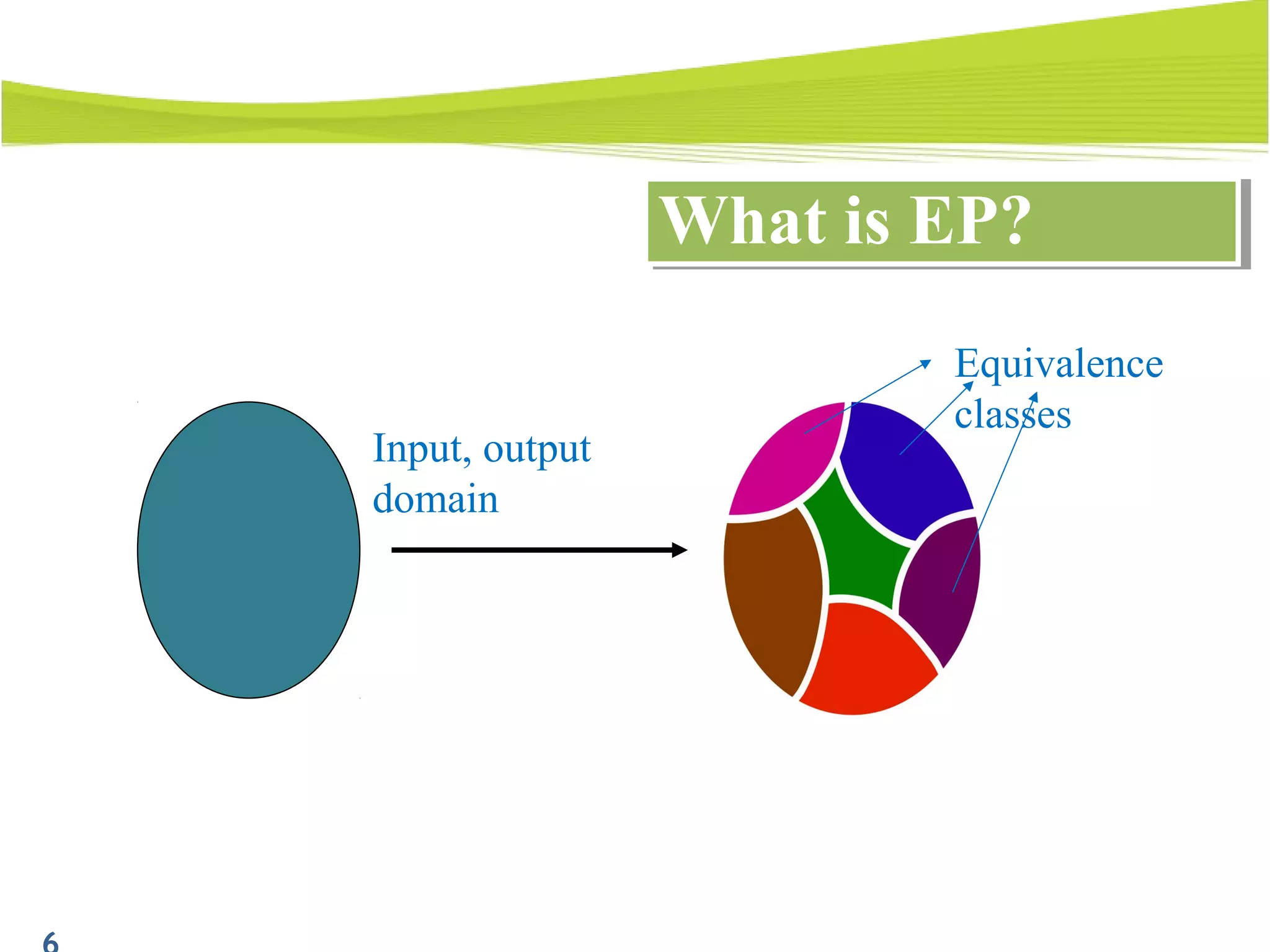
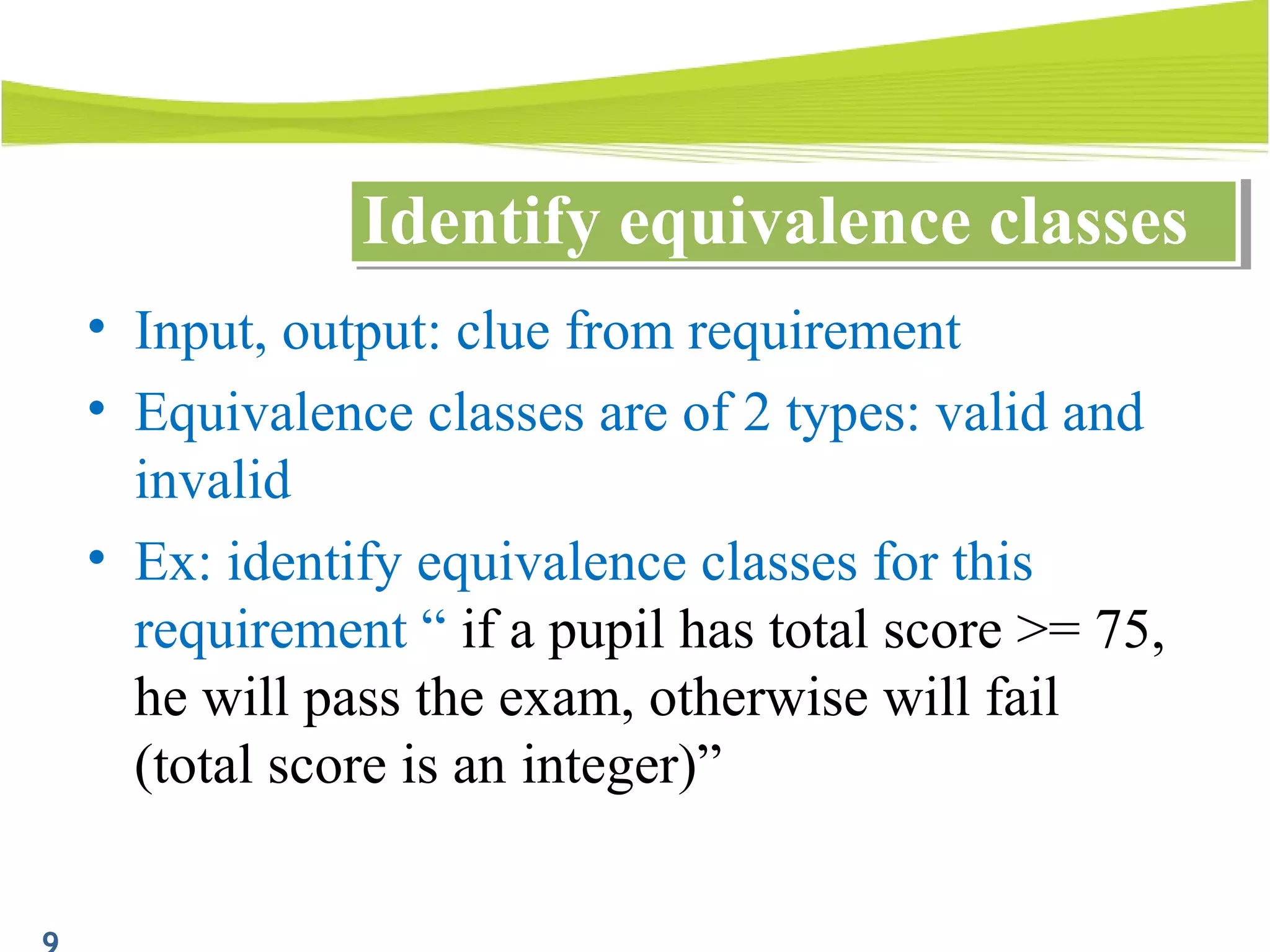
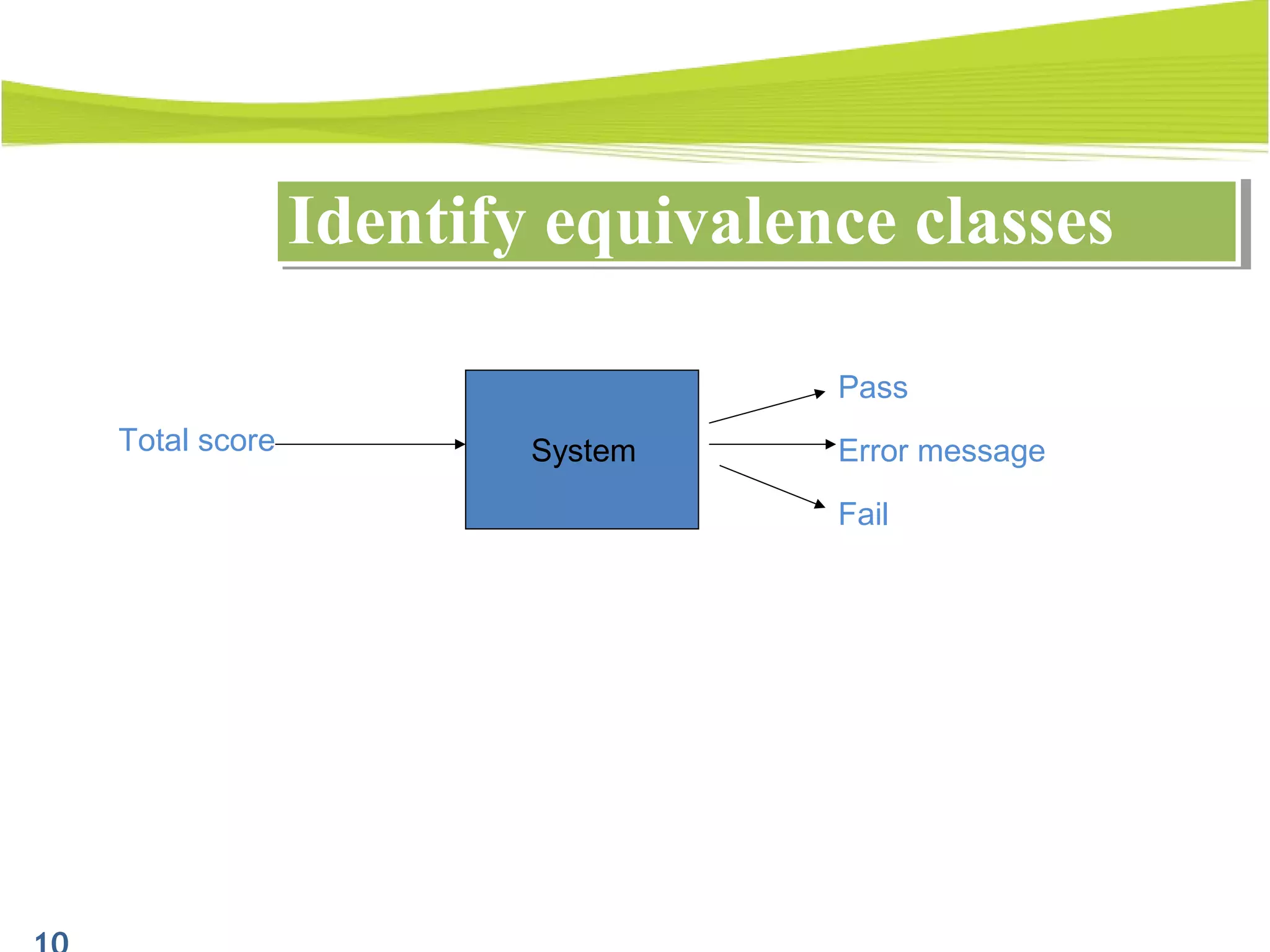
