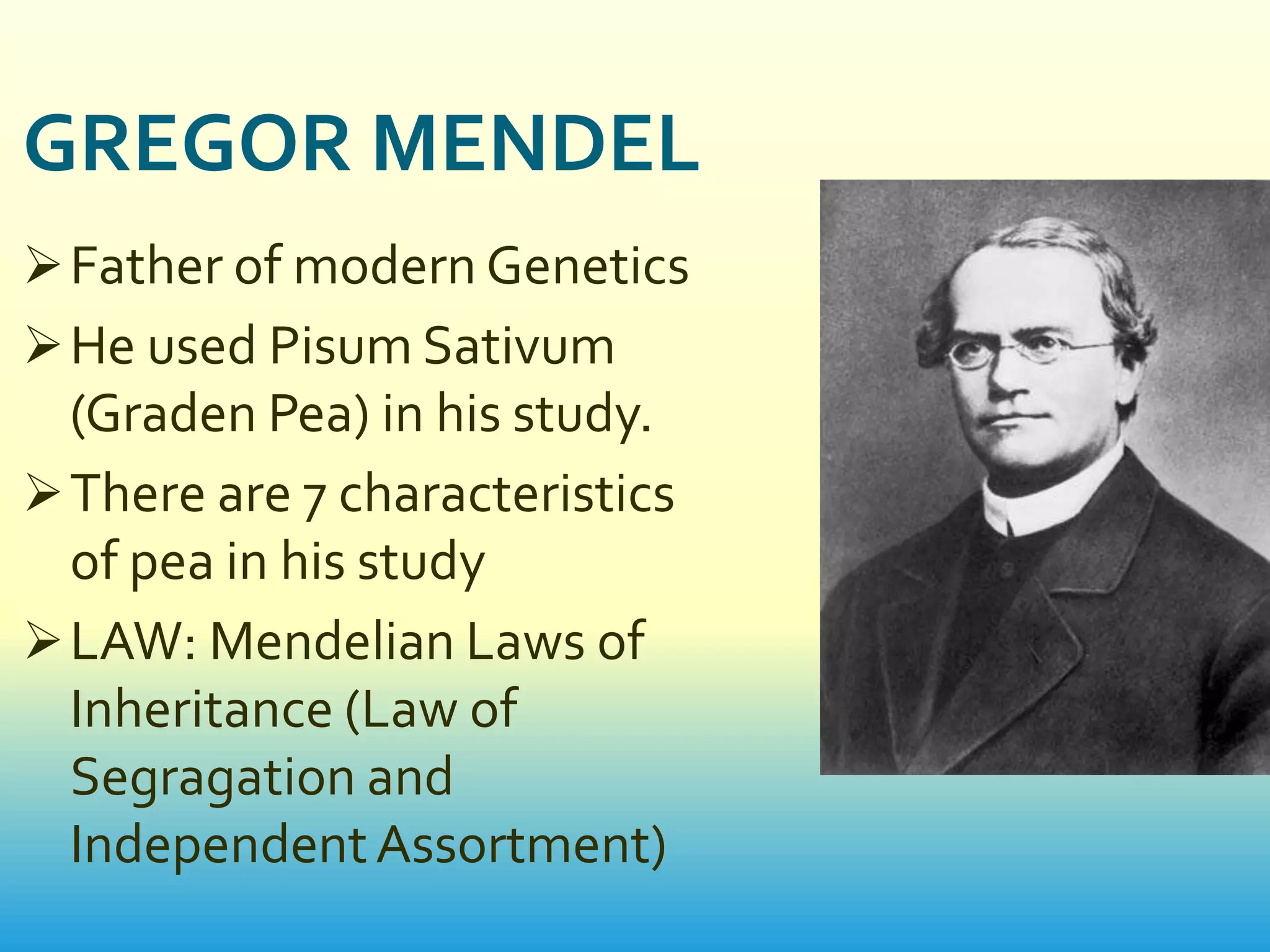
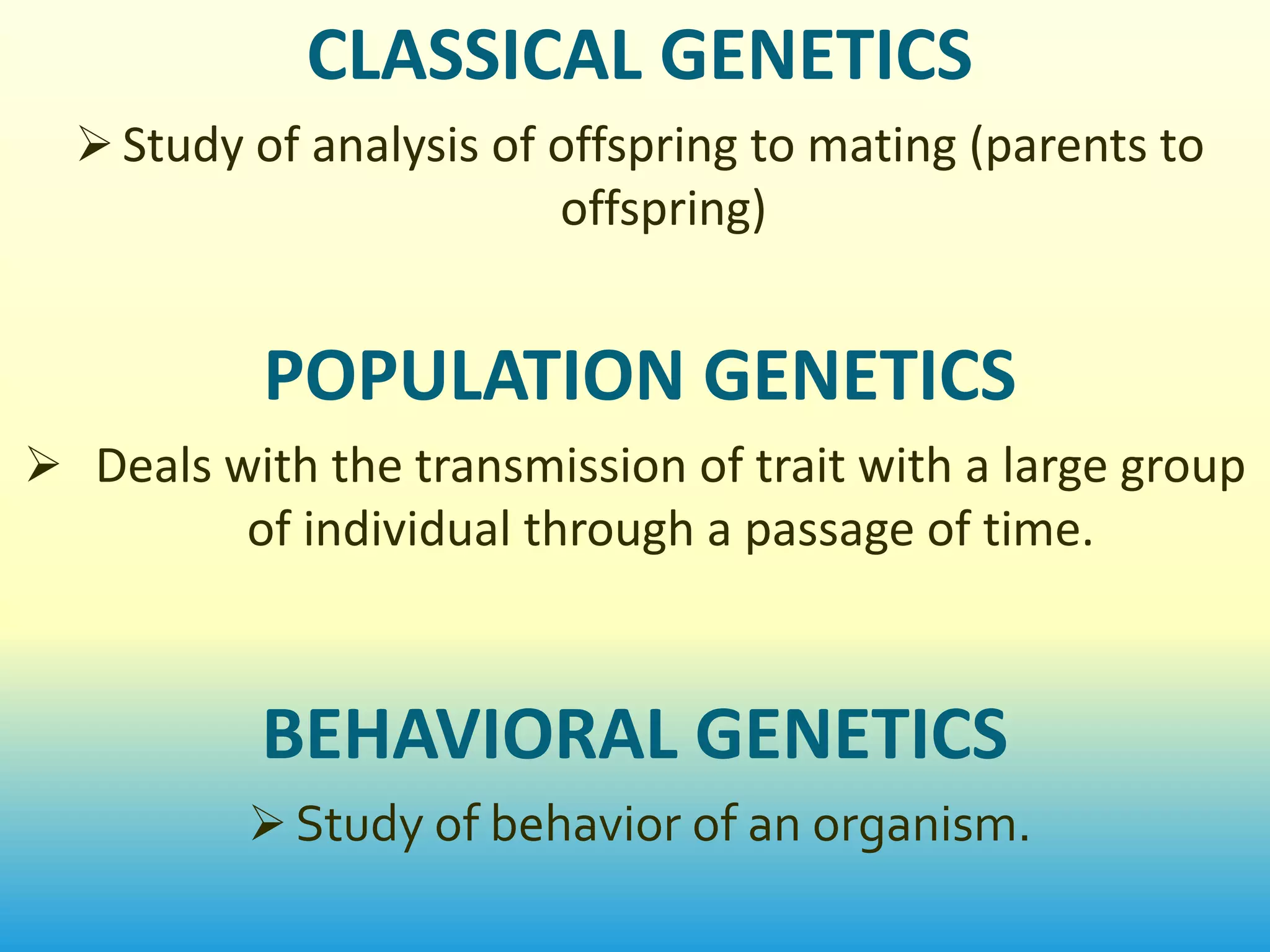
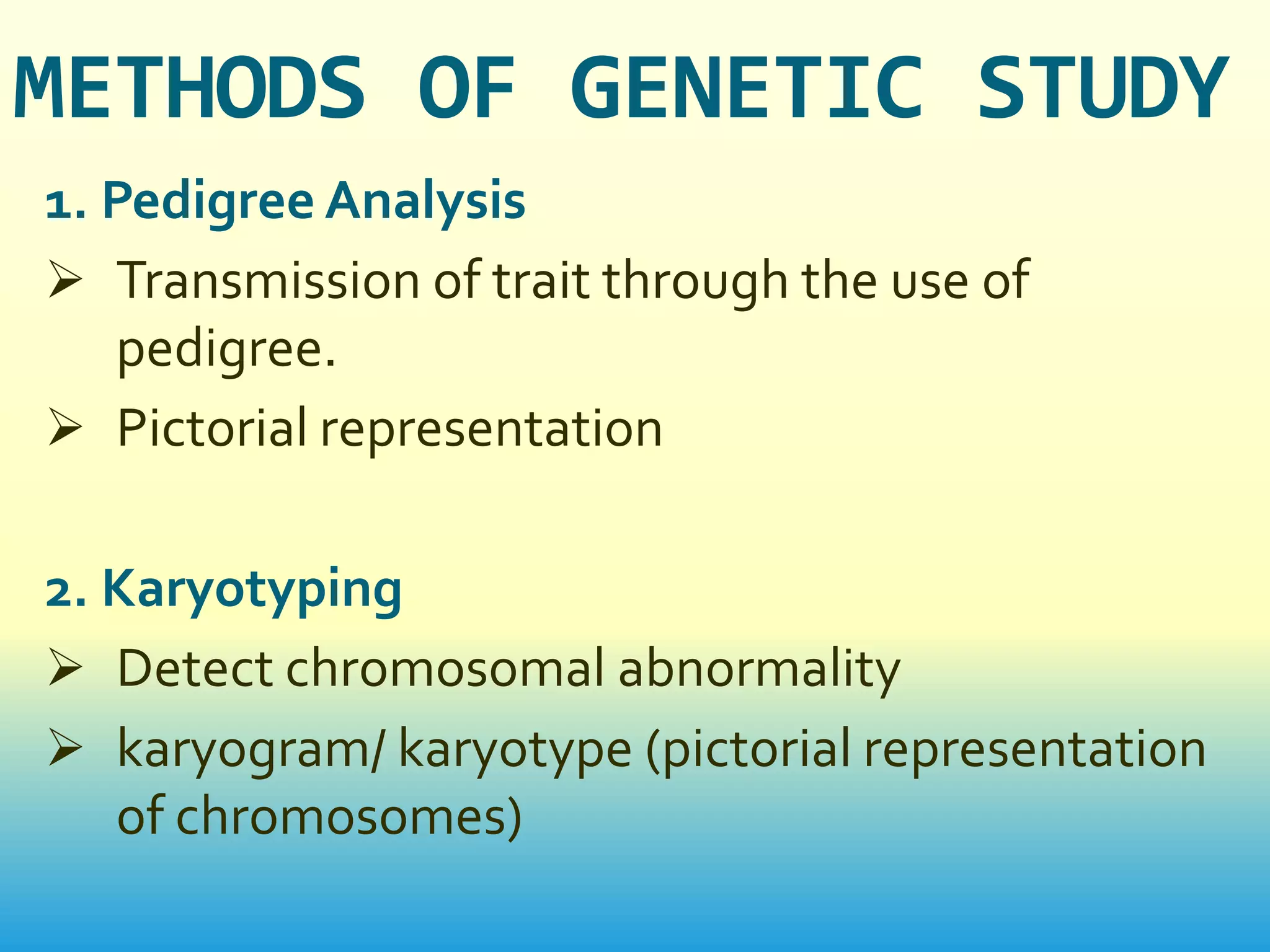
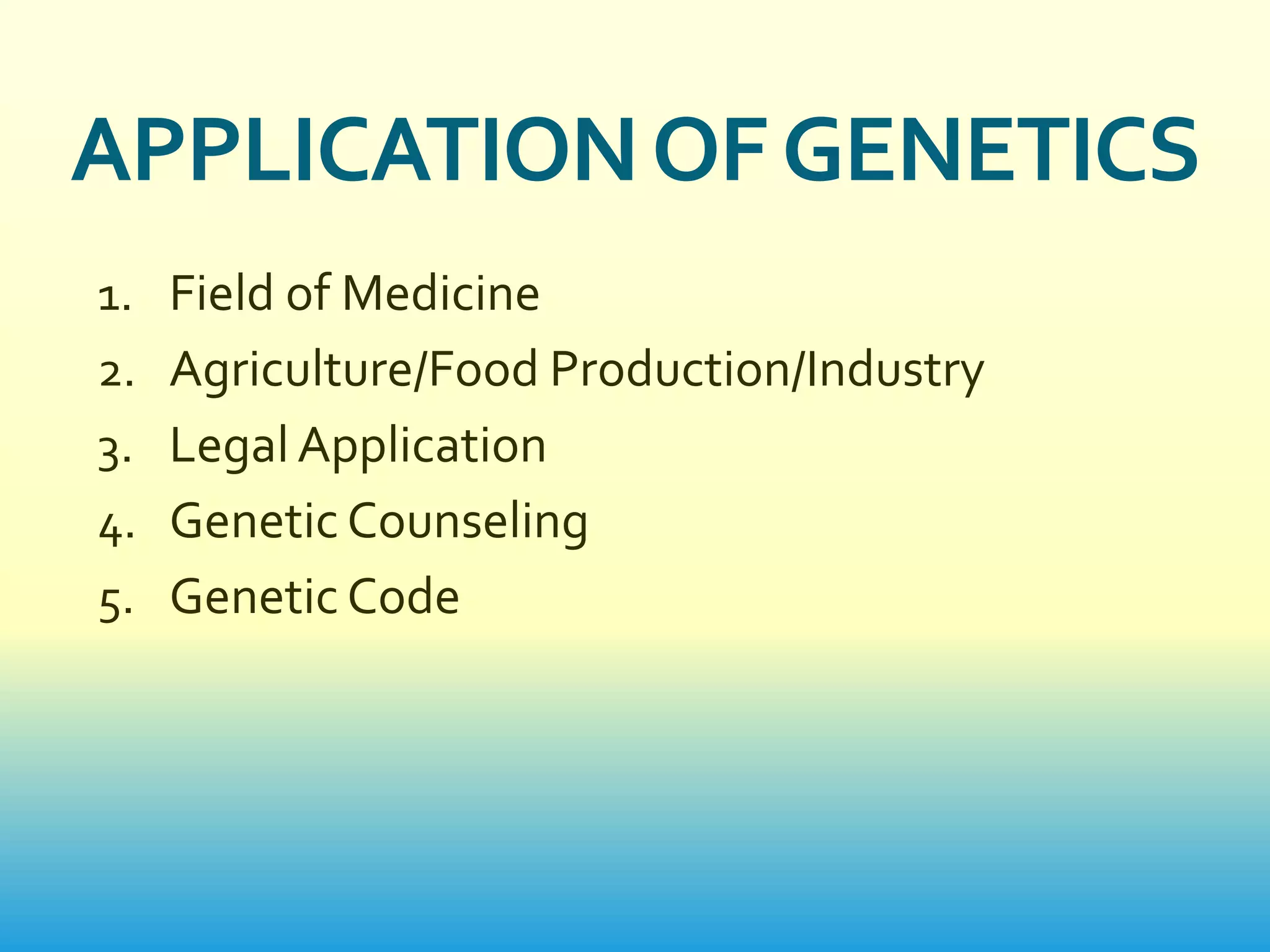
This document provides an introduction to genetics. It discusses how genetics is the study of heredity and variation. Key figures who contributed to genetics are mentioned, including Charles Darwin, Gregor Mendel, and scientists who confirmed that DNA is the genetic material like Oswald Avery. The main branches and scopes of genetics are also outlined, such as cytogenetics, molecular genetics, genomics, and proteomics. Different methods for genetic study are described, including pedigree analysis, karyotyping, planned experimental breeding, and twin studies. The document concludes with discussing applications of genetics in fields like medicine, agriculture, and genetic counseling.