Embed presentation
Download to read offline


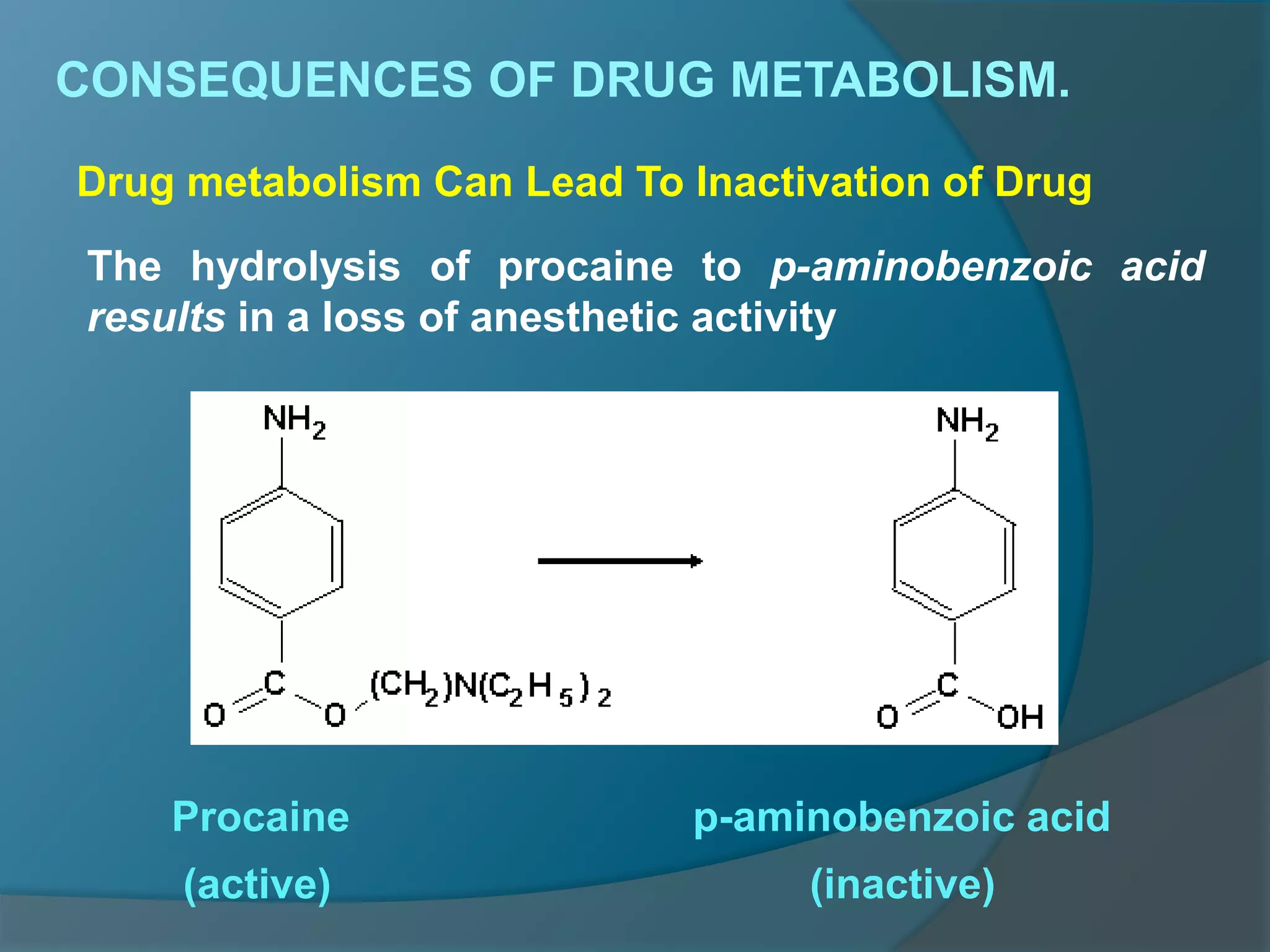
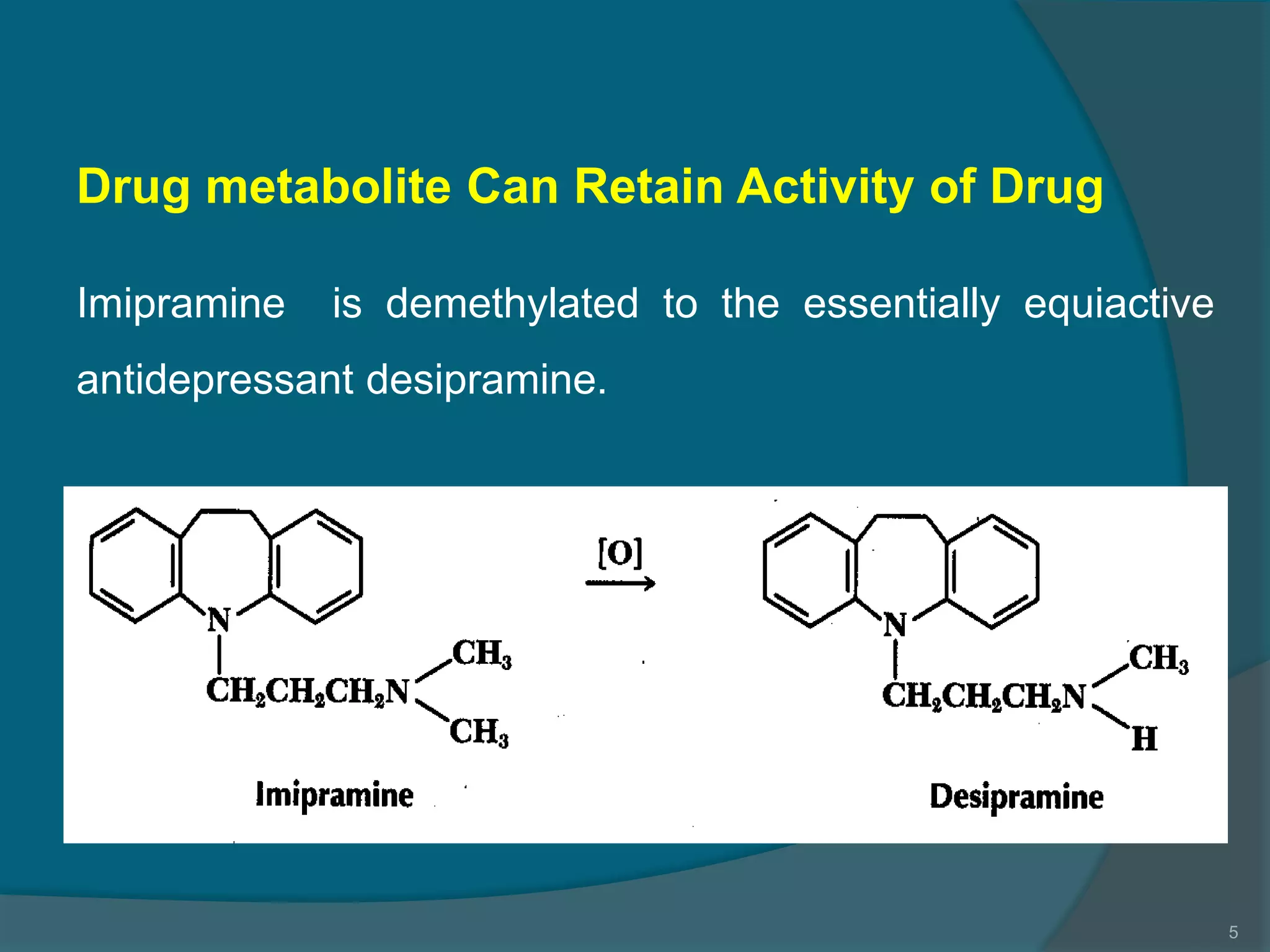

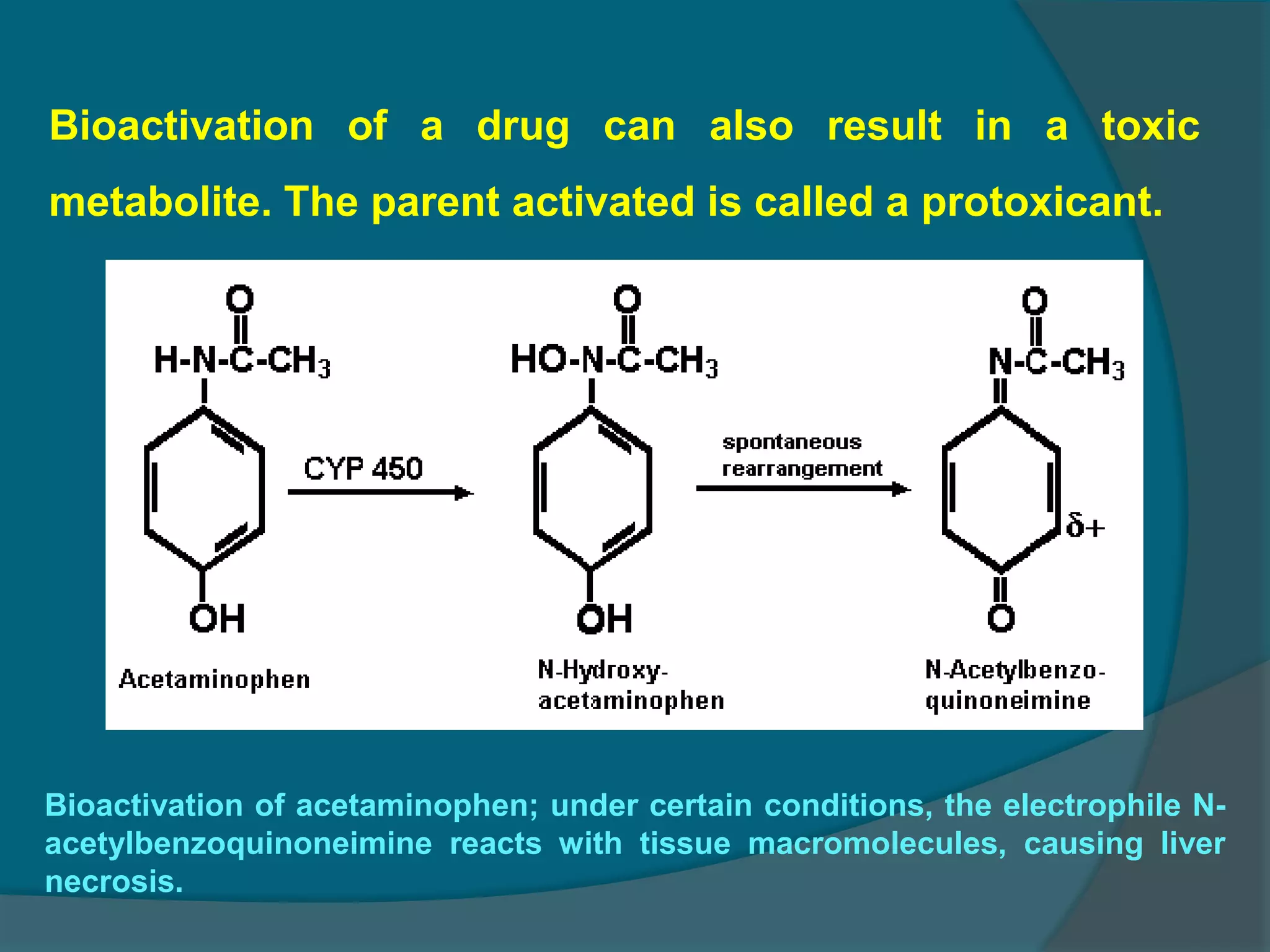
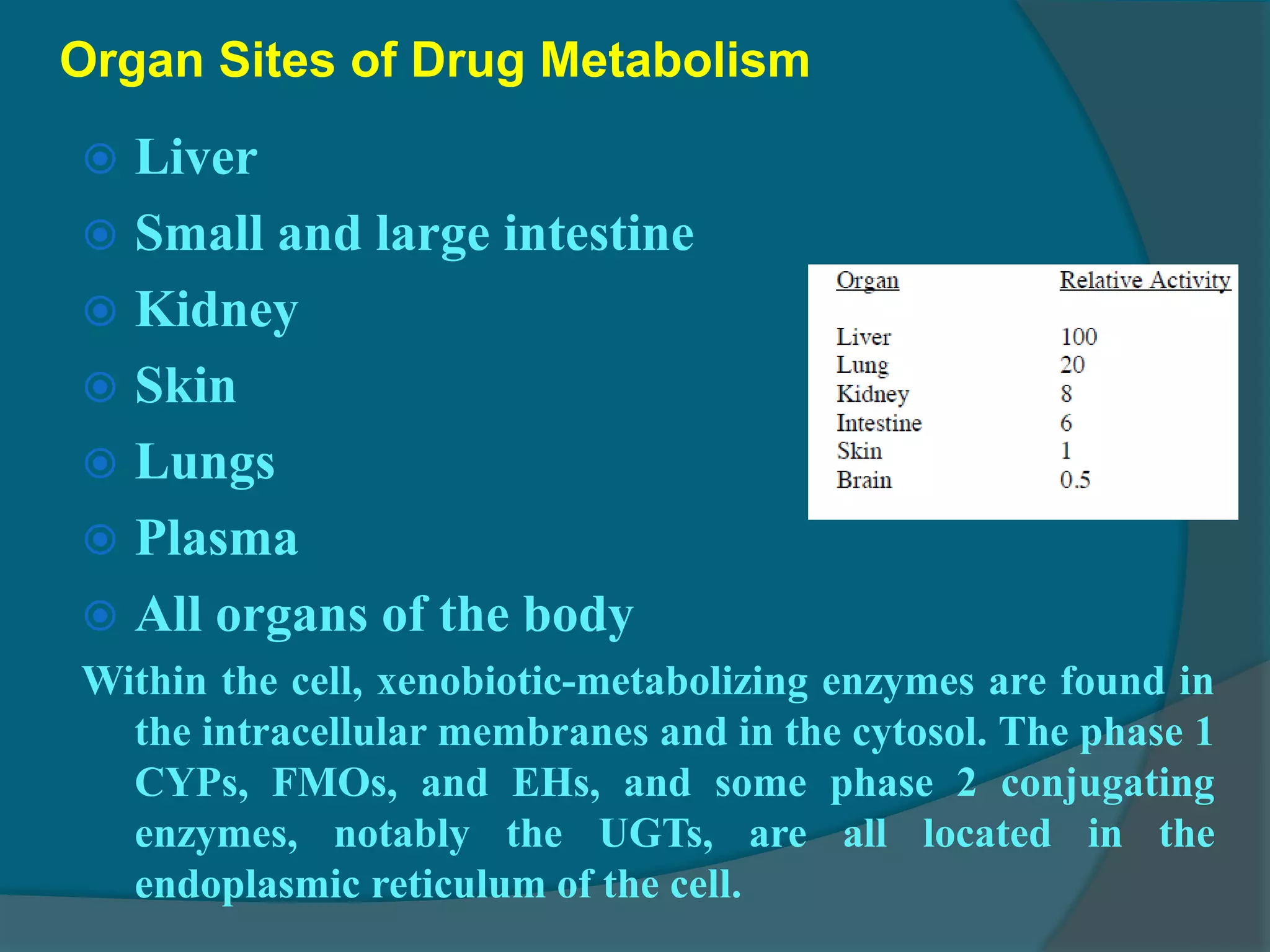
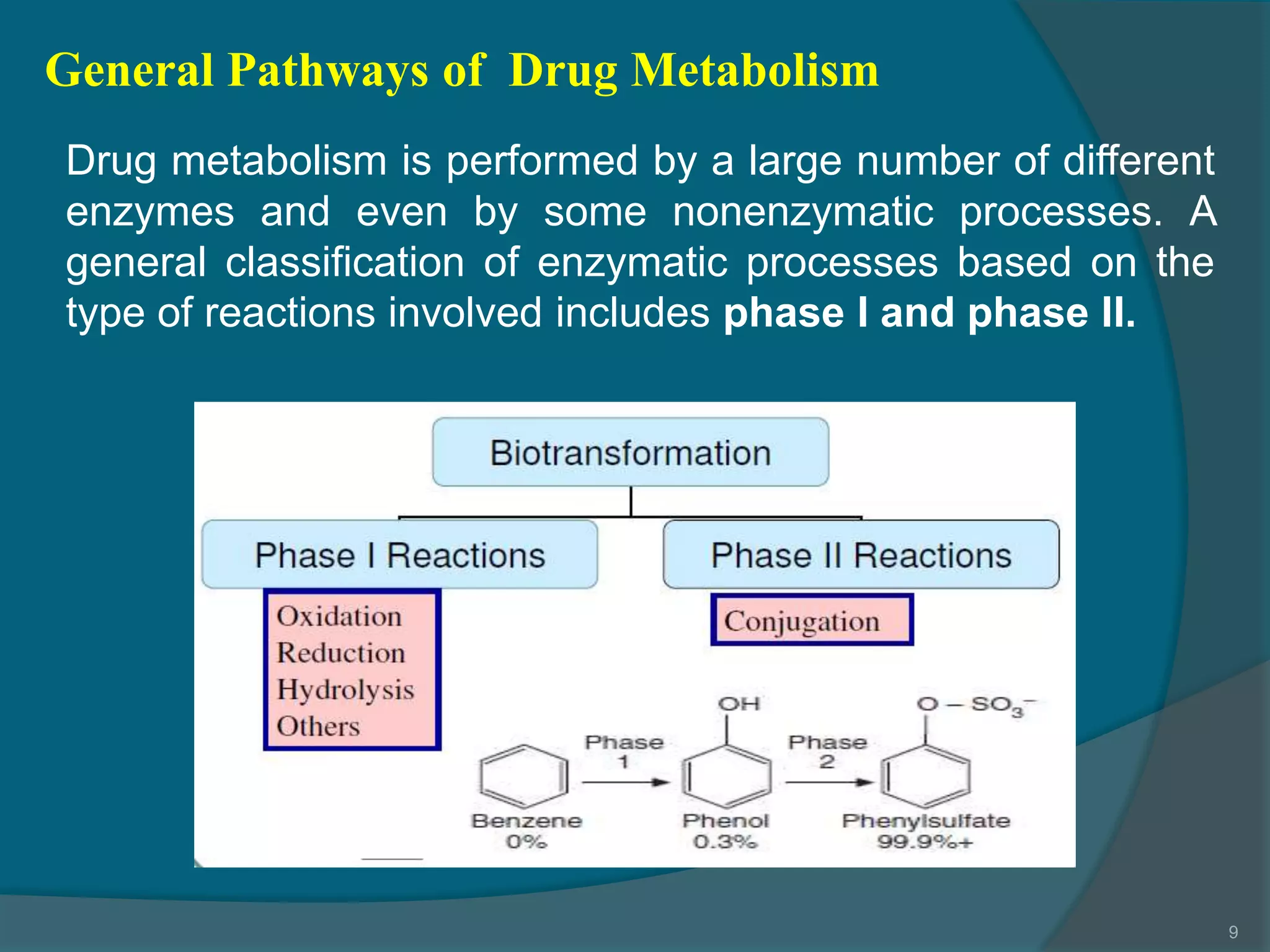


