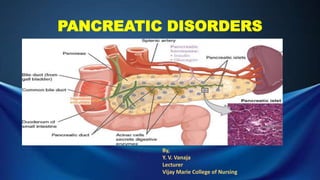
Pancreatic disorders
- 1. PANCREATIC DISORDERS By, Y. V. Vanaja Lecturer Vijay Marie College of Nursing
- 2. PANCREATITIS
- 3. Introduction Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas and it is a serious disorder. The most basic classification system used to describe or categorize the various stages and forms of pancreatitis divides the disorder into • Acute pancreatitis • Chronic pancreatitis Acute pancreatitis can be a medical emergency associated with a high risk for life-threatening complications and mortality Chronic pancreatitis often goes undetected until 80% to 90% of the exocrine and endocrine tissue is destroyed. Acute pancreatitis does not lead to chronic pancreatitis unless complications develop. Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by acute episodes
- 5. Definition Pancreatitis is defined as the inflammation of the pancreas and it is described as autodigestion of the pancreas. “Brunner” Incidence: Typically men 40 to 45 years of age with a history of alcoholism Women- 50 to 55 years of age with a history of biliary disease
- 6. Acute pancreatitis Definition: Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammatory process of the pancreas. The degree of the inflammation varies from mild edema to the severe hemorrhagic necrosis. “Lewis” Acute pancreatitis is a serious and, at times, life-threatening inflammatory process of the pancreas. This process caused by premature activation of the excessive pancreatic enzymes that destroy ductal tissue and pancreatic cells, resulting in autodigestion and fibrosis of the pancreas . “Ignatavicious” Acute pancreatitis ranges from a mild, self- limiting disorder to a severe, rapidly fatal disease that does not respond to any treatment “ Brunner “
- 7. Etiology • Biliary tract disease with gallstones accounts for the half of the cases of obstructive pancreatitis • Trauma from surgical manipulation after biliary tract, pancreatic, gastric, and duodenal procedures such as cholecystectomy, whipple procedure and partial gastrectomy • Trauma – external • Pancreatic obstruction- tumors, cysts • Metabolic disturbances – Eg – hyperlipidemia • Renal disturbances – failure or transplantation • Familial, inherited pancreatitis • Penetration gastric or duodenal ulcers • Viral infections, such as coxsackievirus b infection • Alcoholism • Toxicities of drugs • Pancreatitis also occurs after ERCP
- 10. Clinical manifestations • Severe abdominal pain in the mid- gastric area or left upper quadrant • Pain is described as intense, Boring and continuous, acute in onset, it generally more severe after meals and is unrelieved by antacids. • Pain may be accompanied by abdominal distention • Palpable abdominal mass and decreased peristalsis. • A rigid or board like abdomen may develop • Ecchymosis (bruising) in the flank or around the umbilicus may indicate severe pancreatitis • Nausea and vomiting • Fever • Jaundice • Mental confusion and agitation may also occur • Hypotension • Tachycardia • Cyanosis • Cold and clammy skin • Acute renal failure • Respiratory distress and hypoxia
- 11. • Patient may develop diffuse pulmonary infiltrates • dyspnea • Tachypnea • Abnormal blood gas values • Bowel sounds are decreased or absent Cardinal signs • Grey turner spots or sign: a bluish flank discoloration • Cullen’s sign : bluish periumblical discoloration • Fox sign : bruising is seen over the inguinal ligament • Abdominal guarding : spasm of the abdominal wall muscles
- 12. Complications of Acute pancreatitis 2 significant local complications of pancreatitis are pseudocyst and abscess Pseudocyst: it is a cavity with or surrounding the outside of the pancreas. The pesudocyst is filled with necrotic products and liquid secretions, such as plasma, pancreatic enzymes and inflammatory exudates. Pancreatic abscess : is a large fluid containing cavity with in the pancreas Systemic complications: Pulmonary- pleural effusion, atelectasis, and pneumonia Cardiovascular – hypotension Tetany due to hypocalcemia Trypsin can activate prothrombin and plasminogen, increasing the patient’s risk fro intravascular thrombi, pulmonary emboli
- 14. Diagnosis History collection Serum amylase Serum lipase Serum bilirubin & alakaline phosphatase levels Blood glucose ESR CBC BUN Serum calcium Triglycerides Abdominal ultrasound Endoscopic ultrasound CT scan of the pancreas MRI ERCP Chest X ray
