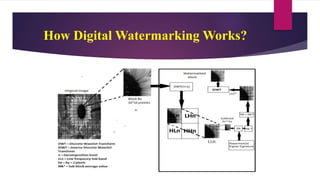
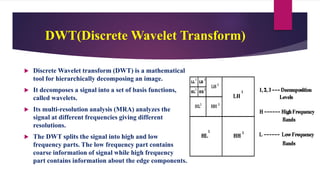
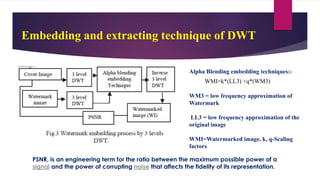
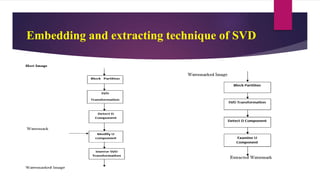
The document presents a novel watermarking algorithm that combines Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to achieve high robustness and perceptual quality in digital images, addressing the limitations of existing methods. It details the principles of digital watermarking, the classification, advantages, and disadvantages of DWT and SVD, and proposes solutions to overcome these drawbacks. The proposed method notably improves watermark recovery from strong attacks while ensuring secure authentication through a signature-based mechanism.