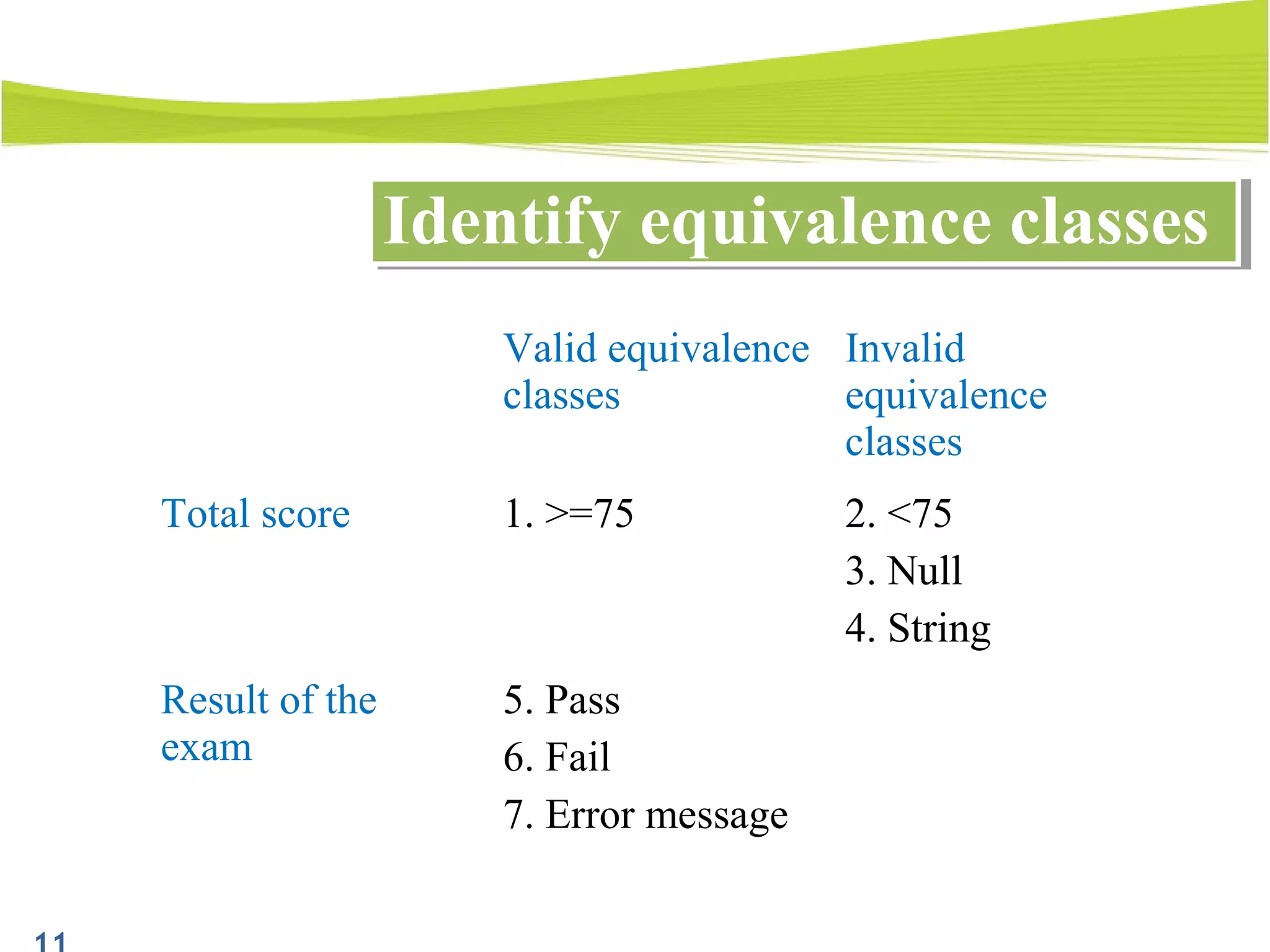
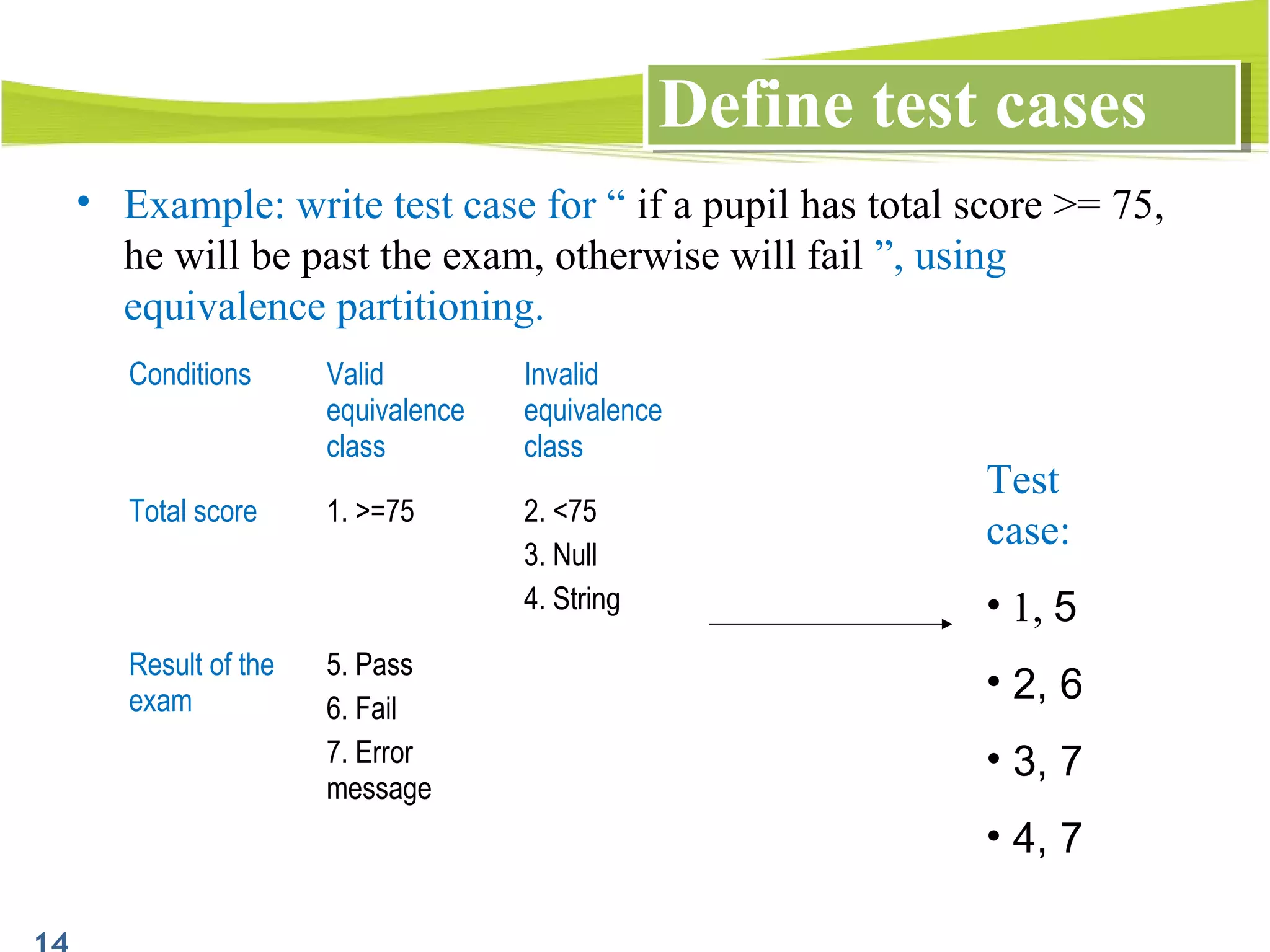
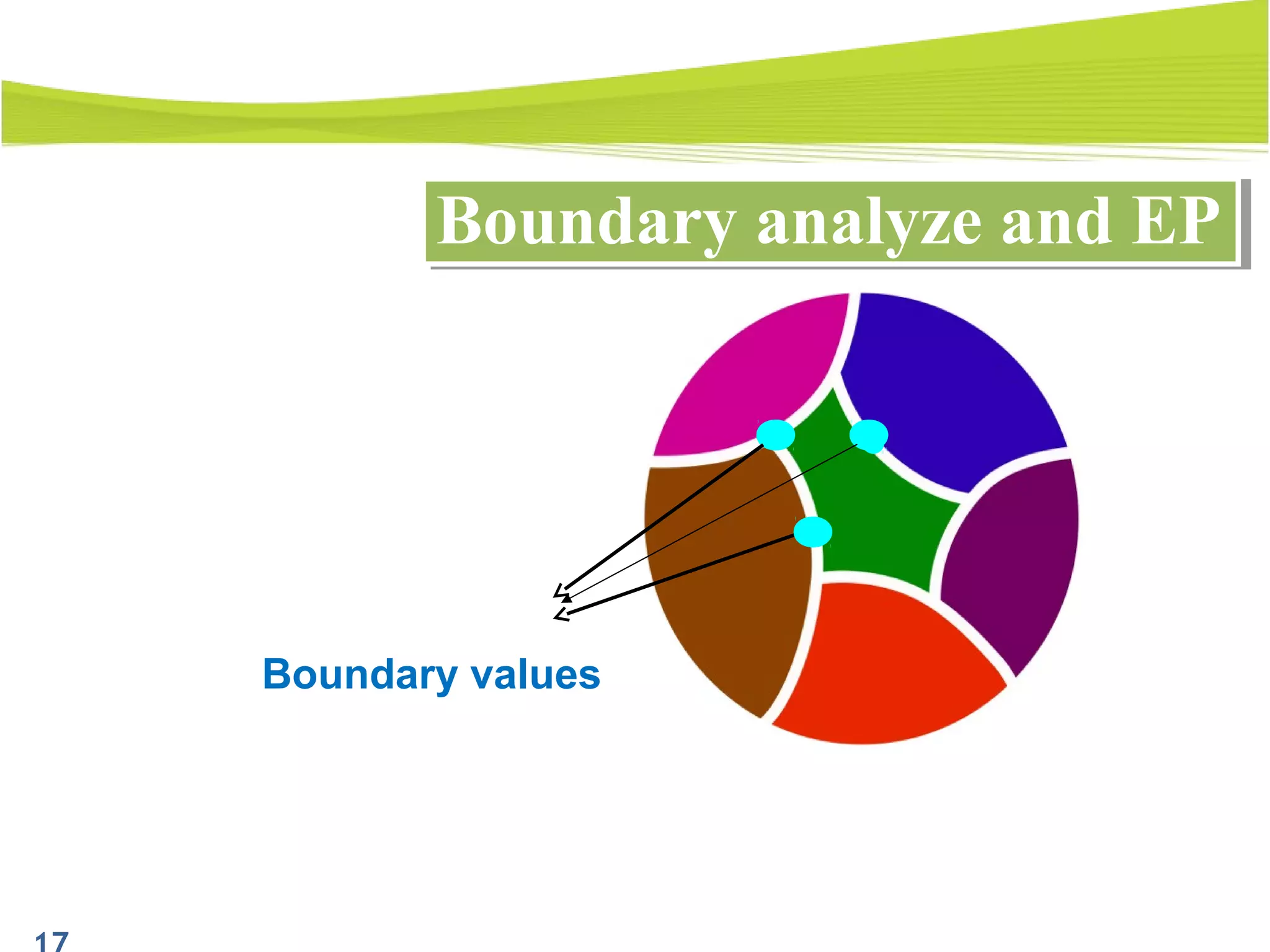
