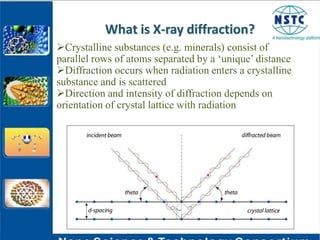
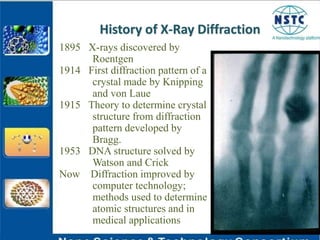
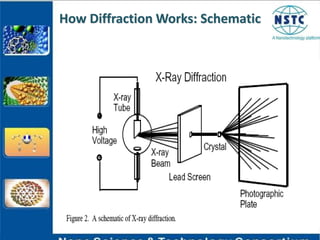
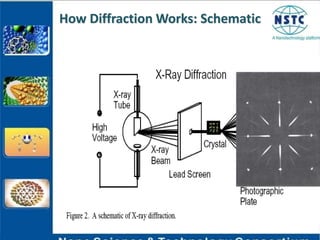
X-ray diffraction is a non-destructive technique used to identify crystalline materials by analyzing the scattering pattern of X-rays hitting a sample. Crystalline materials consist of atoms arranged in a regular repeating pattern that causes X-rays to diffract in specific directions. The diffraction pattern is compared to known patterns to determine the sample's structure and composition. X-ray diffraction is used in fields like solid-state physics, biophysics, and chemistry to study materials at the atomic scale.