Biotech labs - restriction digest and transformation
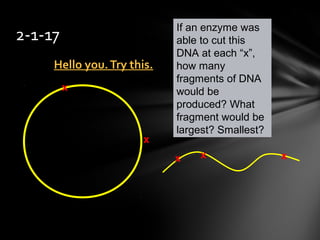
- 1. Hello you.Try this.Hello you.Try this. 2-1-17 If an enzyme was able to cut this DNA at each “x”, how many fragments of DNA would be produced? What fragment would be largest? Smallest? x x x x x
- 3. Your goal – to get theget the basic idea of each labbasic idea of each lab – what we will do for each Today’s Goal
- 4. AP BiologyAP Biology 1.1.Restriction Digest and Analysis ofRestriction Digest and Analysis of λ DNAλ DNA 2.2. BacterialTransformationBacterialTransformation 3.3.DNA Fingerprinting/Crime SceneDNA Fingerprinting/Crime Scene AnalysisAnalysis
- 5. 1. Restriction Digest of Lambda DNA 1. Cut the DNA from a virus with enzymes and analyze the results 2. BacterialTransformation 1. Cut out a gene from the DNA of one organism and insert it into the DNA of another 3. DNA fingerprinting 1. Cut several DNA samples with enzymes and analyze them to look for similarities & differences Our 3 labs
- 6. Restriction Digest & Analysis of Lambda DNA
- 7. Examine restriction enzymes and their use asExamine restriction enzymes and their use as biotech toolsbiotech tools Goal of this lab
- 8. useuse restriction enzymes EcoR1, Pst1, & HindIIIEcoR1, Pst1, & HindIII to digest (cut) bacteriophage lambda DNA use gel electrophoresis to examine these fragments of DNA What we will doWhat we will do
- 9. These enzymes cut DNA at very specific locationsThese enzymes cut DNA at very specific locations Bacteria contain these enzymes as a defenseBacteria contain these enzymes as a defense mechanism against phagesmechanism against phages Restriction enzymes are named after the bacteria from which they were first isolated • EcoRI from Escherichia coli, strain RI • HinDIII from Haemophilus influenzae, strain DIII • PstI from Providencia stuartii, stain I What are restriction enzymesrestriction enzymes?
- 10. • The DNA of a bacteriophage • ~ 48,000 base pairs long • 3 different enzymes to cut this DNA resulting in different length restriction fragments •one sample of DNA uncut for comparison •One “ladder” or “marker” used for estimating sizes of restriction fragments using gel electrophoresis Lambda DNALambda DNA (λ)(λ)
- 13. If a linear strand of DNA is cut 4 times, how many bands will there be in our gel? Restriction Enzymes
- 14. Electrophoresis - to carry w/ electricityElectrophoresis - to carry w/ electricity Separates DNA fragments by sizeSeparates DNA fragments by size DNA fragments loaded into an agarose gel slab • Slab placed in chamber w/ conductive buffer • Direct current passed through • Since DNA molecules are negatively charged, they areSince DNA molecules are negatively charged, they are drawn toward the positive pole (anode) when placed in andrawn toward the positive pole (anode) when placed in an electric fieldelectric field The gel acts like a sieveThe gel acts like a sieve through which smaller fragments move more easily than larger ones Over time, smaller fragments will travel farther than larger ones Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
- 16. DNA is colorless, so a loading dye is added toDNA is colorless, so a loading dye is added to the DNA solutionthe DNA solution •Does not stain the DNA •Makes it easier to load the gels and monitor the progress of the process
- 17. Each restriction enzyme producesEach restriction enzyme produces unique banding patternsunique banding patterns The relative size of the fragments cansize of the fragments can be determinedbe determined by measuring how far each band traveled from its origin
- 18. What are we doing overall in this lab? So…
- 20. DNA splicing, or gene splicing, is the cutting and linking ofDNA splicing, or gene splicing, is the cutting and linking of DNA molecules and it is one of the basic tools of modernDNA molecules and it is one of the basic tools of modern biotechnologybiotechnology The basic concept is to remove a functional DNA fragment, like a gene, from one organism and combine it with the DNA of another organism in order to study how the gene works • The desired result is for the recipient organism to express the newlyThe desired result is for the recipient organism to express the newly acquired geneacquired gene Background
- 21. The ability to cut & paste, or cleave & ligate, a functional piece of DNA is what enables scientists to recombine DNA molecules First step is to locate the gene Next use a restriction enzyme to cutuse a restriction enzyme to cut out the gene from the rest of theout the gene from the rest of the chromosomechromosome Use the same enzyme to cut open thesame enzyme to cut open the DNA of the recipient DNA and thenDNA of the recipient DNA and then insert the fragmentinsert the fragment Recombinant DNA technology
- 23. In this lab we will perform genetic transformation •Genetic transformation occurs when a cell takes up and expresses a new gene We will learn about moving DNA from one organism to another using a plasmidplasmid Overview GFP Beta-lactamase Ampicillin Resistance
- 24. pGLO™ & GFP We will attempt to have our bacteria express the gene for green florescent protein (GFP)