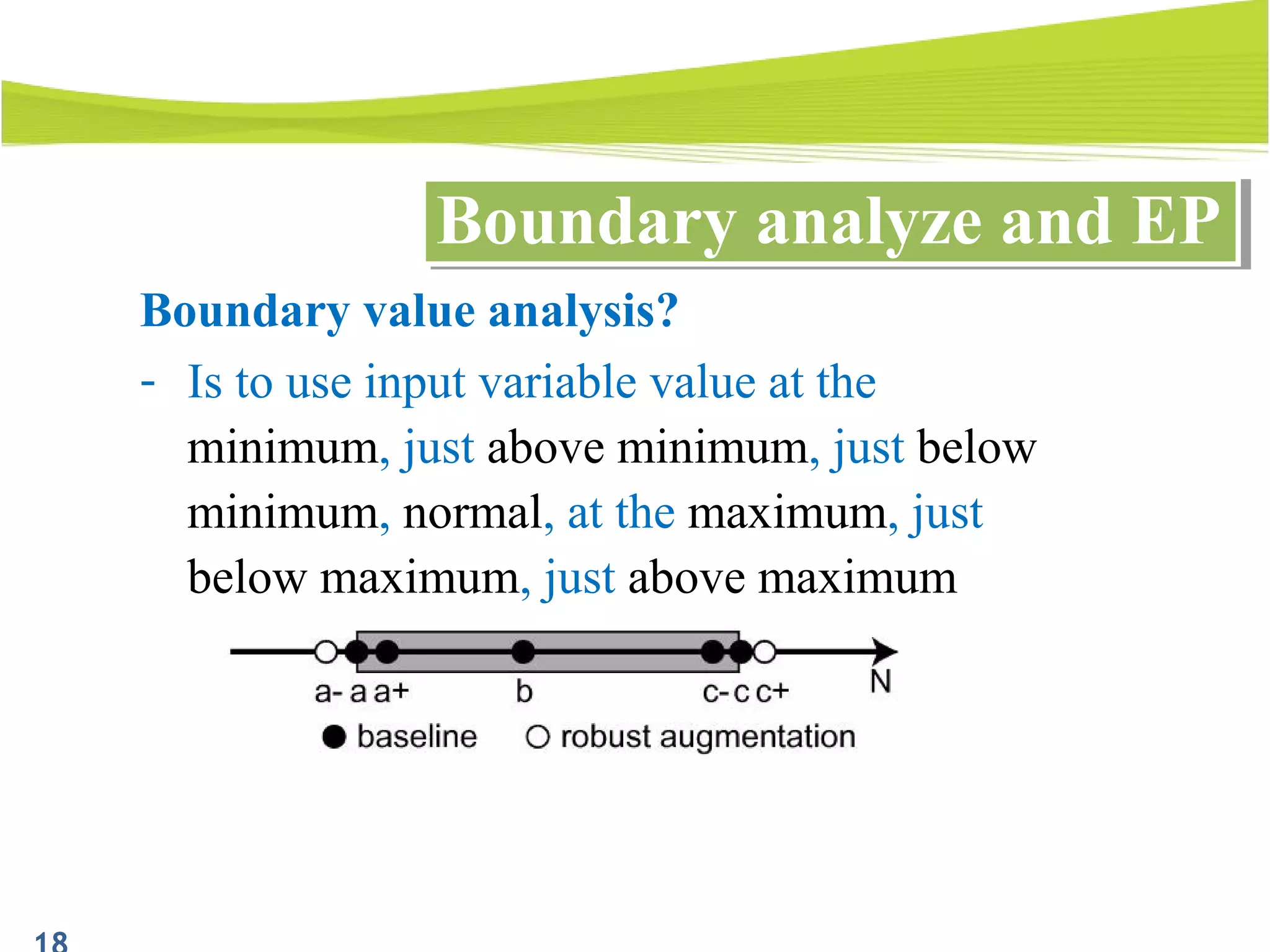
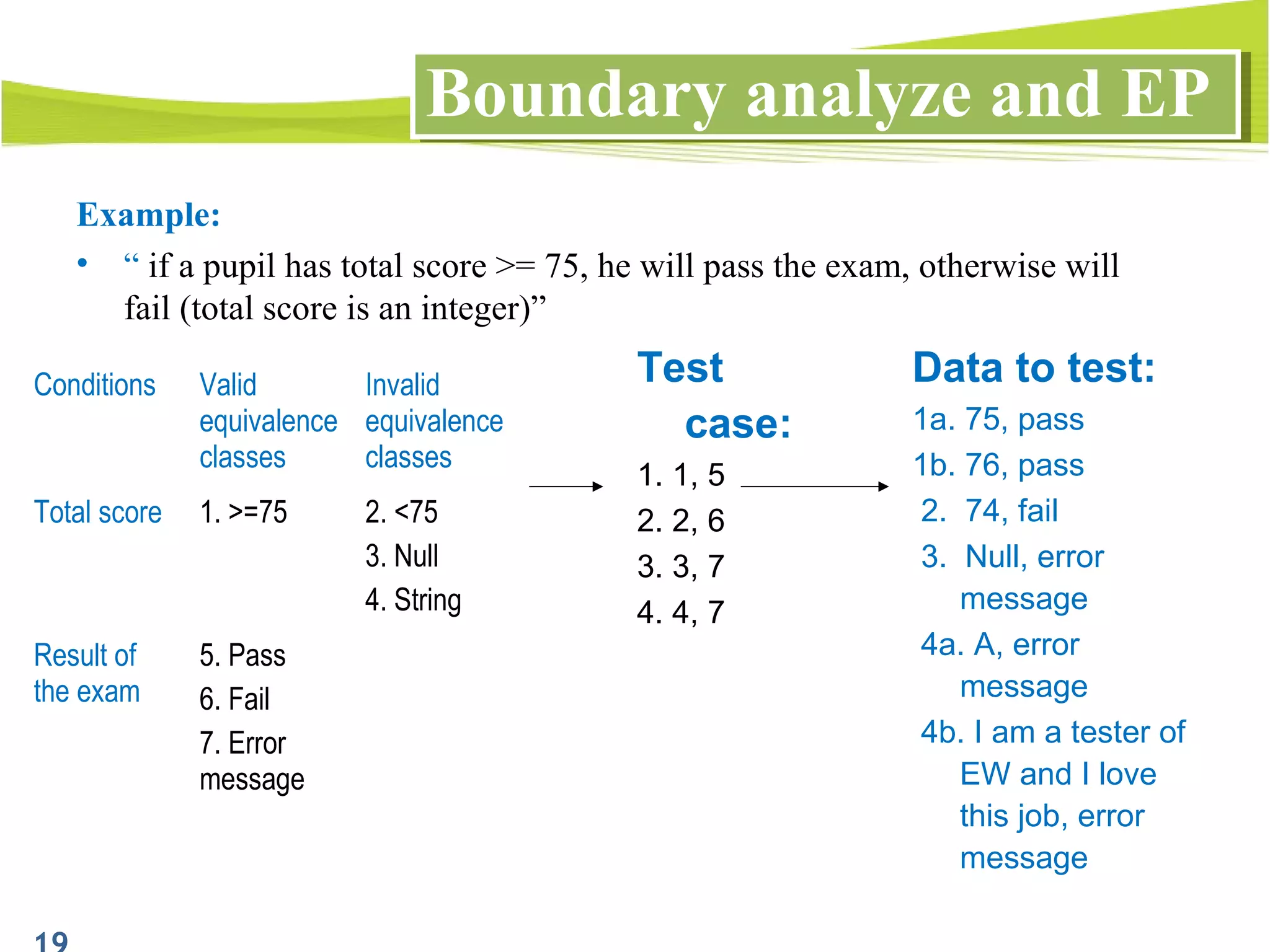
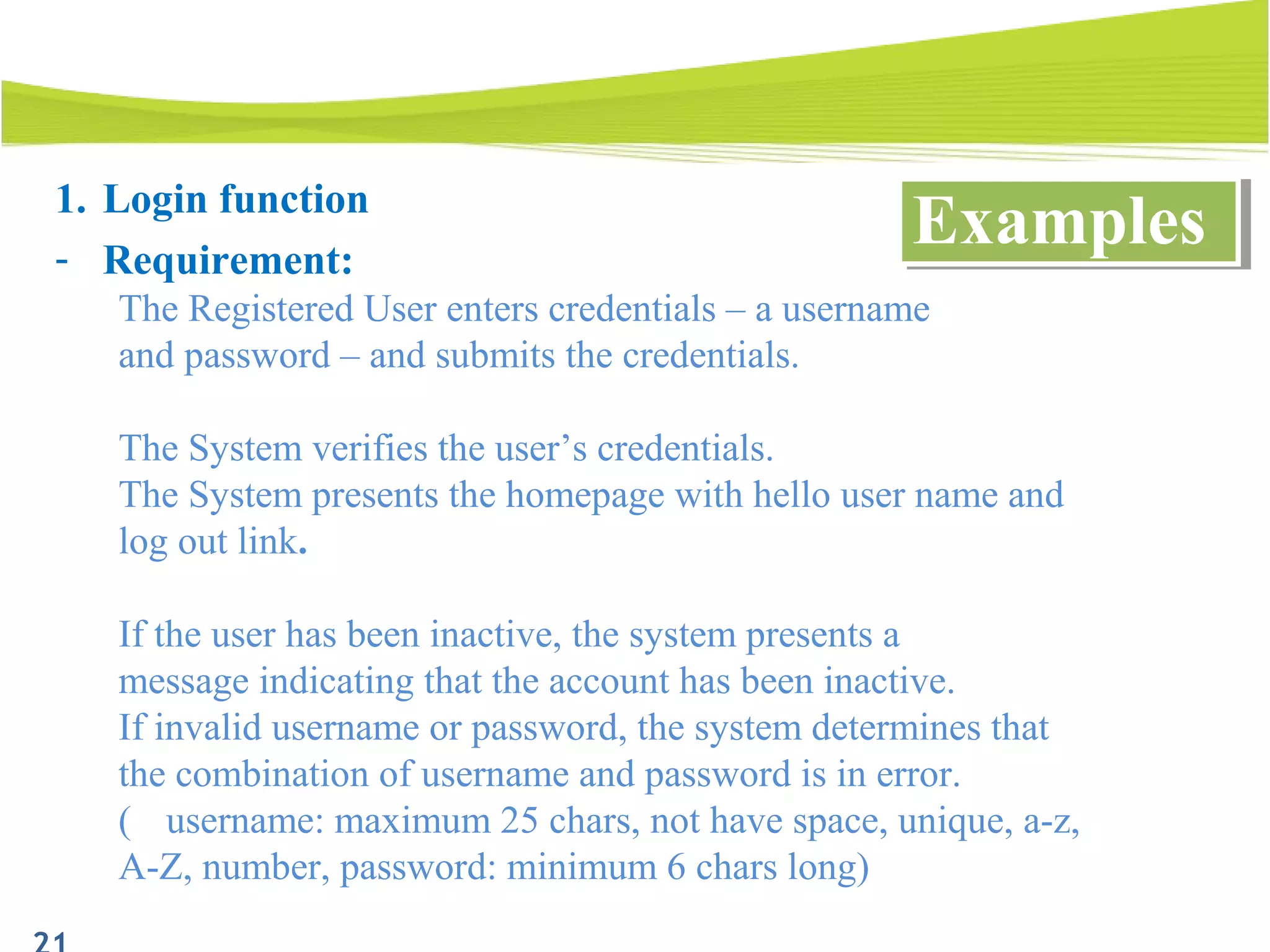