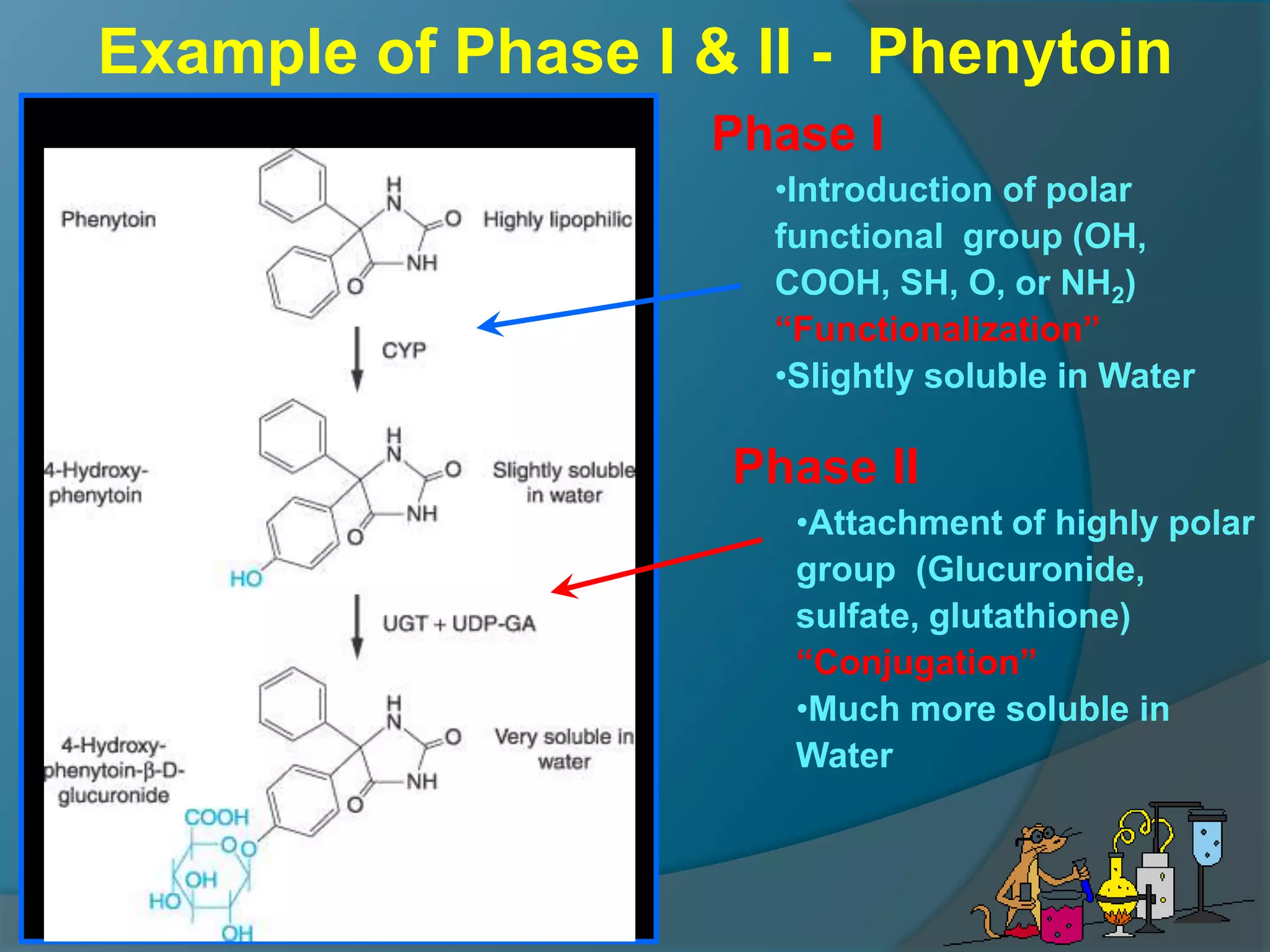
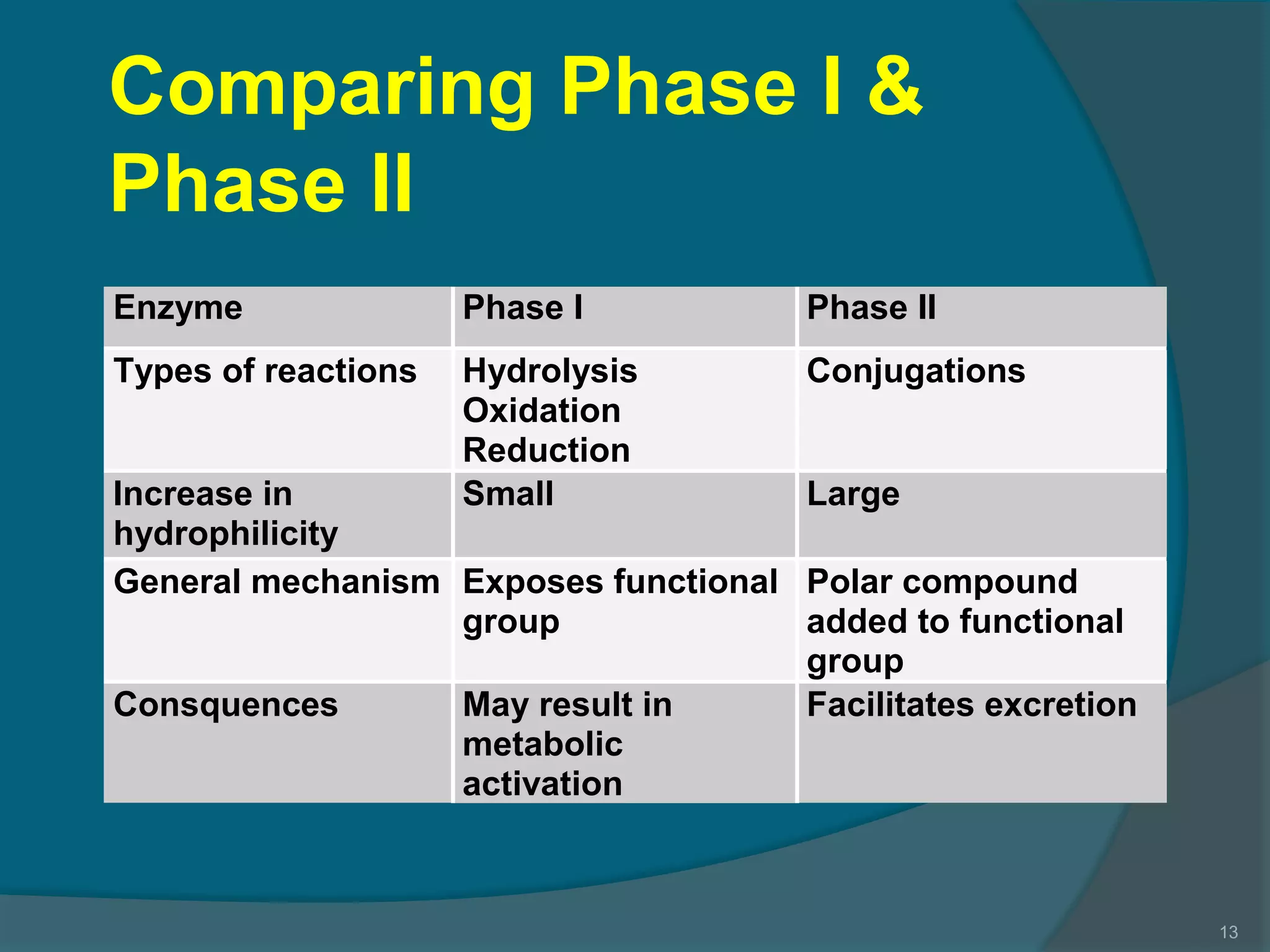
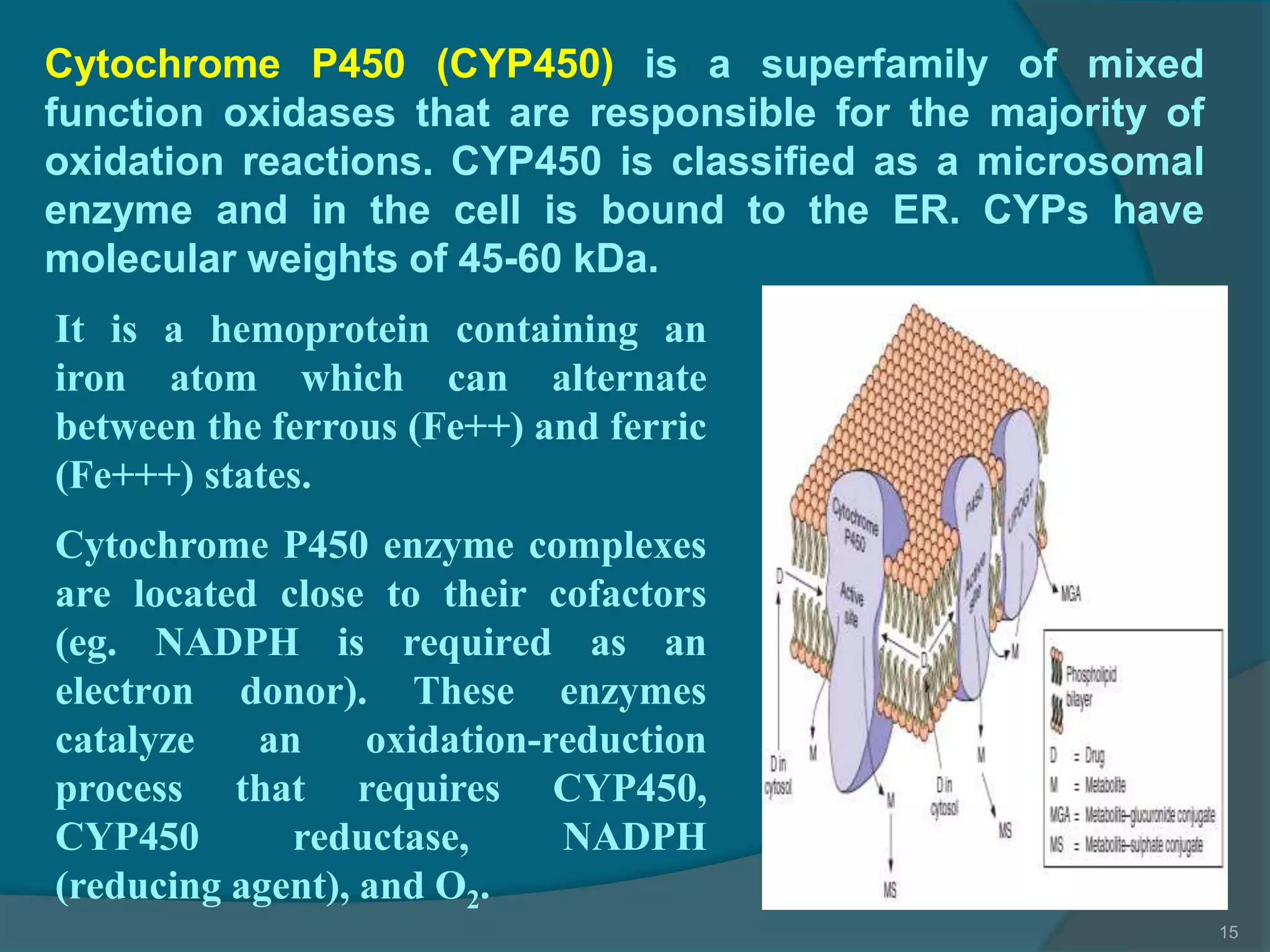
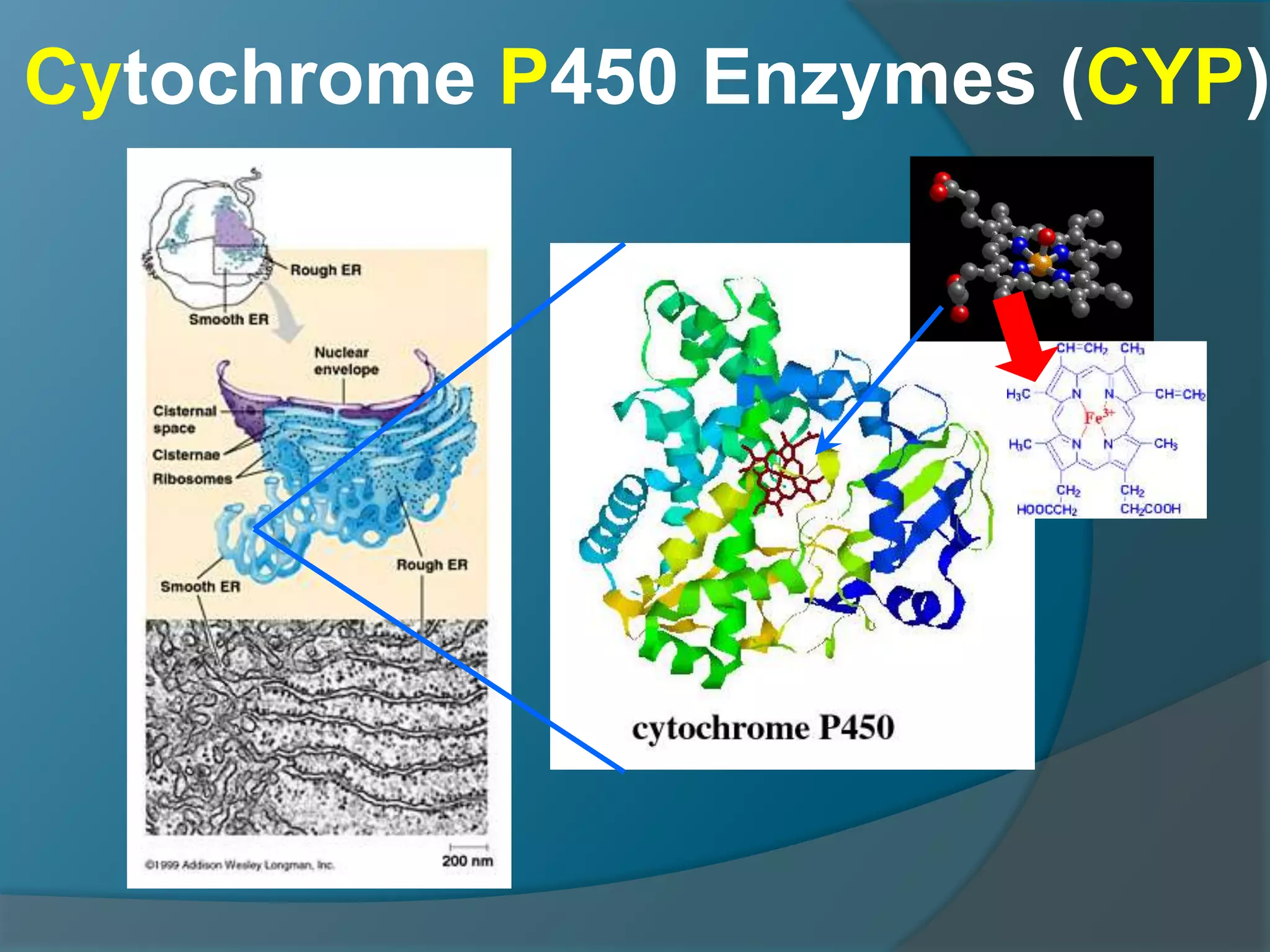

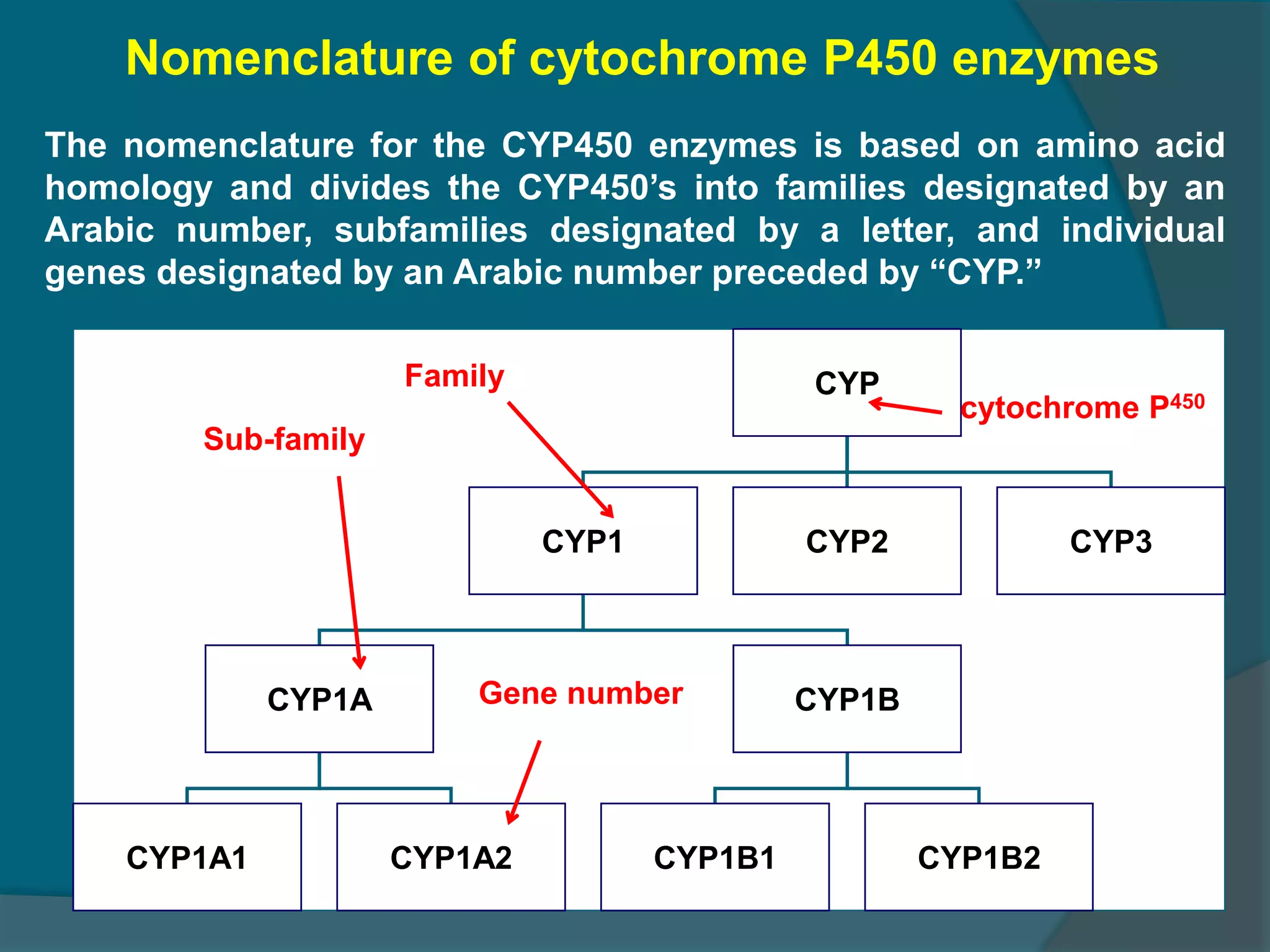
