Electrolysis revision
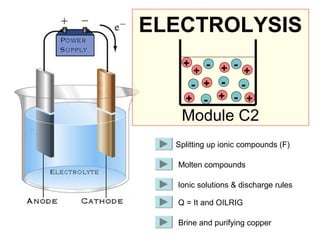
- 1. ELECTROLYSIS + - + - + - + - + - + - + + Module C2 Splitting up ionic compounds (F) Molten compounds Ionic solutions & discharge rules Q = It and OILRIG Brine and purifying copper
- 2. SPLITTING UP IONIC COMPOUNDS 1 Cl- ION Na+ ION Ionic compounds (eg sodium chloride) are made from: POSTIVE IONS (atoms which LOST negative electrons) NEGATIVE IONS (atoms which GAINED negative electrons) As these ions have OPPOSITE CHARGES they attract each other strongly to form IONIC BONDS
- 3. SPLITTING UP IONIC COMPOUNDS 2 2 ways to split up the ions: MELT + - + - + - + - + - + - + + 800°C - + + - + + - - + - DISSOLVE + - + - + + + - - - + 20°C H2O
- 4. SEPARATING THE IONS 1 + _ Metal ELECTRODE ELECTRON Battery pulls electrons off one electrode and pushes them onto the other This IS SHORT OF electrons so becomes POSITIVELY CHARGED “ANODE” This HAS EXTRA electrons so becomes NEGATIVELY CHARGED “CATHODE”
- 5. SEPARATING THE IONS 2 + MOLTEN IONIC COMPOUND - + - + ANODE + + - + - + + + - CATHODE When the battery is switched on, the + IONS move to the – CATHODE the – IONS move to the + ANODE This gives a way to SPLIT UP IONIC COMPOUNDS: “ELECTROLYSIS”
- 6. Example 1: Splitting up MOLTEN SODIUM CHLORIDE (salt) - = Cl- chloride ION, extra 1 electron Cl chlorine ATOM, Cl Cl NEUTRAL Cl2 molecule + Cl Cl- ClCl ClCl - chloride IONS lose their extra electrons and turn into neutral chlorine ATOMS ClCl At ANODE: Clthen: Cl + Cl e- + Cl Cl2 (gas) Both together: 2Cl- → 2e- + Cl2
- 7. Example 1: Splitting up MOLTEN SODIUM CHLORIDE (salt) + = Na+ sodium ION, missing1 electron Na sodium ATOM, NEUTRAL + + sodium IONS gain an extra electron and turn into neutral sodium ATOMS At CATHODE: Na+ + e- Na Na+ Na Na+ Na Na+ Na Na+ Na molten sodium metal sinks to bottom
- 8. Example 1: Splitting up MOLTEN SODIUM CHLORIDE (salt) - CATHODE + ANODE ELECTRONS SODIUM metal Na CHLORINE gas Cl2 Cl- MOLTEN SODIUM CHLORIDE At ANODE: Cle- + Cl Cl + Cl Cl2 (gas) Na+ At CATHODE: Na+ + eNa
- 9. Example 2: Splitting up MOLTEN LEAD BROMIDE PbBr 2 - CATHODE + ANODE ELECTRONS LEAD Metal Pb BROMINE gas Br2 Br- MOLTEN LEAD BROMIDE At ANODE: Bre- + Br Br + Br Br2 (gas) Pb2+ At CATHODE: Pb2+ + 2eBoth together: 2Br- → 2e- + Br2 Pb
- 10. What happens when the ionic compounds are dissolved in water? Here, water molecules break up into HYDROGEN IONS, H+ and HYDROXIDE IONS OH- H2O H+ + OHSo, in an ionic solution (eg sodium chloride solution), there will be FOUR types of ion present: TWO from the ionic compound and TWO from the water ( H+ SODIUM CHLORIDE SOLUTION NaCl (aq) H+ OH- ClNa+ OHH+ H+ Na+ Cl - - OH Na+ Cl- + OH-)
- 11. IONIC SOLUTION H+ OH OH- Cl- + Na H+ + Na Cl- H+ Na+ OHCl- Which ions gain or lose electrons (“get discharged”) and which stay in solution?