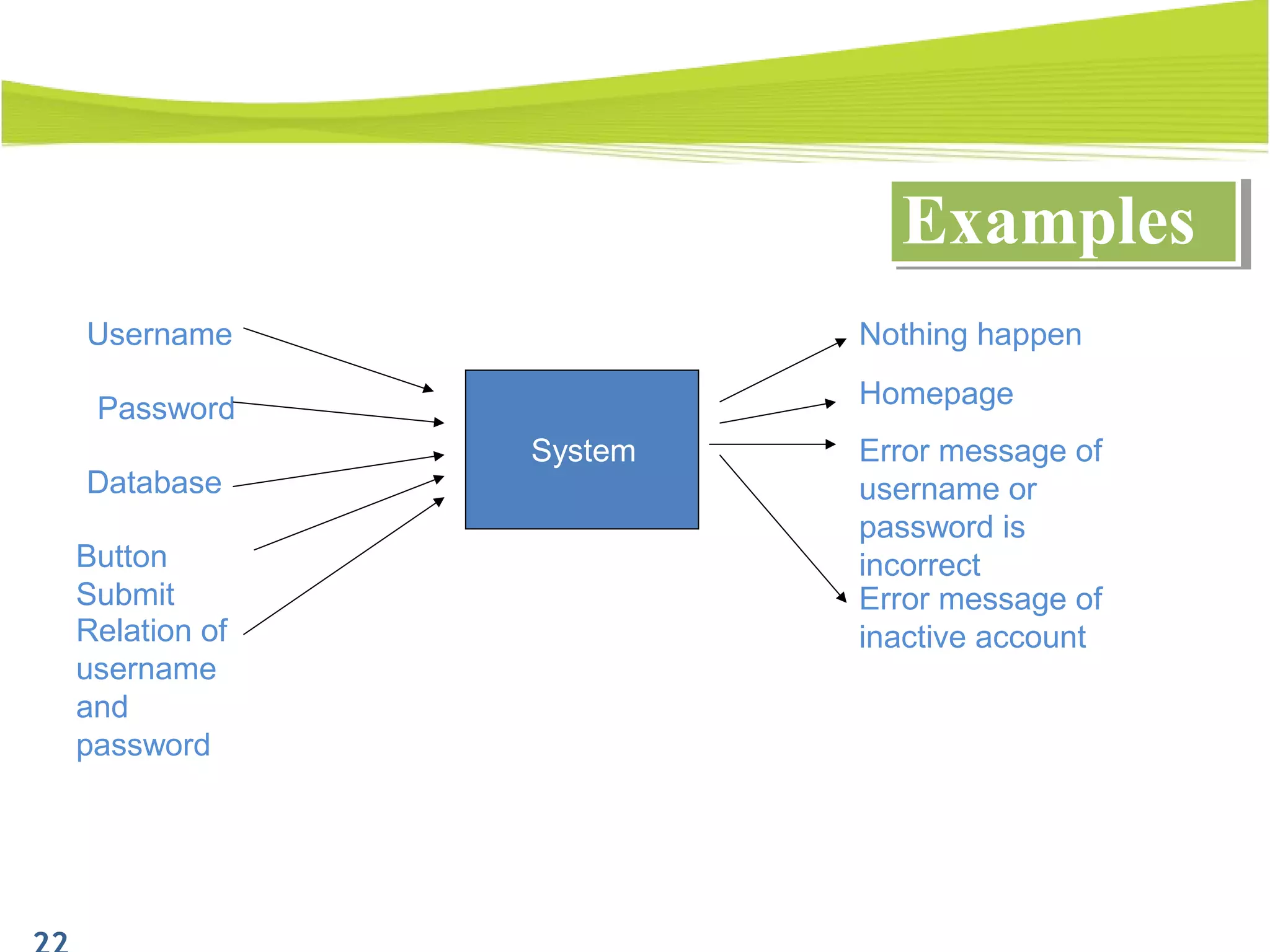
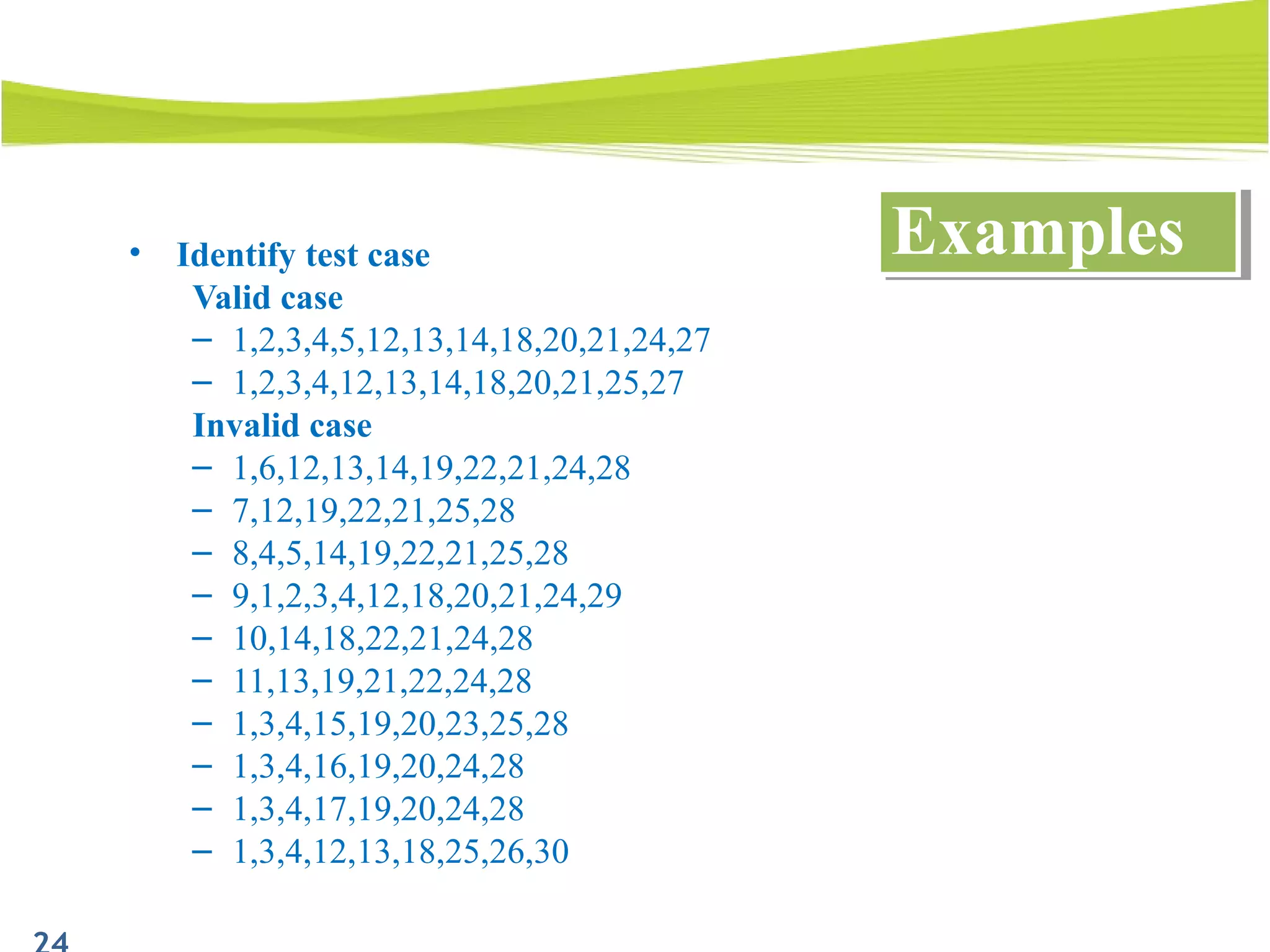
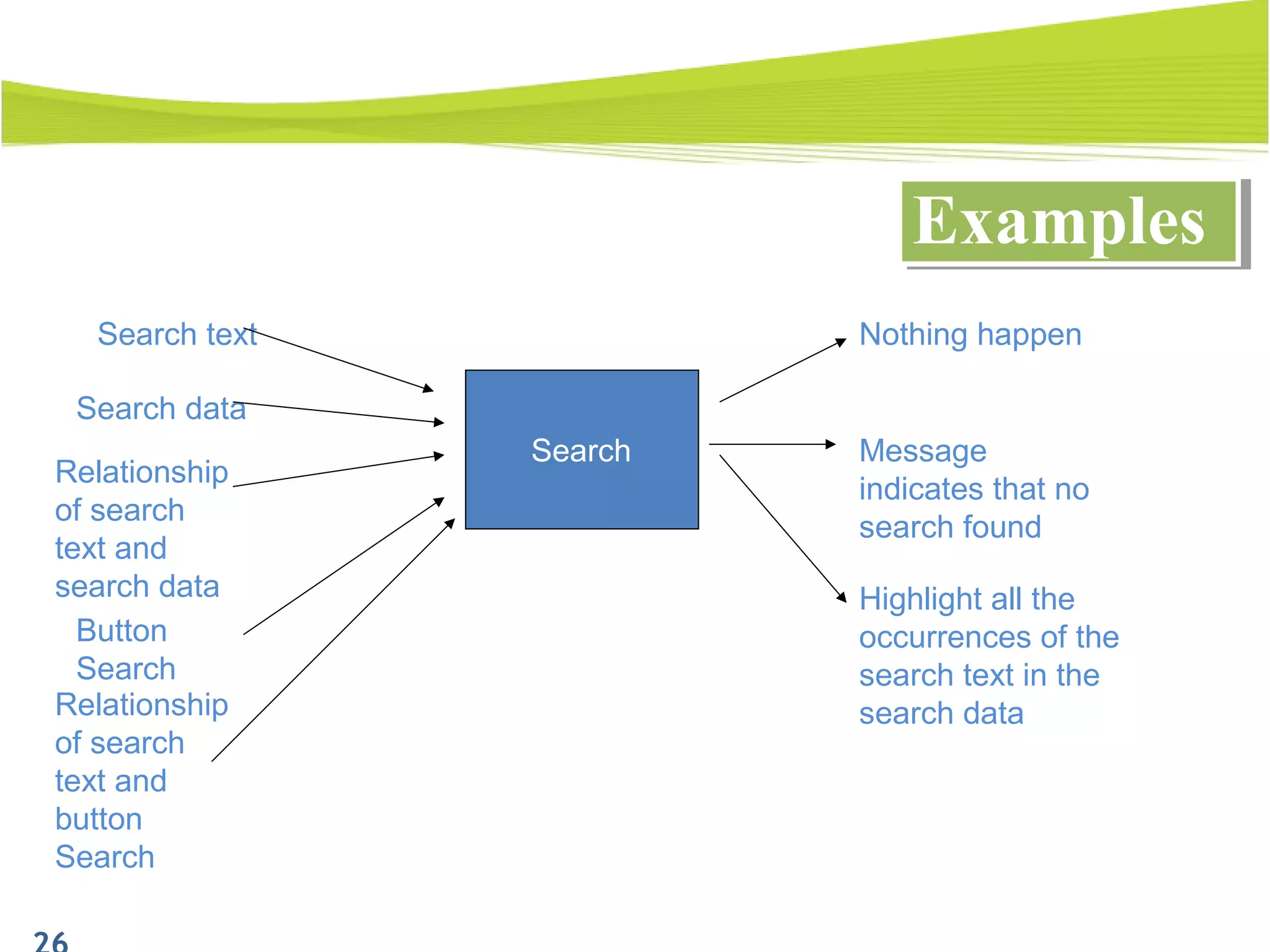
