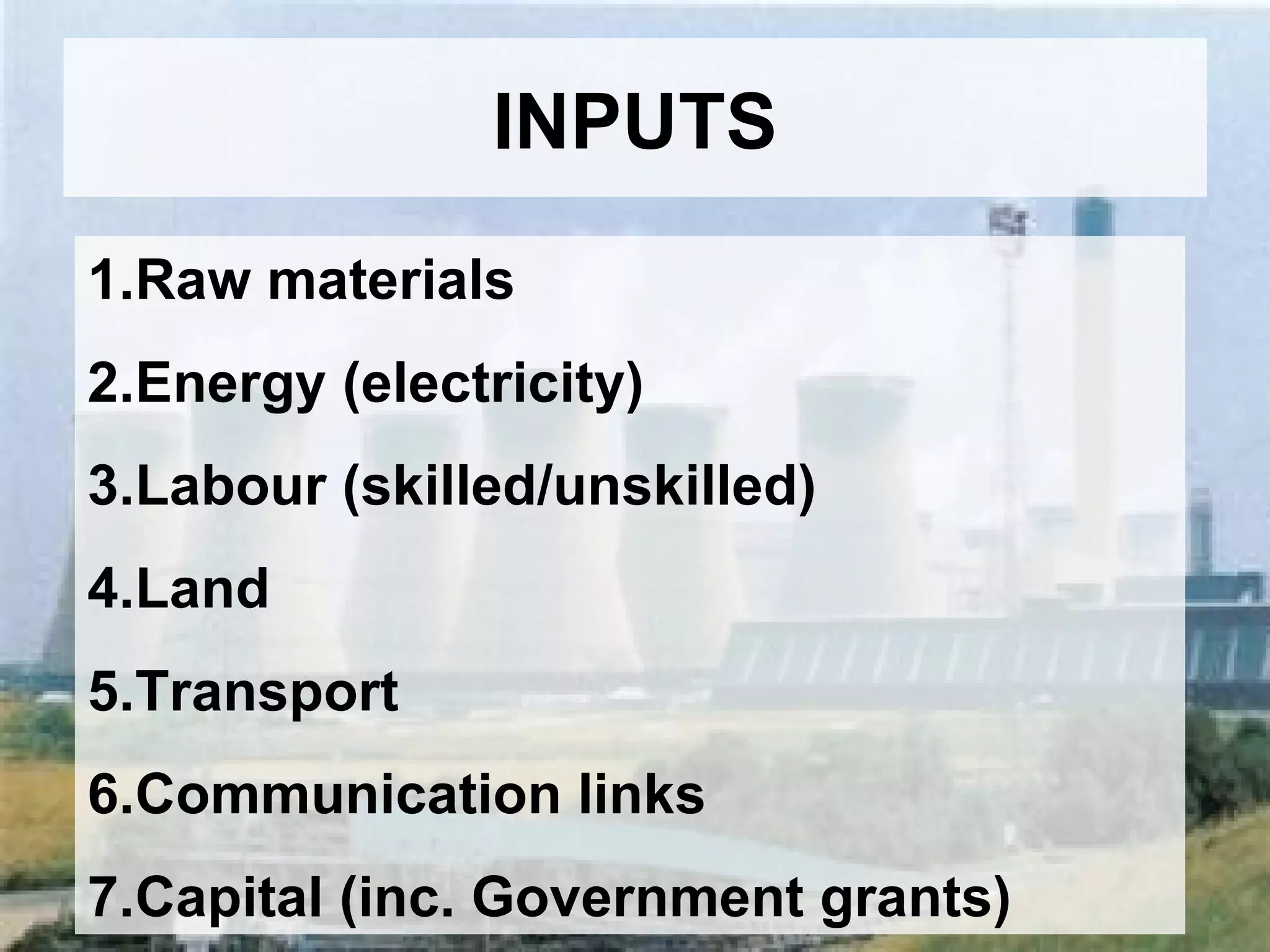
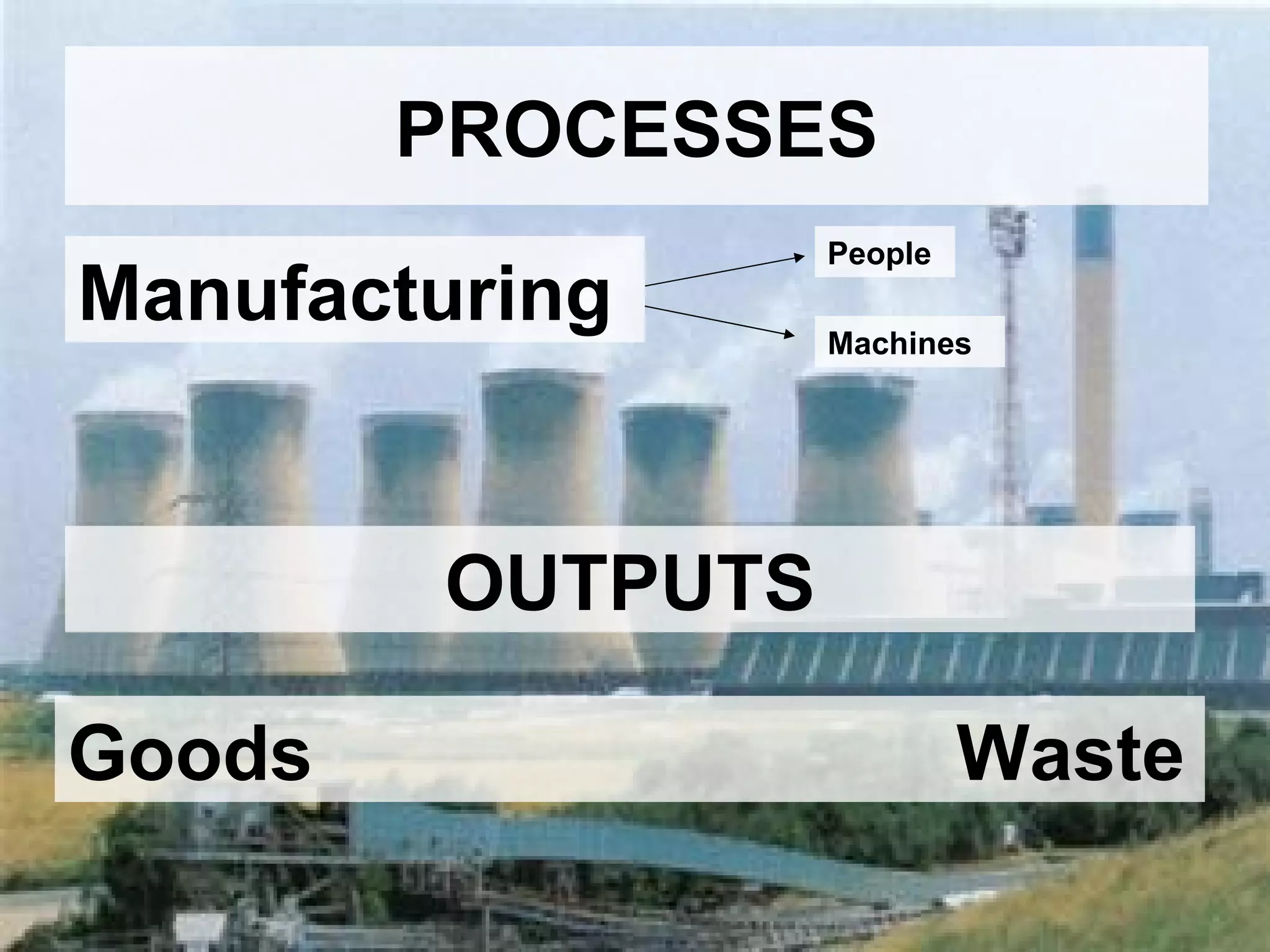
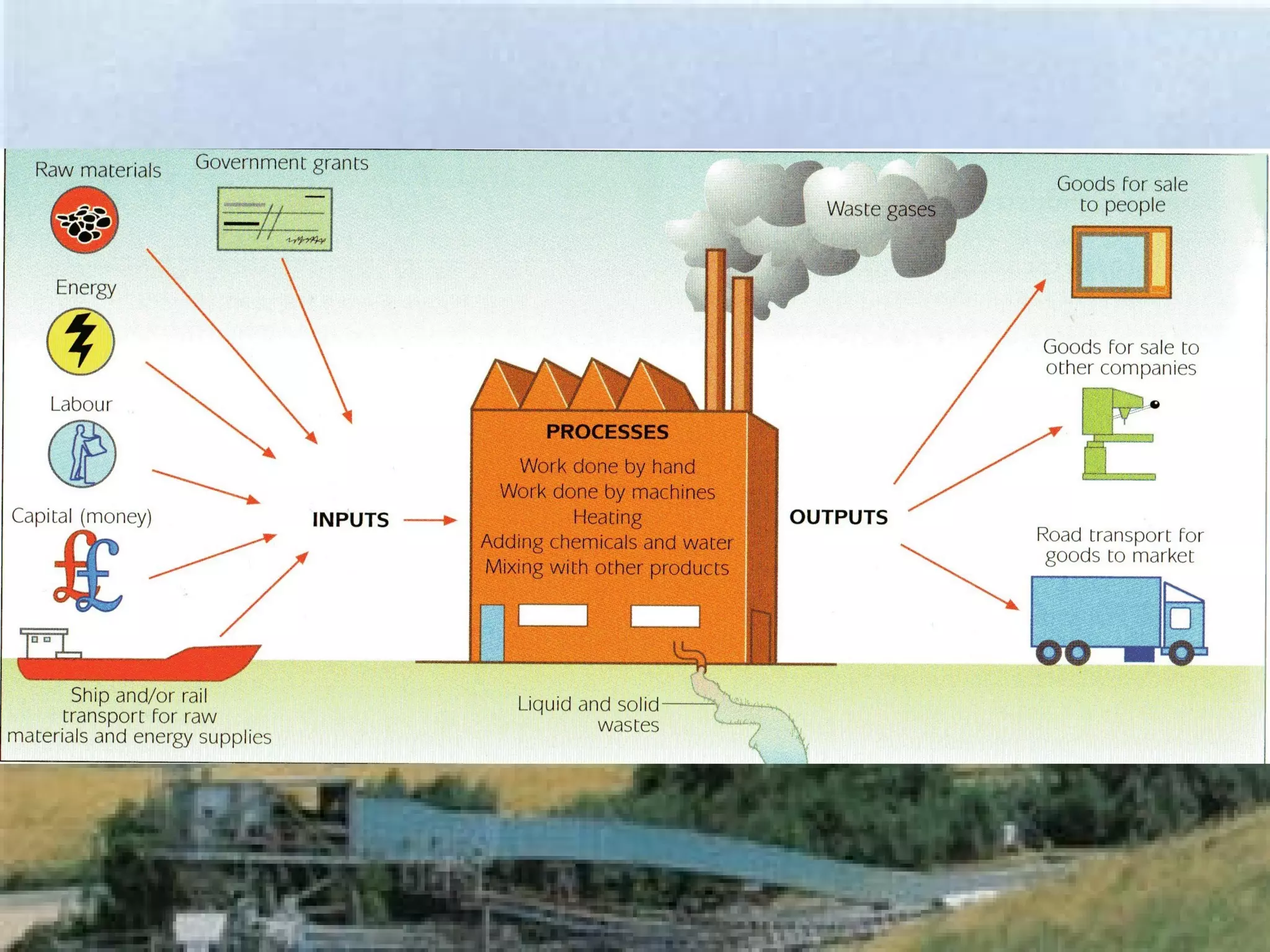
The document discusses different types of industries and how they can be classified. It identifies four main categories of industry: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Primary industries extract raw materials from the earth or sea. Secondary industries process and manufacture raw materials into products. Tertiary industries provide services. Quaternary industries focus on research and technology development. The document also discusses how employment levels in different industry categories vary between countries and over time.