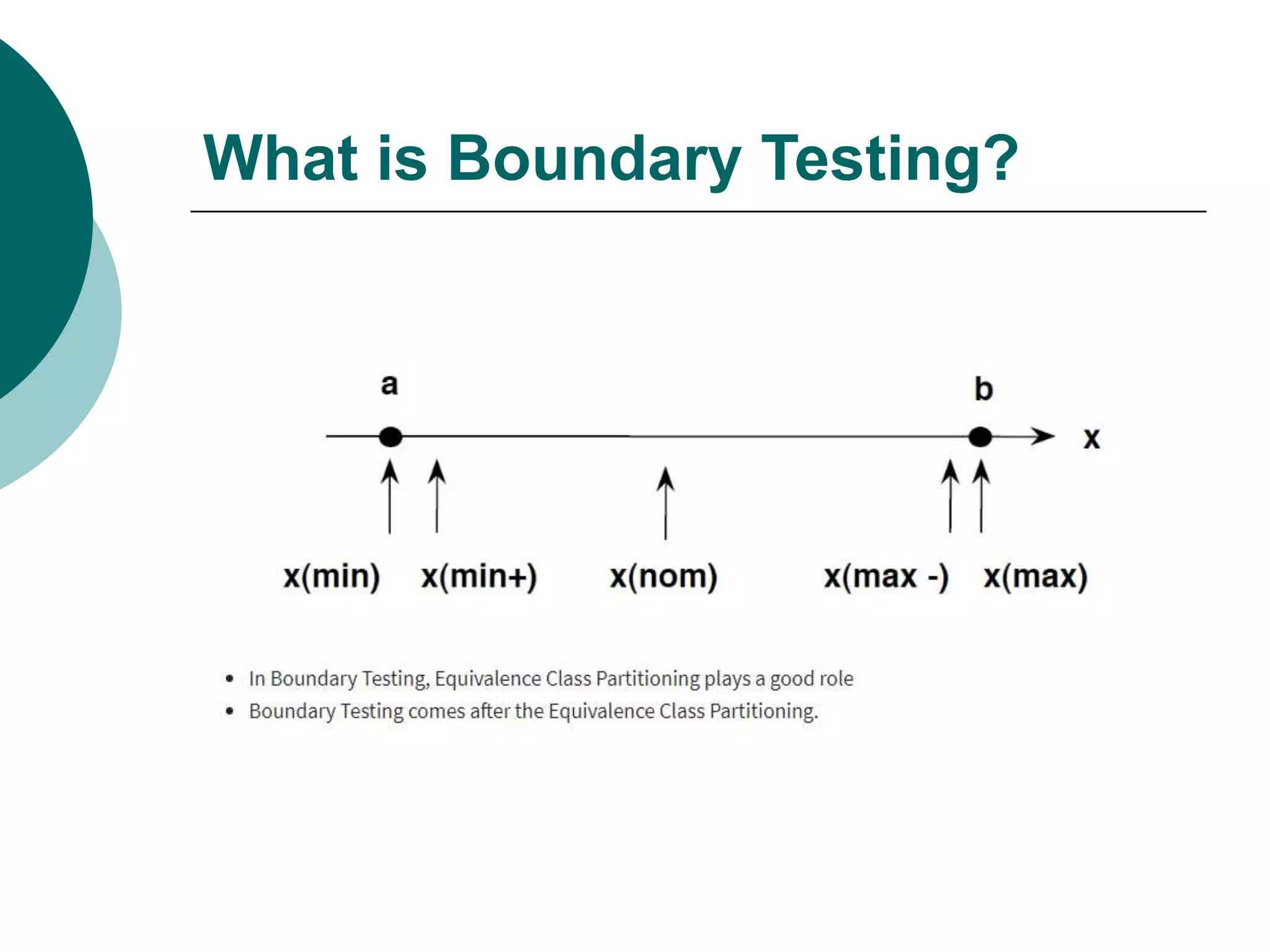
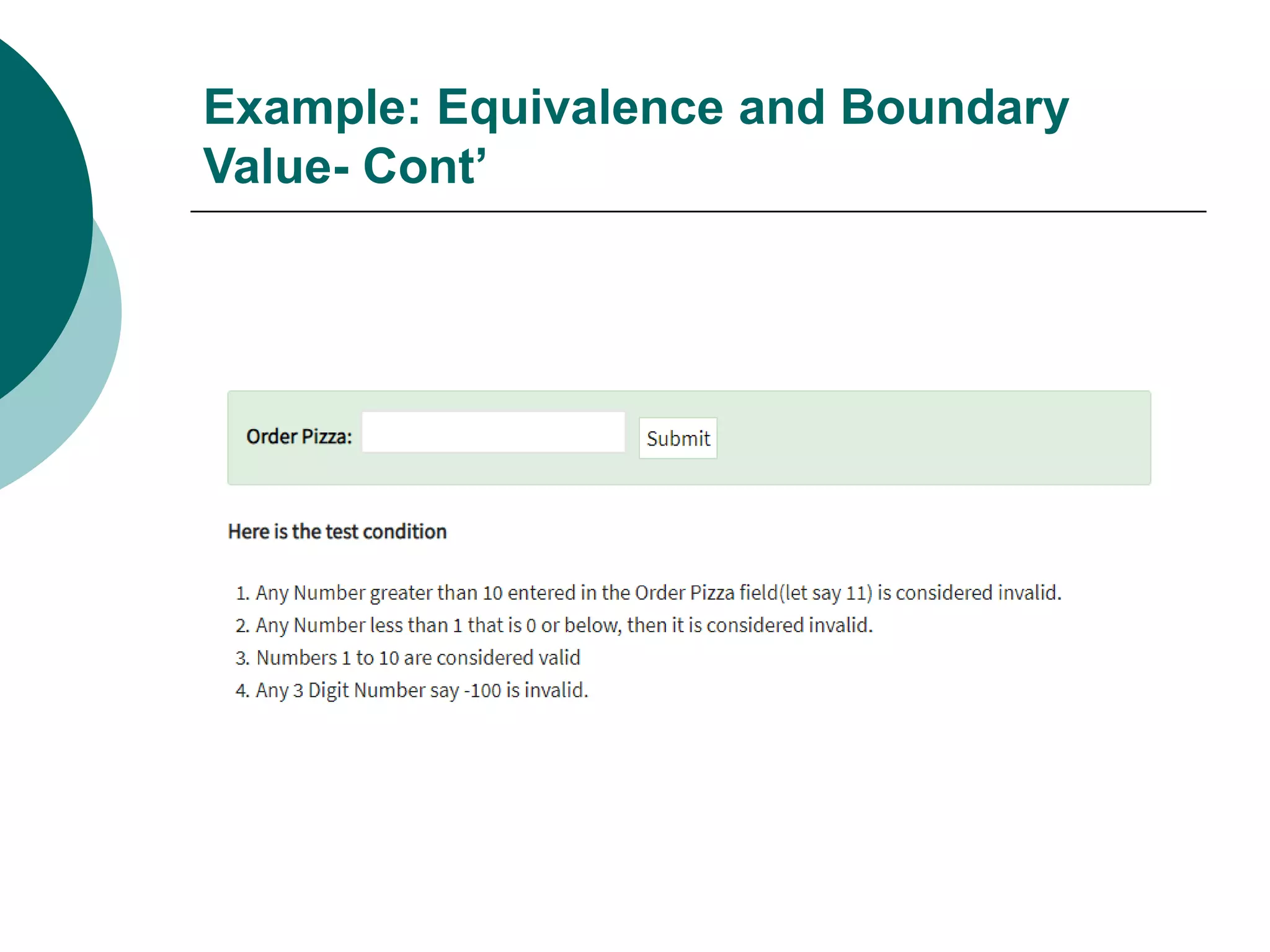
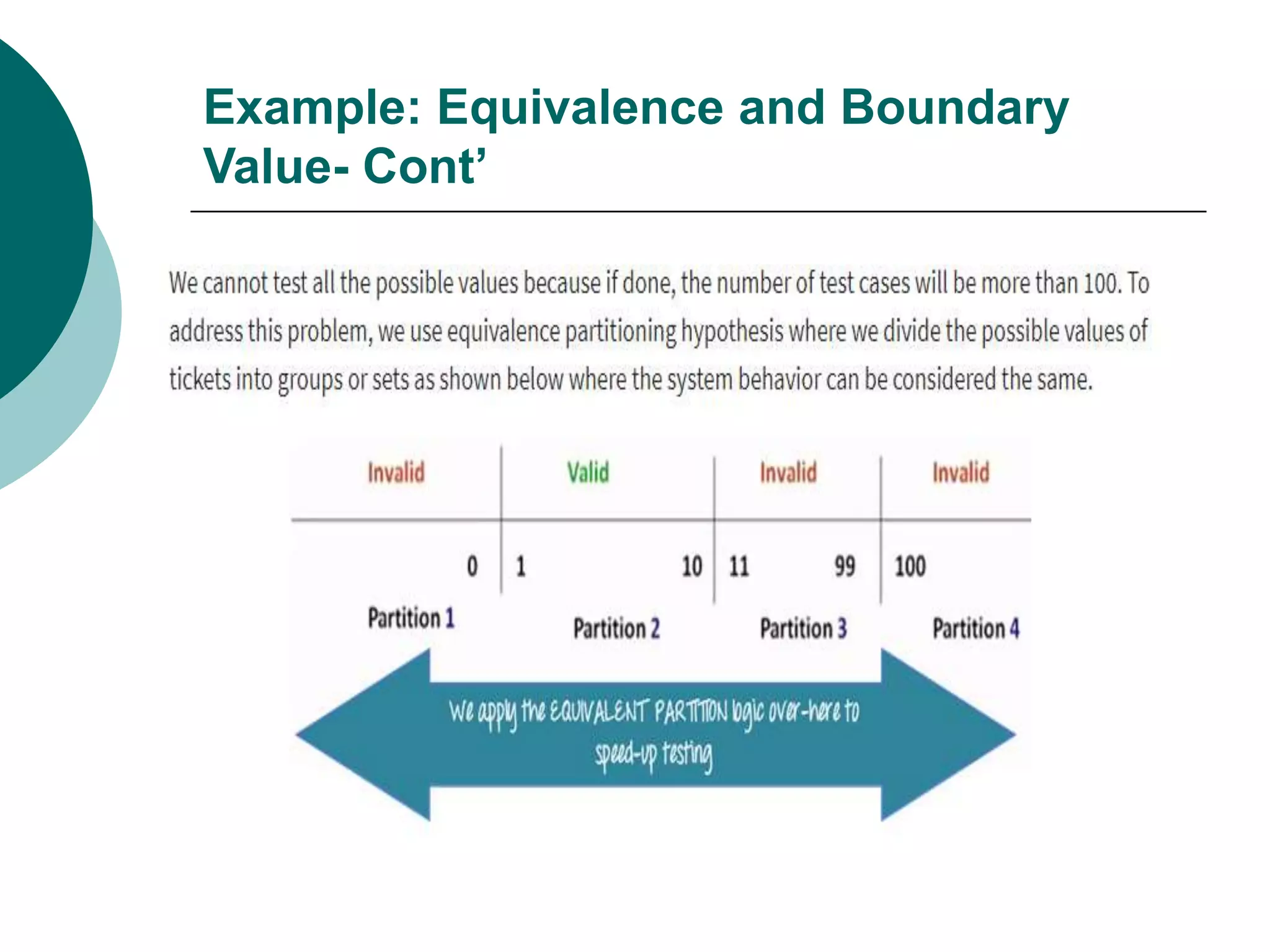
