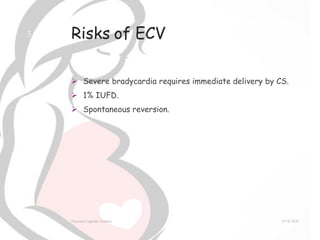
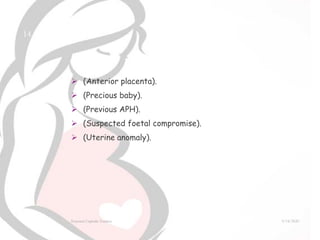
External cephalic version (ECV) is a procedure used to manually turn a fetus from a breech position to a head-down position in utero. ECV is generally performed after 36 weeks of gestation with tocolysis to reduce risks. It can successfully turn 44-57% of breech fetuses, reducing the need for cesarean section. Risks of ECV include brief fetal bradycardia in 8% of cases and 5% risk of fetomaternal hemorrhage. However, meta-analyses show ECV significantly reduces breech birth, cesarean rates, and risks to the fetus and mother when compared to breech vaginal delivery or planned cesarean. ECV