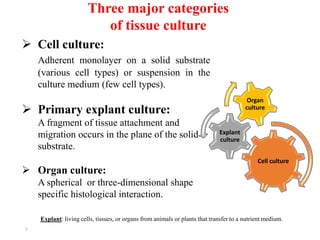
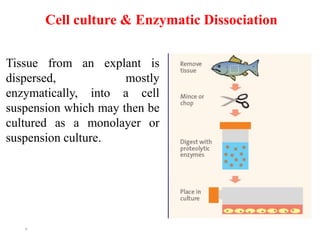
This document summarizes a lecture on animal tissue culture. It defines tissue culture as the in vitro culture of cells, tissues, or organs outside of the organism. There are three main types of tissue culture: cell culture, where cells grow as a monolayer or in suspension; explant culture, where a tissue fragment is attached and cells migrate on a substrate; and organ culture, where an organ maintains its three-dimensional shape and histological interactions. The document discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each type of culture, such as cell lines developing over generations for cell culture but potential loss of differentiation, or normal physiological functions being maintained for organ culture but limited scalability.