- 15. NonSurgical Management Management of patient with acute pancreatitis is directed toward relieving symptoms and preventing or treating complications All oral intake is withheld to inhibit pancreatic stimulation and secretion of pancreatic enzymes Parenteral nutrition & Iv replacement of calcium and magnesium NG tube suction may be used to relieve nausea and vomiting and to decrease the HCL Histamine- 2 antagonists like ranitidine & proton pump inhibitors like omeprazole Pain management: Administration of analgesics – morphine, Meperidine, & iv or transdermal fentanyl Intensive care: • Help the patient to assume side lying position may decrease the abdominal pain of the pancreatitis • Correction of fluid and blood loss and low albumin levels is necessary to maintain fluid volume and renal failure
- 16. Antibiotic therapy Peritoneal lavage or dialysis has been used to remove kinin and phospholipase. Respiratory care monitoring Blood gases to use of humidified oxygen to intubation and mechanical ventilation Biliary Drainage: Placement of biliary drains and stents in the pancreatic duct through endoscopy - to reestablish drainage of pancreas Surgical management: • If the pancreatitis is cause by gallstones an ERCP with sphincterostomy may be performed on an emergency basis • Laparocopic cholecystectomy • Laparoscopy may be done to drain an abscess or pseudocysts or abscess can be treated by percutaneous drainage under CT guidance
- 18. Introduction: it is a benign inflammatory process and fibrosing disorder characterized by • irreversible morphologic changes, • Progressive and • permanent loss of exocrine and endocrine function
- 19. DEFINITION 1) Chronic pancreatitis is an inflammatory disorder characterized by progressive anatomic and functional destruction of the pancreas “Brunner’’ 2) Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive disease of the pancreas that has remissions and exacerbations. Inflammation and fibrosis of the tissue contribute to pancreatic insufficiency and diminished function of the organ “Ignatavicious” 3) Chronic pancreatitis is progressive destruction of the pancreas with fibrotic replacement of pancreatic tissue. Strictures and calcifications may also occur in the pancreas. “Lewis”
- 20. Classification of Chronic pancreatitis • Chronic calcifying pancreatitis • Chronic obstructive pancreatitis • Autoimmune pancreatitis • Idiopathic pancreatitis Chronic calcifying pancreatitis: • Chronic calcifying pancreatitis id also called as alcohol- induced pancreatitis • In chronic pancreatitis there is inflammation and sclerosis, mainly in the head of the pancreas and around the pancreatic duct.
- 21. Chronic obstructive pancreatitis; • Develops from inflammation , spasm and obstruction of the sphincter of oddi, often from cholelithiasis. • Inflammatory sclerotic lesions occur in the head of the pancreas and around the ducts causing an obstruction and back flow of secretions.
- 22. Autoimmune pancreatitis; • Is a chronic inflammatory process in which immunoglobulins invade the pancreas. • Other organs also may infiltrated , including the lungs and liver. Idiopathic and hereditary chronic pancreatitis; May be associated with SPINK1 & CFTR gene mutations The protein encoded by the SPINK1 gene is a trypsin inhibitor. The CFTR gene is associated with cystic fibrosis
- 23. Etiology • Alcohol consumption • Malnutrition • autoimmune disease, • a narrow pancreatic duct, • a blockage of the pancreatic duct by either gallstones or pancreatic stones • cystic fibrosis, which is a hereditary disease that causes mucus to build up in your lungs • genetics • high blood levels of calcium • a high level of triglyceride fats in your blood • Recurrent acute pancreatitis
- 25. Pathophjysiology Chronic calcifying pancreatitis; Alcohol Pancreatic secretions precipitate as insoluble proteins that plug the pancreatic ducts & flow of pancreatic juices As the protein plugs become more widespread, the cellular lining of the ducts changes and ulcerates This inflammatory process causes fibrosis of the pancreatic tissue. Intraductal calcification and marked pancreatic destruction develop. The organ becomes hard and firm as result of cell atrophy and pancreatic insufficiency
- 26. Clinical manifestations • Abdominal Pain accompanied by vomiting • abdominal tenderness • ascites • Exocrine insufficiency occurs in 80% to 90% • anorexia • steatorrhea, • constipation • Endocrine insufficiency - diabetes mellitus • Jaundice or cholangitis • Weight loss & muscle wasting- due to fat malabsorption • Protein malabsorption – ‘starvation’ edema of the feet, legs and hands •
