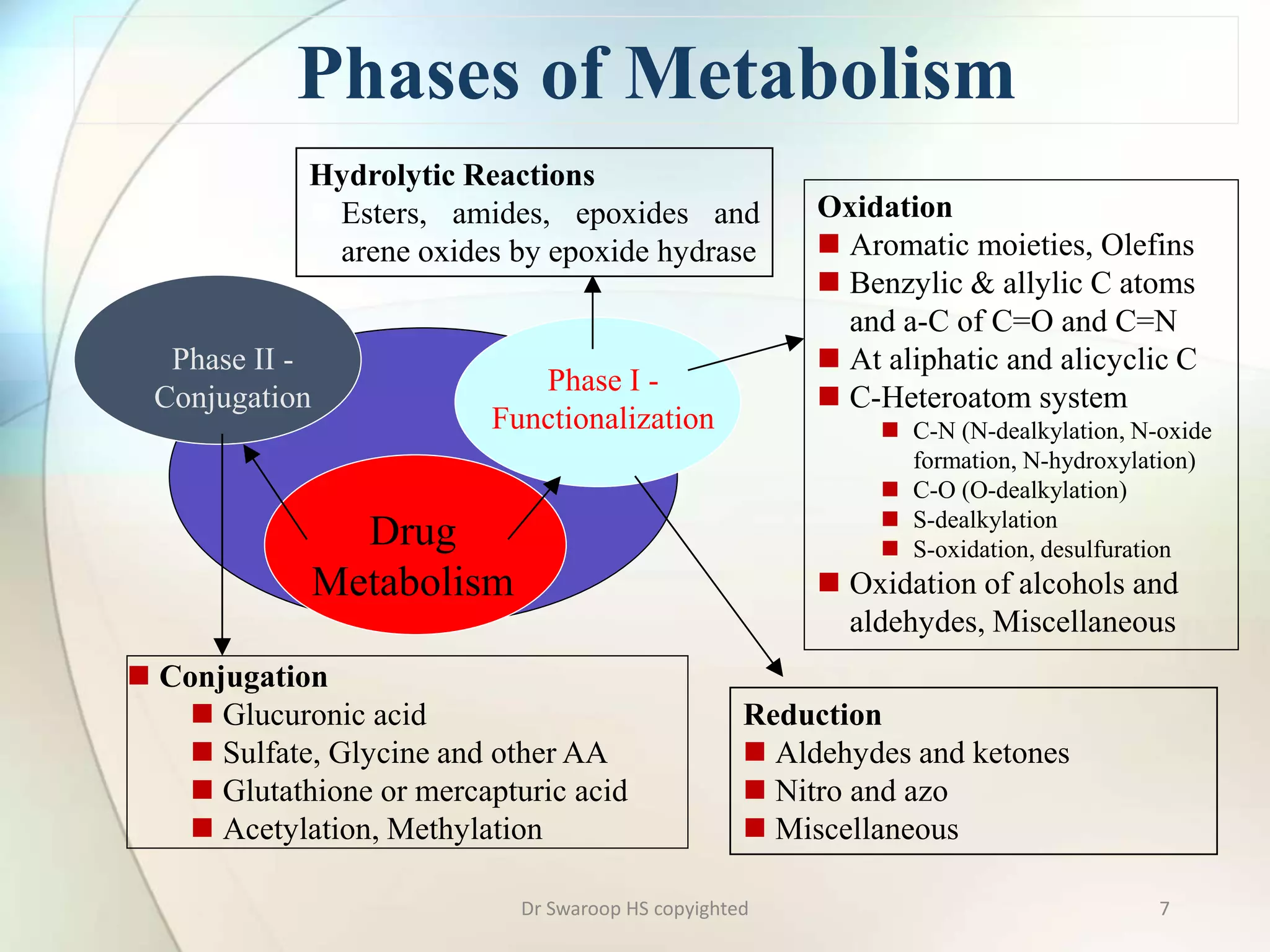
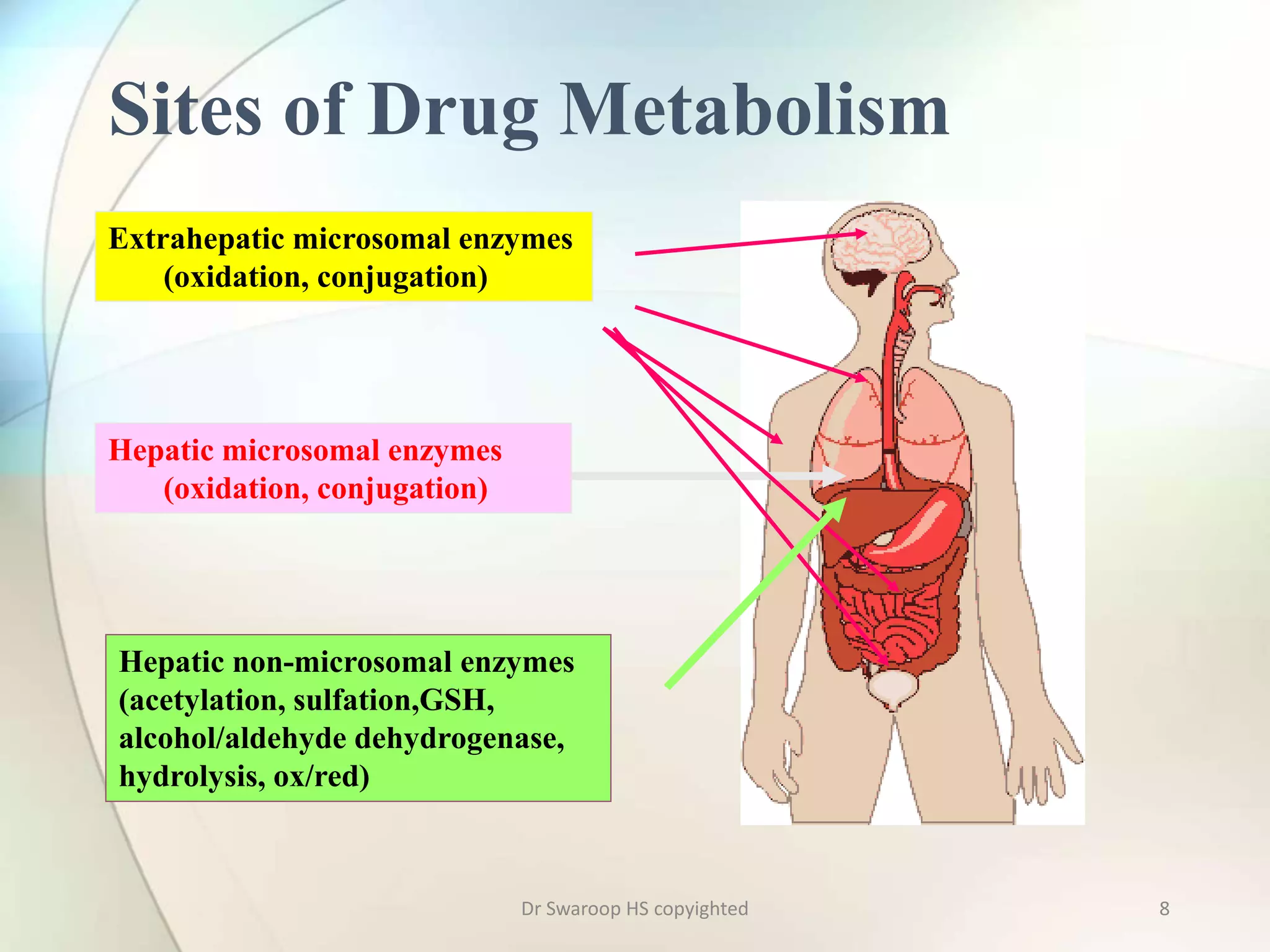
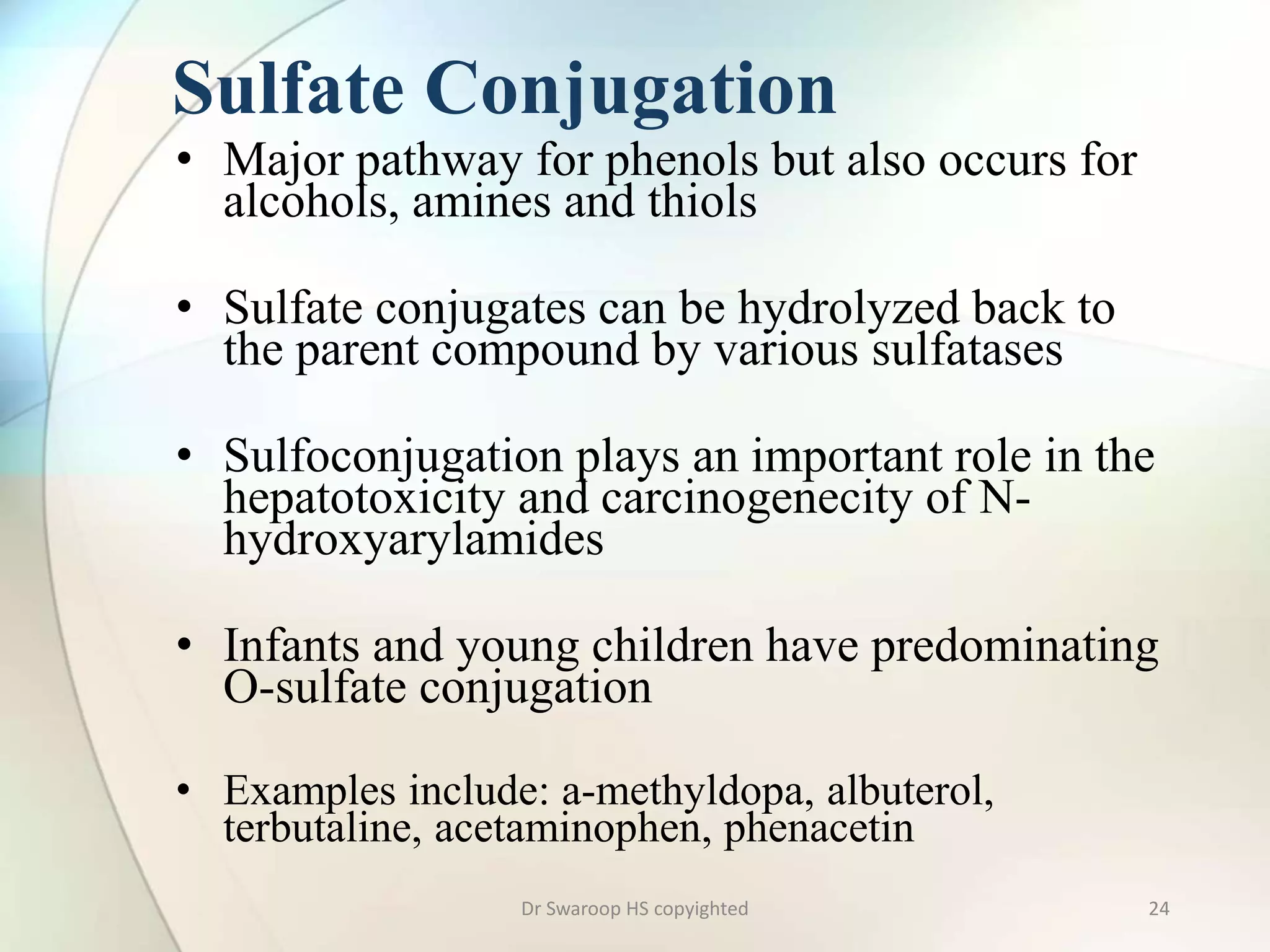
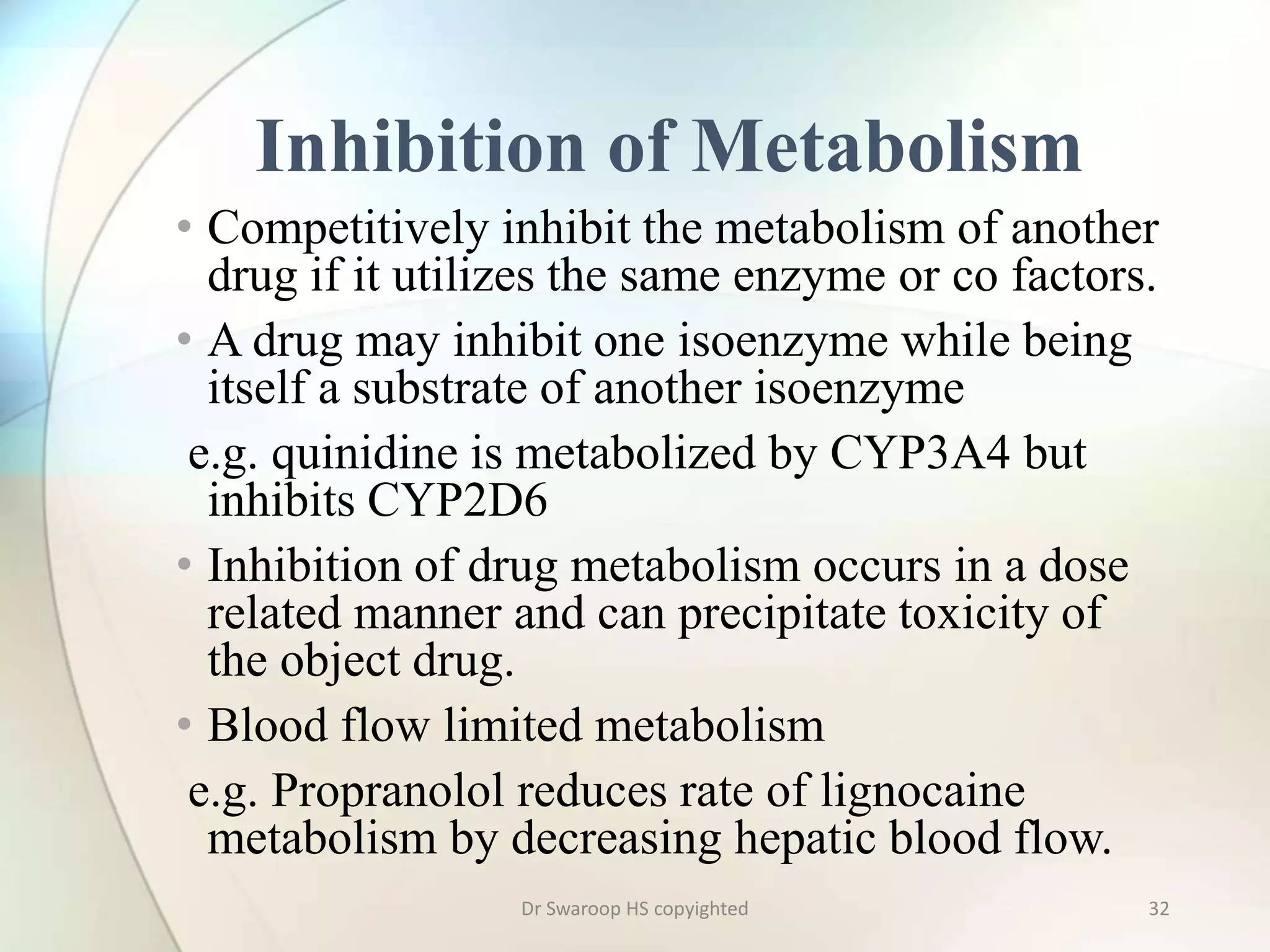
Drug metabolism involves two main phases: Phase I involves reactions like oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis that make the drug more polar. This is mainly done by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. Phase II involves conjugating reactions like glucuronidation, sulfation and acetylation to make the drug more water soluble for excretion. Cytochrome P450 isoenzymes like CYP3A4 metabolize many drugs. Understanding drug metabolism is important in drug discovery and development.