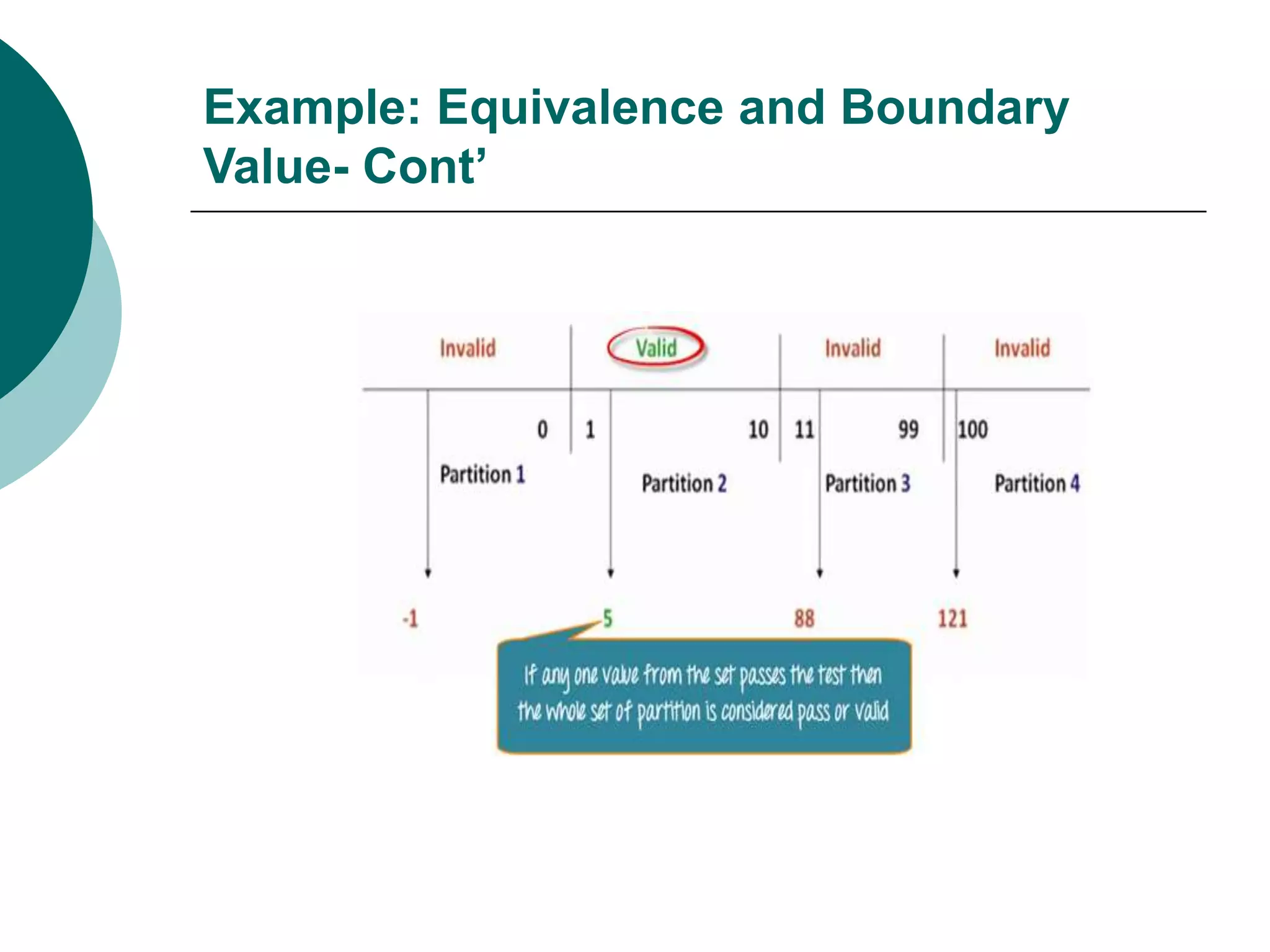
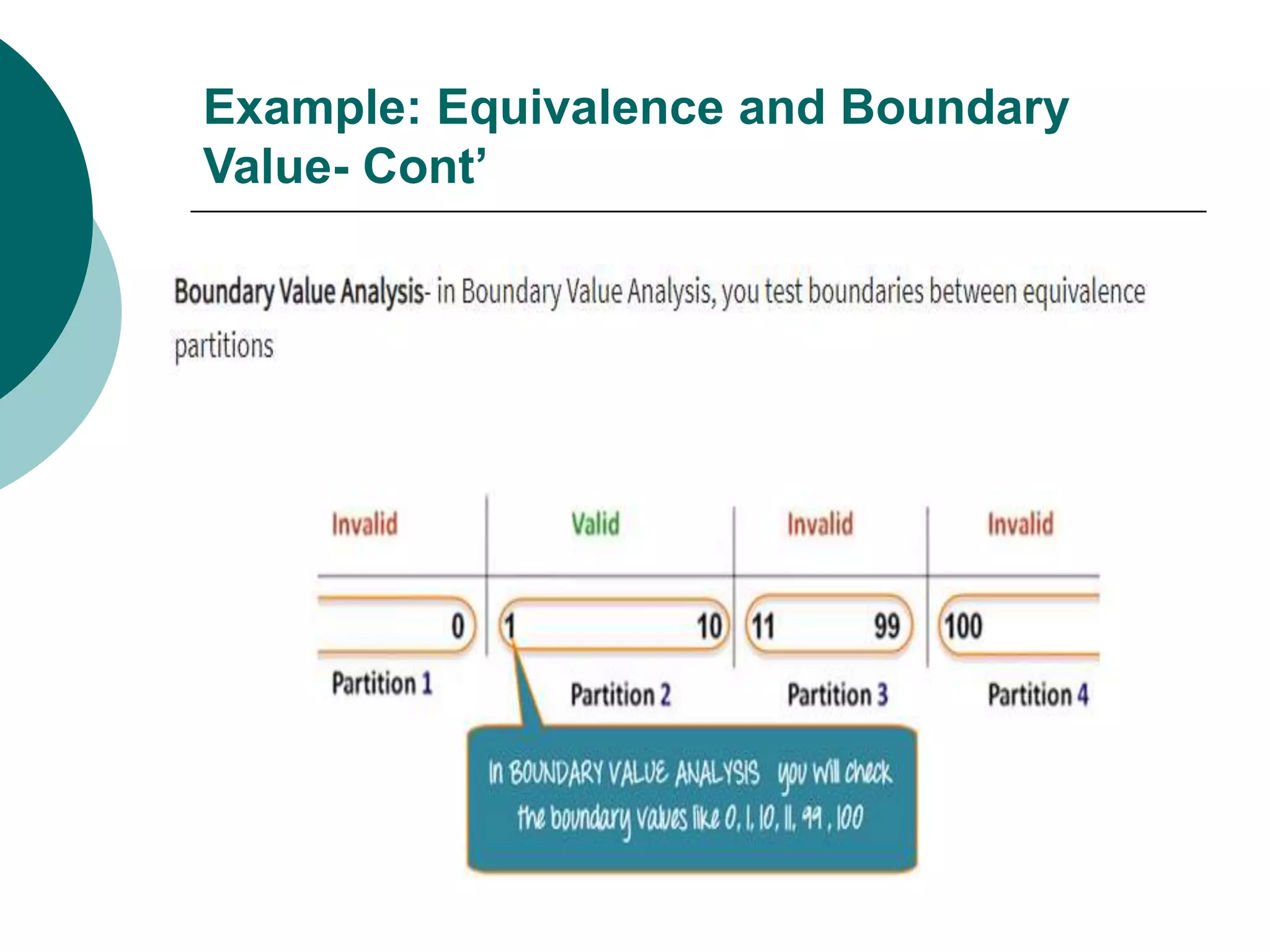
Equivalence partitioning (ECP) is a software testing technique that divides input data into equivalent classes and designs test cases to cover each class. Boundary value analysis tests boundary values between partitions, such as minimum, maximum, and values just inside/outside boundaries. Together, equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis provide guidelines for intelligently selecting a manageable number of test cases to cover all scenarios while reducing the total number of cases.