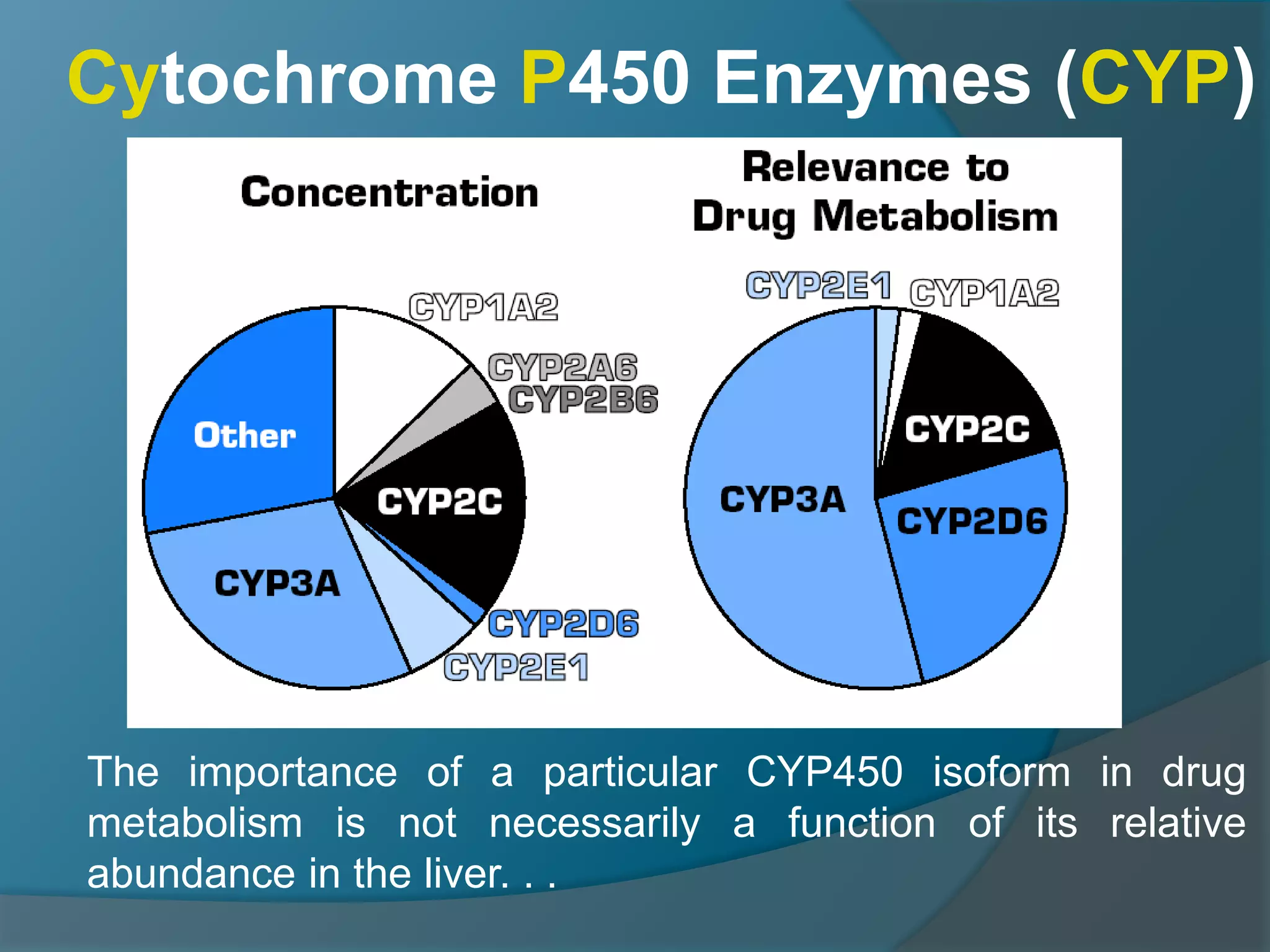
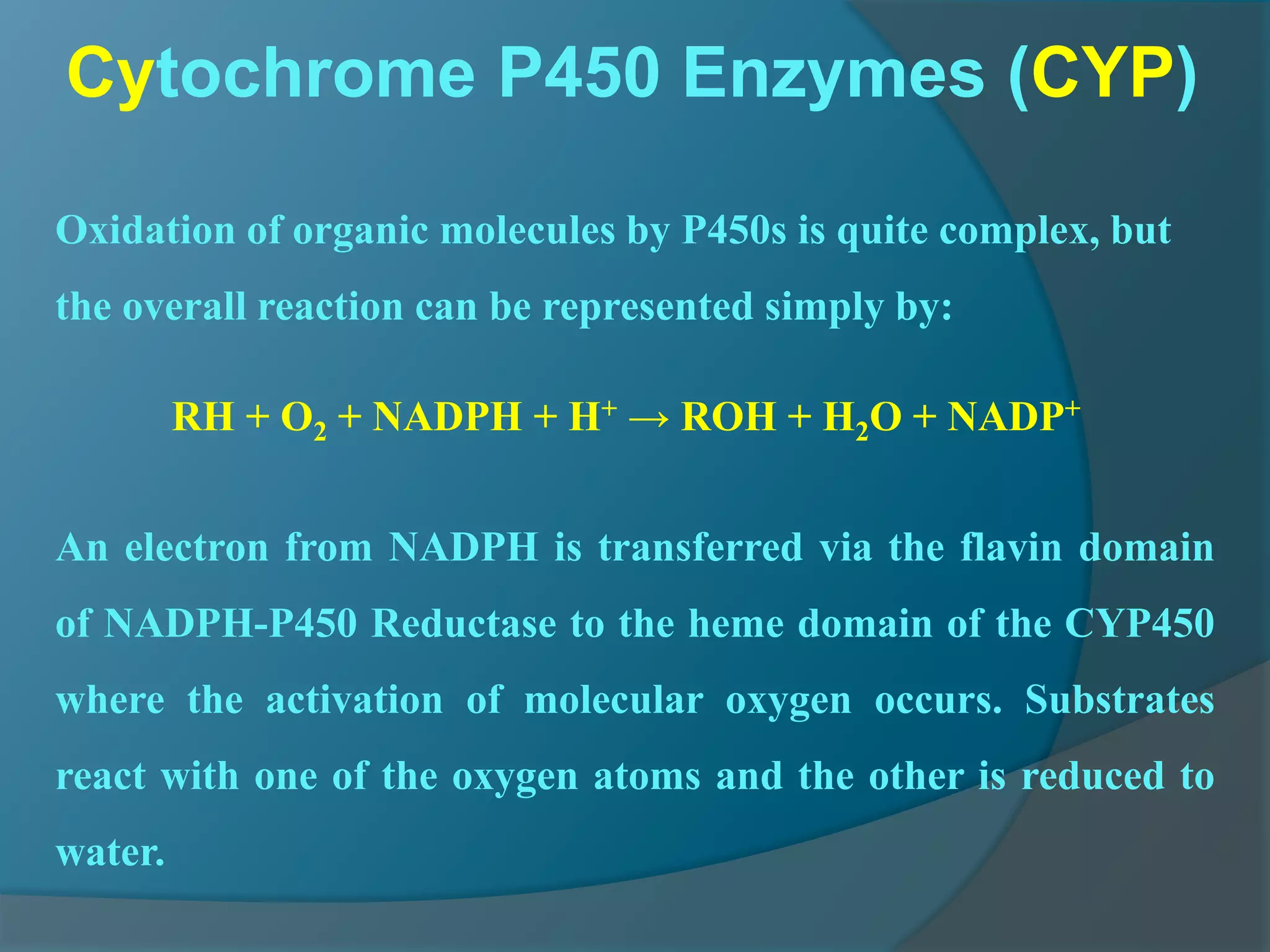
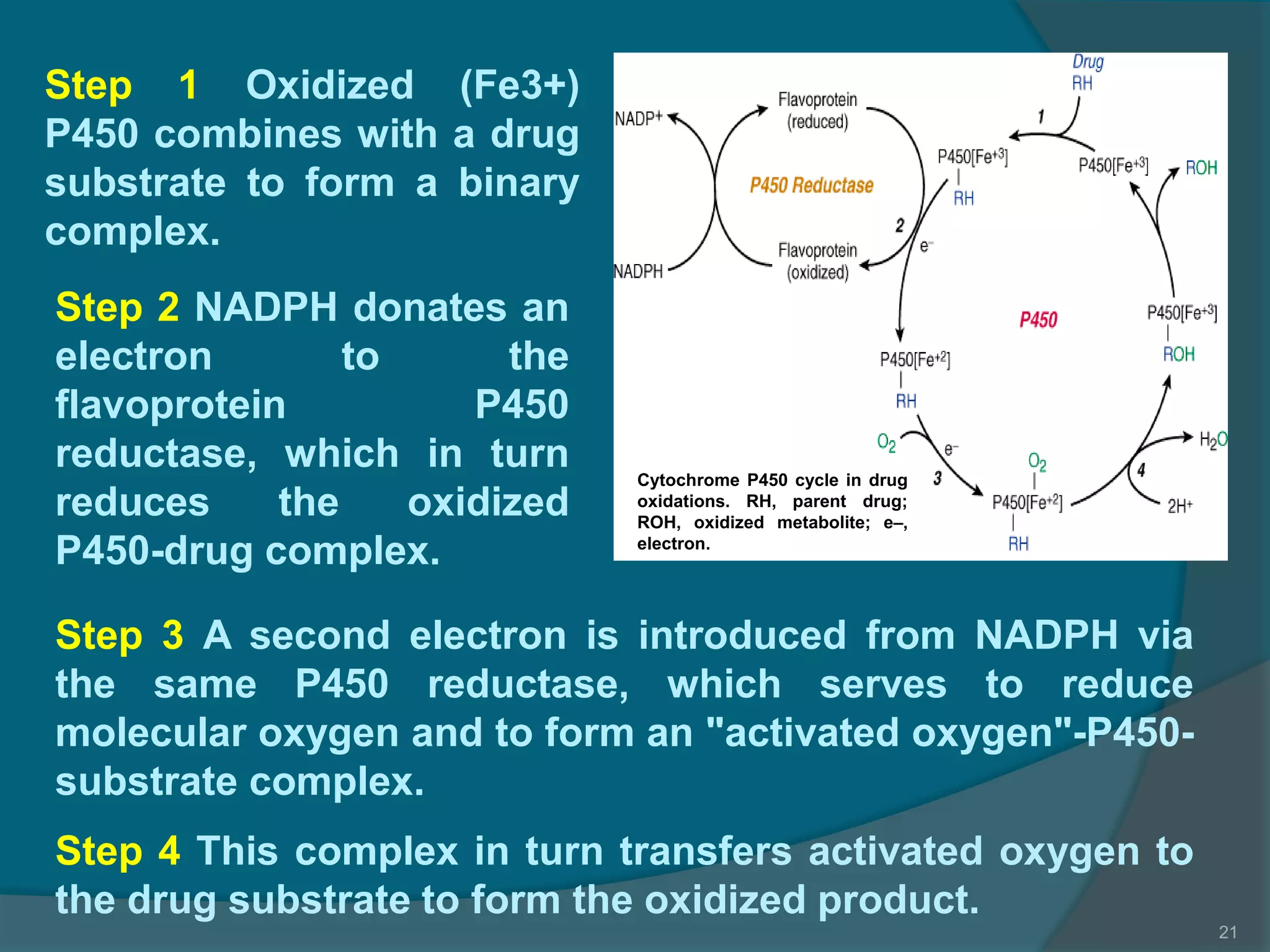
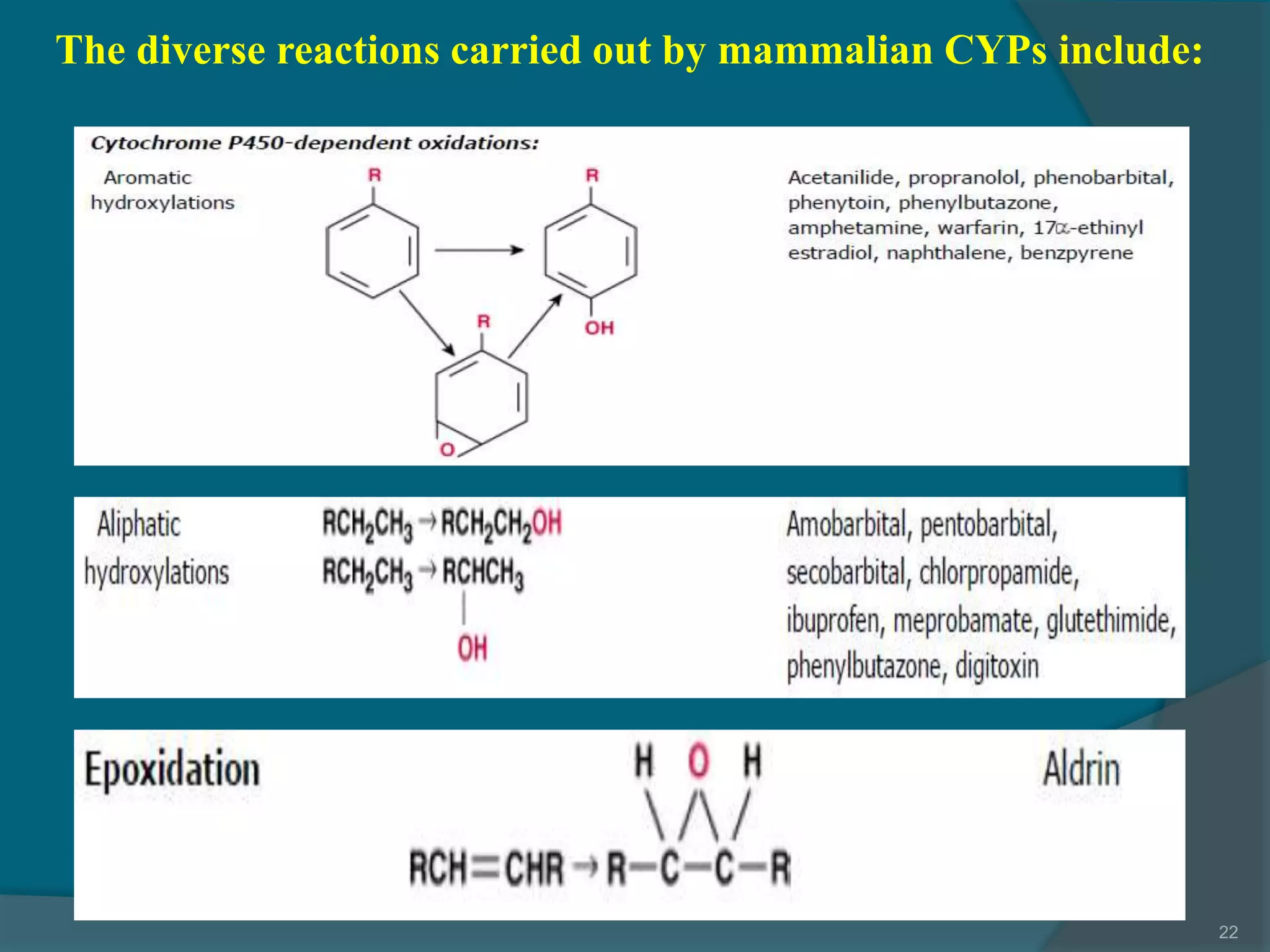
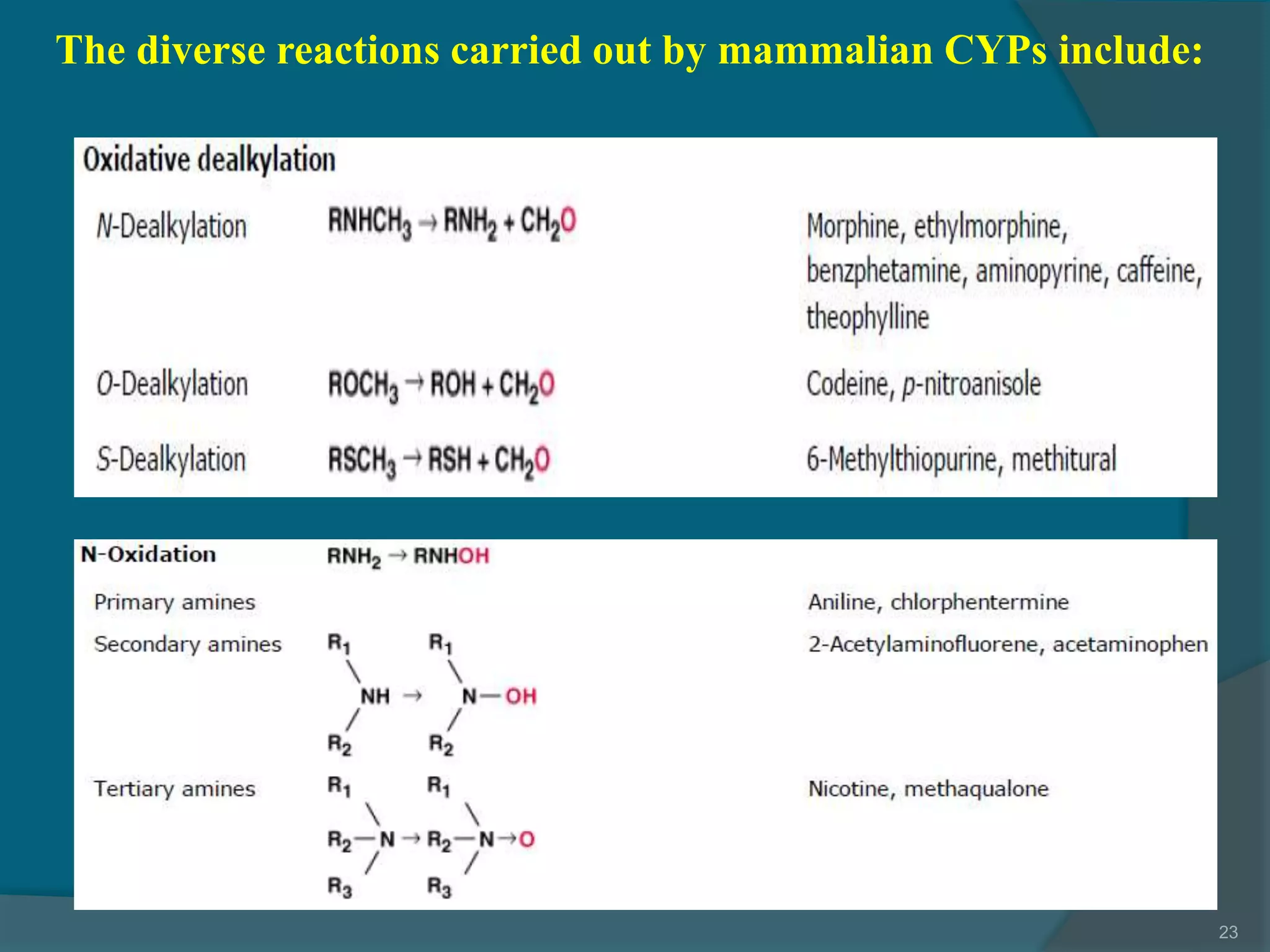
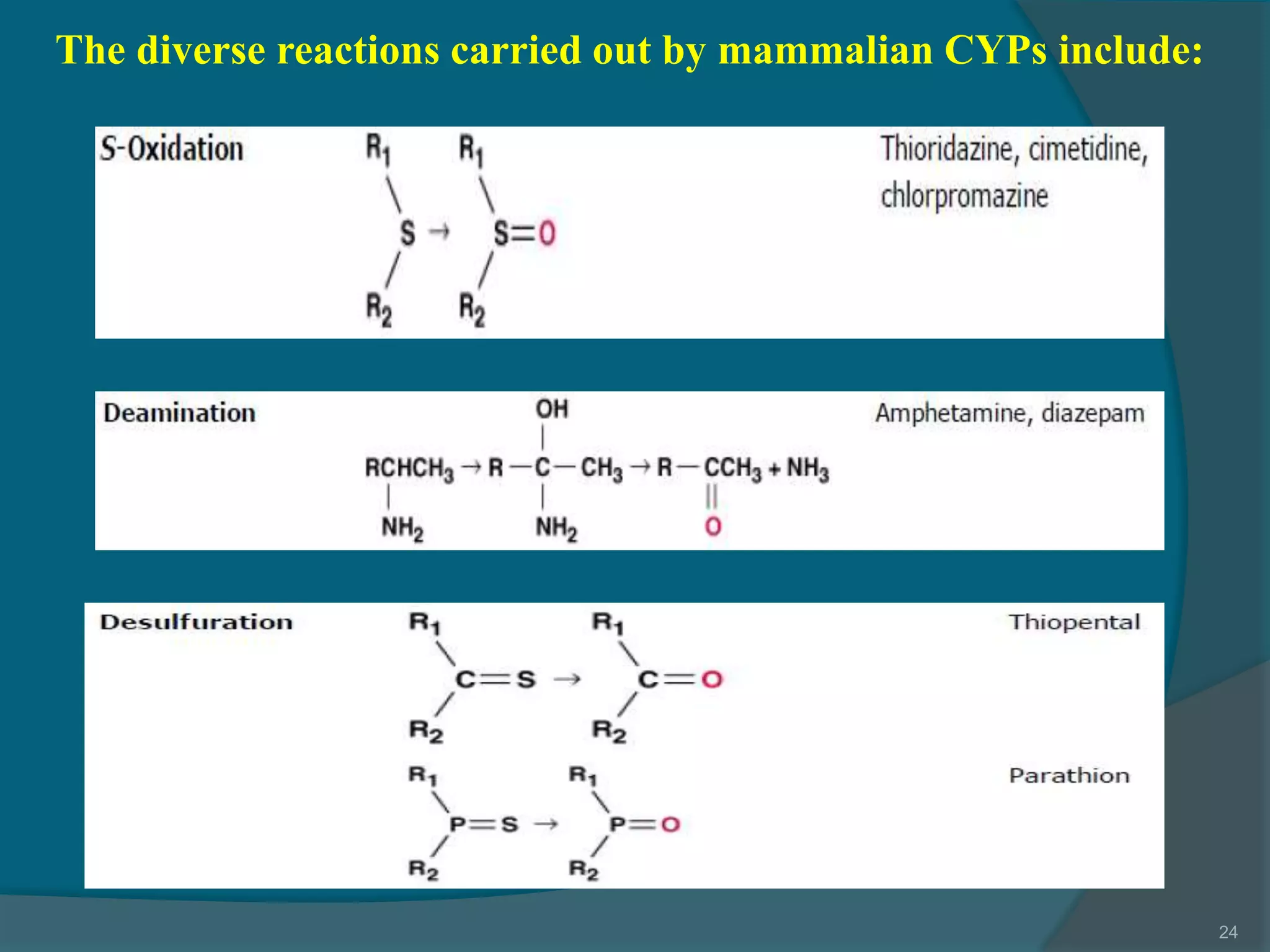