- 12. IONIC SOLUTIONS: At the CATHODE Na + sodium ION, missing 1 electron H+ + hydrogen ION, missing 1 electron As HYDROGEN is LESS REACTIVE than SODIUM, it is discharged. The sodium ions stay in solution. At CATHODE: 2H+ + 2e- H Hydrogen ATOM, NEUTRAL which ions? Na+ H+ H H+ Na+ H2
- 13. IONIC SOLUTIONS: At the CATHODE – halogen compounds Cl- chloride ION, extra 1 electron hydroxide ION, O H from water extra electron chlorine ATOM, NEUTRAL Cl + H O O H Cl Cl- H ClCl O O H ClCl which ions? ClCl At ANODE: If the – ion is a HALOGEN (Cl, Br, I) it is discharged and chlorine (or Br or I) is given off and the OH - ions stay in solution 2Cl- 2e- + Cl2
- 14. IONIC SOLUTIONS: CATHODE – non halogen compounds nitrate ION, extra NO3 1 electron hydroxide ION, OHO H from water, extra electron O Oxygen atom + NO3 H - O NO3H O which ions? NO3- O H NO3- If the – ion is NOT a halogen (eg nitrate, sulphate etc) then the HYDROXIDE ions from the water are discharged to make WATER and OXYGEN gas. The other ions stay in solution. O H At CATHODE: 4OH- 2H2O + O2 + 4e-
- 15. RULES FOR IONIC SOLUTIONS + ANODE Attracts – ions (‘Anions’) - CATHODE Attracts + ions (‘Cations’) If – ions are HALOGENS ie If + ions (metals) are MORE REACTIVE than hydrogen chloride Clbromide Br K, Na, Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe - iodide Ithe HALOGEN is produced. If – ions are NOT HALOGENS Eg sulphate SO4 , 2- Then HYDROGEN is produced If + ions (metals) are LESS REACTIVE than hydrogen nitrate NO3- Cu, Ag, Au carbonate CO32- Then the METAL is produced OXYGEN is produced.
- 16. (REACTIVITY: K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Al3+ Zn2+ Fe3+ H+ Cu2+ Ag+ Au3+ ) Ions Cathode (-) Anode (+) potassium chloride molten K+ Cl- potassium chlorine aluminium oxide molten Al3+ O2- aluminium oxygen copper chloride solution Cu2+ Cl- H+ OH- copper chlorine sodium bromide solution Na+ Br- H+ OH- hydrogen bromine silver nitrate solution Ag+ NO3- H+ OH- silver oxygen potassium chloride solution K+ Cl- H+ OH- hydrogen chlorine zinc sulphate Zn+ SO42- H+ OH- hydrogen oxygen Compound State solution (REACTIVITY: K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Al3+ Zn2+ Fe3+ H+ Cu2+ Ag+ Au3+ )
- 17. ELECTROLYSIS makes a CIRCUIT Complete electric circuit: Current carried by: ELECTRONS in electrodes/wires + + - IONS in the electrolyte - To DOUBLE the MASS of substance discharged at electrodes: 2 x CURRENT (2x batt. voltage) 2 x TIME current flows for (Q = I t)
- 18. OILRIG Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Oxidation is loss, reduction is gain ‘OILRIG’ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ - ions LOSING electrons + ions GAINING electrons to become atoms is called to become atoms is called ‘OXIDATION’ ‘REDUCTION’ (even though oxygen may not be involved)
- 19. INDUSTRIAL USES OF ELECTROLYSIS 1. To extract reactive metals such as ALUMINIUM, sodium, magnesium etc from their compounds. This is EXPENSIVE due to the large amounts of electrical energy needed. Aluminium is extracted from bauxite (Al2O3). 2. Electrolysis of BRINE (salt solution) to produce see below CHLORINE (for disinfectants and plastics) HYDROGEN (for ammonia fertilisers, margarine) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (for soap and cleaning agents) 3. Purifying copper. The copper for wiring etc needs to be more pure than that produced in a blast furnace. see below Electrolysis is used to convert impure copper to pure copper
- 20. INDUSTRIAL ELECTROLYSIS OF BRINE Chlorine gas Hydrogen gas BRINE (NaCl solution) CATHODE H+ and Na+ ANODE OH- and Cl2Cl - 2H+ + 2e- 2e + Cl2 - OH- left in solution so concentration grows Sodium chloride solution (neutral) slowly changed to sodium hydroxide solution (alkaline) H2 Na+ left in solution so concentration grows
- 21. Industrial chlorine production from electrolysis of brine
- 22. PURIFYING COPPER IMPURE COPPER ANODE Copper atoms from impure copper are OXIDISED to copper ions PURE COPPER CATHODE Copper sulphate CuSO4 solution Cu2+ Cu Cu2+ Cu2+ Cu Copper ions transported from anode to cathode Copper ions from impure copper are REDUCED to copper atoms As the atoms of the impurities are not transported, the copper that builds up on the anode is extremely pure.
- 23. IMPURE COPPER ANODE PURE COPPER CATHODE IMPURE COPPER ANODE PURE COPPER CATHODE Over time, the impure anode dissolves away and the impurities sink to the bottom. The pure cathode grows as more pure copper is deposited on it. Why will the concentration of the solution stay the same?