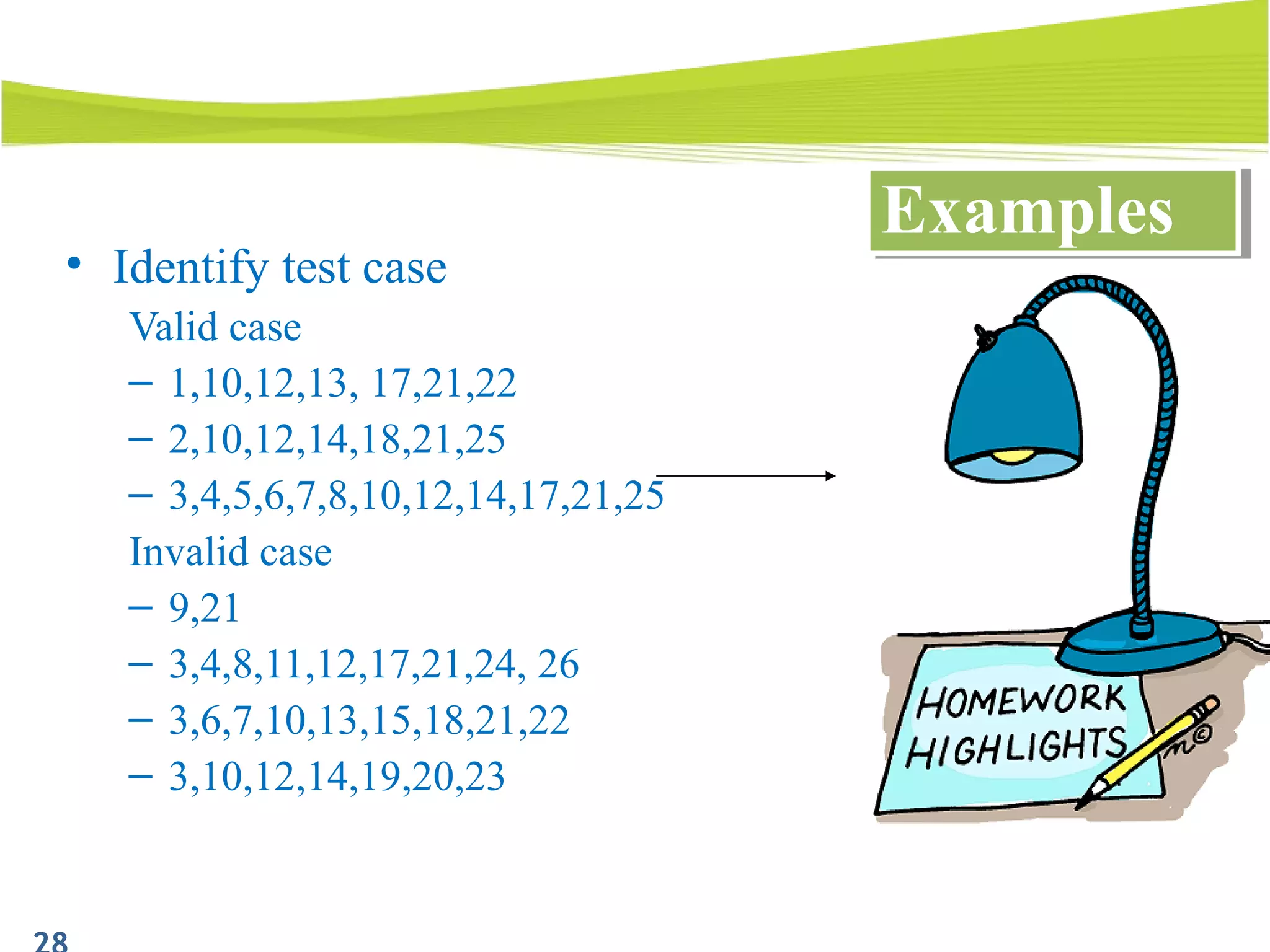
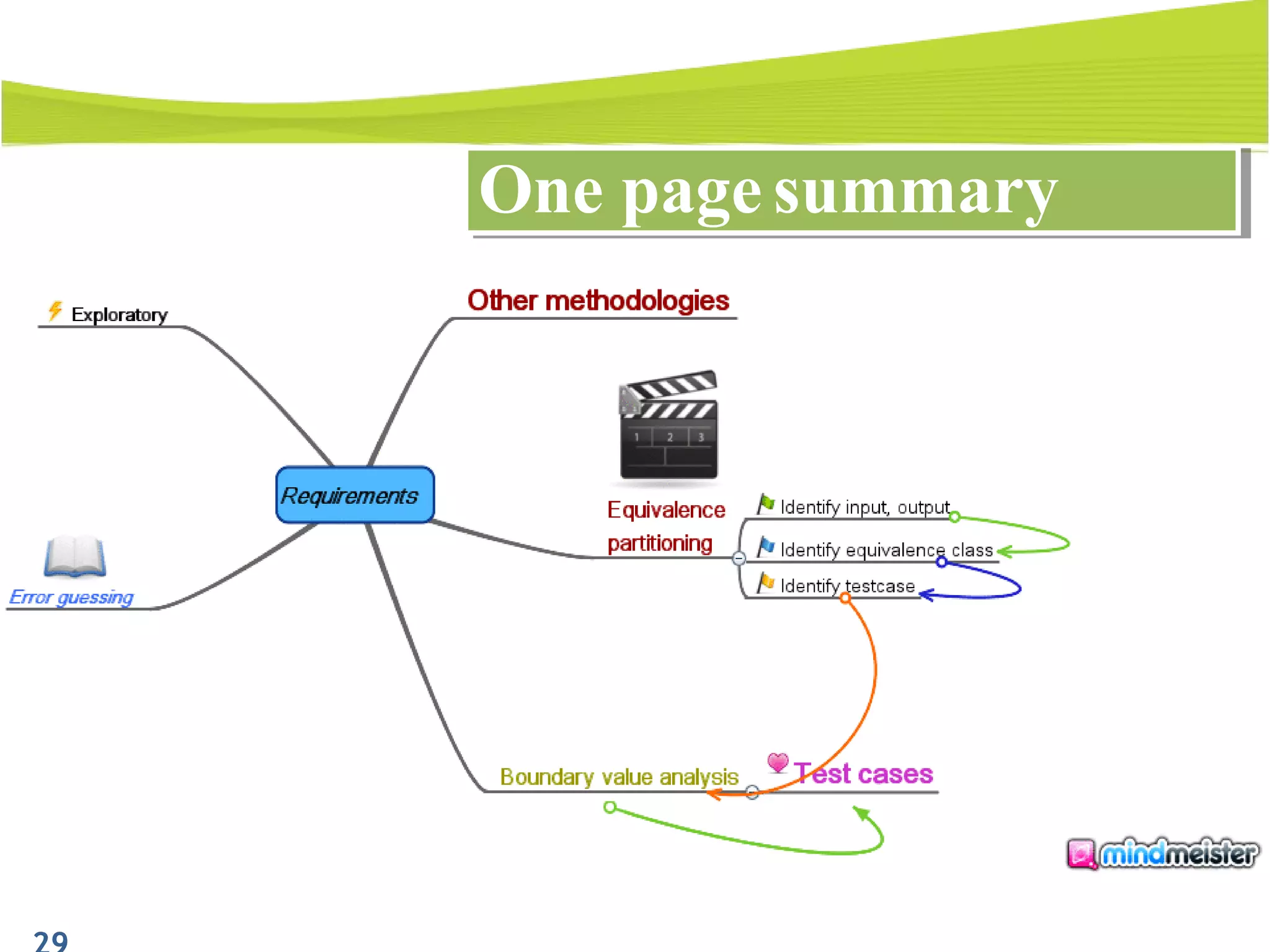
The document outlines a 120-minute training course on designing test cases using equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis. Participants will learn to identify equivalence classes, define test cases, and apply boundary analysis to enhance test case design. Key concepts include valid and invalid equivalence classes, as well as practical examples relevant to user login and search functionalities.