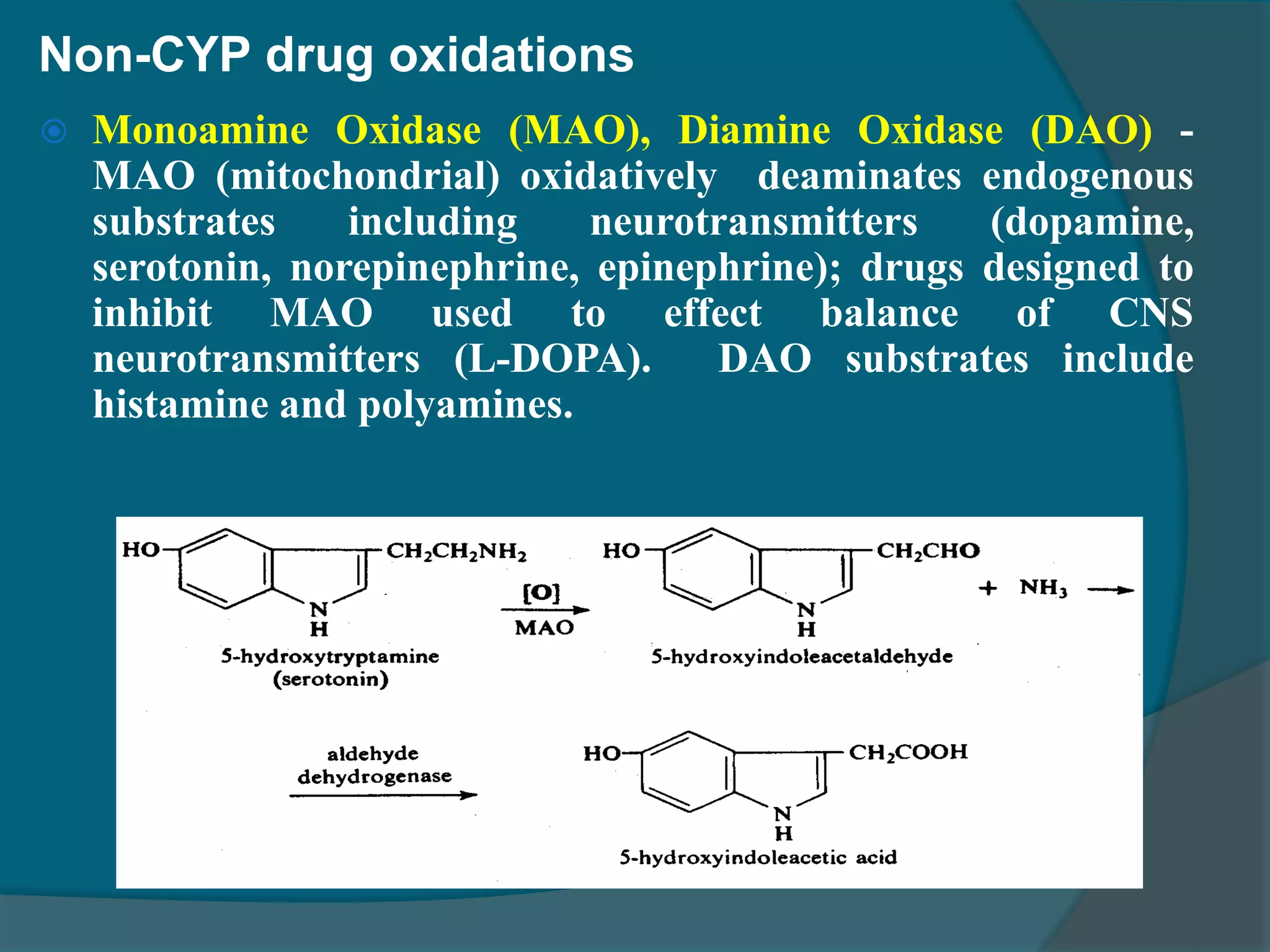
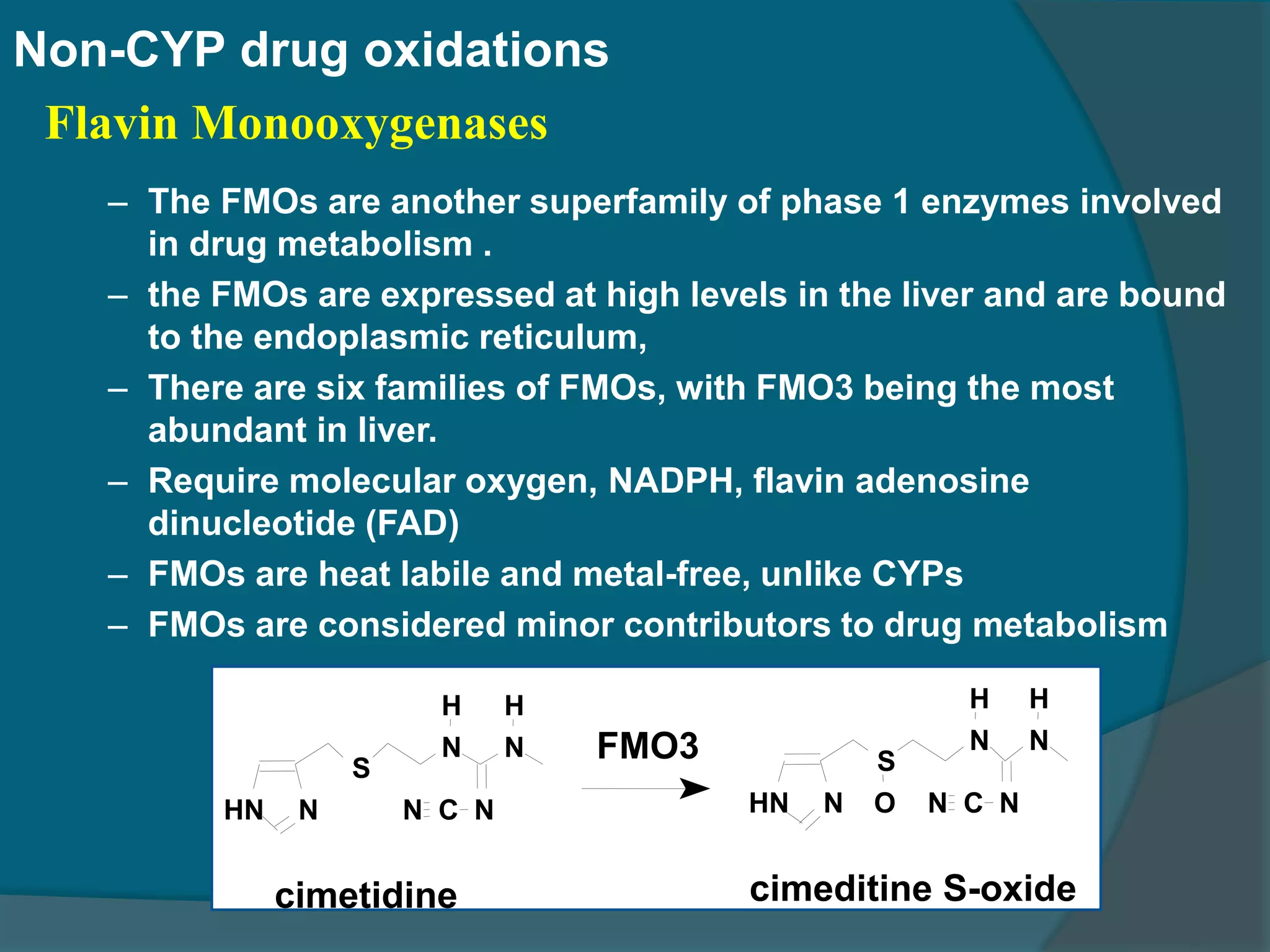
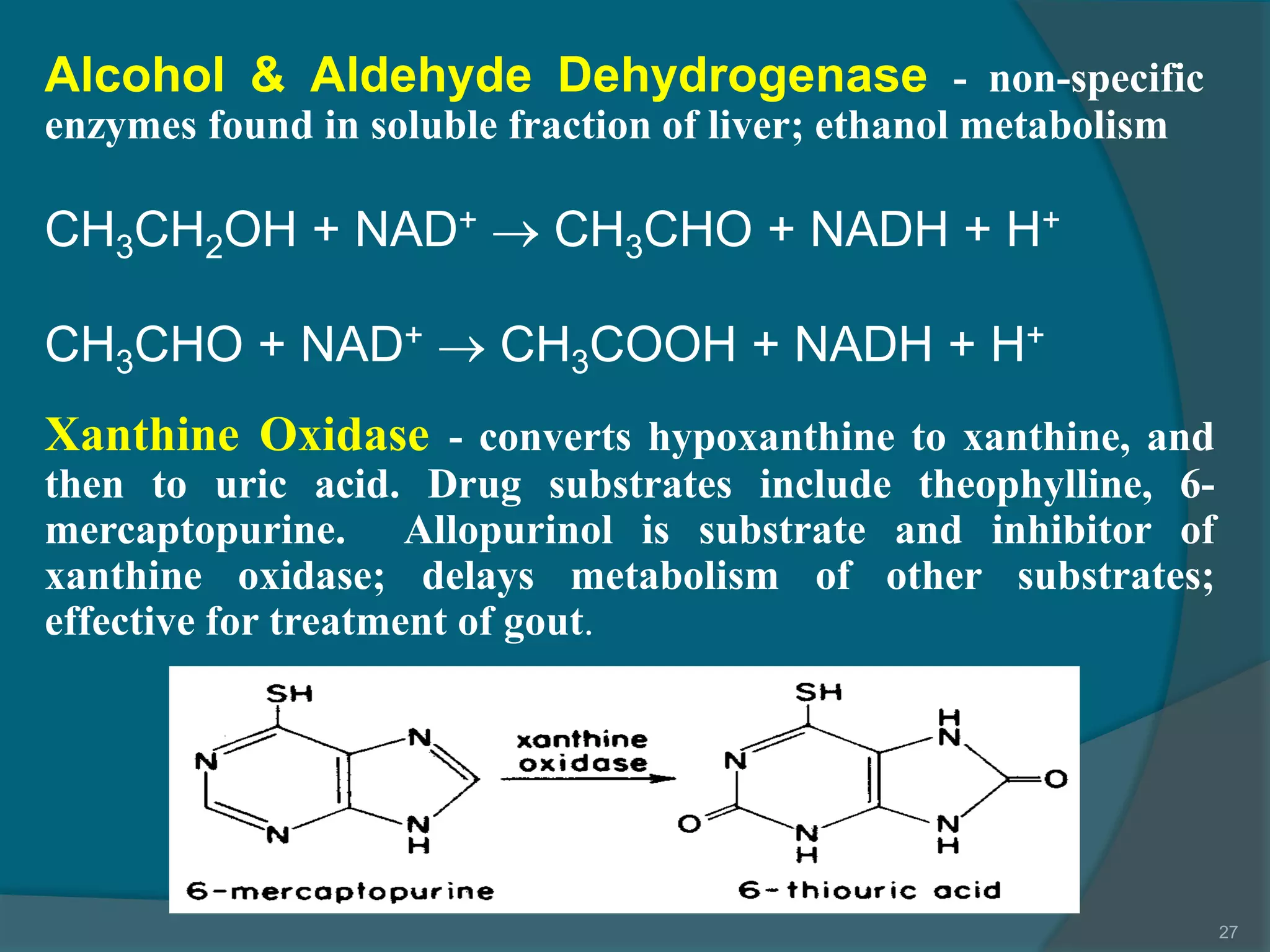
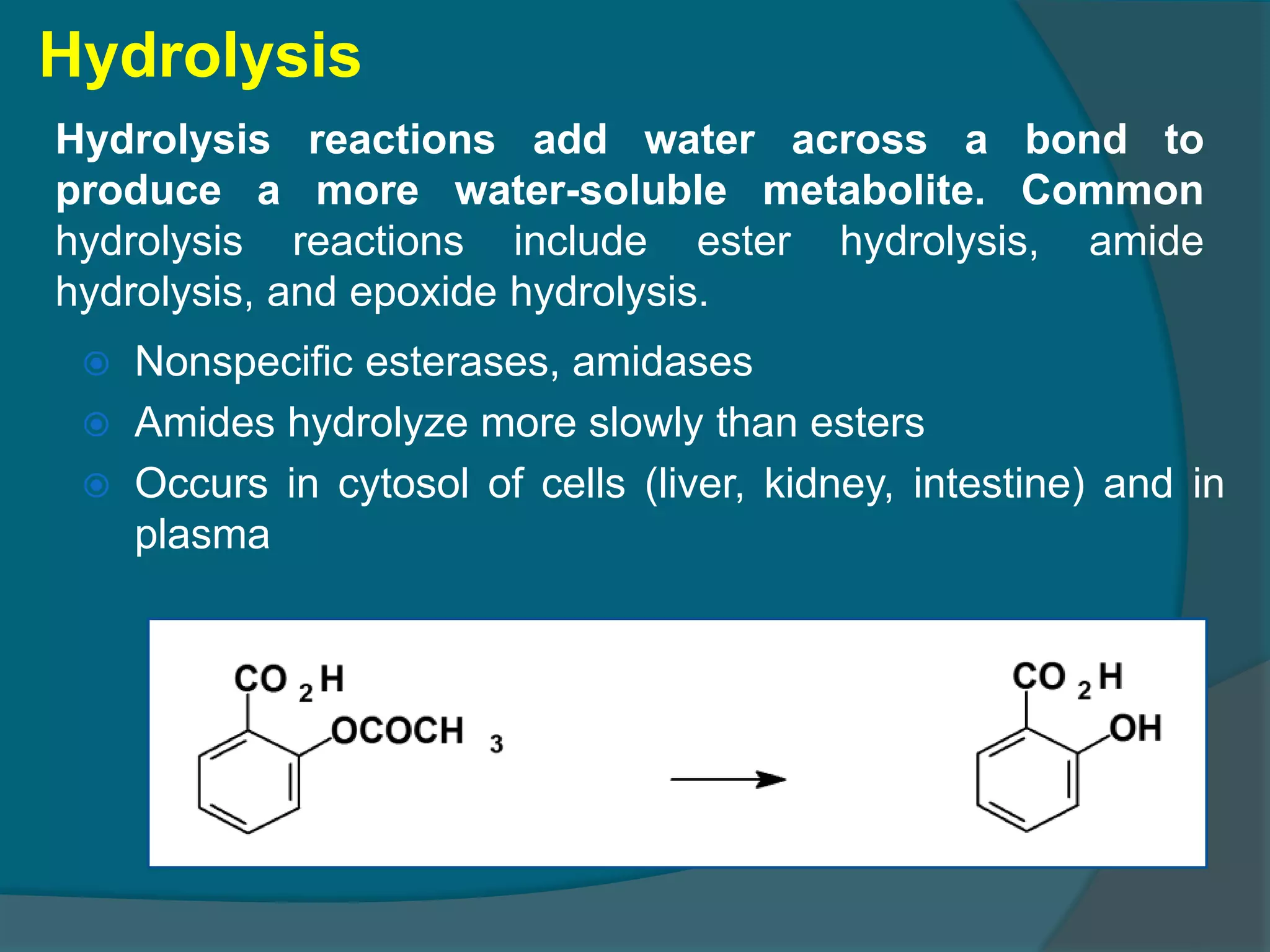
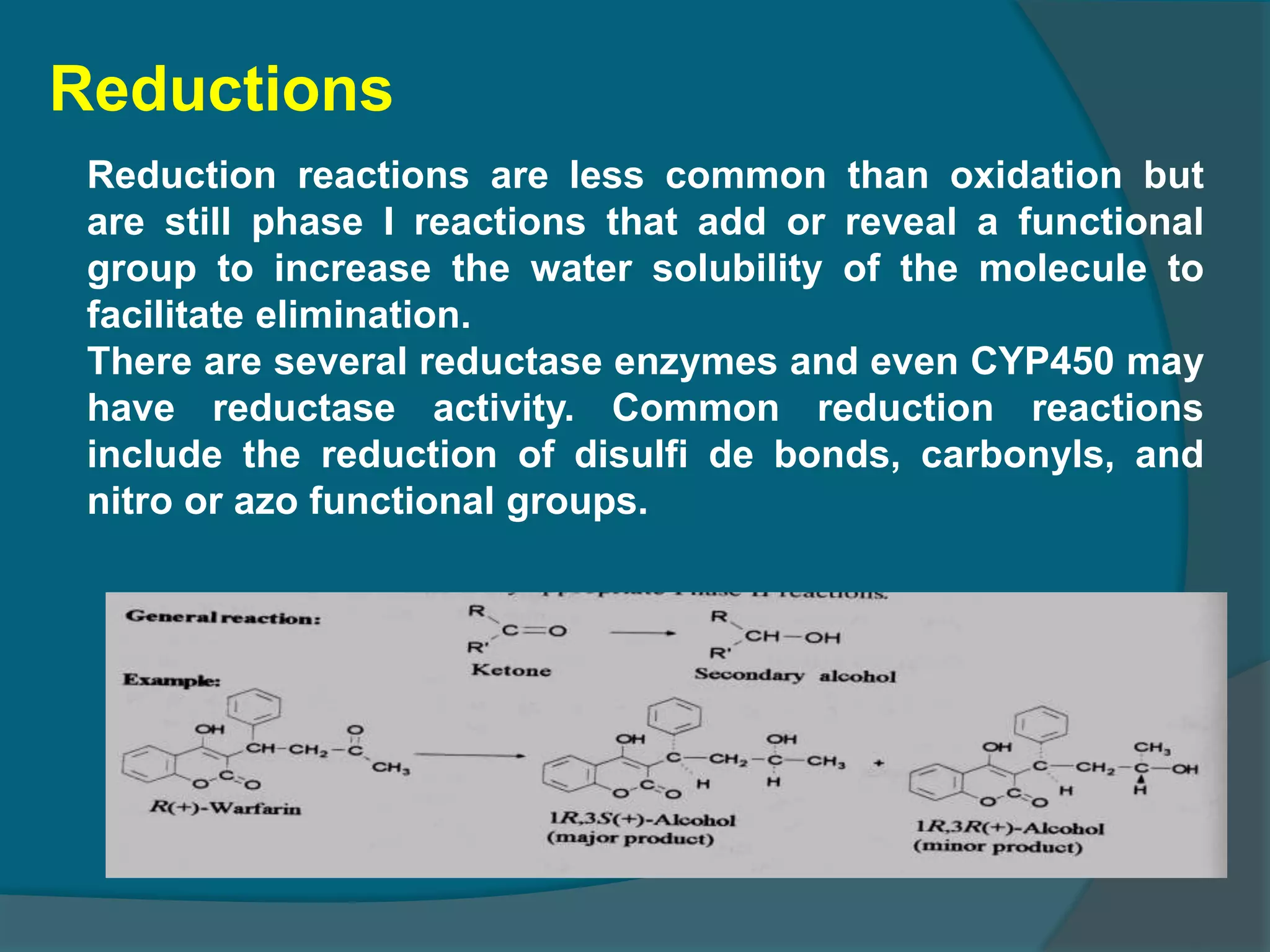
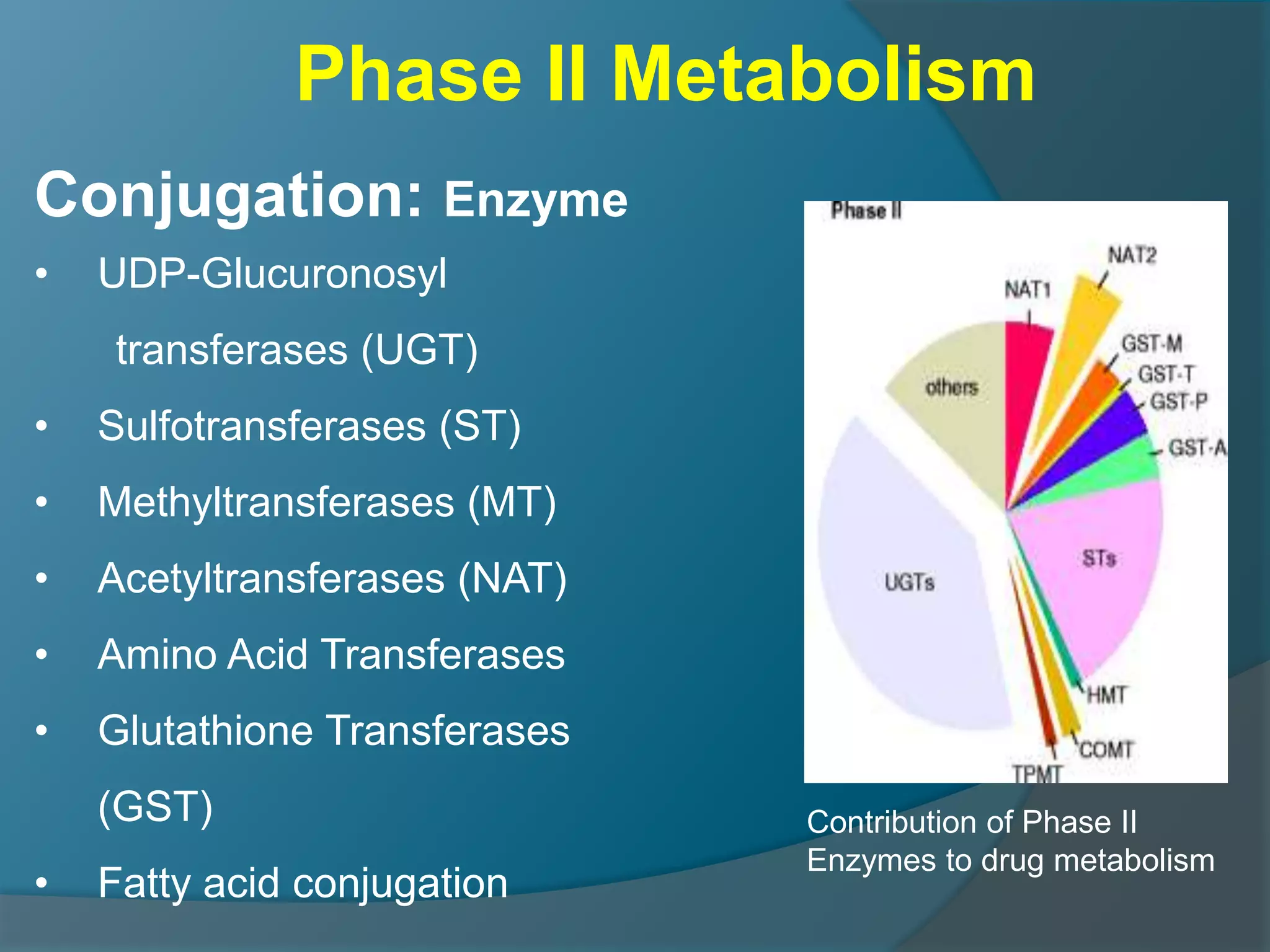