- 28. Diagnostic Studies Serum amylase Serum lipase Serum bilirubin CBP Stool examination Secretin stimulation test – to assess pancreatic function ERCP MRI, CT Ultrasound Glucose tolerance test – to evaluate pancreatic islet function
- 30. NonSurgical Management • Pain management • Pancreatic Enzyme replacement therapy- to prevent malnutrition, malabsorption &weight loss • Pancrelipase – contains amount of amylase, lipase and protease • Record the number and consistency of stools per day to monitor effectiveness of enzyme therapy • If patient has diabetes – insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents to control blood glucose level • TPN • H2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors • Total enteral nutrition TEN, including vitamin and mineral replacement • Food high in CHO and protein and also assist in healing process • Teach patients to avoid alcohol
- 32. Surgical management • Laparoscopic cholecystectomy or choledochotomy ( incision of common bile duct) • Sphincterotomy • Endoscopic sphincterotomy • Laparoscopic pancreatectomy • Endoscopic pancreatic necrosectomy and Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery • Pancreaticojejunostomy • Whipple resection (pancreaticoduodenectomy) • Pancreas transplantation
- 33. Pancreatic Cysts
- 34. Pancreatic cysts are saclike pockets of fluid on or in the pancreas. As a result of the local necrosis that occurs at the time of acute pancreatitis, collections of fluid may form in the vicinity of the pancreas. These become walled off by fibrous tissue and are called as pancreatic pseudocysts Classification The main categories of pancreatic cysts can be divided into two groups, nonneoplastic or neoplastic cysts. Each group includes many different subtypes of cysts, such as Pseudocysts; A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in pancreatic enzymes, blood, and necrotic tissue, typically located in the lesser sac of the abdomen Serous cystadenomas ; Pancreatic serous cystadenoma is a benign tumour of pancreas. It is usually found in the tail of the pancreas, and may be associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. mucinous cystic neoplasms; Mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs) usually are large, septated, thick-walled mucinous cysts that lack communication with the ductal system, and occur almost exclusively in the pancreatic body and tail of middle-aged women. Most aren't cancerous, and many don't cause symptoms. But some pancreatic cysts can be or can become cancerous. Definition
- 35. Etiology • Acute pancreatitis • Chronic pancreatitis • Abdominal trauma Clinical Manifestations of pseudocysts; • Epigastric pain radiating to the back • Abdominal fullness • Nausea • vomiting • Haemorrhage • Infection • Obstruction of the bowel, biliary tract, or splenic vein • Abscess • Fistula formation • Pancreatic ascites
- 36. Diagnosis • Ultrasound • CT • ERCP Management; Psedocysts may spontaneously resolve or they may rupture and produce haemorrhage. Surgical intervention is necessary if the pseudocyst does not resolve within 6 to 8 weeks or if complications develop. Surgeries include; Percutaneous drainage using a needle, usually under CT scan guidance Endoscopic – assisted drainage using an endoscope to locate the pseudocyst Surgical drainage of the pseudocyst into the stomach or jejunum To provide external drainage , the surgeon inserts a sump drainage tube to remove pancreatic secretions and exudate
- 38. Pancreatic abscess is a late complication of acute necrotizing pancreatitis, occurring more than 4 weeks after the initial attack. A pancreatic abscess is a collection of pus resulting from tissue necrosis, liquefaction, and infection. “Wikipedia’’ Pancreatic abscesses are the most serious complication of acute necrotizing pancreatitis. The abscesses form from collections of the purulent liquefaction of the necrotic pancreas. “Ignatavicious” Causes; • Inflammatory necrosis of the pancreas • pancreatic pseudocysts that become infected • penetrating peptic ulcers • gall stones • alcohol consumption • in rare cases, drugs • blunt trauma Definition
- 39. Clinical manifestations • Fever • Pleural effusion • abdominal pain, • chills • inability to eat. • Whereas some patients present an abdominal mass, • Nausea and vomiting
- 40. Diagnosis • History collection • CBP • Abdominal CT scans, • MRIs • ultrasounds • Blood culture
- 41. Management • Antibiotics ] • On the other hand, antibiotics are not recommended in patients with pancreatitis, unless the presence of an infected abscess has been proved. • Drainage via percutaneous method or laparoscopy should be performed to prevent sepsis.