- 25. GFP is a visual markervisual marker Study of biological processes (example: synthesis of proteins) Localization and regulation of gene expression Cell movement Cell fate during development Formation of different organs Screenable marker to identify transgenic organisms Links toLinks to Real-worldReal-world
- 26. In addition to their single circular chromosome, bacteria often have 1 orbacteria often have 1 or more small, circular pieces of DNA calledmore small, circular pieces of DNA called plasmidsplasmids 5- 6 genes in a circle Plasmids often contain genes that help bacteria survive Bacteria can share these plasmids with each other • Antibiotic resistance among bacteria is due to plasmid sharing What is a plasmidWhat is a plasmid? Transmission electron micrograph
- 27. Contains theContains the genes for GFPgenes for GFP and the gene forand the gene for ampicillin (antibiotic) resistanceampicillin (antibiotic) resistance • It is called the pGLO plasmid Our plasmid also has an operon that allows the gene for GFP to be turned on and off the sugar arabinose turns on the operon Our plasmidOur plasmid
- 28. Beta Lactamase •Ampicillin resistance Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) •Aequorea victoria jellyfish gene araC regulator protein •Regulates GFP transcription operon Green fluorescent protein Gene to break down antibiotic Origin of replication
- 29. BacterialTransformation Beta lactamase (ampicillin resistance) pGLO plasmids Bacterial chromosomal DNA Cell wall GFP
- 31. What are we doing overall in this lab? So…
- 33. • Crime scene • Human relatedness • Paternity • Animal relatedness Anthropology studies Disease-causing organisms Food identification Human remains Monitoring transplants DNA Fingerprinting RealWorld Applications
- 34. DNA Restriction Enzymes • Evolved byEvolved by bacteria tobacteria to protect againstprotect against viral DNAviral DNA infectioninfection •Endonucleases = cleave within DNA strands •Over 3,000 known enzymes
- 35. No 2 people are exactly the same genetically except… • Identical siblings All people share 99.9% same DNA • It is the 1/10 of 1% that makes us different from each other Scientists know where these places are, and look there to determine a DNA profile DNA is unique
- 36. ~98% of the DNA in a human cell does not~98% of the DNA in a human cell does not code for any proteincode for any protein Some of this noncoding DNA is tandemtandem repeats:repeats: •The same DNA pattern repeated over and over •For example: ACACACACAC –or- GTCGTCGTCGTC Noncoding DNA
- 37. How many repeats there are in the DNA varies fromHow many repeats there are in the DNA varies from person to personperson to person For example, suppose chromosome 17 had a tandem repeat of ATCGATCGATCG • Some people would have 3 repeats of that sequence • Some people would have 4 repeats of that sequence • Some people would have 11 repeats of that sequence, and so on Noncoding DNA
- 38. Scientists use the tandem repeats in a person toScientists use the tandem repeats in a person to create a DNA profile or “fingerprint”create a DNA profile or “fingerprint” Noncoding DNA
- 39. Step 1: •Get a DNA sample (make copies of it in a lab) Create a DNA profile (DNA fingerprint)
- 40. Step 2: cut the DNAcut the DNA usingusing restriction enzymesrestriction enzymes Create a DNA profile (DNA fingerprint)
- 42. Step 3: sort the DNA fragmentssort the DNA fragments by size using gelby size using gel electrophoresiselectrophoresis 1. DNA is cut with restriction enzymes 2. The cut DNA is placed on a gel 3. Electric current runs through the gel 4. DNA is negative and moves toward the positive charge (opposites attract) 5. The pieces of DNA separate by size; smallest move farthest Create a DNA profile (DNA fingerprint)
- 45. Step 4: compare the DNA to the “Suspect” DNA • Scientists typically look at 13 differentScientists typically look at 13 different tandem repeat areas (loci)tandem repeat areas (loci) •Looking at only 1 does not tell us very much; many people could have that one repeat •Looking at 13, and being a match for all 13, tells us a lot • Being a perfect match for all 13 has aBeing a perfect match for all 13 has a chance of 1 in 100 billion (there are 7chance of 1 in 100 billion (there are 7 billion people on the planet)billion people on the planet) Create a DNA profile (DNA fingerprint)
- 46. DNA fingerprinting lab Victim – Asuzena S1:Yulissa S2: Erica S3: Rajvir S4: Harinder S5: Hernan
- 50. Determine restriction fragment sizes •Create standard curve using DNA marker •Measure distance traveled by restriction fragments •Determine size of DNA fragments Identify the related samples Analysis of Stained Gel
- 51. Electrical current carriescarries negatively-charged DNAnegatively-charged DNA through gel towardsthrough gel towards positive (red) electrodepositive (red) electrode Agarose Electrophoresis Loading Power Supply Buffer Dyes Agarose gel
- 52. • Agarose gel sieves DNADNA fragments accordingfragments according to sizeto size – Small fragmentsSmall fragments move farther thanmove farther than large fragmentslarge fragments Agarose Electrophoresis RunningElectrophoresis Running Power Supply Gel running
- 53. What are we doing overall in this lab? So…
Editor's Notes
- and are the basic procedures used by microbiologists performing recombinant DNA techniques, DNA fingerprinting, and forensics using DNA analysis