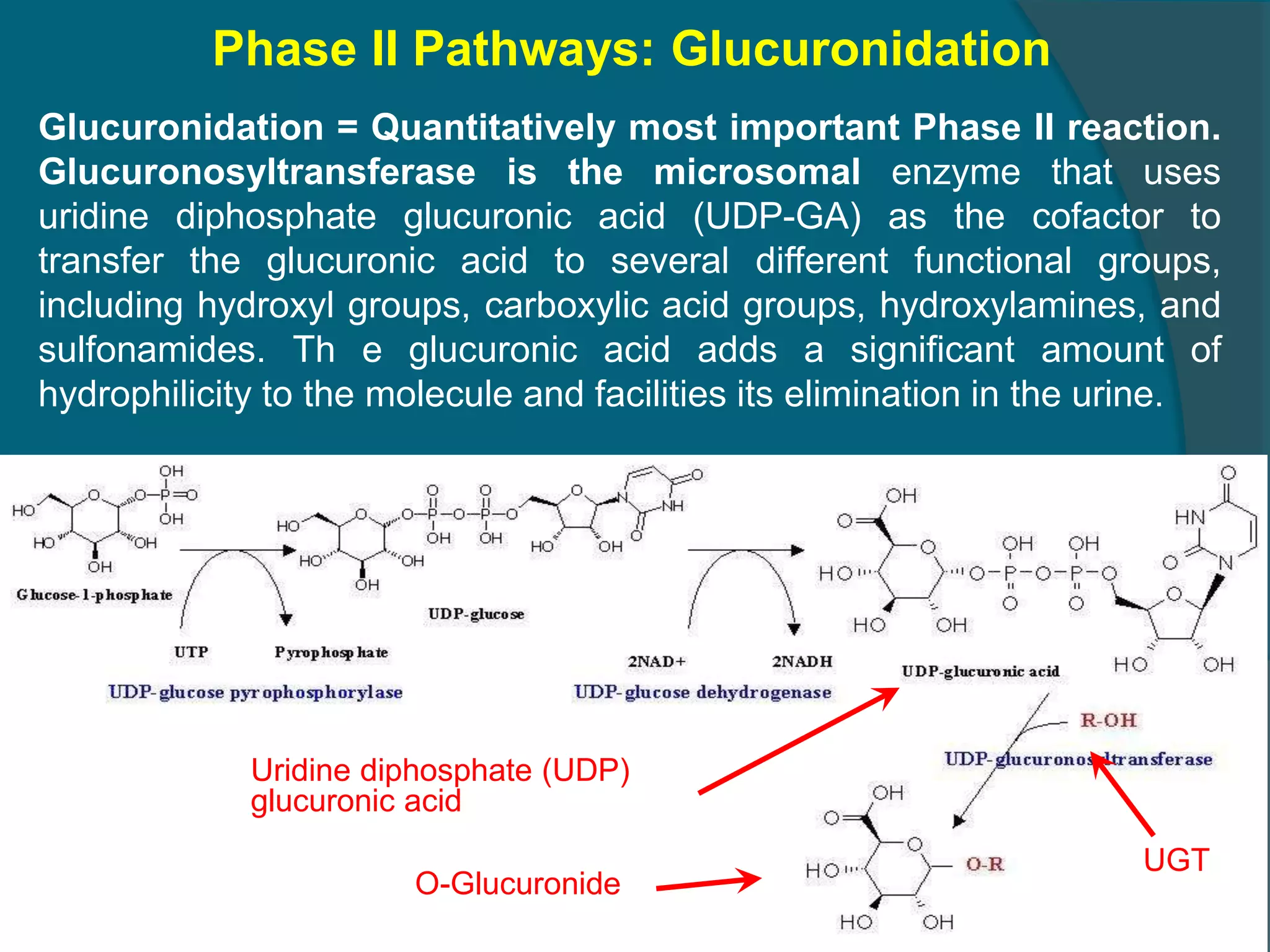
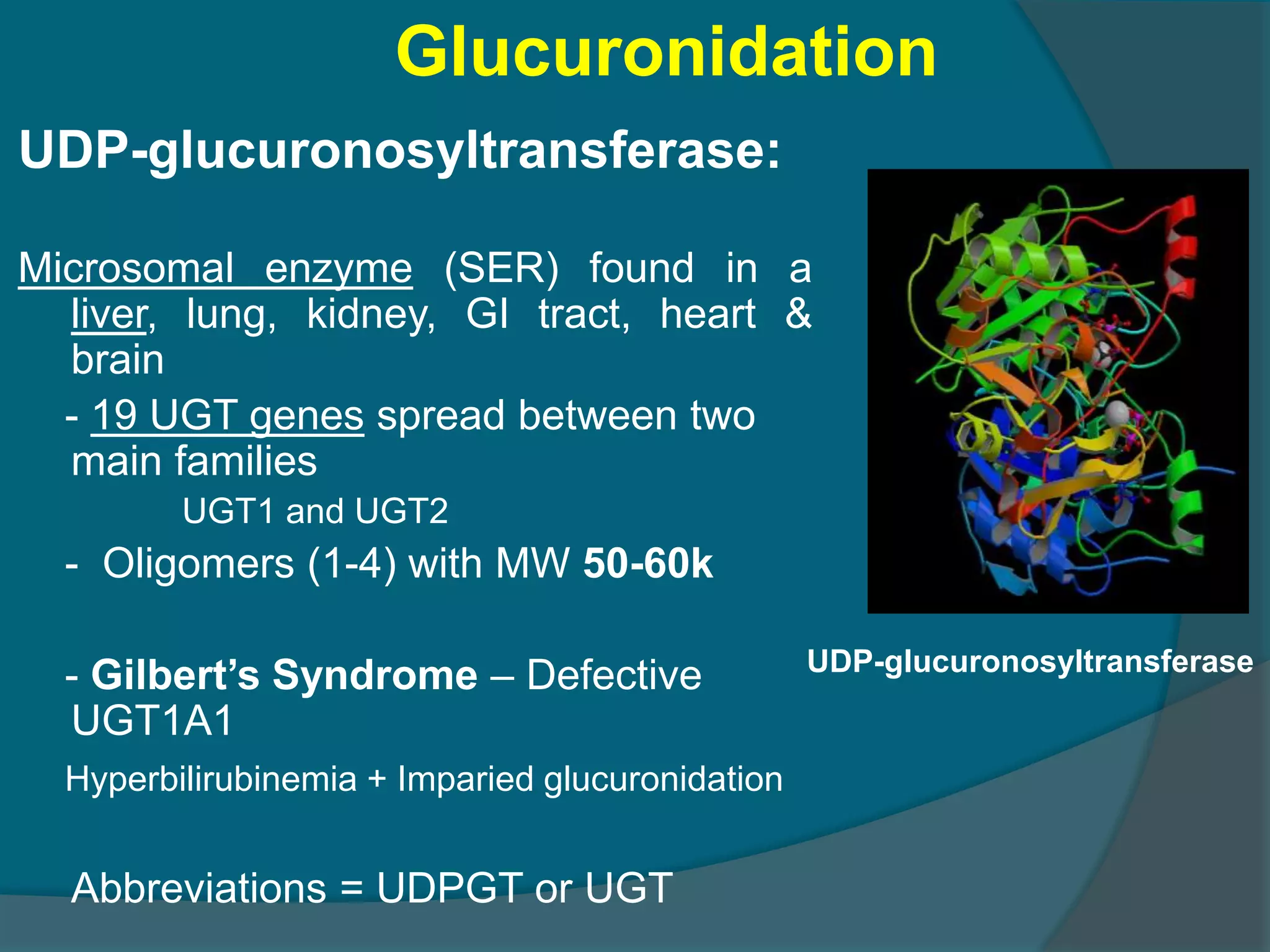
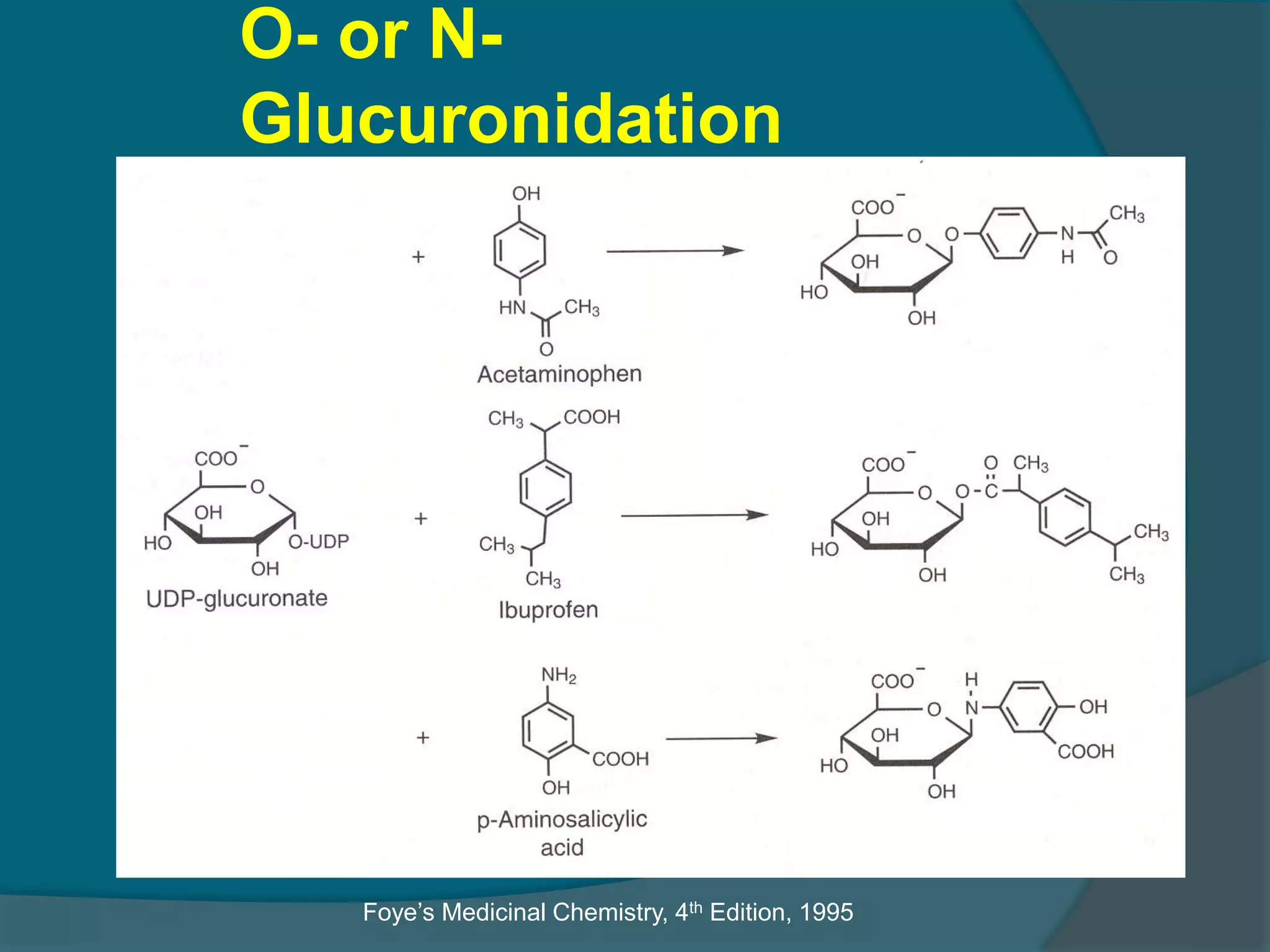
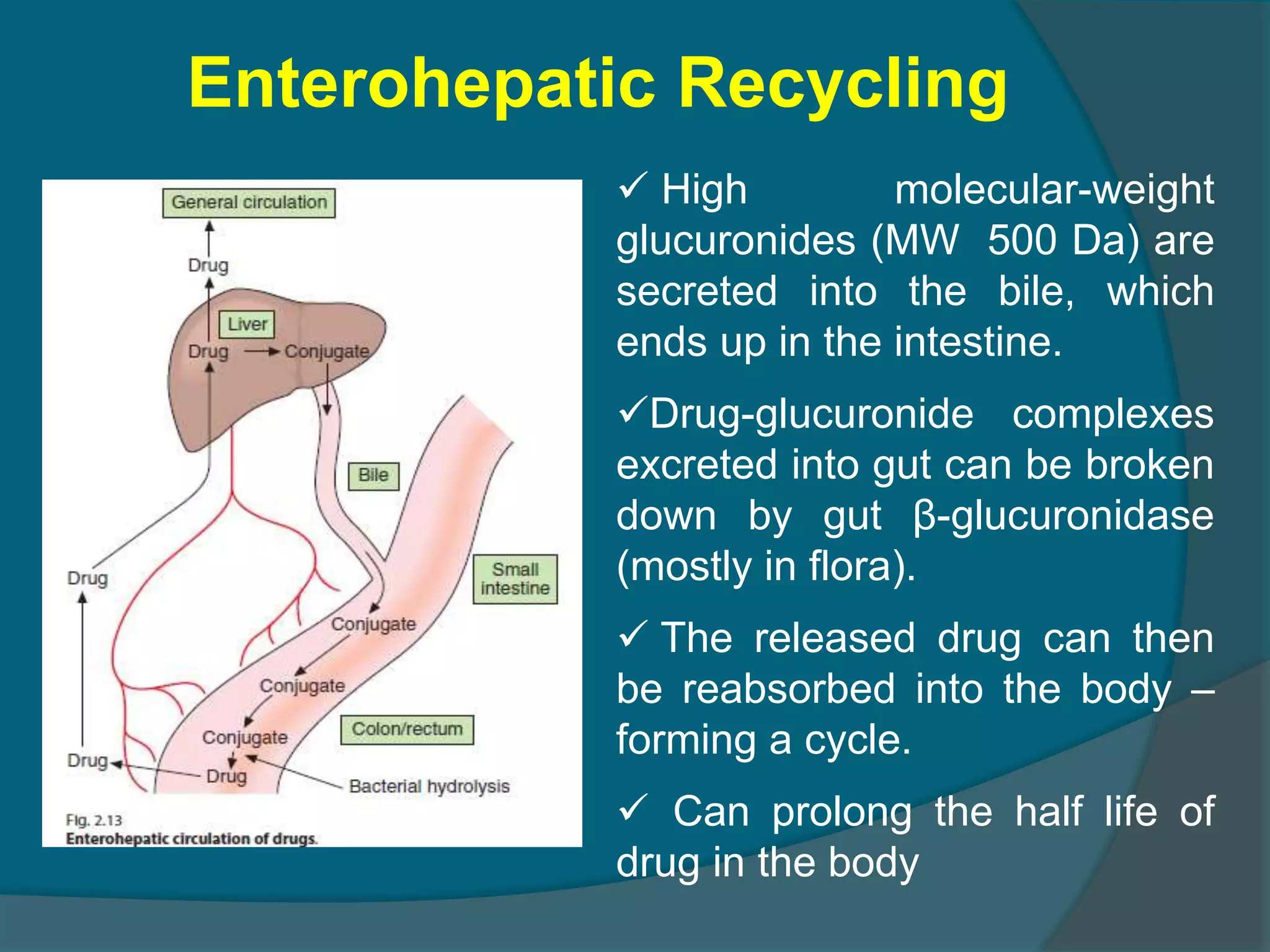
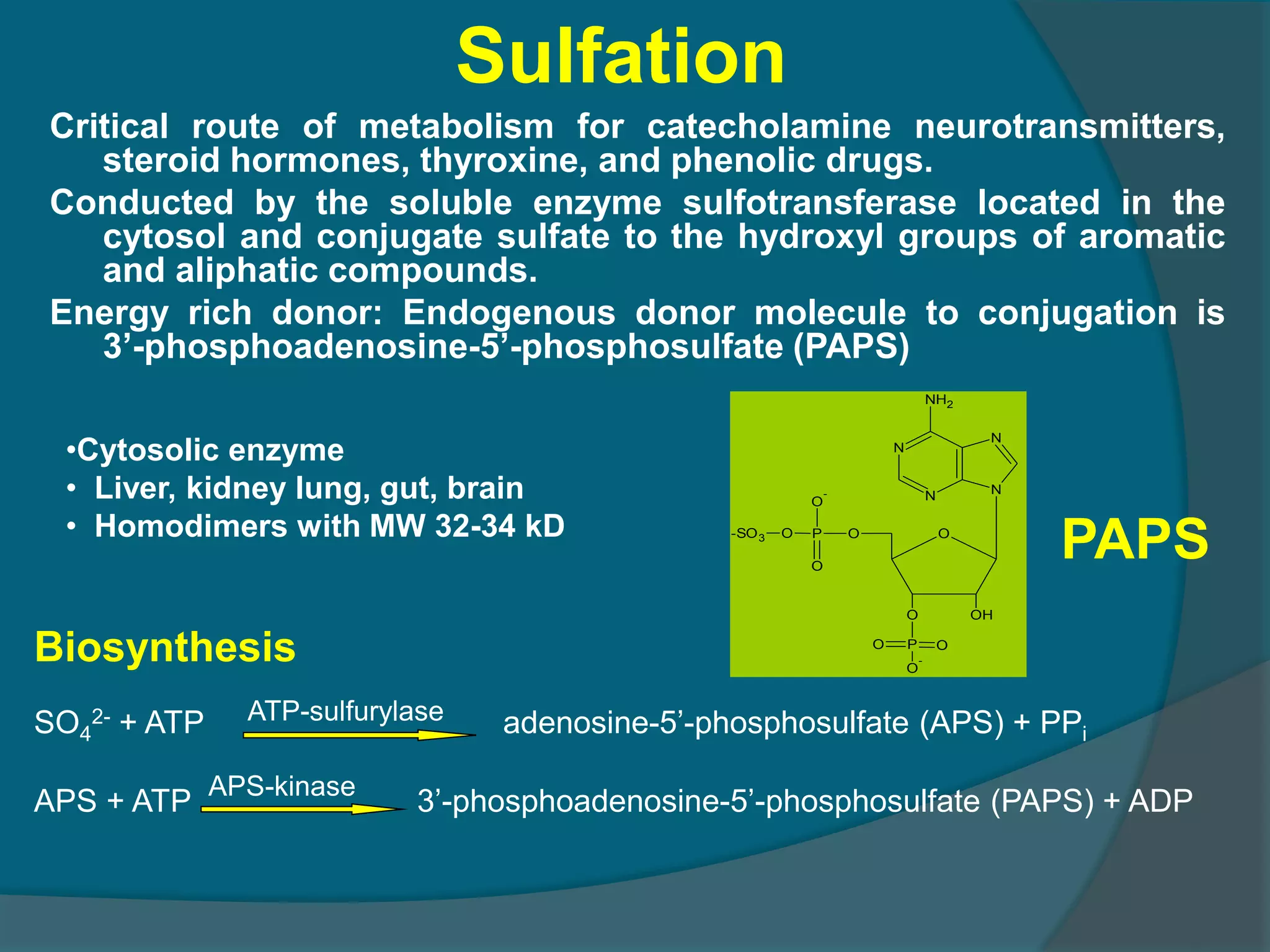
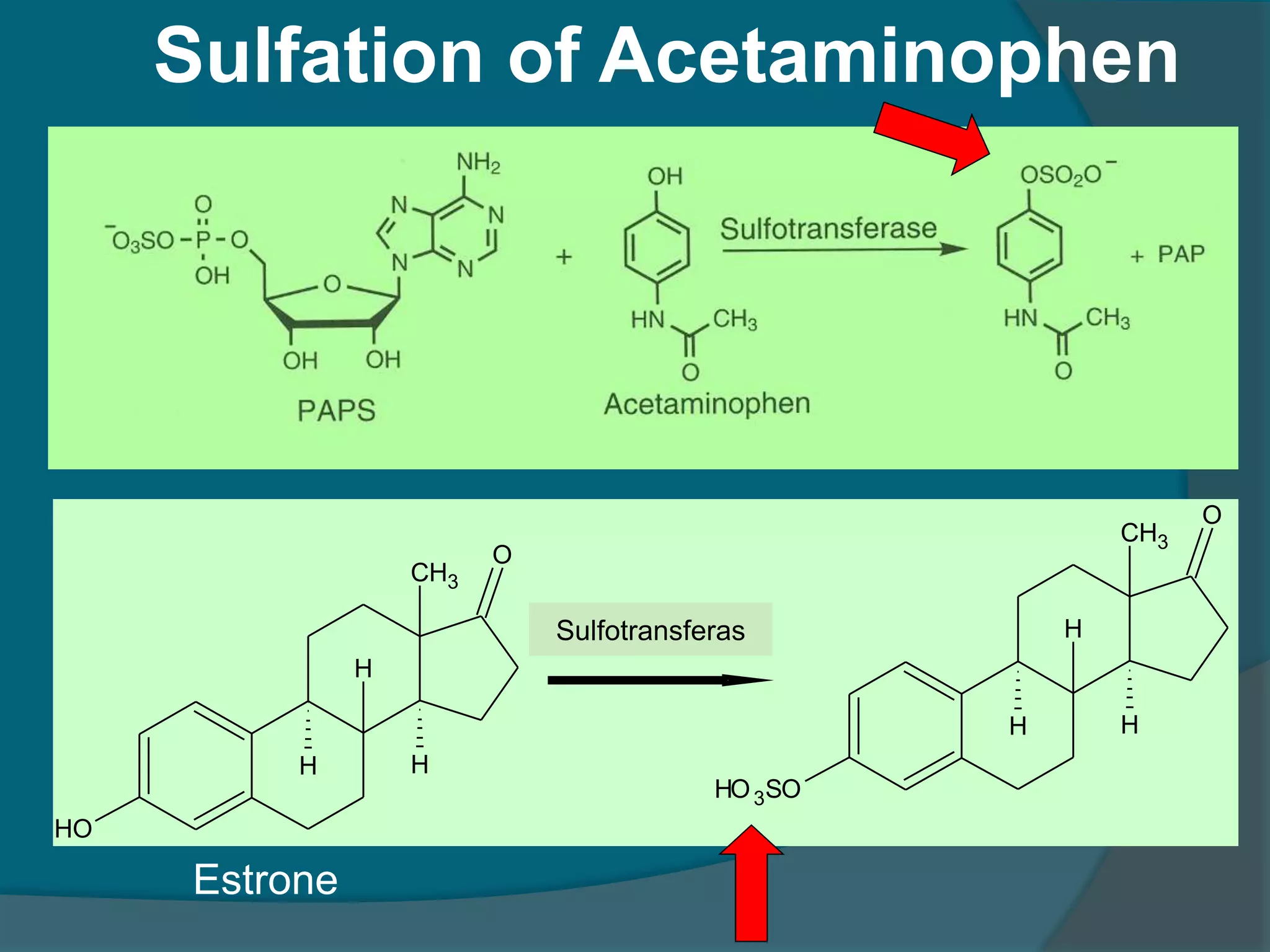
