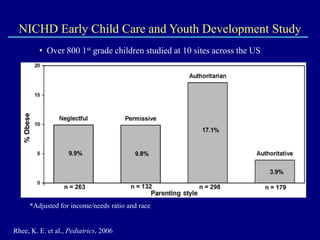
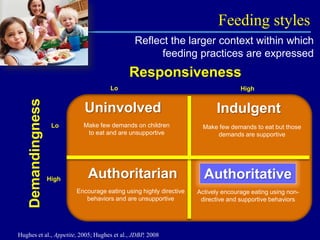
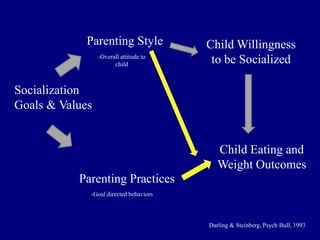
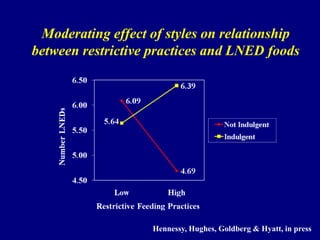
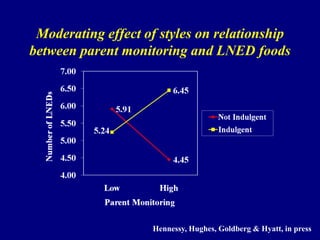
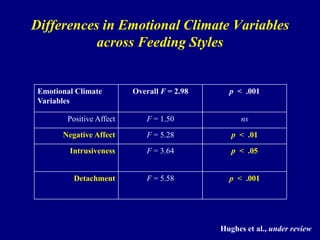
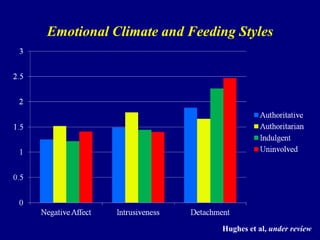
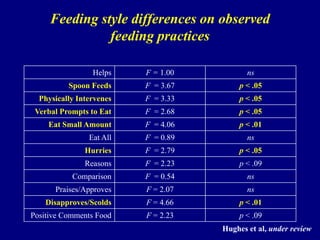
This document discusses research on how parenting styles and feeding styles influence children's eating behaviors and weight outcomes. It finds that:
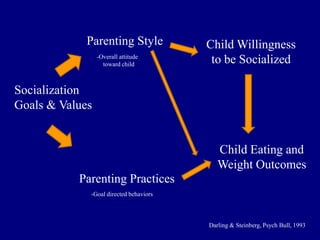
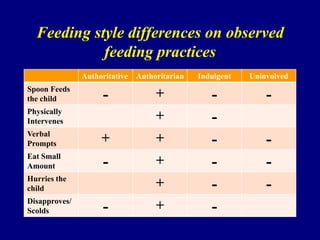
1) Authoritarian parenting styles and indulgent feeding styles are associated with less optimal child eating behaviors and higher risk of obesity.
2) Parents with authoritative feeding styles encourage healthier eating through supportive practices like monitoring intake and making nutritious foods available.
3) Indulgent parents are less involved with meals and make fewer demands, relating to children selecting larger portions and eating more calorie-dense foods.
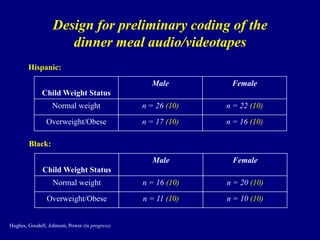
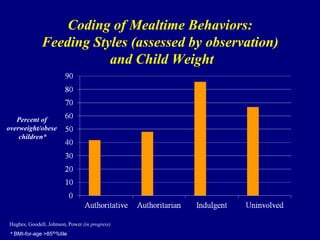
4) Observational research confirms that indulgent parents show more detachment and permissive behaviors during meals, while authoritarian parents display intrusive practices.