Dr. Karl Ulrich Petry presented on quality standards for colposcopy. He discussed several key points:
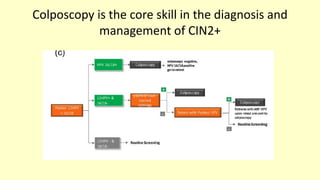
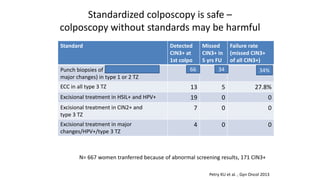
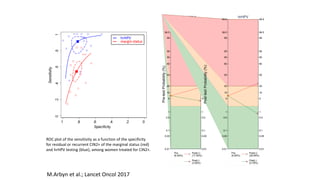
1) Colposcopy alone has shown poor sensitivity and specificity for detecting cervical lesions compared to HPV testing or histology. Standardized colposcopy protocols can improve accuracy.
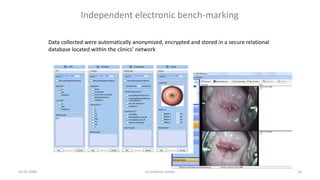
2) Electronic data collection and independent benchmarking allow for objective quality assessment compared to self-assessment.
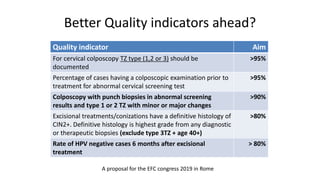
3) The European Federation for Colposcopy's quality indicators for colposcopy are being revised, including lowering the target for clear margins after excisional treatment from 80% to 70% based on evidence.
4) Continuous quality assurance of colposcopy education, training and practice is needed and should