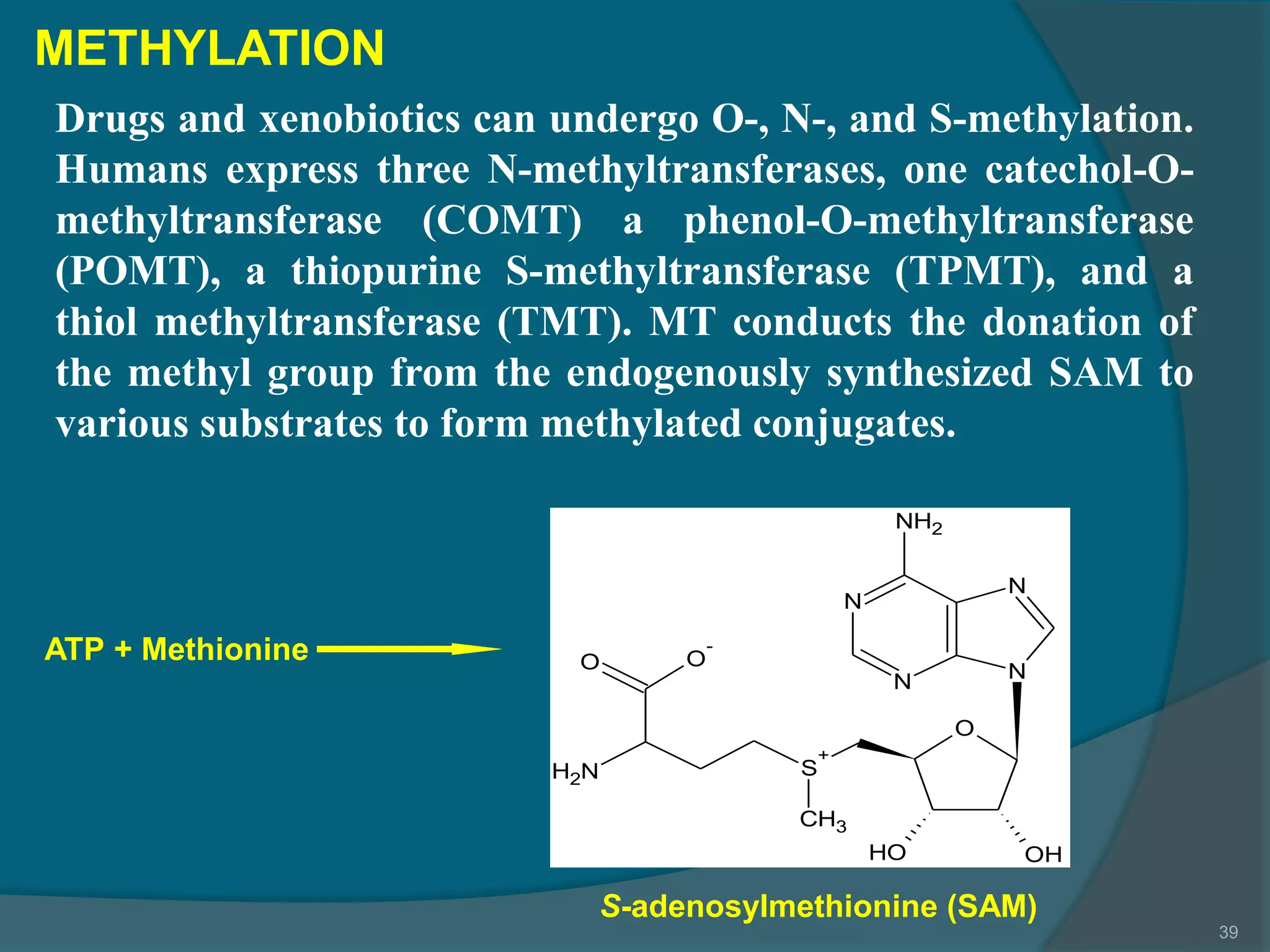
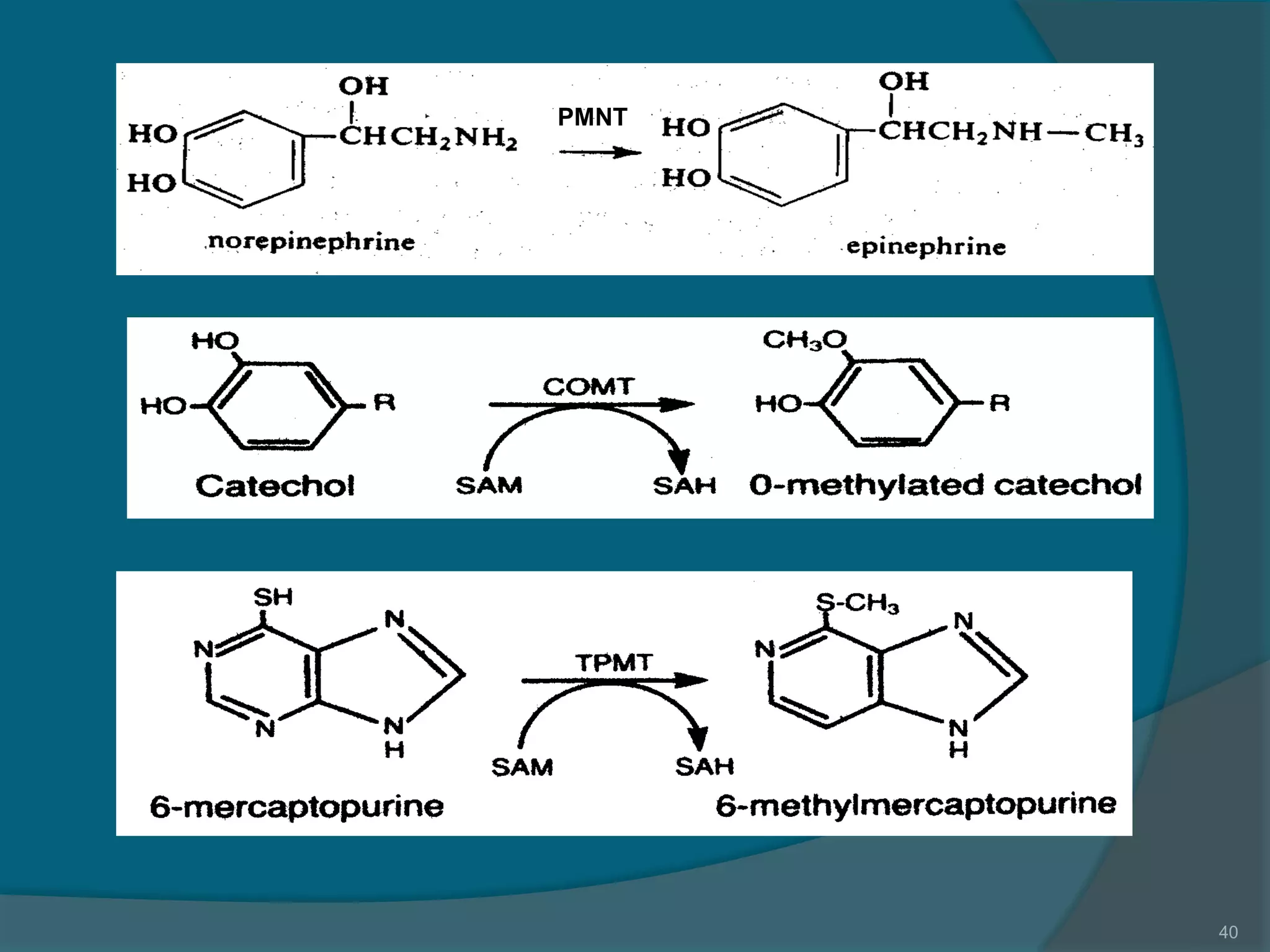
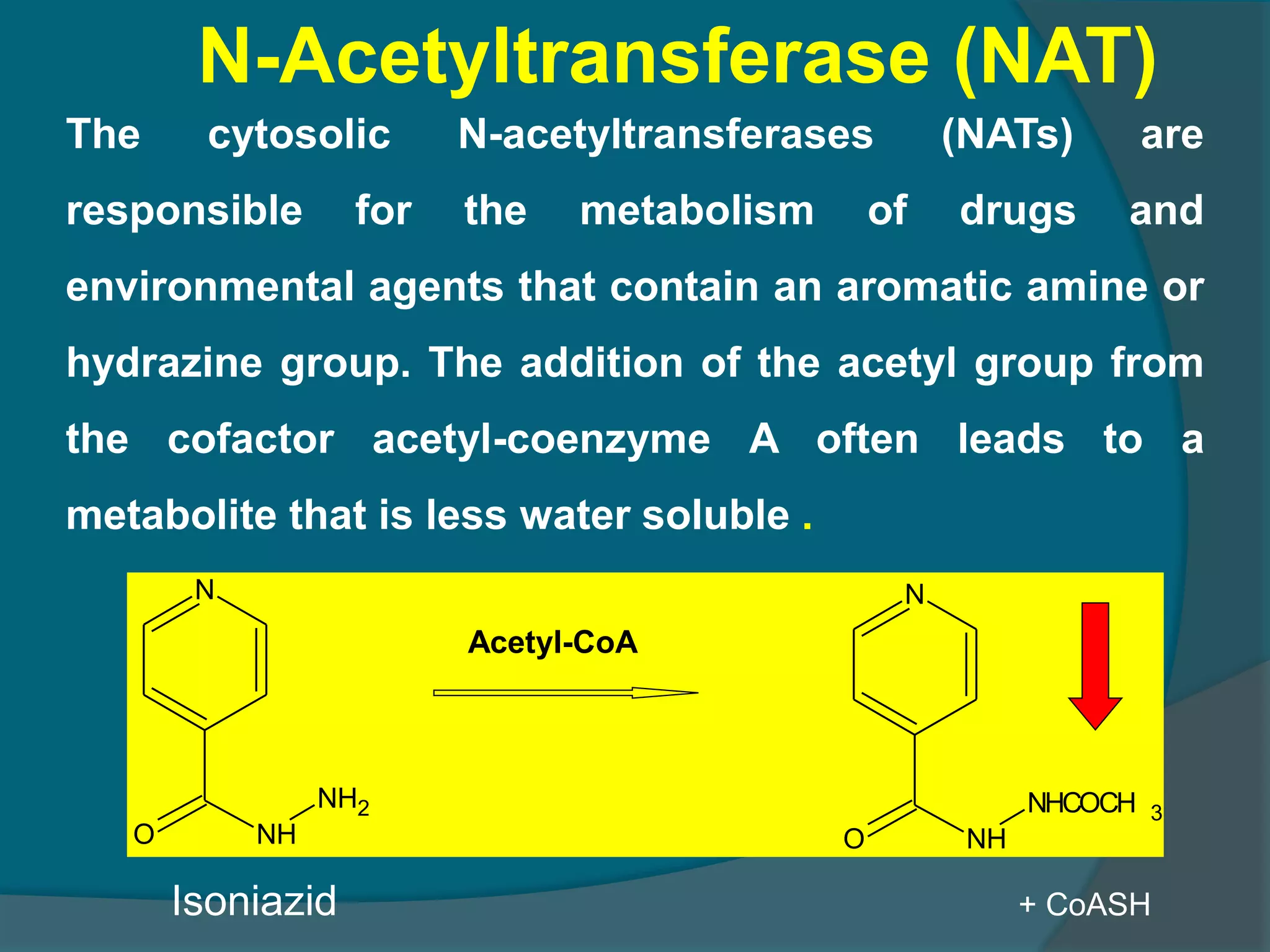

Drug metabolism involves the modification of drugs by the body to make them more water soluble and easier to excrete. Drugs undergo two main phases of metabolism: Phase I involves reactions like oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis that introduce or expose functional groups. Phase II involves conjugating functional groups with molecules like glucuronic acid to facilitate excretion. Understanding a drug's metabolic pathways is crucial for predicting its effects, toxicity and interactions with other drugs.









