- 43. • Cancer of the pancreas is the leading cause of the deaths in each year in United states. • Pancreatic tumors usually originate from epithelial cells of the pancreatic ductal system. • If the tumor is discovered in the early stages the tumor cells may be localized within the glandular organ. • Most often the tumor is discovered in the late stages of development and may be a well- defined mass or is diffusely spread throughout the pancreas. • The tumor may be primary cancer, or it may result from metastasis from cancers of the lung, breast, thyroid, kidney or skin. • Primary cancers are generally adenocarcinomas and grow in a well differentiated patterns. They grow rapidly and spread to surrounding organs.by direct extension and invasion of lymphatic and vascular system. • The highly metastatic lesion may eventually invade the lung, peritoneum, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. Definition: Pancreatic cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancerous) cells form in the tissues of the pancreas. Pancreatic cancer occurs within the tissues of the pancreas, which is a vital endocrine organ located behind the stomach.
- 44. ETIOLOGY • Cigarette smoking • Exposure to industrial chemicals or toxins in the environment • Diet high in fat, meat, or both • DM • Chronic pancreatitis • Hereditary pancreatitis • Cirrhosis • obesity
- 45. Pathophysiology
- 47. Clinical manifestations • Upper Abdominal pain often radiates to back • Anorexia • Rapid and progressive weight loss • Nausea • Jaundice • Weight loss due to poor digestion and absorption • Tumors may be palpable abdominal masses, especially in the thin patient. • Hepatomegaly • Dark urine • Clay colored stools • Glucose intolerance • Splenomegaly • GI bleeding • Ascites
- 49. Diagnosis • Serum amylase. • Serum lipase • Serum bilirubin • CEA – carcinoembryonic antigen • MRI • CT • ERCP • X-ray • Percutaneous FNAB • Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography • Angiograpghy
- 50. Management • Chemotherapy or radiation is used to relieve pain by shrinking the tumor • It may be used before, after, or instead of surgery • Chemotherapy ; • in most cases combining agents has been more successful than single-agent chemotherapy. • 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) may be given alone or with gemcitabine for locally advanced, or unresectable, pancreatic cancer. • Gemcitabine may also be given with capecitabine , docetaxel, and/or erlotinib • Observe for adverse effects, such as fatigue, rash, anorexia, and diarrhea. • other targeted therapies being investigated include growth factor inhibitors, anti – angiogenesis factors, and kinase inhibitors. • To control pain – opioid analgesics ( morphine) • Intensive external beam radiation therapy to the pancreas may offer pain relief by shrinking tumor cells. • Implantation of radioactive iodine seeds, in combination with systemic or intra arterial administration of floxuridine
- 51. For patients experiencing biliary obstruction who are high surgical risks, biliary stents placed percutaneously can ensure patency to relieve pain. Surgical Management; • Partial pancreatectomy – preferred from tumors smaller than3cm in diameter • Minimal invasive surgery via laparoscopy in the staging, palliative and removal of cancer. • For larger tumors – radical pancreatectomy or whipple procedure Preoperative Management; • Jejunostomy feeding – feedings are started in low concentrations and volumes and are gradually increased as tolerated • Provide feeding using a pump to maintain a constant volume and assess for diarrhea frequency to determine tolerance. • TPN • Iv line care to prevent catheter sepsis • Sterile dressing changes and site observation are important. • Patient have nothing by mouth fro at least 6 to 8 hrs before surgery.
- 52. Post operative care • Observe for multiple potential complications of the open whipple procedure. • The patient having the laparoscopic whipple surgery or radical pancreatectomy is also less at risk for severe complications. • Preventive measures for surgical complications like; • Diabetes – check blood glucose often • Hemorrhage – monitor pulse, B.P, Skin color and mental status. • Wound infection – monitor temperature and assess wounds • Bowel obstruction – check for bowel sounds and stools • Intra abdominal abscess – monitor temperature and patients reports of pain Immediately after surgery, the patient is NPO and usually has NGT to decompress the stomach. In open surgical approaches, biliary drainage tubes are placed during surgery – assess the tubes and drainage devices for tension or kinking Monitor drainage for color, consistency and amount Place patient in the semi fowlers’s position to reduce tension on the suture line and anastomosis site
- 53. The development of fistula is the most common and most serious post operative complication. Monitor vital signs, decreased urine output – to detect early signs of hypovolemia Mainatin sequential compressive devices to prevent DVT Maitain IV isotonic fluid replacement with colloid replacement Monitor HB and Haematocrit values – to assess blood loss and need for blood transfusion Maintain electrolyte balance
Editor's Notes
- By, Y.V.Vanaja Lecturer Vijay Marie College of Nursing
- .
- Incidence
- Definition:
- History collection
- Definition